Team:UC Davis/Project Overview
From 2013.igem.org
Arneckelmann (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
<body> | <body> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/ | + | <div> |
| - | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4b/UCD_2013_ProjectOverview_Bannerv3.PNG" class="banner" width="967" height="226"> | |
| + | </div> | ||
| Line 24: | Line 25: | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li><a href="#motivation">Project Motivation</a></li> | <li><a href="#motivation">Project Motivation</a></li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="#projbackground"> | + | <li><a href="#solution">The Solution</a></li> |
| + | <li><a href="#projbackground">Parts Details</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 32: | ||
<div class="floatbox"> | <div class="floatbox"> | ||
<a id="motivation"> | <a id="motivation"> | ||
| - | <h1 class="title"> | + | <h1 class="title">Project Motivation</h1> |
</a> | </a> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | In synthetic biology, every circuit or device contains, at its core, at least one promoter and one protein coding region. While there are countless | + | In synthetic biology, every circuit or device contains, at its core, at least one promoter and one protein coding region. While there are a countless number of proteins we could use, circuit design is limited by the small number of well characterized inducible promoters at our disposal, and their respective transcription factors. TetR, LacI, AraC, LuxR, and cI...do these sound familiar? |
</p> | </p> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/ac/ProjMotive_UCDavis.png" class="centerimg"/> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/ac/ProjMotive_UCDavis.png" class="centerimg"/><br></br> |
| + | <center><h3>We need more available inputs for transcriptional and translational control.</h3></center> | ||
<p>What if ... | <p>What if ... | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>we had transcriptional regulators that could be used in any strain or any chassis?</li> | <li>we had transcriptional regulators that could be used in any strain or any chassis?</li> | ||
| - | <li>we could directly engineer repressors for target sequences, instead of having to assemble parts to place them | + | <li>we could directly engineer repressors for target sequences, instead of having to assemble parts to place them under the control of an inducible promoter? </li> |
| - | <li>we could control | + | <li>we could control repression with our molecule of choice?</li> |
| - | <li>we could increase the degrees of freedom that we as researchers have | + | <li>we could increase the degrees of freedom that we as researchers have over the control of gene expression?</li> |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | We would have the ability to host multiple, orthogonal systems within the same chassis | + | We would have the ability to host multiple, orthogonal systems within the same chassis. A large part of synthetic biology is, ultimately, designing constructs that generate a response to an input stimulus. A construct that is entirely flexible both at its inputs and outputs is the ideal tool to facilitate the engineering of synthetic biology devices. If we decoupled transcription and translation of a repressor device, maintaining fine-tuned control of both processes, and characterized the behavior of all the parts involved, the dynamic range achievable would be stupendous. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="floatbox"> | <div class="floatbox"> | ||
| - | <a id=" | + | <a id="solution"></a> |
| - | <h1 class=" | + | <h1>The Solution <a href="#top" class="to_top">^back to top</a></h1> |
| - | </a> | + | |
| - | <p>Transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) are proteins secreted by the bacterial pathogen <i>Xanthomonas</i> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/94/Ucdavisoverview2.gif" width=600 height=245 border-radius=10 class="centerimg genpic" /> |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="floatbox"> | ||
| + | <a id="projbackground"></a> | ||
| + | <h1 class="title">Parts Details <a href="#top" class="to_top">^back to top</a></h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) are proteins secreted by the bacterial plant pathogen <i>Xanthomonas</i>. TALEs contain sequence specific DNA binding domains and can act as transcriptional repressors or activators <a href="#ref">[1]</a>. This binding occurs through hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions and is stabilized by the protein's secondary structure. The DNA binding domains are sequence specific due to consecutive protein repeats, which are composed to correspond to a certain base preference <a href="#ref">[2]</a>. TAL repressors can therefore be engineered to bind to any DNA sequence of interest, following now well-understood rules for TAL-DNA binding <a href="#ref">[3,4]</a>. TALEs are thus a powerful and modular tool for the control of gene expression in genetic circuits. Current efforts to quantify and predict TALE binding affinities and functionalities are being made in order to create libraries of TALE systems that will serve to streamline research and the development of genetic devices <a href="#ref">[2]</a>.</p> | ||
<p><br />Riboswitches, on the other hand, are regulatory structures in the 5’-UTR of mRNA that undergo a conformational change in the presence of a specific ligand that binds to the aptamer domain of the structure <a href="#ref">[5]</a>. This conformational change can regulate the initiation of translation by sequestering the ribosome binding site of the mRNA sequence, making it unavailable for binding <a href="#ref">[5]</a>. Riboswitches have been shown to work in diverse bacterial species and many natural examples have been found for riboswitches that turn off translation in the presence of the target ligand as well <a href="#ref">[6,7]</a>. Riboswitches have also been well characterized, are dose-dependent and have been engineered to respond to non-natural ligands thus providing an orthogonal control system <a href="#ref">[8]</a>. These RNA-based devices, like the TALE proteins, are also modular and powerful tools for the control of gene expression.</p> | <p><br />Riboswitches, on the other hand, are regulatory structures in the 5’-UTR of mRNA that undergo a conformational change in the presence of a specific ligand that binds to the aptamer domain of the structure <a href="#ref">[5]</a>. This conformational change can regulate the initiation of translation by sequestering the ribosome binding site of the mRNA sequence, making it unavailable for binding <a href="#ref">[5]</a>. Riboswitches have been shown to work in diverse bacterial species and many natural examples have been found for riboswitches that turn off translation in the presence of the target ligand as well <a href="#ref">[6,7]</a>. Riboswitches have also been well characterized, are dose-dependent and have been engineered to respond to non-natural ligands thus providing an orthogonal control system <a href="#ref">[8]</a>. These RNA-based devices, like the TALE proteins, are also modular and powerful tools for the control of gene expression.</p> | ||
| - | <p><br />The fusion of these two devices--placing the TAL repressors under the control of riboswitches--offers a means by which to control | + | <p><br />The fusion of these two devices--placing the TAL repressors under the control of riboswitches--offers a means by which to control the expression of any gene of interest, using wider variety of inducers than there are currently available. As our understanding of riboswitches and our ability to engineer aptamer binding domains develop, it will be possible to develop a fully orthogonal, highly versatile systems for control of gene expression. There is a potential for multiplexing, as riboswitches designed to respond to different molecules and fused to different TAL repressors can be used in parallel within a single chassis, or can be induced in a temporally sequential manner for applications such as developmental research. We have to demonstrated that RiboTALes function as synthetic transcription factors that are orthogonal to the natural biochemistry of the cell and increase the degrees of freedom available to us in the control of genetic circuits.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="floatbox2"> | <div class="floatbox2"> | ||
| - | <h2>TALE binding to DNA</h2> | + | <h2>TALE binding to DNA <a href="#ref">[1]</a></h2> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/bf/TALpic_UCDavis.jpg" width=195 height=195 /> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/bf/TALpic_UCDavis.jpg" width=195 height=195 class="genpic"></img> |
| - | <h2>Riboswitch with inducer bound</h2> | + | <h2>Riboswitch with inducer bound <a href="#ref">[9]</a></h2> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7e/Riboswitchpic_UCDavis.jpg" width=195 height=195 /> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7e/Riboswitchpic_UCDavis.jpg" width=195 height=195 class="genpic"><img/> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <!--Begin Showbox--> | ||
<div class="floatbox"> | <div class="floatbox"> | ||
<table class="showbox"> | <table class="showbox"> | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/ | + | <div><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Project_Overview"> |
| - | <p>Learn about how we combine riboswitches and | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/bf/TALpic_UCDavis.jpg" class="blur"></a> |
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Project_Overview"><h3>Project Overview</h3></a> | ||
| + | <p>Learn about how we combine riboswitches and TALs into robust orthogonal mechanisms for inducible repression. | ||
</p></a> | </p></a> | ||
| + | |||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| - | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Data"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/d5/Resultsicon_UCDavis.jpg"></a> | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Data"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/d5/Resultsicon_UCDavis.jpg" class="blur"></a> |
<a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Data"><h3>Results</h3></a> | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Data"><h3>Results</h3></a> | ||
| - | <p>Check out the results of our experiments. | + | <p>Check out the cool results of our experiments with RiboTALs. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 87: | Line 102: | ||
<tr> | <tr> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| - | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/HumanPracticesOverview"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/ | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/HumanPracticesOverview"> |
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/35/Humanpracbutton2_UCDavis.jpg" class="blur" /> | ||
| + | <!--img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/97/UCD_2013_HO_Button.jpg" class="blur"--></a> | ||
<a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/HumanPracticesOverview"><h3>Human Practices</h3></a> | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/HumanPracticesOverview"><h3>Human Practices</h3></a> | ||
| - | <p>Take a look at how we | + | <p>Take a look at how we promote sharing in iGEM through The Depot, an open BioBrick characterization database.<br /> |
| + | <a href="http://dilbert.cs.ucdavis.edu/Depot" class="bold">Visit the Depot!</a> | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
<td> | <td> | ||
| - | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Criteria"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/Judgingbutton_UCDavis.jpg" | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Criteria"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/Judgingbutton_UCDavis.jpg" class="blur"</a> |
<a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Criteria"><h3>Judging Criteria</h3></a> | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:UC_Davis/Criteria"><h3>Judging Criteria</h3></a> | ||
<p>Here's the criteria that we met for this year's team. | <p>Here's the criteria that we met for this year's team. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <!--End Showbox--> | ||
| + | |||
<div class="floatbox"> | <div class="floatbox"> | ||
<a id="ref"><h3>References</h3></a> | <a id="ref"><h3>References</h3></a> | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
| - | [1] D. Dong, Y. Chuangye, P. Xiaojing, M. Mahfouz, W. Jiawei, Z. Jian-Kang, et al., "Structural Basis for Sequence-Specific Recognition of DNA by TAL Effectors," Science, vol. 335, pp. 720-723, 10 2012. | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Structural+Basis+for+Sequence-Specific+Recognition+of+DNA+by+TAL+Effectors">[1] D. Dong, Y. Chuangye, P. Xiaojing, M. Mahfouz, W. Jiawei, Z. Jian-Kang, et al., "Structural Basis for Sequence-Specific Recognition of DNA by TAL Effectors," Science, vol. 335, pp. 720-723, 10 2012.</a> |
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Quantitative+analysis+of+TALE-DNA+interactions+suggests+polarity+effects">[2] J. F. Meckler, M. S. Bhakta, M. S. Kim, R. Ovadia, C. H. Habrian, A. Zykovich, et al., "Quantitative analysis of TALE-DNA interactions suggests polarity effects," Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 41, pp. 4118-28, Apr 2013.</a> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | [ | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Breaking+the+Code+of+DNA+Binding+Specificity+of+TAL-Type+III+Effectors">[3] J. Boch, H. Scholze, S. Schornack, A. Landgraf, S. Hahn, S. Kay, et al., "Breaking the Code of DNA Binding Specificity of TAL-Type III Effectors," Science, vol. 326, pp. 1509-1512, Dec 2009.</a> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=A+Simple+Cipher+Governs+DNA+Recognition+by+TAL+Effectors">[4] M. J. Moscou and A. J. Bogdanove, "A Simple Cipher Governs DNA Recognition by TAL Effectors," Science, vol. 326, pp. 1501-1501, Dec 11 2009.</a> | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | [ | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Dual-acting+riboswitch+control+of+translation+initiation+and+mRNA+decay">[5] M. P. Caron, L. Bastet, A. Lussier, M. Simoneau-Roy, E. Masse, and D. A. Lafontaine, "Dual-acting riboswitch control of translation initiation and mRNA decay," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 109, pp. E3444-E3453, Dec 2012.</a> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | [ | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Synthetic+Riboswitches+That+Induce+Gene+Expression+in+Diverse+Bacterial+Species">[6] S. Topp, C. M. K. Reynoso, J. C. Seeliger, I. S. Goldlust, S. K. Desai, D. Murat, et al., "Synthetic Riboswitches That Induce Gene Expression in Diverse Bacterial Species (vol 76, pg 7881, 2010)," Applied and Environmental Microbiology, vol. 77, pp. 2199-2199, Mar 2011.</a> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Mechanism-Guided+Library+Design+and+Dual+Genetic+Selection+of+Synthetic+OFF+Riboswitches">[7] N. Muranaka, K. Abe, and Y. Yokobayashi, "Mechanism-Guided Library Design and Dual Genetic Selection of Synthetic OFF Riboswitches," Chembiochem, vol. 10, pp. 2375-2381, Sep 2009.</a> | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | [ | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Reengineering+orthogonally+selective+riboswitches">[8] N. Dixon, J. N. Duncan, T. Geerlings, M. S. Dunstan, J. E. G. McCarthy, D. Leys, et al., "Reengineering orthogonally selective riboswitches," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 107, pp. 2830-2835, Feb 16 2010.</a> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| - | + | <a href="http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=A+flow+cytometry-based+screen+for+synthetic+riboswitches">[9] S. A. Lynch and J. P. Gallivan, "A flow cytometry-based screen for synthetic riboswitches," Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 37, pp. 184-192, Jan 2009.</a> | |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:59, 18 October 2013

Project Links
Project Motivation
In synthetic biology, every circuit or device contains, at its core, at least one promoter and one protein coding region. While there are a countless number of proteins we could use, circuit design is limited by the small number of well characterized inducible promoters at our disposal, and their respective transcription factors. TetR, LacI, AraC, LuxR, and cI...do these sound familiar?
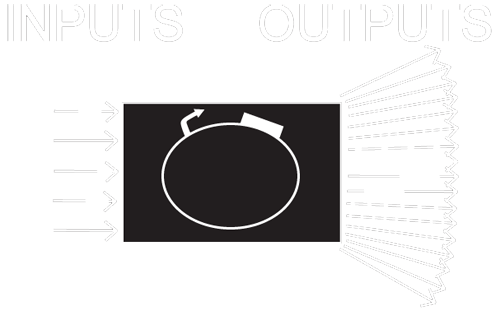
We need more available inputs for transcriptional and translational control.
What if ...
- we had transcriptional regulators that could be used in any strain or any chassis?
- we could directly engineer repressors for target sequences, instead of having to assemble parts to place them under the control of an inducible promoter?
- we could control repression with our molecule of choice?
- we could increase the degrees of freedom that we as researchers have over the control of gene expression?
Parts Details ^back to top
Transcription activator-like effectors (TALEs) are proteins secreted by the bacterial plant pathogen Xanthomonas. TALEs contain sequence specific DNA binding domains and can act as transcriptional repressors or activators [1]. This binding occurs through hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions and is stabilized by the protein's secondary structure. The DNA binding domains are sequence specific due to consecutive protein repeats, which are composed to correspond to a certain base preference [2]. TAL repressors can therefore be engineered to bind to any DNA sequence of interest, following now well-understood rules for TAL-DNA binding [3,4]. TALEs are thus a powerful and modular tool for the control of gene expression in genetic circuits. Current efforts to quantify and predict TALE binding affinities and functionalities are being made in order to create libraries of TALE systems that will serve to streamline research and the development of genetic devices [2].
Riboswitches, on the other hand, are regulatory structures in the 5’-UTR of mRNA that undergo a conformational change in the presence of a specific ligand that binds to the aptamer domain of the structure [5]. This conformational change can regulate the initiation of translation by sequestering the ribosome binding site of the mRNA sequence, making it unavailable for binding [5]. Riboswitches have been shown to work in diverse bacterial species and many natural examples have been found for riboswitches that turn off translation in the presence of the target ligand as well [6,7]. Riboswitches have also been well characterized, are dose-dependent and have been engineered to respond to non-natural ligands thus providing an orthogonal control system [8]. These RNA-based devices, like the TALE proteins, are also modular and powerful tools for the control of gene expression.
The fusion of these two devices--placing the TAL repressors under the control of riboswitches--offers a means by which to control the expression of any gene of interest, using wider variety of inducers than there are currently available. As our understanding of riboswitches and our ability to engineer aptamer binding domains develop, it will be possible to develop a fully orthogonal, highly versatile systems for control of gene expression. There is a potential for multiplexing, as riboswitches designed to respond to different molecules and fused to different TAL repressors can be used in parallel within a single chassis, or can be induced in a temporally sequential manner for applications such as developmental research. We have to demonstrated that RiboTALes function as synthetic transcription factors that are orthogonal to the natural biochemistry of the cell and increase the degrees of freedom available to us in the control of genetic circuits.
Project OverviewLearn about how we combine riboswitches and TALs into robust orthogonal mechanisms for inducible repression. |
ResultsCheck out the cool results of our experiments with RiboTALs. |

Human PracticesTake a look at how we promote sharing in iGEM through The Depot, an open BioBrick characterization database. |

Judging CriteriaHere's the criteria that we met for this year's team. |
References
[1] D. Dong, Y. Chuangye, P. Xiaojing, M. Mahfouz, W. Jiawei, Z. Jian-Kang, et al., "Structural Basis for Sequence-Specific Recognition of DNA by TAL Effectors," Science, vol. 335, pp. 720-723, 10 2012.
[2] J. F. Meckler, M. S. Bhakta, M. S. Kim, R. Ovadia, C. H. Habrian, A. Zykovich, et al., "Quantitative analysis of TALE-DNA interactions suggests polarity effects," Nucleic Acids Res, vol. 41, pp. 4118-28, Apr 2013.
[3] J. Boch, H. Scholze, S. Schornack, A. Landgraf, S. Hahn, S. Kay, et al., "Breaking the Code of DNA Binding Specificity of TAL-Type III Effectors," Science, vol. 326, pp. 1509-1512, Dec 2009.
[4] M. J. Moscou and A. J. Bogdanove, "A Simple Cipher Governs DNA Recognition by TAL Effectors," Science, vol. 326, pp. 1501-1501, Dec 11 2009.
[5] M. P. Caron, L. Bastet, A. Lussier, M. Simoneau-Roy, E. Masse, and D. A. Lafontaine, "Dual-acting riboswitch control of translation initiation and mRNA decay," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 109, pp. E3444-E3453, Dec 2012.
[6] S. Topp, C. M. K. Reynoso, J. C. Seeliger, I. S. Goldlust, S. K. Desai, D. Murat, et al., "Synthetic Riboswitches That Induce Gene Expression in Diverse Bacterial Species (vol 76, pg 7881, 2010)," Applied and Environmental Microbiology, vol. 77, pp. 2199-2199, Mar 2011.
[7] N. Muranaka, K. Abe, and Y. Yokobayashi, "Mechanism-Guided Library Design and Dual Genetic Selection of Synthetic OFF Riboswitches," Chembiochem, vol. 10, pp. 2375-2381, Sep 2009.
[8] N. Dixon, J. N. Duncan, T. Geerlings, M. S. Dunstan, J. E. G. McCarthy, D. Leys, et al., "Reengineering orthogonally selective riboswitches," Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, vol. 107, pp. 2830-2835, Feb 16 2010.
[9] S. A. Lynch and J. P. Gallivan, "A flow cytometry-based screen for synthetic riboswitches," Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 37, pp. 184-192, Jan 2009.
 "
"


