Team:Imperial College/Communication work
From 2013.igem.org
| (52 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<h1>Communicating our Project</h1> | <h1>Communicating our Project</h1> | ||
| - | We | + | <b>What do you know what happens to your rubbish? Is your rubbish a resource?</b> |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Our outreach work has been very important to us. We were really keen to discuss our project with members of the public to hear their thoughts about whether this system could be used in the real world. We were delighted to feature on <b>BBC Radio 4's Inside Science</b> show and to present at the Kensington and Chelsea Council's <b>Celebration of Science</b> event. To grab the attention of the public, we have also founded an art movement, called <b>BioNouveau</b>. | ||
| + | <h2>What would you 3D print?</h2> | ||
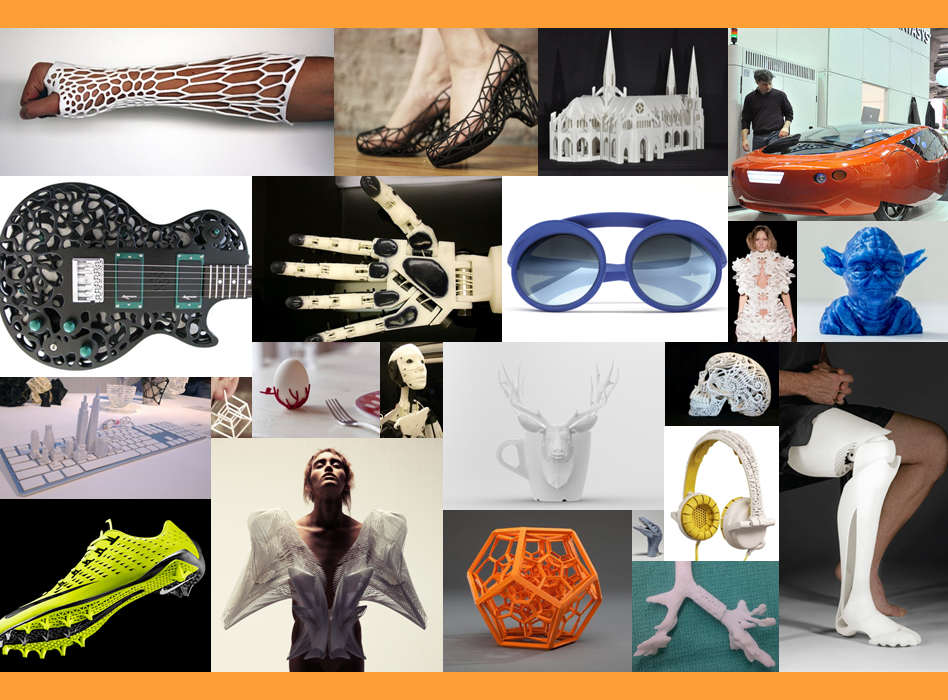
| - | + | From our research into waste management, it has been suggested that 'local solutions' and small scale schemes could have a great impact on how waste is dealt with in the future. Could people be empowered to use the waste they generate directly as a resource? With this notion in mind we designed the futuristic company [https://2013.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College/MAPLE M.A.P.L.E.], which sells a range of appliances that turn domestic rubbish into new 3D printed, bioplastic objects. | |
| - | + | Although M.A.P.L.E. is (currently) fictional, we really wanted to know whether people would be interested in such devices. Were they excited by the idea of being able to design and print their own unique objects at home? This discussion quickly turned into a survey: <b>If you owned your own M.A.P.L.E. device, what would you 3D print?</b> Some of the responses can be seen below. | |
| - | <h2> | + | [[File:What_would_you_3d_print.png|800px|centre]] |
| - | [[File:ZScream.jpg|left| | + | [[File:Responses_to_what_would_you_3d_print.png|800px|centre]] |
| - | + | ||
| + | <h2>Interview on BBC Radio 4</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Last week our project featured on the BBC Radio 4 show, Inside Science. Science journalist and Nature editor Dr. Adam Rutherford visited our lab to talk to us about our project. The piece includes interviews with our advisor Prof. Paul Freemont and with iGEM team member Jemma Pilcher. If you would like to catch up with the show, [[File:Insidescience imperialigem.mp3]] to listen to the podcast or find it [http://www.bbc.co.uk/podcasts/series/inscience| here]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Photo with adam.JPG|centre|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Introductory video</h2> | ||
| + | With our collaborators at the Royal College of art, we shot this video to share and communicate the overview of our project. It also encouraged the "What would you 3D print?" discussion. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <iframe width="420" height="315" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/SJAHLzswQhY" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2 class="clear">Celebration of Science</h2> | ||
| + | |||
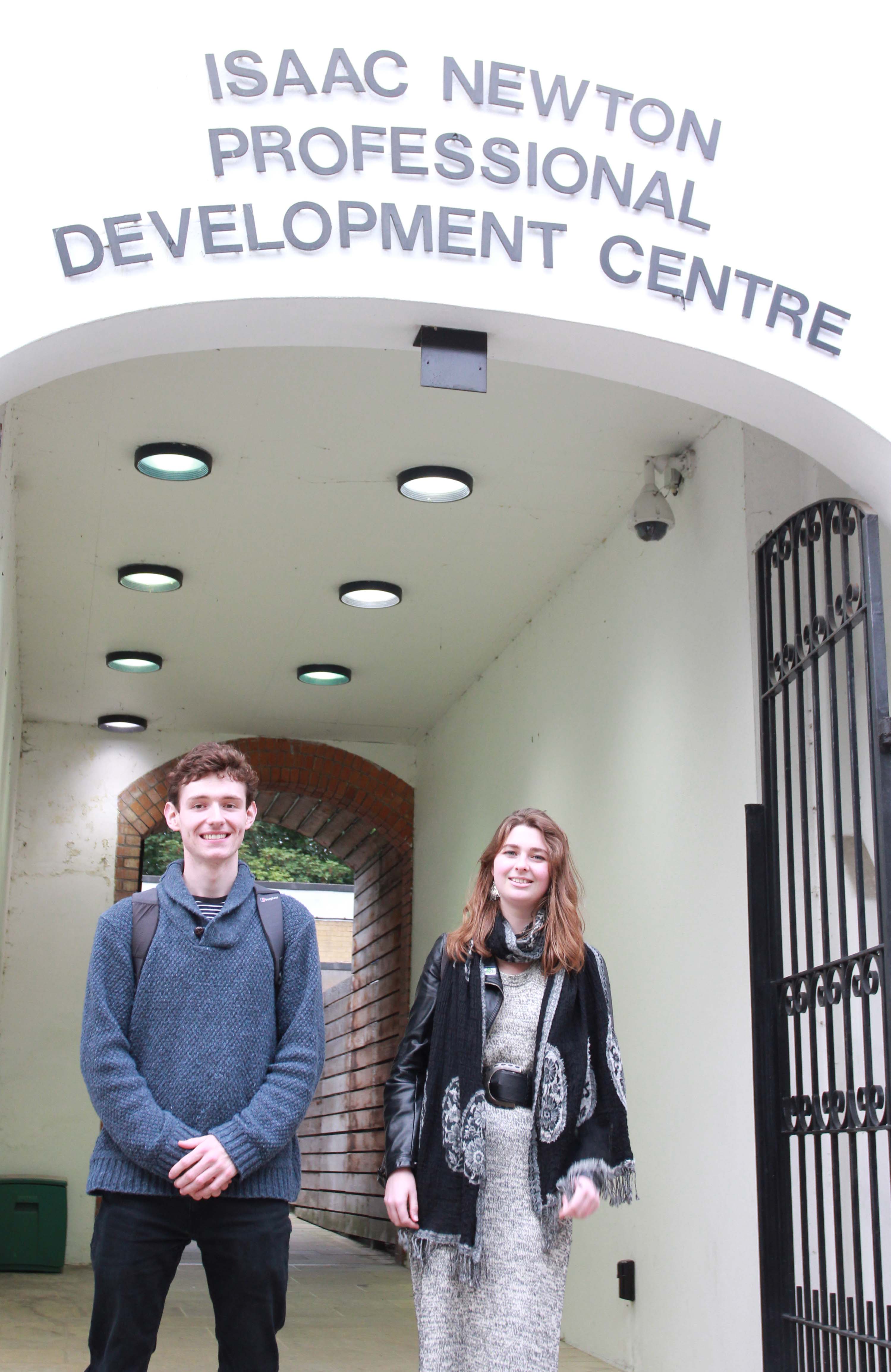
| + | <p>From 20th-28th of september Kensington and Chelsea Council hosted a Celebration of Science week. Distinguished guests from the scientific, political and academic worlds took part, as well as from the Arts. We were privileged to present synthetic biology and our project in the Isaac Newton Centre on the 28th of September. </p> | ||
| + | [[File:Warwick quote.png|700px|left]] | ||
| + | [[File:Isaac_Newton.png|200px|right]] | ||
| + | [[File:Celebration_of_science.png|250px|right]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <p>"A team of students from Imperial College presented a research project at the Science Cafe, held as part of the the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea's Celebration of Science. This project spoke directly to the practical concerns of a local authority, exploring how we can be make use of our rubbish and refuse collections. It offered a fascinating glimpse of the potential of modern biology and life sciences to make new materials, such as plastics that until now have come from oil and hydrocarbon processes are often relatively expensive. The students offered a glimpse of the manner in which biology is changing rapidly and of the kind of innovative processes that have the potential to save all of us, including local councils, money." <b>Councillor Warwick Lightfoot, Cabinet Member for Finance and Strategy Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea.</b></p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Living Art: Bionouveau</h2> | ||
| + | |||
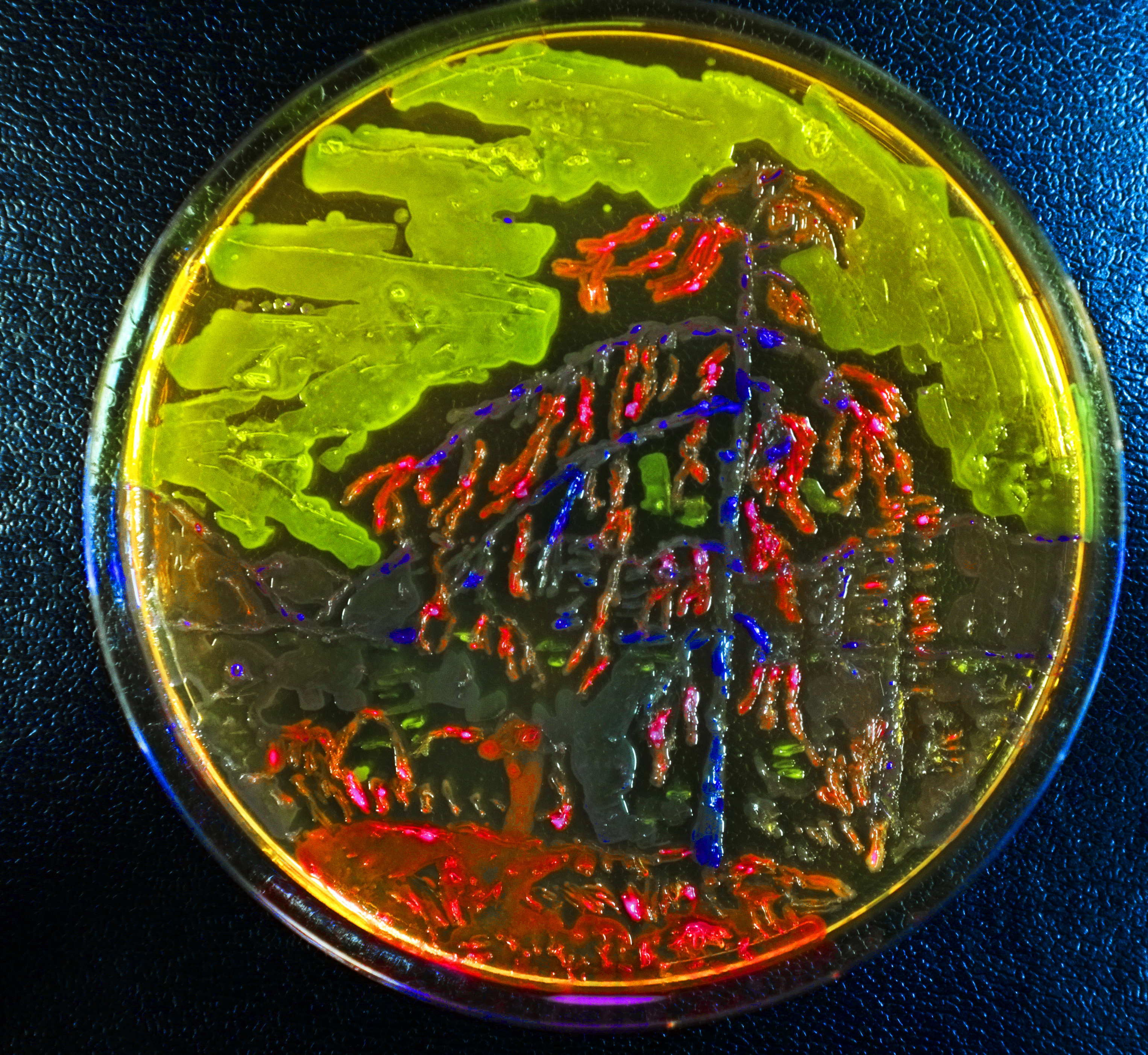
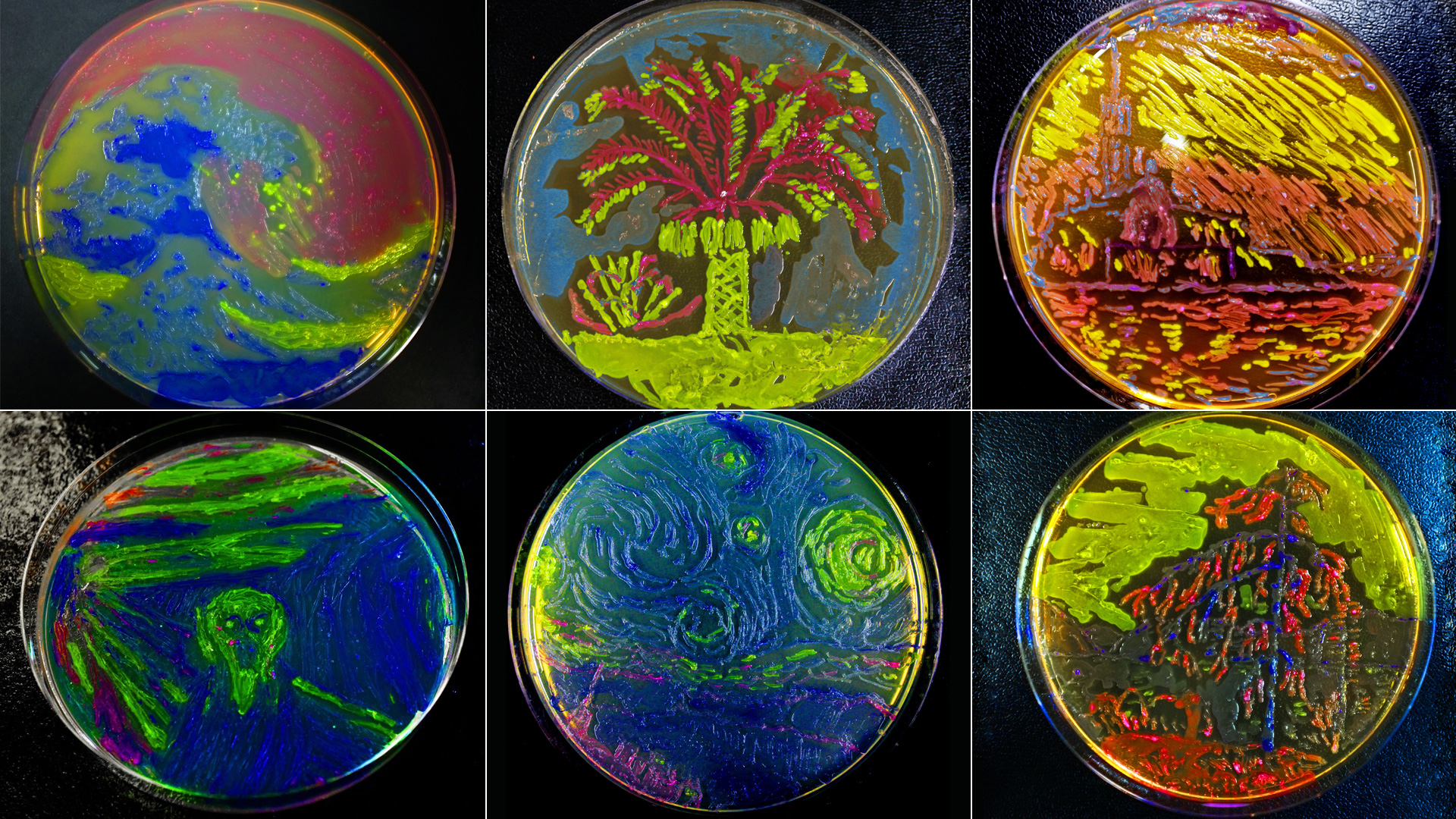
| + | We wanted to communicate Synthetic Biology in an engaging and novel way. We developed a method of painting with highly cultured E. coli. Our paintings are incredibly popular and have provoked discussions with us about our project and SynBio as a whole. Our paintings were displayed at the European Jamboree as part of ATOMS Turkiye iGEM's SynArt exhibition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:CombinedBacteriaArt.jpg|1000px]] | ||
| + | <p style="clear">A vignette of all of our bacterial art.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
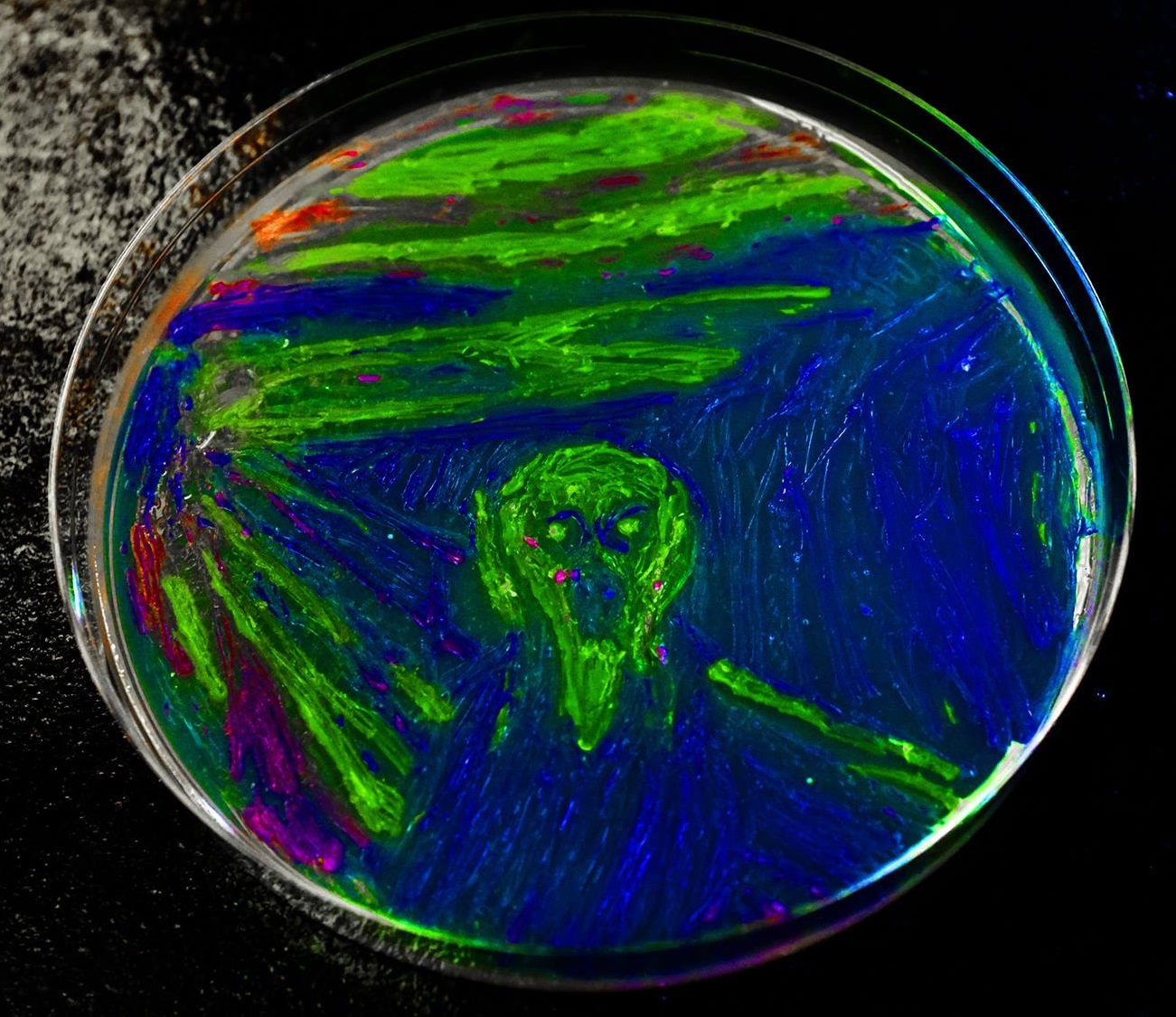
| + | [[File:ZScream.jpg|left|300px|One of Edvard Munch's greatest successes, The Scream, now expressed in all new splendour by the novel art form of <i>E. coli</i>]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
The Scream, a masterpiece, clearly depicts an individual on a pier with a haunting expression with a heady back drop of a yellow and red sky. Reforging this painting with bacteria has created 5th rendition of this magnificent work of art. Originally painted in 1893 by Edvard Munch, The Scream characterised a tempestuous time in art as a precursor to the advent of Expressionism. As such, it is perfectly placed to represent the potential power of SynBio to revolutionise the modern world, and this in and of itself represents the verve behind team Plasticity to add value to waste with our MAPLE system. | The Scream, a masterpiece, clearly depicts an individual on a pier with a haunting expression with a heady back drop of a yellow and red sky. Reforging this painting with bacteria has created 5th rendition of this magnificent work of art. Originally painted in 1893 by Edvard Munch, The Scream characterised a tempestuous time in art as a precursor to the advent of Expressionism. As such, it is perfectly placed to represent the potential power of SynBio to revolutionise the modern world, and this in and of itself represents the verve behind team Plasticity to add value to waste with our MAPLE system. | ||
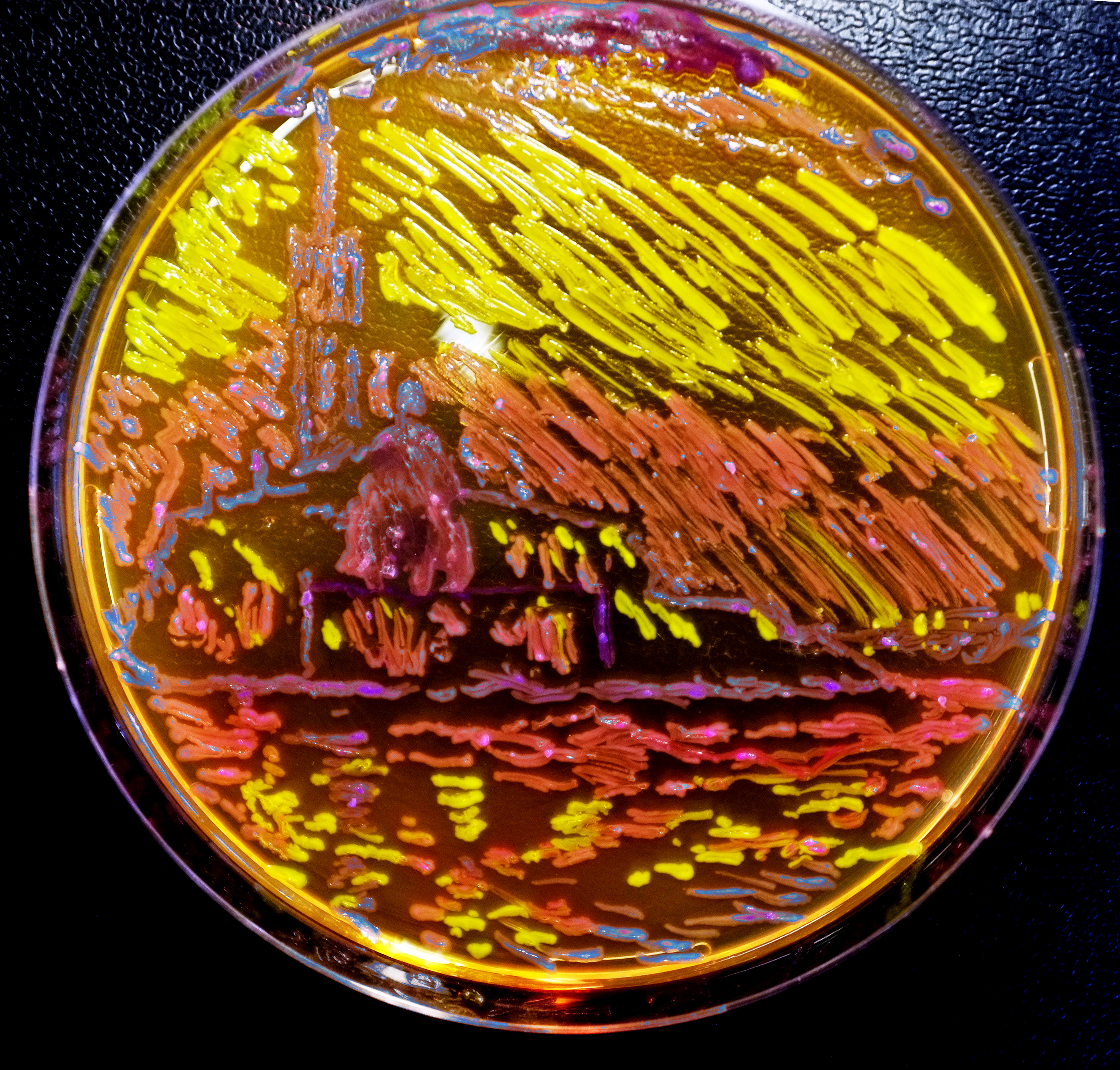
| - | [[File:DSCF1933_edited.jpg|right| | + | [[File:DSCF1933_edited.jpg|right|300px|Claude Monet's San Giorgio Maggiore, depicted by highly cultured <i>E. coli</i>]] |
| - | <br><br><br><br><br> | + | <p style="clear: left"><br><br>Claude Monet's San Giorgio Maggiore, depicted by highly cultured <i>E. coli</i>. |
| + | San Giorgio Maggiore is an island in Venice, best known for the prominent church that sits upon it. In 1908, Claude Monet produced this impressionist painting. It was originally received with great awe due to the vibrancy of the colours. Similarly with the bacterial copy, it also shows great vibrancy of colour, courtesy of the GFP in the bdh2, which appears yellow and the RFP present in the stress response sensor, providing the red pigment. Indeed the radiance of the sunset is reflected magnificently in the calm waters of the Laguna Veneta.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Z_Great_Wave_of_Kanagawa.jpg|left|300px|Hokusai's masterpiece, the Great Wave of Kanagawa, brought to you by pigmented and fluorescence <i>E. coli</i>.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p style="clear: right"><br><br>To the left is depicted Hokusai's world renowned masterpiece, the Great Wave of Kanagawa. The painting depicts an enormous wave off of the Japanese prefecture of Kanagawa. The key difference here is the presence, or lack thereof of Mount Fuji, which has been swallowed by the ominous blood red sky that overshadows the entire scene. The work was produced during the Edo Period of Shogunate rule, sometime between 1830-1833 and does not constitute a painting of a deadly tsunami as many people commonly assume.</p> | ||
| + | |||
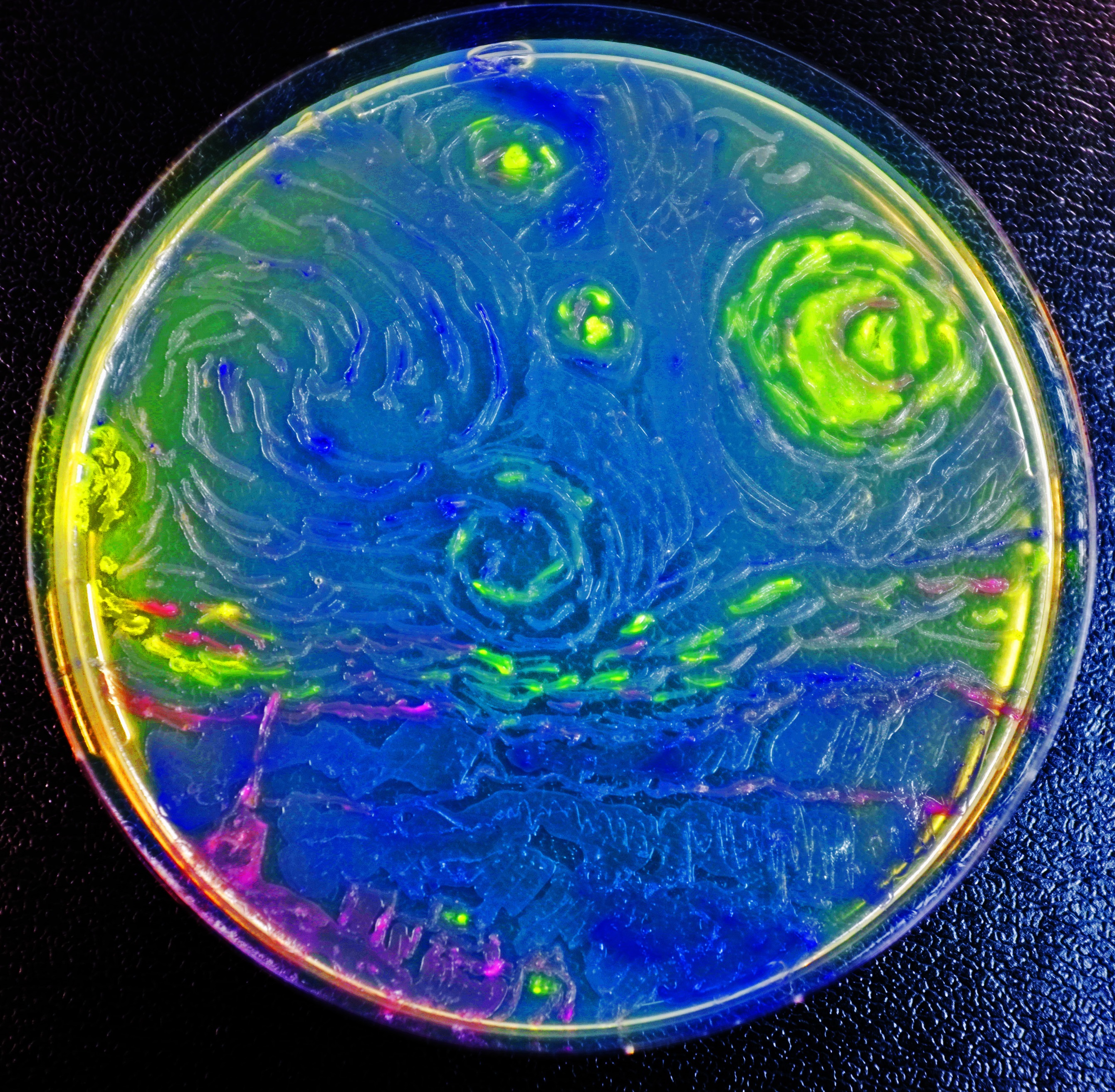
| + | [[File:Z_Starry_Night.jpg|right|300px|One of Claude Monet's greatest works, Starry Night, now here to light up our page, courtesy of our bacteria that become more and more cultured by the day.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p style="clear: left"><br><br>Painted by Vincent van Gogh in 1889 with oil on canvas, Starry Night depicts a night scene from Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. We can see here clearly the glowing crescent moon high in the sky, hovering over the deep blue hills beyond the town. Interestingly the scene was painted completely from memory the next day by van Gogh. It represents a point in the life whereby he was institutionalised due to incapacitation by nervous troubles. </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Z_The_Jack_Pine.jpg|left|300px|The original was an oil painting by Tom Thomson in 1917.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p style="clear: right"><br><br>Originally painted in 1917 by Tom Thompson, The Jack Pine is a symbolic work of art, representing one of Canada's most iconic native pine trees, found east of the Rocky Mountains. It is not to be confused with Canada's most well known broad-leaf Maple, for which the country is famous. The scene depicted is at evening with a serene backdrop into the fading light. Tom Thompson was a forerunner to the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_of_Seven_%28artists%29 Group of Seven] before its inception had even been brought about, such was the influence of this iconic painting.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Z_Mc_Escher_Palm.jpg|right|300px|M.C. Escher was a woodcut artist, making art from trees. Here we have his work streaked with Escherichia coli in the form of his work, the Palm.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p style="clear: left"><br><br>M.C. Escher was a woodcut artist, making art from trees. Here we have recreated his work by streaking media with Escherichia coli to form one of his art pieces, the Palm. Escher was a dutch artist and completed the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Woodcut xylograph] in 1933. Xylographs are produced by etching and carving an image into a block of wood. The non-printing parts are removed and the printing process can commence, allowing the printing of the Palm to be done in black and white.</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Other publications</h2> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h3>GetSynBio Blog</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Our project was featured on the GetSynBio Blog! | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:GetSynBioblog.jpg|thumbnail|left|600px|]] | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<br><br><br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | http://getsynbio.com/igem-page/ | ||
| - | < | + | <h3>Imperial Bioengineering Departmental News</h3> |
| - | < | + | Our project was featured on a departmental newsletter. In addition to informing our colleagues about our project we also conveyed the importance of the social challenges facing waste management and recycling.<br> |
| - | + | https://workspace.imperial.ac.uk/bioengineering/Public/Newsletters/Newsletter%20August%202013.pdf | |
| - | |||
| - | < | + | <h3>Felix</h3> |
| - | + | We published an article in the Imperial College newspaper, Felix. | |
| - | + | http://felixonline.co.uk/features/3912/from-trash-to-treasure-via-synthetic-biology/ | |
| - | |||
| - | + | <h3>Online newspaper</h3> | |
| + | |||
| + | This automated online newspaper collates the top and most popular news stories from our twitter and facebook feeds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <p>Check out our online newspaper for news and updates from our project, the iGEM community and global discussions about waste management. | ||
| + | http://paper.li/imperialigem/1377382636</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <h2>Social Media</h2> | ||
<h3>Facebook</h3> | <h3>Facebook</h3> | ||
| - | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/ | + | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/8e/Facebook_analytics.jpg |
<h3>Twitter</h3> | <h3>Twitter</h3> | ||
[[File:Twitter_analytics.jpg]] | [[File:Twitter_analytics.jpg]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:08, 29 October 2013
Contents |
Communicating our Project
What do you know what happens to your rubbish? Is your rubbish a resource?
Our outreach work has been very important to us. We were really keen to discuss our project with members of the public to hear their thoughts about whether this system could be used in the real world. We were delighted to feature on BBC Radio 4's Inside Science show and to present at the Kensington and Chelsea Council's Celebration of Science event. To grab the attention of the public, we have also founded an art movement, called BioNouveau.
What would you 3D print?
From our research into waste management, it has been suggested that 'local solutions' and small scale schemes could have a great impact on how waste is dealt with in the future. Could people be empowered to use the waste they generate directly as a resource? With this notion in mind we designed the futuristic company M.A.P.L.E., which sells a range of appliances that turn domestic rubbish into new 3D printed, bioplastic objects.
Although M.A.P.L.E. is (currently) fictional, we really wanted to know whether people would be interested in such devices. Were they excited by the idea of being able to design and print their own unique objects at home? This discussion quickly turned into a survey: If you owned your own M.A.P.L.E. device, what would you 3D print? Some of the responses can be seen below.
Interview on BBC Radio 4
Last week our project featured on the BBC Radio 4 show, Inside Science. Science journalist and Nature editor Dr. Adam Rutherford visited our lab to talk to us about our project. The piece includes interviews with our advisor Prof. Paul Freemont and with iGEM team member Jemma Pilcher. If you would like to catch up with the show, File:Insidescience imperialigem.mp3 to listen to the podcast or find it [http://www.bbc.co.uk/podcasts/series/inscience| here].
Introductory video
With our collaborators at the Royal College of art, we shot this video to share and communicate the overview of our project. It also encouraged the "What would you 3D print?" discussion.
Celebration of Science
From 20th-28th of september Kensington and Chelsea Council hosted a Celebration of Science week. Distinguished guests from the scientific, political and academic worlds took part, as well as from the Arts. We were privileged to present synthetic biology and our project in the Isaac Newton Centre on the 28th of September.
"A team of students from Imperial College presented a research project at the Science Cafe, held as part of the the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea's Celebration of Science. This project spoke directly to the practical concerns of a local authority, exploring how we can be make use of our rubbish and refuse collections. It offered a fascinating glimpse of the potential of modern biology and life sciences to make new materials, such as plastics that until now have come from oil and hydrocarbon processes are often relatively expensive. The students offered a glimpse of the manner in which biology is changing rapidly and of the kind of innovative processes that have the potential to save all of us, including local councils, money." Councillor Warwick Lightfoot, Cabinet Member for Finance and Strategy Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea.
Living Art: Bionouveau
We wanted to communicate Synthetic Biology in an engaging and novel way. We developed a method of painting with highly cultured E. coli. Our paintings are incredibly popular and have provoked discussions with us about our project and SynBio as a whole. Our paintings were displayed at the European Jamboree as part of ATOMS Turkiye iGEM's SynArt exhibition.
A vignette of all of our bacterial art.
The Scream, a masterpiece, clearly depicts an individual on a pier with a haunting expression with a heady back drop of a yellow and red sky. Reforging this painting with bacteria has created 5th rendition of this magnificent work of art. Originally painted in 1893 by Edvard Munch, The Scream characterised a tempestuous time in art as a precursor to the advent of Expressionism. As such, it is perfectly placed to represent the potential power of SynBio to revolutionise the modern world, and this in and of itself represents the verve behind team Plasticity to add value to waste with our MAPLE system.
Claude Monet's San Giorgio Maggiore, depicted by highly cultured E. coli.
San Giorgio Maggiore is an island in Venice, best known for the prominent church that sits upon it. In 1908, Claude Monet produced this impressionist painting. It was originally received with great awe due to the vibrancy of the colours. Similarly with the bacterial copy, it also shows great vibrancy of colour, courtesy of the GFP in the bdh2, which appears yellow and the RFP present in the stress response sensor, providing the red pigment. Indeed the radiance of the sunset is reflected magnificently in the calm waters of the Laguna Veneta.
To the left is depicted Hokusai's world renowned masterpiece, the Great Wave of Kanagawa. The painting depicts an enormous wave off of the Japanese prefecture of Kanagawa. The key difference here is the presence, or lack thereof of Mount Fuji, which has been swallowed by the ominous blood red sky that overshadows the entire scene. The work was produced during the Edo Period of Shogunate rule, sometime between 1830-1833 and does not constitute a painting of a deadly tsunami as many people commonly assume.
Painted by Vincent van Gogh in 1889 with oil on canvas, Starry Night depicts a night scene from Saint-Rémy-de-Provence. We can see here clearly the glowing crescent moon high in the sky, hovering over the deep blue hills beyond the town. Interestingly the scene was painted completely from memory the next day by van Gogh. It represents a point in the life whereby he was institutionalised due to incapacitation by nervous troubles.
Originally painted in 1917 by Tom Thompson, The Jack Pine is a symbolic work of art, representing one of Canada's most iconic native pine trees, found east of the Rocky Mountains. It is not to be confused with Canada's most well known broad-leaf Maple, for which the country is famous. The scene depicted is at evening with a serene backdrop into the fading light. Tom Thompson was a forerunner to the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Group_of_Seven_%28artists%29 Group of Seven] before its inception had even been brought about, such was the influence of this iconic painting.
M.C. Escher was a woodcut artist, making art from trees. Here we have recreated his work by streaking media with Escherichia coli to form one of his art pieces, the Palm. Escher was a dutch artist and completed the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Woodcut xylograph] in 1933. Xylographs are produced by etching and carving an image into a block of wood. The non-printing parts are removed and the printing process can commence, allowing the printing of the Palm to be done in black and white.
Other publications
GetSynBio Blog
Our project was featured on the GetSynBio Blog!
http://getsynbio.com/igem-page/
Imperial Bioengineering Departmental News
Our project was featured on a departmental newsletter. In addition to informing our colleagues about our project we also conveyed the importance of the social challenges facing waste management and recycling.
https://workspace.imperial.ac.uk/bioengineering/Public/Newsletters/Newsletter%20August%202013.pdf
Felix
We published an article in the Imperial College newspaper, Felix.
http://felixonline.co.uk/features/3912/from-trash-to-treasure-via-synthetic-biology/
Online newspaper
This automated online newspaper collates the top and most popular news stories from our twitter and facebook feeds.
Check out our online newspaper for news and updates from our project, the iGEM community and global discussions about waste management. http://paper.li/imperialigem/1377382636
Social Media

 "
"