Large Phage
From 2013.igem.org
(→3/20/13) |
(→3/20/13) |
||
| Line 114: | Line 114: | ||
Today we learned about phage titering. | Today we learned about phage titering. | ||
pfu's are plaque forming units. We tried to see how competent our phage was, unfortunately we ran into quite a few problems. Much of it due to our lack of experience. We put 10 microliters of phage with 90 microliters of LB and did a 1:10 dilution series. we put 20 microliters of each of the dilution series with .5mLs of E.coli. After we let a twenty minute incubation period pass we added 5 mLs of top agar and plated the phage. With the way everything went, I would imagine there will be a lot of contamination, but I certainly learned quite a bit about the process. Hopefully we see some good growth! | pfu's are plaque forming units. We tried to see how competent our phage was, unfortunately we ran into quite a few problems. Much of it due to our lack of experience. We put 10 microliters of phage with 90 microliters of LB and did a 1:10 dilution series. we put 20 microliters of each of the dilution series with .5mLs of E.coli. After we let a twenty minute incubation period pass we added 5 mLs of top agar and plated the phage. With the way everything went, I would imagine there will be a lot of contamination, but I certainly learned quite a bit about the process. Hopefully we see some good growth! | ||
| - | + | ||
20 March 2013 - BDM | 20 March 2013 - BDM | ||
Procedure Description - Titering all stock samples of E. coli phage from Dr. Breakwell’s fridge | Procedure Description - Titering all stock samples of E. coli phage from Dr. Breakwell’s fridge | ||
Revision as of 20:12, 29 May 2013
Contents |
March
3/15/13
3/15/13 - Friday - Bryan Merrill (BDM) Spreadsheet for plasmids, primers, and bacterial strains (and phage) Notes on what we found: Largest: Phage G, lytic, capsid, BSL1, generation time = 40 mins. Smallest: RH1 infects Rhodococcus, capsid size of 43 nm, 50kb? Smallest for E. coli: Spreadsheet (Jade) MS2, capsid protein size 137 aa, 27 nm. Well charaterized, Qbeta as well
Dissertation on capsid design – do longer protein sequences correspond to bigger capsids? Are bigger capsids built from bigger monomers or more monomers? T7 – list of all genes, Gp10a and Gp10b (major and minor capsid proteins) Read the thesis/dissertation – 3 Groups: Large phage Small phage How to build the capsids (heat shock or self-assembly)
Find phage which are well-characterized
Find: How phage are used for drug delivery (applications) Find out how capsid sizes change and mutate (targeted mutagenesis) Start by selecting, move towards targeted mutagenesis What are the applications for phage already
Cloning, sequence, and expression of the temperature-dependent phage T4 capsid assembly gene 31 Modulation of bacteriophage T4 capsid size.
Goal: Build a library of multiple sizes of phage capsids and provide tools to assemble these phage capsids so they can be used for drug delivery and nanotechnology
Look
into:
Metabolic
load on bacteria based on capsid size?
Screening methods: Increasingly harsh environments, less nutrients, smaller phage? Using ozone for selection
3/15/13-Keltzie Smith Today we narrowed in on the phage we are going to use as a starting point for expansion. We found that it wasn’t as easy as we thought to simply look up what would be best for us since there are bits information here and there, but not all in the same location- I suppose this is why we are doing the research that we are- filling a gap! In deciding which to use we took into account genome size as well as how characterized it is. We decided that T4 is the simplest and most effective route to take even though it is technically not the largest phage that infects E. coli.
Large phage procedures:
Paper about UV light and backup genes?
Decreasing agar concentration – select for small plaque sizes
Find T4 phage and host
Start growing them (archive sample of the phage)
Determine sequence of the relevant capsid proteins
Mutate them
Determine the sequence again
Find a way to create just capsids of the larger size
3/18/13
3/18/13-Keltzie Smith As of right now our main priority is making sure the T4 we have now is working. Today we started our K12 E.Coli. Next time we’ll see if our T4 is viable, once we see plaques on our plates our next step will be to sequence our phage to determine what we have to start out with an we’ll mutate from there. One thing we are hoping to look deeper into is UV irradiation to select for bigger bacteriophages.
18 March 2013 - BDM 18 March 2013 – Monday – BDM Notes: Cholera group Biofilm – grow a cholera biofilm in the lab to test constructs that have already been created Plasmid prep – sequencing inserts in plasmid to see if the genes were inserted correctly. 2 membrane proteins, 2 phosphorylation proteins, 2 genes turned on (RFP and GFP), small RNAs. Need to clone in protein interaction and siRNA degradation.
Phage group Protein prep/capsid purification – T7 proteins, requires scaffold protein and capsid proteins to assemble. Other phage, sometimes this doesn’t happen. T4 forms procapsids, but not large ones in vitro. No DNA in capsids – knock out polymerases. Capsid size can depend on environmental factors. Small phage – Directed and random mutagenesis
Genetic Control of Capsid Length in Bacteriophage T4 Genetic studies on capsid-length determination in bacteriophage T4 Evolution of Phage Capsid and Genome Size The Capsid of the T4 Phage Superfamily
Hendrix, R.W. (2009) Jumbo bacteriophages. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 328:229-240
Lee, K.K., L. Gan, H. Tsuruta, C. Moyer, J.F. Conway, R.L. Duda, R.W. Hendrix, A.C. Steven, and J.E. Johnson (2008) Virus capsid expansion driven by the capture of mobile surface loops. Structure 16:1491-1502
3/20/13
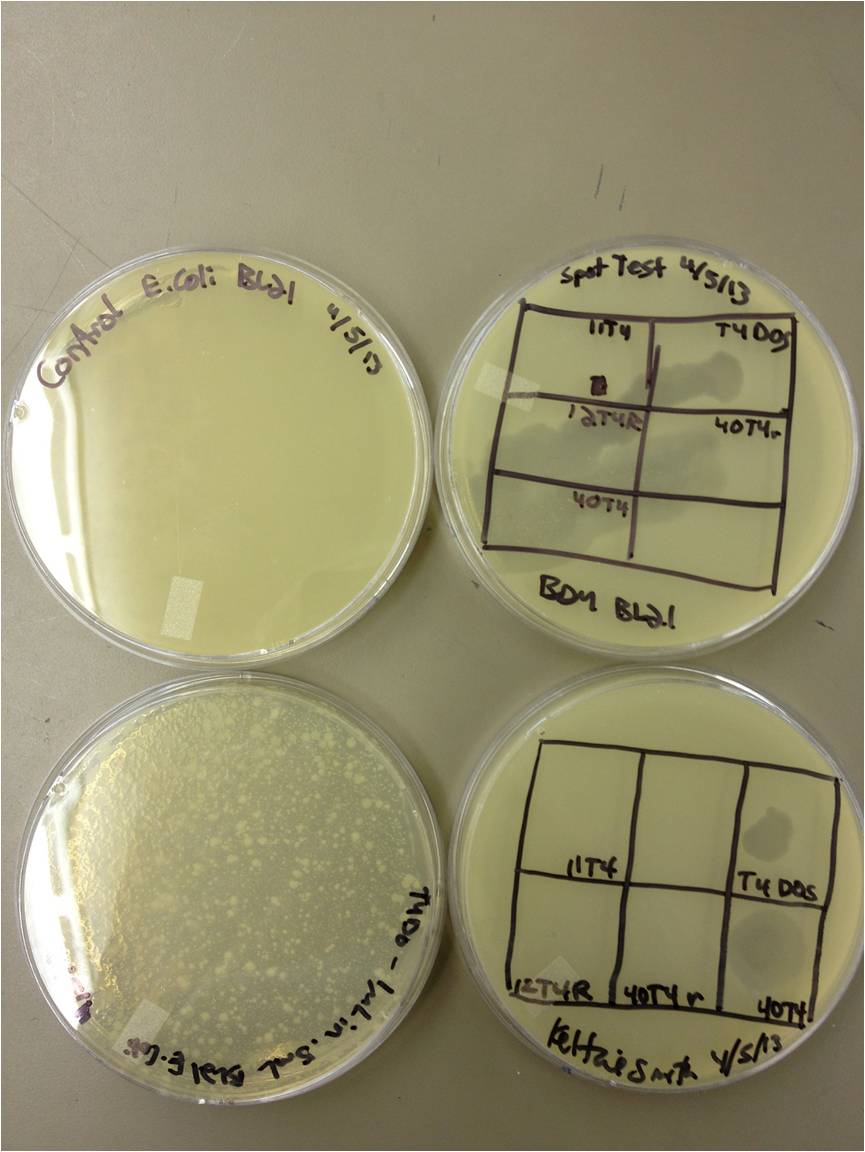
3/20/13-Keltzie Smith Today we learned about phage titering. pfu's are plaque forming units. We tried to see how competent our phage was, unfortunately we ran into quite a few problems. Much of it due to our lack of experience. We put 10 microliters of phage with 90 microliters of LB and did a 1:10 dilution series. we put 20 microliters of each of the dilution series with .5mLs of E.coli. After we let a twenty minute incubation period pass we added 5 mLs of top agar and plated the phage. With the way everything went, I would imagine there will be a lot of contamination, but I certainly learned quite a bit about the process. Hopefully we see some good growth!
20 March 2013 - BDM Procedure Description - Titering all stock samples of E. coli phage from Dr. Breakwell’s fridge Purpose - See which phage stocks are viable, and how many PFUs/mL they have. Theoretical Protocol - We performed a 1:10 dilution series (10^0 to 10^-5) on each of the stock samples. We infected 0.5 mL of an overnight growth of E. coli K12 with 20 uL of each dilution series tube. After infecting for 20 minutes, we added 5 mL of 1x LB top agar and plated them on LB plates. We let them incubate at 37C overnight. I also tried a spot test of each sample on an E. coli lawn (to check for plaque formation) and on a plain LB plate (to check for phage lysate contamination). Results Actual Protocol - We performed this experiment as we planned on doing it. The agar frequently boiled over in the microwave which made it difficult to use.Next time we will use 2X and mix it right before we need it. Results - None of the samples showed signs of plaques after 24 hours. I will let them incubate one more night. Three of the phage lysates were contaminated. Observations - It is very likely that these phage samples are no longer viable. We ought to make a list of which phages we would like from Dr. Casjens at U of U and start from fresh samples instead of these ones.
3/22/13
3/25/13
3/27/13
3/29/13
April
4/1/13
4/4/13
4/5/13
4/8/13
4/10/13
4/12/13
4/15/13
May
5/1/13
5/3/13
5/6/13
5/8/13
5/10/13
5/13/13
5/15/13
5/17/13
5/20/13
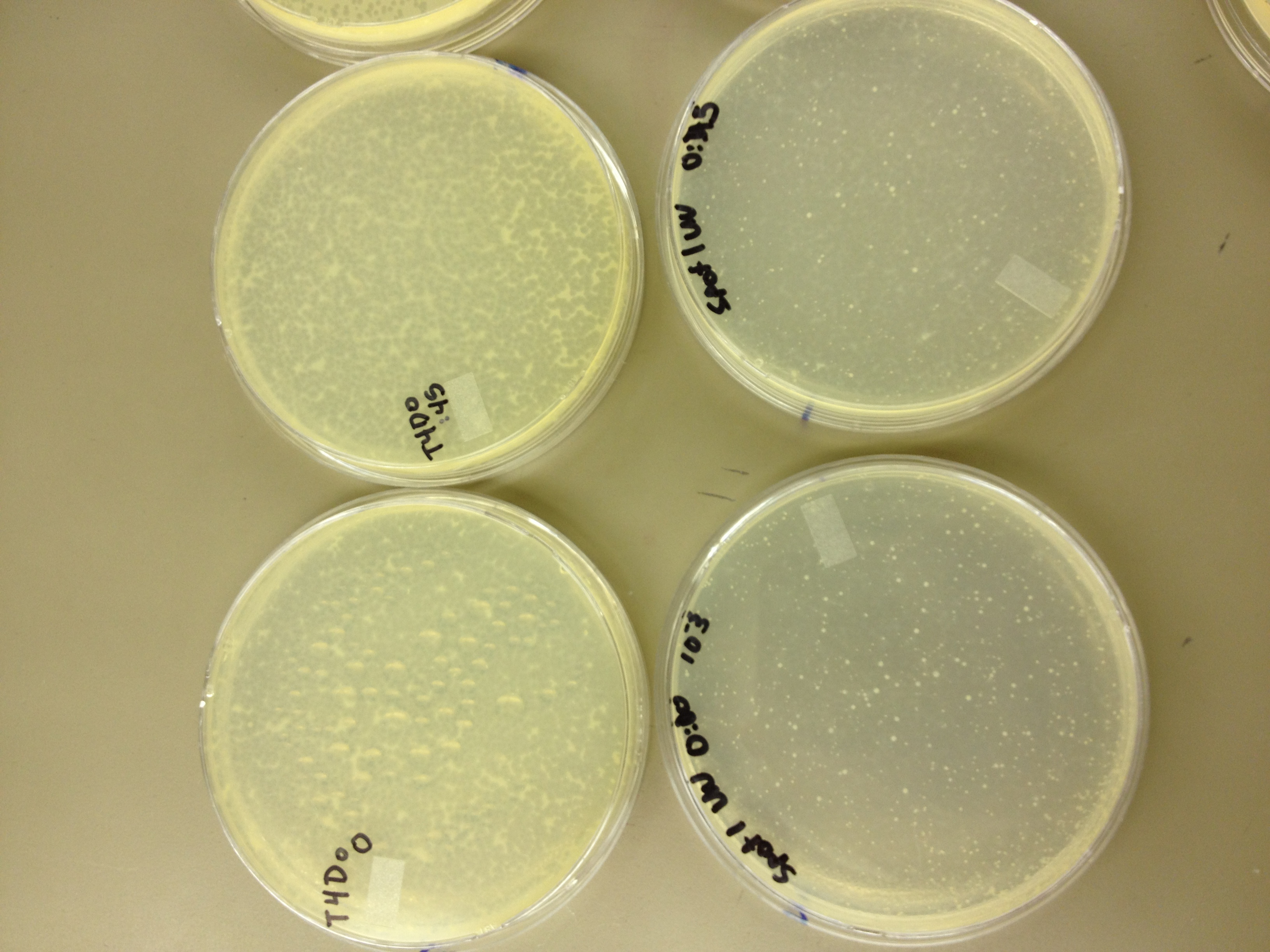
Today we need to run a dilution series to test the titer of our mutated phage stock. We also need to start selecting for small plaques and learning how to pick them and titer them out. We also should run a UV test on the mutated phage stock compared to the normal stock.
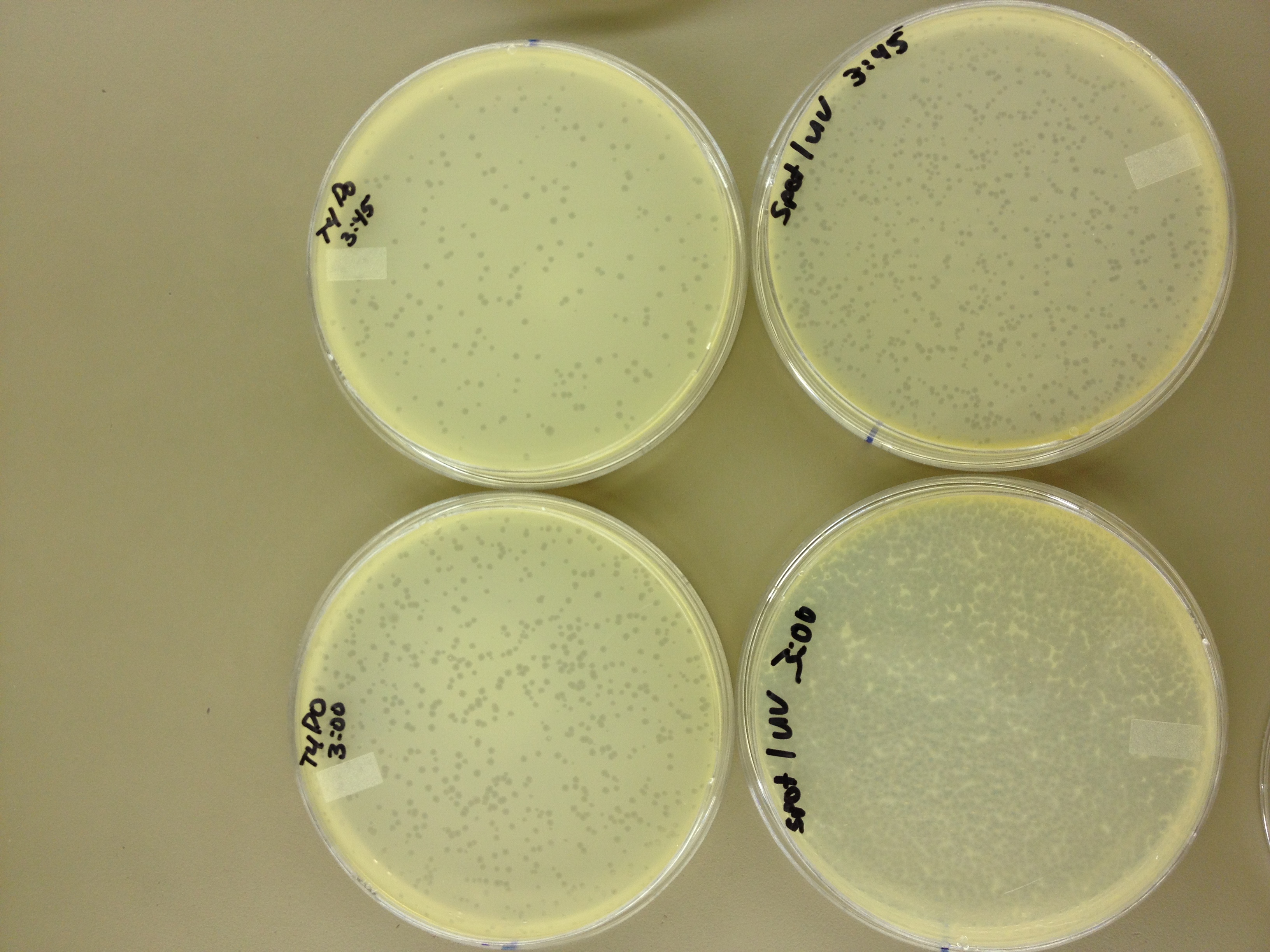
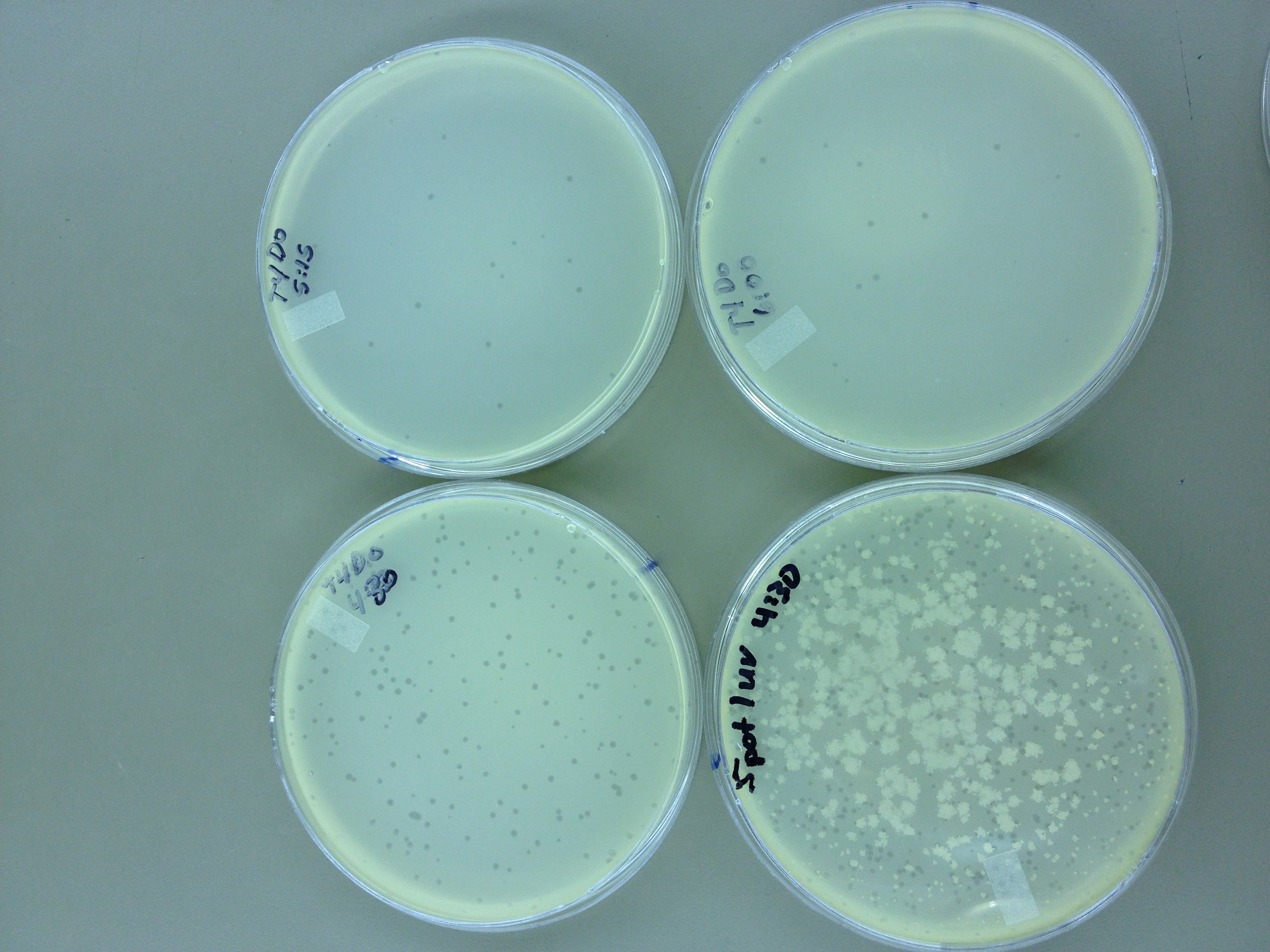
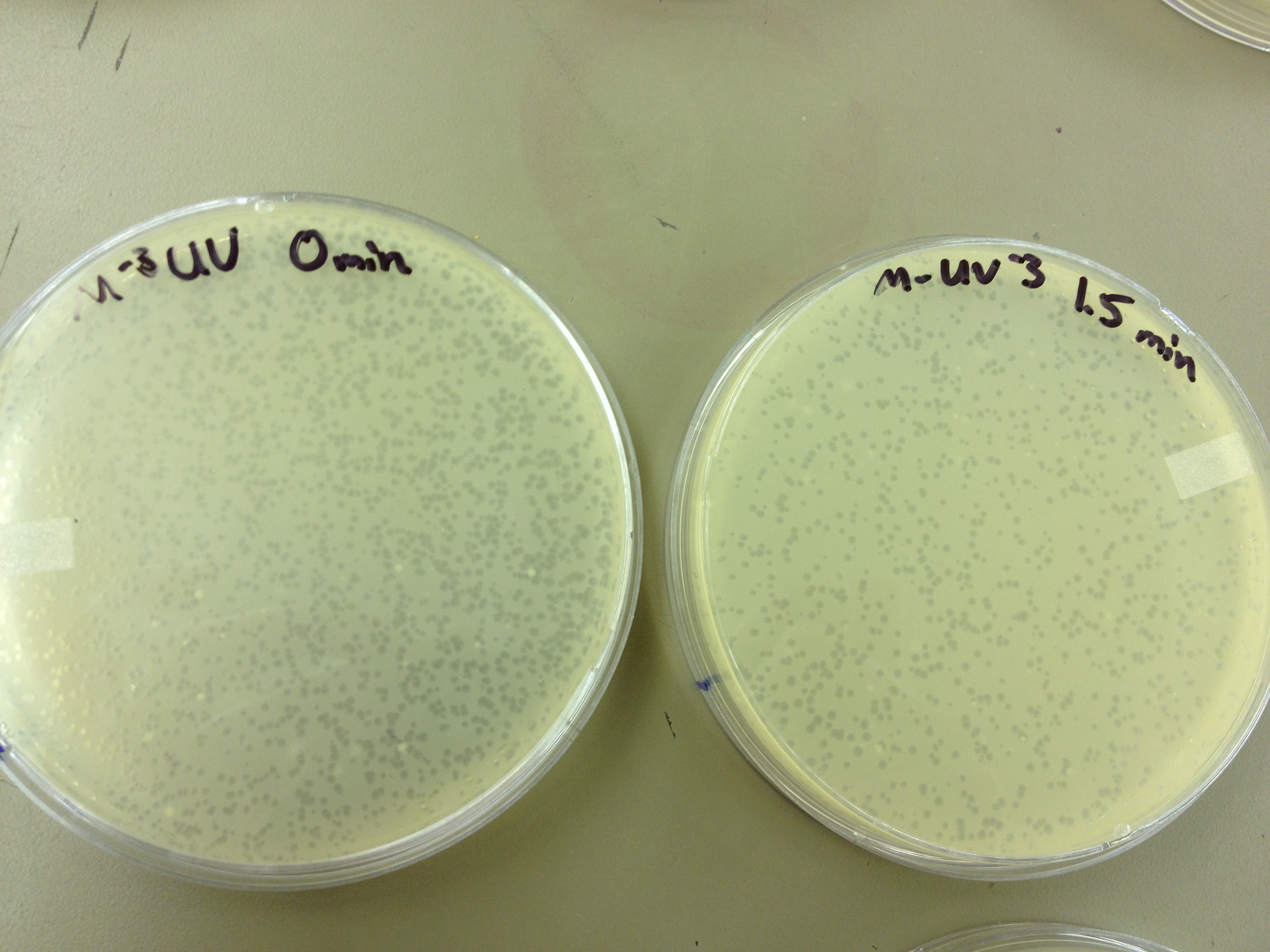
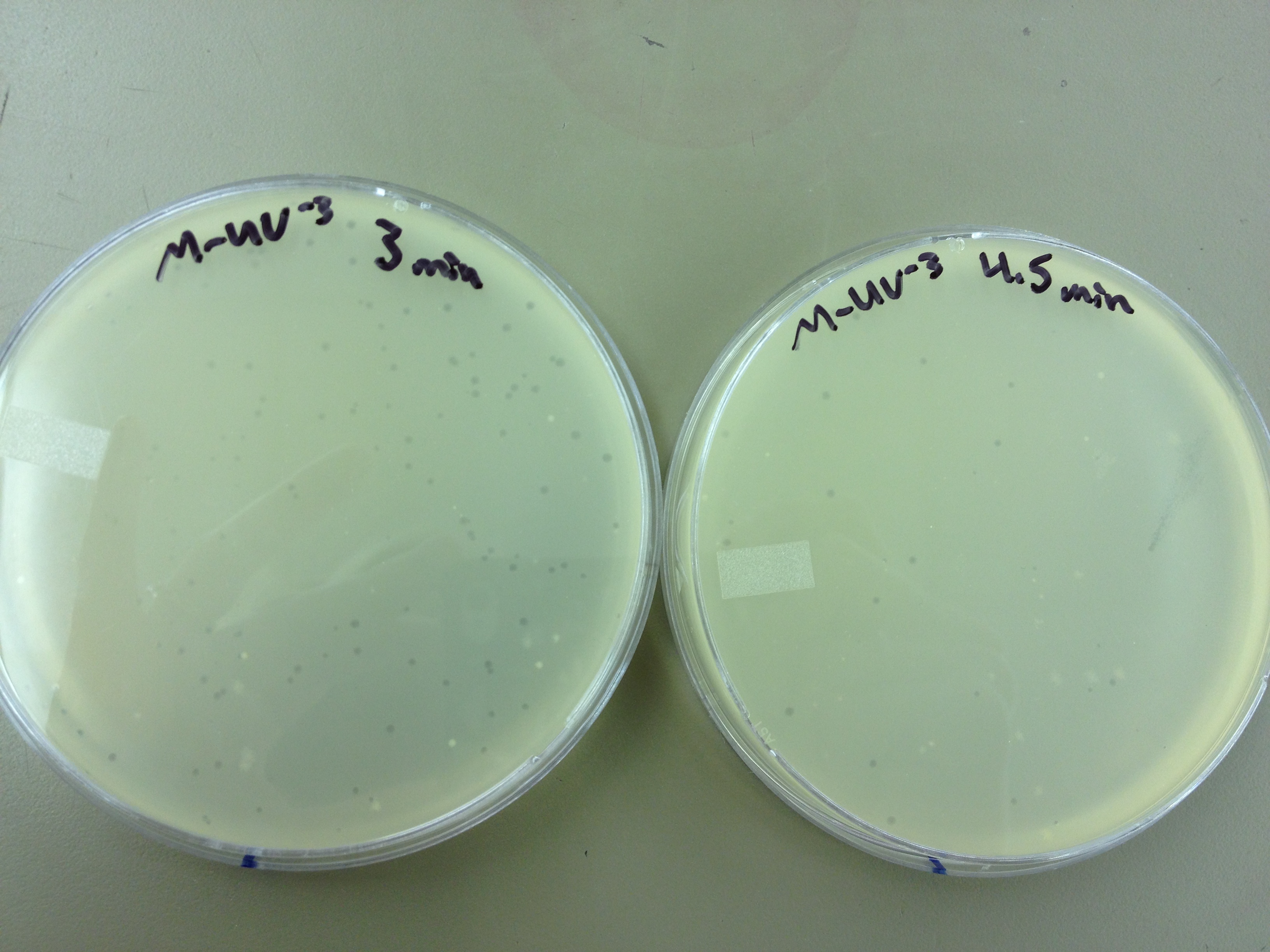
We picked one plaque off of the 180 sec UV plate sample. We suspended it in 1 mL of broth, and then UV-ed 20 uL samples at 45 second intervals. The number of plaques decreased the longer the samples sat under UV light. The samples were irradiated from 0 sec to 4 min 30 sec.
As a control, we diluted the T4Do stock to 10^-6 and tested 20 uL at 45 sec intervals (up to 6 min) under UV light.
Also, we diluted the T4 mutagenized stock to 10^-6 and tested 20 uL at 45 sec intervals (up to 4 min 30 sec) under UV light.
UV tests were done by placing 20 uL spots on parafilm and placed in a BSL-2 hood with the UV light turned on.
5/22/13
Results from 5/20/13 - We left the plates in the incubator for 48 hours, which caused contamination on many plates to grow.
When checked at 24 hours, the T4 mutagenized stock had a web plate at 10^-3 and less than 5 plaques at 10^-6. This experiment will need to be redone from 10^0 down through 10^-6. The whole mutagenesis may need to be redone if this only represents a dilution of our titer when we were trying to grow it in liquid culture. (We infected with ___ mL of phage at ___ titer in ____ vol of resuspended bacteria.)
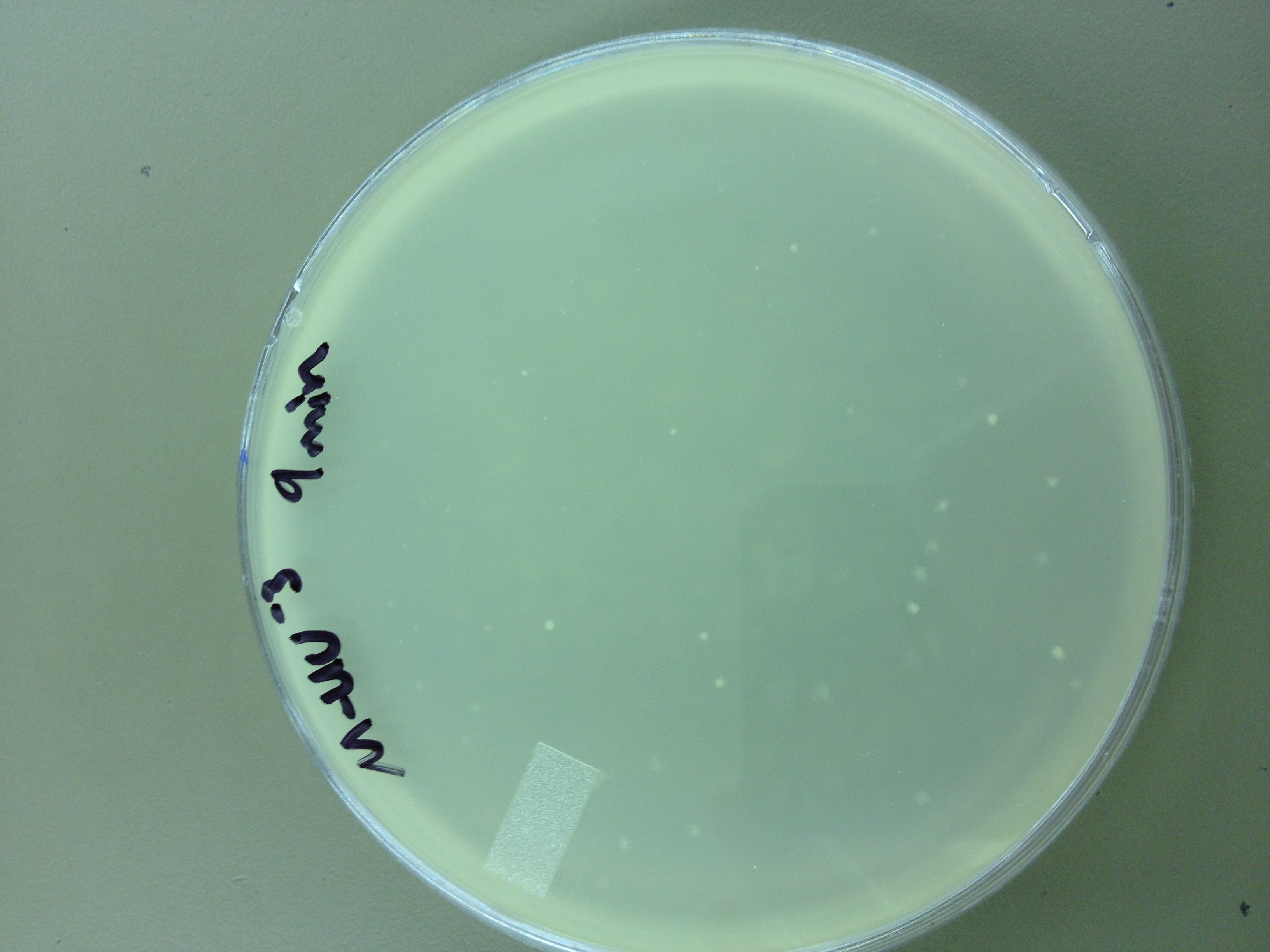
Under UV light, the T4Do stock (diluted to 10^-6) has 19 plaques after being irradiated for six minutes (down from almost cleared at 0 min). Under UV light, the 180 sec UV plate spot (diluted in 1 mL) has a few hundred plaques on it, but the amount dropped significantly at 4 min 30 sec from when it was UV-ed for 0 min.
We will re-titer the T4-Mut stock so we can learn whether it was diluted or whether an infection worked. We will also re-run the UV test comparing the T4-Mut (10^-3) with the T4-Do stock (at 10^-6) for survivability. The mutagenized phage should survive better.
Since the loss of plaques seemed to level off for the T4Do stock at 5:15 (23 plaques) and 6 min (19 plaques), we will test a 7 min and 8 min timepoint to see if it stays level, suggesting these phage have multiple genomes and are severely mutated.
5/24/13
5/27/13
5/29/13
5/31/13
June
6/3/13
6/5/13
6/7/13
6/10/13
6/12/13
6/14/13
6/17/13
6/19/13
6/21/13
6/24/13
6/26/13
6/28/13
July
7/1/13
7/3/13
7/5/13
7/8/13
7/10/13
7/12/13
7/15/13
7/17/13
7/19/13
7/22/13
7/24/13
7/26/13
7/29/13
7/31/13
August
8/2/13
8/5/13
8/7/13
8/9/13
8/12/13
8/14/13
8/16/13
8/19/13
8/21/13
8/23/13
8/26/13
8/28/13
8/30/13
September
9/2/13
9/4/13
9/6/13
9/9/13
9/11/13
9/13/13
9/16/13
9/18/13
9/20/13
9/23/13
9/25/13
9/27/13
9/30/13
 "
"