PET-mCherry
From 2013.igem.org
(→Design) |
(→Characterization) |
||
| (83 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ''' | + | {{:Team:GeorgiaTech/template}} |
| + | =PET-mCherry= | ||
| + | [[File:MCherry.PNG|right|200px|border]] | ||
| + | '''PET-mCherry''' is a β-barrel autotransporter with a mCherry passenger. | ||
| + | [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1156000# BBa_K1156000] | ||
| + | <div style="clear: both"></div> | ||
| + | |||
==Motivation== | ==Motivation== | ||
In 2012 the Georgia Tech iGEM team developed a novel biosensor based off of green fluorescent protein. The sensor consisted of two subunits of the protein that separately were inactive but once dimerized expressed fluorescence. From this project, we began thinking about how we could develop more complex sensing technology in bacteria. Taking into consideration how mammalian cells sense and react to their environment, we started asking the question: Can bacteria express human integrins? | In 2012 the Georgia Tech iGEM team developed a novel biosensor based off of green fluorescent protein. The sensor consisted of two subunits of the protein that separately were inactive but once dimerized expressed fluorescence. From this project, we began thinking about how we could develop more complex sensing technology in bacteria. Taking into consideration how mammalian cells sense and react to their environment, we started asking the question: Can bacteria express human integrins? | ||
| Line 6: | Line 12: | ||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
| - | + | In a 2012 paper, a research group from the University of Birmingham demonstrated that the β-barrel PET could successfully transport and translocate the RFP, mCherry.[http://www.microbialcellfactories.com/content/11/1/69|] We wanted to use their construct to determine whether or not PET would be a good candidate for integrin transport. | |
| - | To comply with BioBrick standard 10, Phe-76 was re-optimized to remove a EcoRI site withing the part. A T7 promoter with a lacI operator was added with the RBS (AGGA) to the PET_mCherry. A standard assembly 10 prefix and suffix was then added. In future work, other autodisplay technologies are hoped to be tested to express a number of proteins. | + | The sequence that was provided in the paper was already optimized for E. coli expression, however we checked it again. There were also a number of compatibility issues that need to be resolved. To comply with BioBrick standard 10, Phe-76 was re-optimized to remove a EcoRI site withing the part. A T7 promoter with a lacI operator was added with the RBS (AGGA) to the PET_mCherry. A standard assembly 10 prefix and suffix was then added. In future work, other autodisplay technologies are hoped to be tested to express a number of proteins.[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O68900 Uniprot] |
| - | [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O68900 Uniprot] | + | |
[[File:PET_mCherry_sequence_map.jpg]] | [[File:PET_mCherry_sequence_map.jpg]] | ||
| + | Because of a generous offer from IDT for discount synthesis we chose to synthesize our protein construct using their '''gBlock''' method which consists of blocks of 500bp. Our construct fit into 6 blocks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below are the primers that we designed to amplify each block. | ||
Primers: | Primers: | ||
| - | + | ig12 SP/Pet_mCherry_b1/0 AGTCAGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGG | |
| - | ig12 SP/Pet_mCherry_b1/0 AGTCAGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGG | + | ig13 SP/Pet_mCherry_b2/469 CGTATGAAGGCACCCAGACCGCTAAACTGAAA |
| - | ig13 SP/Pet_mCherry_b2/469 CGTATGAAGGCACCCAGACCGCTAAACTGAAA | + | ig14 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b1/500 TTTCAGTTTAGCGGTCTGGGTGCCTTCATACG |
| - | ig14 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b1/500 TTTCAGTTTAGCGGTCTGGGTGCCTTCATACG | + | ig15 SP/Pet_mCherry_b3/928 CGGGTGCTTACAACGTGAACATCAAACTGGAC |
| - | ig15 SP/Pet_mCherry_b3/928 CGGGTGCTTACAACGTGAACATCAAACTGGAC | + | ig16 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b2/959 GTCCAGTTTGATGTTCACGTTGTAAGCACCCG |
| - | ig16 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b2/959 GTCCAGTTTGATGTTCACGTTGTAAGCACCCG | + | ig17 SP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1352 CAAACTGGAAGGTGCGAACAACCTGCTGC |
| - | ig17 SP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1352 CAAACTGGAAGGTGCGAACAACCTGCTGC | + | ig18 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b3/1380 GCAGCAGGTTGTTCGCACCTTCCAGTTTG |
| - | ig18 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b3/1380 GCAGCAGGTTGTTCGCACCTTCCAGTTTG | + | ig19 SP/Pet_mCherry_b5/1816 TGTTCACCGGTGTTACCATGACCTACACCGAC |
| - | ig19 SP/Pet_mCherry_b5/1816 TGTTCACCGGTGTTACCATGACCTACACCGAC | + | ig20 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1847 GTCGGTGTAGGTCATGGTAACACCGGTGAACA |
| - | ig20 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1847 GTCGGTGTAGGTCATGGTAACACCGGTGAACA | + | ig21 SP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2265 GGTTACCAGTTCGACCTGTTCGCTAACGGTGA |
| - | ig21 SP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2265 GGTTACCAGTTCGACCTGTTCGCTAACGGTGA | + | ig22 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b5/2296 TCACCGTTAGCGAACAGGTCGAACTGGTAACC |
| - | ig22 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b5/2296 TCACCGTTAGCGAACAGGTCGAACTGGTAACC | + | ig23 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2516 ACTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTATC |
| - | ig23 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2516 ACTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTATC | + | |
| - | + | ||
==Assembly== | ==Assembly== | ||
| + | The 6 gBlocks that we synthesized using IDT were assembled using overlap extension PCR. | ||
| + | |||
==Characterization== | ==Characterization== | ||
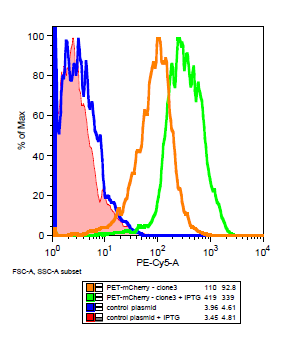
| + | The cells for the colonies BEP1 and BEP3 were characterized using flow cytometry. Our goals for this characterization were to show activity of the LacI operator and confirm the expression of mCherry on the outside of the cell. Cells expressing '''H6''', a single strand antibody that favors fibrin, were used as a '''negative control'''. | ||
| + | [[File:Flow_gate.png|center|frame| | ||
| + | '''Flow cytometry data for PET-mCherry and H6 negative control''' Data was gated to capture the population of interest for the control and BEP3. The increase in events outside of the gate post-induction withIPTG for the control indicates cell induced death due to over-expression. Increased expression of mCherry after induction does not induce cytotoxicity.]] | ||
| + | <div style="clear: both"></div> | ||
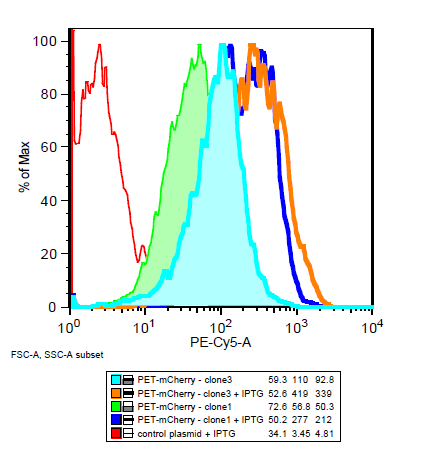
| + | ===Is the LacI operator working?=== | ||
| + | [[File:Flow_induction_w-wt.PNG|left|frame| BEP3 compared to the control with and without IPTG induction]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''Yes!''' an increase in mCherry expression after induction with IPTG shows that the LacI operator in conjunction with the T7 promoter is working. | ||
| + | [[File: Flow_induction_w-wt2.PNG|left||frame| BEP1 compared to BEP3 and the control with induction and without ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div style="clear: both"></div> | ||
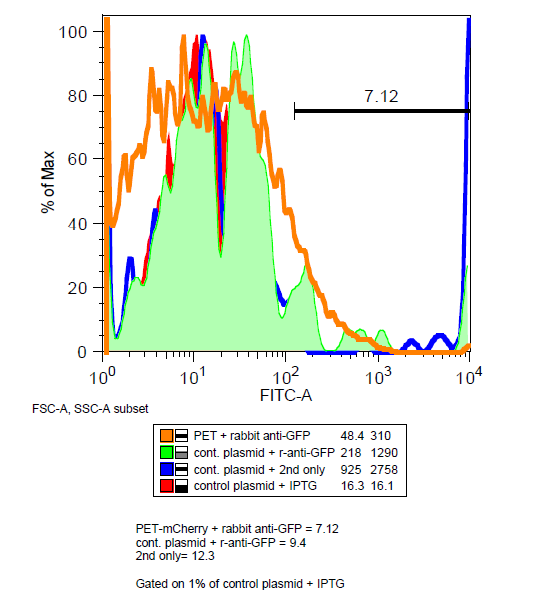
| + | ===Is mCherry on the outside of the cell?=== | ||
| + | '''Maybe...''' Unlike GFP, mCherry has been shown to be functional in the periplasm.[http://jb.asm.org/content/early/2011/07/15/JB.00315-11.full.pdf] In order to determine if mCherry was being expressed outside the cell, BEP3 cells were stained with mouse and rabbit anti-GFP antibodies and then fluorescent tagged anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies. | ||
| + | [[File:Antibody_stain.png|left|400 px]] | ||
| + | Very little decrease in the mCherry signal after washing suggest that the protein is not being cleaved if it is expressed externally. Results of the antibody were inconclusive as the amount of instances for BEP3 was less in the gated data than the control. However a decrease in mCherry signal after treatment of mouse anti-GFP does suggest that at least some of the proteins are on the surface of the cells. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| - | + | [1]Sevastynovich et al."A generalised module for the selective extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins." Microbial Cell Factories. 2012. | |
| + | |||
| + | [2]Dinh, T., & Bernhardt, T. G. (2011). Using superfolder green fluorescent protein for periplasmic protein localization studies. Journal of bacteriology, 193(18), 4984-4987. | ||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 29 October 2013

Main Page

Contents |
PET-mCherry
PET-mCherry is a β-barrel autotransporter with a mCherry passenger. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1156000# BBa_K1156000]
Motivation
In 2012 the Georgia Tech iGEM team developed a novel biosensor based off of green fluorescent protein. The sensor consisted of two subunits of the protein that separately were inactive but once dimerized expressed fluorescence. From this project, we began thinking about how we could develop more complex sensing technology in bacteria. Taking into consideration how mammalian cells sense and react to their environment, we started asking the question: Can bacteria express human integrins?
To start answering this question, we needed to find a way to transport large proteins and anchor them to the outside of the cell. Autodisplay technology seemed like one possible solution to this problem.
Design
In a 2012 paper, a research group from the University of Birmingham demonstrated that the β-barrel PET could successfully transport and translocate the RFP, mCherry.[http://www.microbialcellfactories.com/content/11/1/69|] We wanted to use their construct to determine whether or not PET would be a good candidate for integrin transport. The sequence that was provided in the paper was already optimized for E. coli expression, however we checked it again. There were also a number of compatibility issues that need to be resolved. To comply with BioBrick standard 10, Phe-76 was re-optimized to remove a EcoRI site withing the part. A T7 promoter with a lacI operator was added with the RBS (AGGA) to the PET_mCherry. A standard assembly 10 prefix and suffix was then added. In future work, other autodisplay technologies are hoped to be tested to express a number of proteins.[http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/O68900 Uniprot]
Because of a generous offer from IDT for discount synthesis we chose to synthesize our protein construct using their gBlock method which consists of blocks of 500bp. Our construct fit into 6 blocks.
Below are the primers that we designed to amplify each block.
Primers: ig12 SP/Pet_mCherry_b1/0 AGTCAGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGG ig13 SP/Pet_mCherry_b2/469 CGTATGAAGGCACCCAGACCGCTAAACTGAAA ig14 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b1/500 TTTCAGTTTAGCGGTCTGGGTGCCTTCATACG ig15 SP/Pet_mCherry_b3/928 CGGGTGCTTACAACGTGAACATCAAACTGGAC ig16 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b2/959 GTCCAGTTTGATGTTCACGTTGTAAGCACCCG ig17 SP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1352 CAAACTGGAAGGTGCGAACAACCTGCTGC ig18 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b3/1380 GCAGCAGGTTGTTCGCACCTTCCAGTTTG ig19 SP/Pet_mCherry_b5/1816 TGTTCACCGGTGTTACCATGACCTACACCGAC ig20 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b4/1847 GTCGGTGTAGGTCATGGTAACACCGGTGAACA ig21 SP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2265 GGTTACCAGTTCGACCTGTTCGCTAACGGTGA ig22 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b5/2296 TCACCGTTAGCGAACAGGTCGAACTGGTAACC ig23 ASP/Pet_mCherry_b6/2516 ACTCTGCAGCGGCCGCTACTAGTATTATTATC
Assembly
The 6 gBlocks that we synthesized using IDT were assembled using overlap extension PCR.
Characterization
The cells for the colonies BEP1 and BEP3 were characterized using flow cytometry. Our goals for this characterization were to show activity of the LacI operator and confirm the expression of mCherry on the outside of the cell. Cells expressing H6, a single strand antibody that favors fibrin, were used as a negative control.
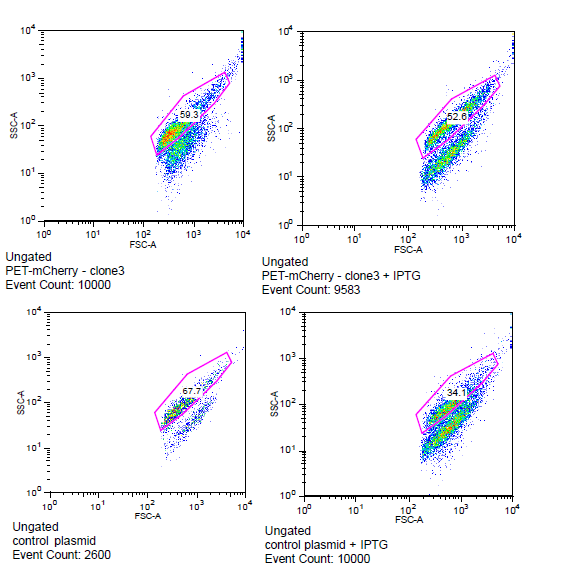
Is the LacI operator working?
Yes! an increase in mCherry expression after induction with IPTG shows that the LacI operator in conjunction with the T7 promoter is working.
Is mCherry on the outside of the cell?
Maybe... Unlike GFP, mCherry has been shown to be functional in the periplasm.[http://jb.asm.org/content/early/2011/07/15/JB.00315-11.full.pdf] In order to determine if mCherry was being expressed outside the cell, BEP3 cells were stained with mouse and rabbit anti-GFP antibodies and then fluorescent tagged anti-mouse and anti-rabbit antibodies.
Very little decrease in the mCherry signal after washing suggest that the protein is not being cleaved if it is expressed externally. Results of the antibody were inconclusive as the amount of instances for BEP3 was less in the gated data than the control. However a decrease in mCherry signal after treatment of mouse anti-GFP does suggest that at least some of the proteins are on the surface of the cells.
References
[1]Sevastynovich et al."A generalised module for the selective extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins." Microbial Cell Factories. 2012.
[2]Dinh, T., & Bernhardt, T. G. (2011). Using superfolder green fluorescent protein for periplasmic protein localization studies. Journal of bacteriology, 193(18), 4984-4987.
 "
"