Team:Uppsala/results
From 2013.igem.org
| (35 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| - | < | + | <link href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/lightbox-css-code.css?action=raw&ctype=text/css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"> |
| - | / | + | |
| - | / | + | <script src="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/jquery-code.js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript" type="text/javascript"></script> |
| - | / | + | |
| - | </script> | + | <script src="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/lightbox-code.js?action=raw&ctype=text/javascript" type="text/javascript"></script> |
</head> | </head> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/metabolic-engineering">Metabolic engineering</a> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/metabolic-engineering">Metabolic engineering</a> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/p-coumaric-acid"> | + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/p-coumaric-acid">p-Coumaric acid</a></li> |
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/resveratrol">Resveratrol</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/resveratrol">Resveratrol</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/lycopene">Lycopene</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/lycopene">Lycopene</a></li> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/modeling" id="list_type1"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/63/Uppsala2013_Modeling.png"></a> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/modeling" id="list_type1"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/63/Uppsala2013_Modeling.png"></a> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/P-Coumaric-acid-pathway"> | + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/P-Coumaric-acid-pathway">Kinetic model</a></li> |
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/modeling-tutorial">Modeling tutorial </a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/modeling-tutorial">Modeling tutorial </a></li> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/toxicity-model">Toxicity model</a></li> | ||
</ul></li> | </ul></li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/parts" id="list_type2"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/eb/Uppsala2013_parts.png"></a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/parts" id="list_type2"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/eb/Uppsala2013_parts.png"></a></li> | ||
| Line 96: | Line 98: | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/carotenoid-group">Carotenoid group</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/carotenoid-group">Carotenoid group</a></li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/chassi-group">Chassi group</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/chassi-group">Chassi group</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/advisors">Advisors</a></li> | ||
</ul></li> | </ul></li> | ||
| Line 105: | Line 108: | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/public-opinion">Public opinion </a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/public-opinion">Public opinion </a></li> | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/Outreach">High school & media </a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/Outreach">High school & media </a></li> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/bioart">BioArt</a></li> | |
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/LactonutritiousWorld">A LactoWorld</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/killswitches">Killswitches</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/realization">Patent</a></li> | ||
</ul></li> | </ul></li> | ||
| - | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/attribution" id="list_type4"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/5d/Uppsala2013_Attributions.png"></a | + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/attribution" id="list_type4"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/5d/Uppsala2013_Attributions.png"></a></li> |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/notebook" id="list_type3"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/36/Uppsala2013_Notebook.png"></a> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/notebook" id="list_type3"><img class="nav-text" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/36/Uppsala2013_Notebook.png"></a> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/safety-form">Safety form</a></li> | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/safety-form">Safety form</a></li> | ||
| + | <li><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/protocols">Protocols</a></li> | ||
</ul></li> | </ul></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| Line 131: | Line 135: | ||
<div id="cell"> | <div id="cell"> | ||
<div id="pokal"> | <div id="pokal"> | ||
| - | <img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"> | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/parts"><img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 148: | Line 152: | ||
<div id="cell"> | <div id="cell"> | ||
<div id="pokal"> | <div id="pokal"> | ||
| - | <img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"> | + | <a hred="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/parts"><img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 164: | Line 168: | ||
<div id="pokal"> | <div id="pokal"> | ||
| - | <img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"> | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/results#b1"><img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 201: | Line 205: | ||
<div id="achievement-text"> | <div id="achievement-text"> | ||
| - | <b class="text"> | + | <b class="text">Executed several successful human practice projects <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/human-practice">Read more</a>.</b> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 212: | Line 216: | ||
<div id="pokal"> | <div id="pokal"> | ||
| - | <a href=" | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/vectors"><img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="achievement-text"> | <div id="achievement-text"> | ||
| - | <b class="text">Created a new standard backbone for | + | <b class="text">Created a new standard backbone for Lactobacillus. <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/vectors"> Read more </a></b> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 233: | Line 237: | ||
<div id="achievement-text"> | <div id="achievement-text"> | ||
| - | <b class="text">Useful mathematical | + | <b class="text">Useful mathematical modeling of metabolic pathways. <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/modeling"> Read more </a> </b> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 244: | Line 248: | ||
<div id="pokal"> | <div id="pokal"> | ||
| - | <img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"> | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/chromoproteins#l1"><img class="pokal" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/af/Uppsala2013_pokal.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="achievement-text"> | <div id="achievement-text"> | ||
| - | <b class="text"> Completed our <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/chromoproteins"> chromoprotein collection </a> and displayed 8 new chromoproteins </b> | + | <b class="text"> Completed our <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/chromoproteins#l1"> chromoprotein collection </a> and displayed 8 new chromoproteins </b> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 263: | Line 267: | ||
<a id="b1"></a><h1>Results</h1> | <a id="b1"></a><h1>Results</h1> | ||
| - | <h3> | + | <h3>p-Coumaric acid</h3> |
| - | <p>We managed to clone out and biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase and verify the biobrick by sequencing. Also we did succeful characterization on this part, showing that it works as expected. We managed to express our enzyme and detect it in a western blot, and also detect our metabolite in both spectrophotometry and hplc. The biobrick was characterized in | + | <p>We managed to clone out and biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase and verify the biobrick by sequencing. Also we did succeful characterization on this part, showing that it works as expected. We managed to express our enzyme and detect it in a western blot, and also detect our metabolite in both spectrophotometry and hplc. The biobrick was characterized in E. coli d5 alpha and E. coli nissle. For detailed information about the characterization methods, see the <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/protocols">protocol</a> section. To read more about p-coumaric acid, click <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/p-coumaric-acid">here</a></p> |
| - | <div class="pc-wblot">< | + | <div class="pc-wblot"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/8/8d/Uppsala_pic_coumaric_wblot.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="SDS-page and western blot. Expression of Tyrosine ammonia lyase with constitutive promoters. The negative control is empty, showing that there is no natural protein in E. coli with the same attributes.<br> |
1. Positive control<br> | 1. Positive control<br> | ||
| - | 2. TAL with Cp8 | + | 2. TAL with Cp8 promoter<br> |
| - | 3. TAL with J23110 | + | 3. TAL with J23110 promoter<br> |
| + | 4. Negative control<br>"><img class="results_pic_wblot_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/8/8d/Uppsala_pic_coumaric_wblot.png"></a><div> | ||
| + | 1. Positive control<br> | ||
| + | 2. TAL with Cp8 promoter<br> | ||
| + | 3. TAL with J23110 promoter<br> | ||
4. Negative control<br></div> | 4. Negative control<br></div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <p id="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 1:</b>SDS-page and western blot. Expression of Tyrosine ammonia lyase with constitutive | + | <p id="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 1:</b>SDS-page and western blot. Expression of Tyrosine ammonia lyase with constitutive promoters. The negative control is empty, showing that there is no natural protein in E. coli with the same attributes.</i><br><br></p> |
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7e/SpectroA.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures. Samples were collected 21 h and 48 h after 30 °C incubation. The negative control is an extract from a strain with no TAL gene on transformed plasmid. The positive control is an extract a culture of the same strain as the negative control but with added p-coumaric acid to a concentration of 500 µM before extraction. p-Coumaric acid absorbance spectra has two peaks. The one around 305 nm is preferable to detect because of background from bacteria. (a) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23110.(b) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter CP8. (c) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23101."><img class="results_pic_wblot_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7e/SpectroA.png"></a> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/d/da/Uppsala_pic_coumaric_Spectrophotometry.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures. Samples were collected 21 h and 48 h after 30 °C incubation. The negative control is an extract from a strain with no TAL gene on transformed plasmid. The positive control is an extract a culture of the same strain as the negative control but with added p-coumaric acid to a concentration of 500 µM before extraction. p-Coumaric acid absorbance spectra has two peaks. The one around 305 nm is preferable to detect because of background from bacteria. (a) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23110.(b) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter CP8. (c) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23101."><img class="results_pic_wblot_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/d/da/Uppsala_pic_coumaric_Spectrophotometry.png"></a> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0d/SpectroC.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures. Samples were collected 21 h and 48 h after 30 °C incubation. The negative control is an extract from a strain with no TAL gene on transformed plasmid. The positive control is an extract a culture of the same strain as the negative control but with added p-coumaric acid to a concentration of 500 µM before extraction. p-Coumaric acid absorbance spectra has two peaks. The one around 305 nm is preferable to detect because of background from bacteria. (a) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23110.(b) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter CP8. (c) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23101."><img class="results_pic_wblot_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0d/SpectroC.png"></a> | ||
| - | + | <p id="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 2:</b>Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures. Samples were collected 21 h and 48 h after 30 °C incubation. The negative control is an extract from a strain with no TAL gene on transformed plasmid. The positive control is an extract a culture of the same strain as the negative control but with added p-coumaric acid to a concentration of 500 µM before extraction. p-Coumaric acid absorbance spectra has two peaks. The one around 305 nm is preferable to detect because of background from bacteria. (a) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23110.(b) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter CP8. (c) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23101.</i> | |
| - | <p id="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 2:</b>Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures | + | |
<table> | <table> | ||
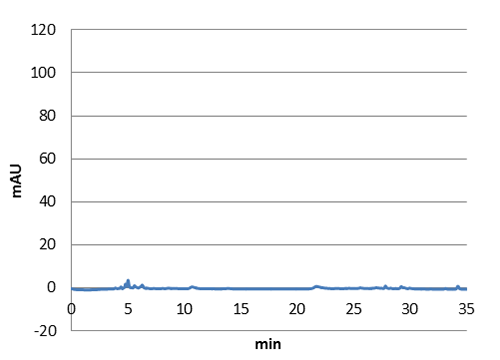
| - | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ef/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_plasmid.png"></td><td class="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 3:</b> Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample prepared from | + | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"> |
| - | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/be/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_standard.png"></td><td class="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 4:</b> Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample standard with p-coumaric acid</i></td></tr> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ef/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_plasmid.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample prepared from E. coli expressing tyrosine ammonia lyase. Reverse phase HPLC with a C18 matrix was used. The peak for p-coumaric acid can be seen ~10 min, as shown by the standard sample below."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ef/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_plasmid.png"></td><td class="fig-text"></a><i><b>Figure 3:</b> Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample prepared from E. coli expressing tyrosine ammonia lyase. Reverse phase HPLC with a C18 matrix was used. The peak for p-coumaric acid can be seen ~10 min, as shown by the standard sample below.</i> </td></tr> |
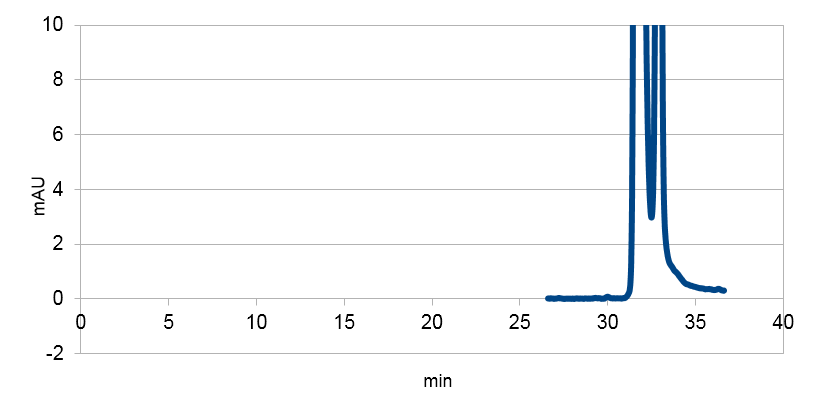
| - | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png"></td><td class="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 5:</b> E | + | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"> |
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/be/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_standard.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample standard with p-coumaric acid."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/be/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_standard.png"></a></td><td class="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 4:</b> Graph showing the HPLC result of a sample standard with p-coumaric acid.</i></td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr><td class="pic_col_results_pc"> | ||
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip" title="E. coli culture injected to the hplc without our biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase. Here we can see that there is originally no peak at 10 minutes."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png"></a></td><td class="fig-text"><i><b>Figure 5:</b> E. coli culture injected to the hplc without our biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase. Here we can see that there is originally no peak at 10 minutes.</i> </td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| Line 290: | Line 306: | ||
<h3 class="title-border">Resveratrol</h3> | <h3 class="title-border">Resveratrol</h3> | ||
| - | <p>Although we managed to clone out and sequence verify the genes for resveratrol production, we have had some problems in the characterization. The results are unclear, and we did not have time for further investigations.For detailed information about the | + | <p>Although we managed to clone out and sequence verify the genes for resveratrol production, we have had some problems in the characterization. The results are unclear, and we did not have time for further investigations.For detailed information about the characterization methods, see the <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/protocols">protocol section</a> and to read more about resveratrol, click <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/resveratrol">here</a> </p> |
<div> | <div> | ||
<div id="results-image-left"> | <div id="results-image-left"> | ||
| - | <img id="sts_westp_uppsala" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/39/Resv_westblot_uppsala.png"> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/39/Resv_westblot_uppsala.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip2" title="Number 2 shows a very weak band of our protein at around 43 kDA.<br> |
| + | Positive control -> 1, Stilbene synthase -> 2"><img id="sts_westp_uppsala" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/39/Resv_westblot_uppsala.png"></a> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="fig-text-right"> | <div id="fig-text-right"> | ||
| - | <i class="results-fig-right"><b>Figure 6:</b>Number 2 shows a very weak band of our protein at around 43 kDA.<br> | + | <i class="results-fig-right"><b>Figure 6: </b>Number 2 shows a very weak band of our protein at around 43 kDA.<br> |
Positive control -> 1, Stilbene synthase -> 2</i> | Positive control -> 1, Stilbene synthase -> 2</i> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 304: | Line 321: | ||
<div id="clear"></div> | <div id="clear"></div> | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | <b>4Cl-STS translational fusion expressed in | + | <b>4Cl-STS translational fusion expressed in E. coli</b> |
<div> | <div> | ||
<div id="results-image-left"> | <div id="results-image-left"> | ||
| - | <img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_1" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/dc/Resva_uppsala_tab1.png"></div> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/dc/Resva_uppsala_tab1.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip2" title="E. coli supposed to produce resveratrol. As we can see, we got very low absorbance peaks at ~30 min, ~33 min and ~36 min."><img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_1" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/dc/Resva_uppsala_tab1.png"></a></div> |
<div id="fig-text-right3"> | <div id="fig-text-right3"> | ||
<i><b>Figure 7:</b> E. coli supposed to produce resveratrol. As we can see, we got very low absorbance peaks at ~30 min, ~33 min and ~36 min. </i> | <i><b>Figure 7:</b> E. coli supposed to produce resveratrol. As we can see, we got very low absorbance peaks at ~30 min, ~33 min and ~36 min. </i> | ||
| Line 322: | Line 339: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
<div id="results-image-left"> | <div id="results-image-left"> | ||
| - | <img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_2" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/33/Resva_uppsala_tab2.png"></div> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/33/Resva_uppsala_tab2.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip2" title="Resveratrol standard, peaks around 33-34 min."><img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_2" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/33/Resva_uppsala_tab2.png"></a></div> |
<div id="fig-text-right1"> | <div id="fig-text-right1"> | ||
| - | <i><b>Figure 8:</b> Resveratrol standard, peaks around | + | <i><b>Figure 8:</b> Resveratrol standard, peaks around 33-34 min. </i> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 335: | Line 352: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| - | <div id="results-image-left"><img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_3" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/82/Resva_uppsala_tab3.png"><br> | + | <div id="results-image-left"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/82/Resva_uppsala_tab3.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip2" title="Resveratrol standard that is scaled down to correspond to the absorbations of our E. coli supposed to produce the corresponding metabolite. The peaks are at around 33-34min."><img class="results_pic_pc" id="Resveratrol_fig_3" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/82/Resva_uppsala_tab3.png"></a><br> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="fig-text-right2"> | <div id="fig-text-right2"> | ||
| - | <i><b>Figure 9:</b> Resveratrol standard that is scaled down to correspond to the absorbations of our | + | <i><b>Figure 9:</b> Resveratrol standard that is scaled down to correspond to the absorbations of our E. coli supposed to produce the corresponding metabolite. The peaks are at around 33-34min. </i> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 349: | Line 366: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| - | <div id="results-image-left"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png"><br> | + | <div id="results-image-left"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip2" title="E. coli culture injected to the hplc without our biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase. Here we can see that there is originally no peaks around 30-35 minutes."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/4f/Uppsala_char_coumaric-acid_blank.png"></a><br> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 10:</b> E. coli culture injected to the hplc without our biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase. Here we can see that there is originally no peaks around 30-35 minutes.</i> | <div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 10:</b> E. coli culture injected to the hplc without our biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase. Here we can see that there is originally no peaks around 30-35 minutes.</i> | ||
| Line 364: | Line 381: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| - | <div id="results-image-left"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/ba/Uppsala2013_Shuttle_Vector_pSBLBC_cp29_amilCP.JPG"/><br> | + | <div id="results-image-left"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/ba/Uppsala2013_Shuttle_Vector_pSBLBC_cp29_amilCP.JPG" data-lightbox="roadtrip3" title="Here you can see our shuttle vector BBa_K1033206 with the insert BBa_K1033282 in E. coli, after growing for 24 hours. This showed that we can subclone a new construct to our shuttle vector and that it works in E. coli."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/ba/Uppsala2013_Shuttle_Vector_pSBLBC_cp29_amilCP.JPG"/></a><br> |
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | <div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 11:</b> Here you can see our shuttle vector <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1033206">BBa_K1033206</a> | + | <div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 11:</b> Here you can see our shuttle vector <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1033206">BBa_K1033206</a> with the insert <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1033282">BBa_K1033282</a> in E. coli, after growing for 24 hours. This showed that we can subclone a new construct to our shuttle vector and that it works in E. coli. |
</i> | </i> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 376: | Line 393: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
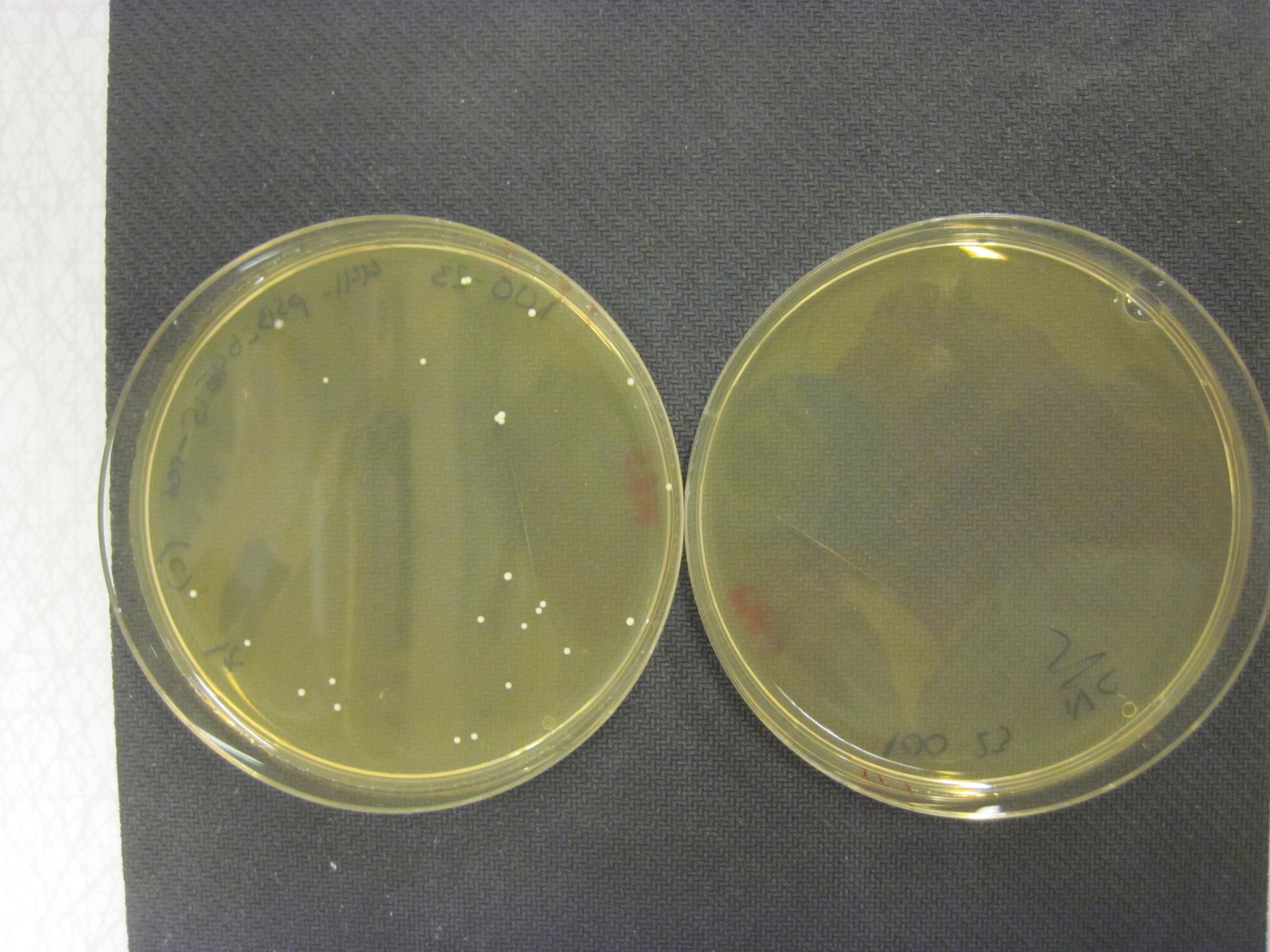
| - | <div id="results-image-left"><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e1/IMG_6644.JPG"/><br> | + | <div id="results-image-left"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e1/IMG_6644.JPG" data-lightbox="roadtrip3" title="Here we can see a transformation of BBa_K1033207 to Lactobacillus reuteri 100-23. The plate on the left is the result of a transformation with our shuttle vector and the plate on the right is without the shuttle vector. Controls were also done on antibiotic free plates yielding hundreds of colonies."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e1/IMG_6644.JPG"/></a><br> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 12:</b> Here we can see a transformation of <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1033207">BBa_K1033207</a> to Lactobacillus reuteri 100-23. The plate on the left is the result of a transformation with our shuttle vector and the plate on the right is without the shuttle vector. Controls were also done on antibiotic free plates yielding hundreds of colonies.</i> | <div id="fig-text-right"><i><b>Figure 12:</b> Here we can see a transformation of <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1033207">BBa_K1033207</a> to Lactobacillus reuteri 100-23. The plate on the left is the result of a transformation with our shuttle vector and the plate on the right is without the shuttle vector. Controls were also done on antibiotic free plates yielding hundreds of colonies.</i> | ||
| Line 389: | Line 406: | ||
<div> | <div> | ||
| - | <div id="results-image-left"><img class="results_pic_pc1" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/64/Uppsala2013_Promoterdiagram.png"> | + | <div id="results-image-left"><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/64/Uppsala2013_Promoterdiagram.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip4" title="The CP promoters strength relative to J23101 in E. coli."><img class="results_pic_pc1" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/64/Uppsala2013_Promoterdiagram.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="fig-text-right5"><i class="promoter-image-pic"><b>Figur 13:</b> The CP promoters strength relative to J23101 in E. coli.</i> | <div id="fig-text-right5"><i class="promoter-image-pic"><b>Figur 13:</b> The CP promoters strength relative to J23101 in E. coli.</i> | ||
| Line 400: | Line 417: | ||
<h3 class="title-border">Competition test</h3> | <h3 class="title-border">Competition test</h3> | ||
| - | <p>We grew our | + | <p>We grew our E. coli Nissle containing the TAL biobrick together with wild type Nissle (mixed 1:1) in antiobiotic free LB medium. The culture was maintained by a thousandfold dilution in new medium every day, and letting it grow again overnight. To be able to track the fraction of each population over time, a dilution of the culture was plated on both selective, and non selective plates. The amount of colonies on the non selective plates gives us the total amount of cells, while the amount of colonies on the selective plates gives us the number of cells carrying the biobrick plasmid. The fraction of cells carrying the plasmid declined rapidly, and already after 5 days (approximately 50 generations of growth), we saw no trace of our E. coli Nissle with TAL on the selective plates, while the wild type still grew on the non selective plates. This clearly shows that our genetically engineered probiotic have a hard time competing against the wild type, and if released into the environment, they would most likely be outcompeted by other bacteria within days. To read more about the competition test, click <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Uppsala/safety-experiment">here</a> </p> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <b>Competition experiments between TAL and wild type</b><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div> | ||
| + | <div id="results-image-left"> | ||
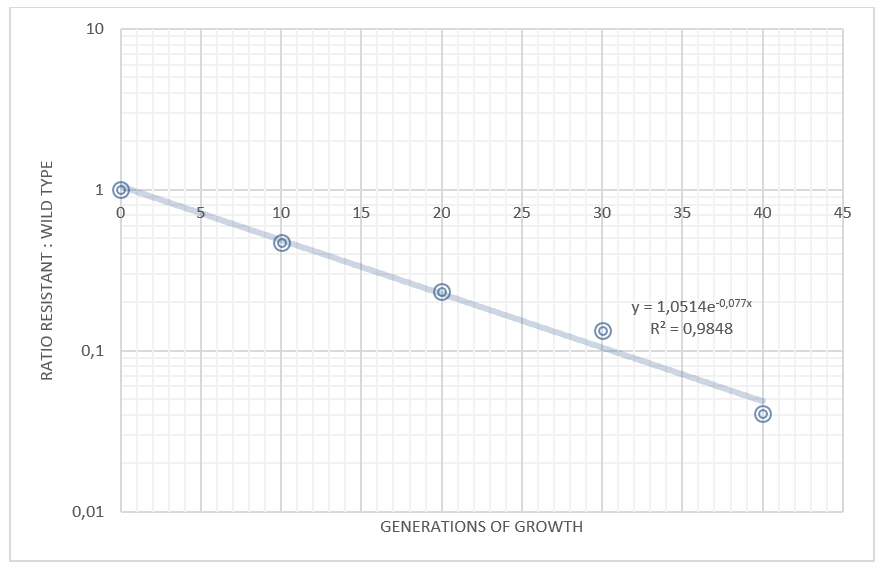
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/6f/Table_safety_uppsala.png" data-lightbox="roadtrip5" title="Competition experiments between E. coli Nissle carrying the TAL plasmid and wild type Nissle."><img class="results_pic_pc" src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/6f/Table_safety_uppsala.png"></a><br> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="fig-text-right"> | ||
| + | <b><i>Figure 13:</b> Competition experiments between E. coli Nissle carrying the TAL plasmid and wild type Nissle.</i> | ||
| + | </div><br><br> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div id="clear"></div> | ||
| - | |||
</div> <!-- main_ontent ends --> | </div> <!-- main_ontent ends --> | ||
<div id="bottom-pic"> | <div id="bottom-pic"> | ||
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:10, 28 October 2013
Results and achievement
Achievements
Results
p-Coumaric acid
We managed to clone out and biobrick tyrosine ammonia lyase and verify the biobrick by sequencing. Also we did succeful characterization on this part, showing that it works as expected. We managed to express our enzyme and detect it in a western blot, and also detect our metabolite in both spectrophotometry and hplc. The biobrick was characterized in E. coli d5 alpha and E. coli nissle. For detailed information about the characterization methods, see the protocol section. To read more about p-coumaric acid, click here
Figure 1:SDS-page and western blot. Expression of Tyrosine ammonia lyase with constitutive promoters. The negative control is empty, showing that there is no natural protein in E. coli with the same attributes.
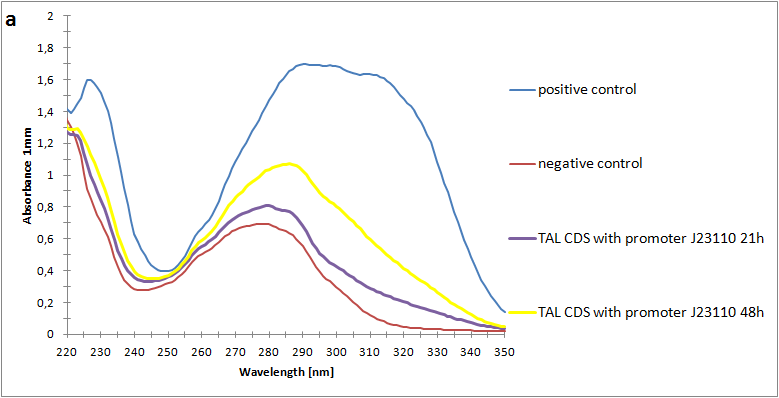
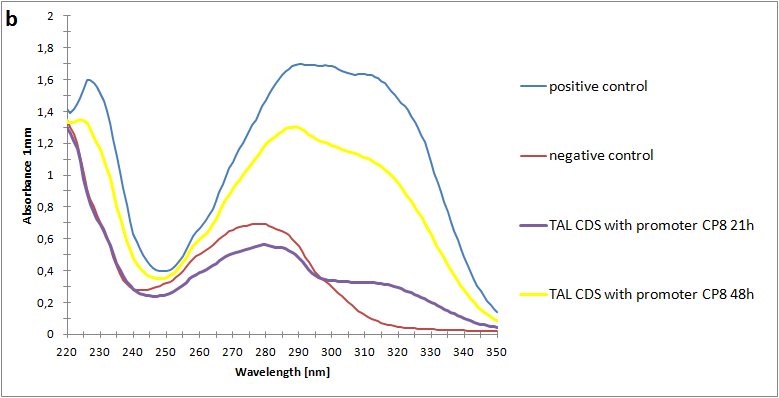

Figure 2:Absorbance spectra of extracts collected from bacterial cultures. Samples were collected 21 h and 48 h after 30 °C incubation. The negative control is an extract from a strain with no TAL gene on transformed plasmid. The positive control is an extract a culture of the same strain as the negative control but with added p-coumaric acid to a concentration of 500 µM before extraction. p-Coumaric acid absorbance spectra has two peaks. The one around 305 nm is preferable to detect because of background from bacteria. (a) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23110.(b) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter CP8. (c) Spectra from the strain with TAL CDS with promoter J23101.
Resveratrol
Although we managed to clone out and sequence verify the genes for resveratrol production, we have had some problems in the characterization. The results are unclear, and we did not have time for further investigations.For detailed information about the characterization methods, see the protocol section and to read more about resveratrol, click here
Positive control -> 1, Stilbene synthase -> 2
4Cl-STS translational fusion expressed in E. coli
Resveratrol standard
Resveratrol standard scaled
Lysed bacterial culture without plasmid of assembly
Shuttle vector
We constructed two shuttle vectors able to replicate and provide resistance in both Lactobacillus and E. coli. We have shown that they can both be used in E. coli for assembly and subcloning as well as transforming them to Lactobacillus. To read more about the shuttle vector, click here
Promoters
We have provided a constitutive promoter collection with 6 promoters with different strength measured by a fluorescence-activated cellsorting machine (FACS) in RPU, a unit based on the strength of the promoter J23101 in standard parts. These promoters works in both gram-negative bacterium E. coli and gram-positive bacterium Lactobacillus and are therefore also believed to be universal for all prokaryotic organisms. To read more about promoters, click here
Competition test
We grew our E. coli Nissle containing the TAL biobrick together with wild type Nissle (mixed 1:1) in antiobiotic free LB medium. The culture was maintained by a thousandfold dilution in new medium every day, and letting it grow again overnight. To be able to track the fraction of each population over time, a dilution of the culture was plated on both selective, and non selective plates. The amount of colonies on the non selective plates gives us the total amount of cells, while the amount of colonies on the selective plates gives us the number of cells carrying the biobrick plasmid. The fraction of cells carrying the plasmid declined rapidly, and already after 5 days (approximately 50 generations of growth), we saw no trace of our E. coli Nissle with TAL on the selective plates, while the wild type still grew on the non selective plates. This clearly shows that our genetically engineered probiotic have a hard time competing against the wild type, and if released into the environment, they would most likely be outcompeted by other bacteria within days. To read more about the competition test, click here
Competition experiments between TAL and wild type "
"