Team:Wageningen UR/Notebook
From 2013.igem.org
(→notebook entries) |
(→notebook entries) |
||
| (27 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 202: | Line 202: | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | + | <img src=" https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/14/Progresar.jpg "/> | |
| + | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <h3>Work in progress</h3> | ||
<p class="date">26.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">26.08.2013</p> | ||
<p>Performed some more Gibson assemblies and tried to ligate DH and MT together in the same vector. Made chemically competent cells and the primers for our mini-genes arrived.</p> | <p>Performed some more Gibson assemblies and tried to ligate DH and MT together in the same vector. Made chemically competent cells and the primers for our mini-genes arrived.</p> | ||
| Line 224: | Line 226: | ||
<h3>iGEM Netherlands</h3> | <h3>iGEM Netherlands</h3> | ||
<p class="date">24.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">24.08.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p> We works really hard to participate and organize iGEM activities and now deserve a rainy BBQ as the end of a busy communication day. It is not only about eating, we are actually talking about science mainly.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 237: | Line 239: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f9/Tumblr_mazjjagDVw1rg4kjpo1_500.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon wetlab"></div> | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 267: | Line 269: | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/d6/Computer_preview.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon wetlab"></div> | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 292: | Line 294: | ||
<h3>Transformations</h3> | <h3>Transformations</h3> | ||
<p class="date">19.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">19.08.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p>We have two kinds of competent <i>E.coli</i> cells to do the transformation. Both of the Electro-competent cells and chemical-competent work.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/3d/1318499684245084009blocks-g-md.png"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 314: | Line 316: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1d/1001236_594110660639411_81079043_n.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 345: | Line 347: | ||
<div class="item human"> | <div class="item human"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1c/Berlin_conference.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon human"></div> | <div class="icon human"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 357: | Line 359: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<div class="item date" id="week10"> | <div class="item date" id="week10"> | ||
<div class="midden"> | <div class="midden"> | ||
| Line 375: | Line 368: | ||
<div class="item human"> | <div class="item human"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/88/Vitruvian_man.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon human"></div> | <div class="icon human"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 399: | Line 392: | ||
<h3>Workshop by Paulien Poelarends</h3> | <h3>Workshop by Paulien Poelarends</h3> | ||
<p class="date">09.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">09.08.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p>Paulien did her master thesis on last year’s iGEM teams and their way of communicating with the public and politicians. We have a wonderful afternoon with her, obtaining a lot by her workshop. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/79/Michiel.gif"/> |
<div class="icon wetlab"></div> | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 414: | Line 407: | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7b/Golden_man.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Lovastatin</h3> | <h3>Lovastatin</h3> | ||
<p class="date">06.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">06.08.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>The restriction enzymes that we ordered last week have arrived. After a few attempts the sequences have been optimized and the G-blocks can be ordered. Also some Lovastatin has been ordered to perform some experiments with A. niger. Lovastatin may be fatal to cell growth of A. niger therefore experiments have to indicate whether A. niger is resistant to Lovastatin. Otherwise | + | <p>The restriction enzymes that we ordered last week have arrived. After a few attempts the sequences have been optimized and the G-blocks can be ordered. Also some Lovastatin has been ordered to perform some experiments with <i>A. niger</i>. Lovastatin may be fatal to cell growth of <i>A. niger</i> therefore experiments have to indicate whether <i>A. niger</i> is resistant to Lovastatin. Otherwise <i>A. niger</i> has to be transformed with the resistance gene from <i>A. terreus</i>.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 439: | Line 432: | ||
<h3>Expanding the database</h3> | <h3>Expanding the database</h3> | ||
<p class="date">05.08.2013</p> | <p class="date">05.08.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> In order to expand the database, more information on secondary metabolite backbone enzymes from Aspergilli needs to be added. Luckily there is a recent publication on secondary metabolites from A. nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae. <br /> <br /> | + | <p> In order to expand the database, more information on secondary metabolite backbone enzymes from Aspergilli needs to be added. Luckily there is a recent publication on secondary metabolites from A. nidulans, A. fumigatus, <i>A. niger</i> and <i>A. oryzae</i>. <br /> <br /> |
| - | - D.O. Inglis et al., 2013. <i> Comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of Aspergillus nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae | + | - D.O. Inglis et al., 2013. <i> Comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of <i>Aspergillus nidulans</i>, <i>A. fumigatus</i>, <i>A. niger</i> and <i>A. oryzae</i>. BMC Microbiology, Vol. 13, p. 1-23.</i> |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 463: | Line 456: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/94/Bbq.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 486: | Line 479: | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>First transformation of <i>A. niger</i></h3> | <h3>First transformation of <i>A. niger</i></h3> | ||
| - | <p class="date"> | + | <p class="date">01.08.2013</p> |
<p>Finally it was time to transform <i>A. niger</i> with the first construct we got. This would be the actin GFP fusion. This was introduced into <i>A. niger</i> and transormation worked as it appeared 4 days later.</p> | <p>Finally it was time to transform <i>A. niger</i> with the first construct we got. This would be the actin GFP fusion. This was introduced into <i>A. niger</i> and transormation worked as it appeared 4 days later.</p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 493: | Line 486: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f0/Shopping.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Shopping</h3> | <h3>Shopping</h3> | ||
<p class="date">30.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">30.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> This week we ordered the restriction enzymes for the assembly strategy. Also other stuff should be ordered like pJET, lovastatin, A. niger & A. terrus strain, Gibson assembly kit... | + | <p> This week we ordered the restriction enzymes for the assembly strategy. Also other stuff should be ordered like pJET, lovastatin, <i>A. niger</i> & <i>A. terrus</i> strain, Gibson assembly kit... |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 512: | Line 505: | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/05/Color_plate.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon wetlab"></div> | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| - | <h3>Obtained E.coli expressing chromoproteins from Braunschweig</h3> | + | <h3>Obtained <i>E.coli</i> expressing chromoproteins from Braunschweig</h3> |
<p class="date">26.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">26.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We obtained the E.coli from Braunschweig that have plasmids with an chromoprotein encoding gene insert. Lets start introducing it into Aspergillus Niger!</p> | + | <p>We obtained the <i>E.coli</i> from Braunschweig that have plasmids with an chromoprotein encoding gene insert. Lets start introducing it into <i>Aspergillus Niger</i>!</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 547: | Line 540: | ||
<h3>Metabolic activity: GFP</h3> | <h3>Metabolic activity: GFP</h3> | ||
<p class="date">22.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">22.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> In a similar way that the DAPI stained cells give an indication of metabolic activity by showing an increase in nuclei, GFP-transformed A. niger also give an indication of metabolic activity by giving an indication on whether transcription and translation occur. | + | <p> In a similar way that the DAPI stained cells give an indication of metabolic activity by showing an increase in nuclei, GFP-transformed <i>A. niger</i> also give an indication of metabolic activity by giving an indication on whether transcription and translation occur. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f6/3d.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 570: | Line 563: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/bc/Wiki.png"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 579: | Line 572: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1e/In-a-mess.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 589: | Line 582: | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/b4/Sql.gif"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Database design</h3> | <h3>Database design</h3> | ||
<p class="date">16.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">16.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p> MySQL the world's most widely used open-source relational database management system. Now we will also check the possibility to use it as our method.</p> |
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 646: | Line 638: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/66/Bioke_logo.png"style="width:125%;height:100%;"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 656: | Line 648: | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e6/Pills.png"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Lovastatin</h3> | <h3>Lovastatin</h3> | ||
<p class="date">05.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">05.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>Finally the search has begun, this week we have started with literature research for the Lovastatin project. Some topics were for example what is Lovastatin, which genes are involved in Lovastatin production in Aspergillus terreus, and how to measure Lovastatin production. The first idea was to introduce the Lovastatin pathway of A. terreus into A.niger. During the research we found that one of the bigger genes involved is composed of several domains. Our new idea now is to synthesize these domains, making several modules that we can assemble as we wish. </p> | + | <p>Finally the search has begun, this week we have started with literature research for the Lovastatin project. Some topics were for example what is Lovastatin, which genes are involved in Lovastatin production in <i>Aspergillus terreus</i>, and how to measure Lovastatin production. The first idea was to introduce the Lovastatin pathway of <i>A. terreus</i> into <i>A.niger</i>. During the research we found that one of the bigger genes involved is composed of several domains. Our new idea now is to synthesize these domains, making several modules that we can assemble as we wish. </p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item human"> | <div class="item human"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/30/LogoSCW.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon human"></div> | <div class="icon human"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 674: | Line 666: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1d/Database_3.png"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Database planning</h3> | <h3>Database planning</h3> | ||
<p class="date">03.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">03.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p> A database of <i>Aspergillus niger</i> is planned to set. Thus we can get insight to comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of it. |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 692: | Line 682: | ||
<h3>Primers for septa visualizition arrived</h3> | <h3>Primers for septa visualizition arrived</h3> | ||
<p class="date">02.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">02.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>After some waiting time the primers needed for the visualization of the septa using a proton-ATPase finally arrived and this part of the project could also get started by isolating the gene from genomic A. niger DNA.</p> | + | <p>After some waiting time the primers needed for the visualization of the septa using a proton-ATPase finally arrived and this part of the project could also get started by isolating the gene from genomic <i>A. niger</i> DNA.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 712: | Line 702: | ||
<h3>Actin gene in house internal brick system</h3> | <h3>Actin gene in house internal brick system</h3> | ||
<p class="date">01.07.2013</p> | <p class="date">01.07.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>The actin gene for cytoskeleton visualization purposes was ligated into a house internal brick system with a n-terminal GFP fusion. This construct was then introduced into E. coli for amplification purposes.</p> | + | <p>The actin gene for cytoskeleton visualization purposes was ligated into a house internal brick system with a n-terminal GFP fusion. This construct was then introduced into <i>E. coli</i> for amplification purposes.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 738: | Line 728: | ||
<h3>Lovastatin Pathway</h3> | <h3>Lovastatin Pathway</h3> | ||
<p class="date">25.06.2013</p> | <p class="date">25.06.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>The lovastatin pathway has been added to the metabolic model of Aspergillus niger. Because the medium composition of the model is not yet properly defined, the maximum flux towards lovastatin can be achieved. This however is not realistic and therefore the next thing is to redefined the medium composition. <br /> <br /> | + | <p>The lovastatin pathway has been added to the metabolic model of <i>Aspergillus niger</i>. Because the medium composition of the model is not yet properly defined, the maximum flux towards lovastatin can be achieved. This however is not realistic and therefore the next thing is to redefined the medium composition. <br /> <br /> |
- B.D. Ames et al., 2011. <i> Crystal structure and biochemical studies of the trans-acting polyketide enoyl reductase LovC from lovastatin biosynthesis. </i> PNAS, doi/10.1073/pnas.1113029109 | - B.D. Ames et al., 2011. <i> Crystal structure and biochemical studies of the trans-acting polyketide enoyl reductase LovC from lovastatin biosynthesis. </i> PNAS, doi/10.1073/pnas.1113029109 | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 750: | Line 740: | ||
<h3>Calcofluor staining</h3> | <h3>Calcofluor staining</h3> | ||
<p class="date">24.06.2013</p> | <p class="date">24.06.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> | + | <p> Calcofluor is known to stain cellulose and chitin. In <i>A.niger</i>, chitin is found in the cell wall, thus if we find cells in this specific stage of mitosis, just before division is completed and when the cytoplasm is connected, we might be able to visualize this with the use of this staining method. </p> |
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 767: | Line 756: | ||
<h3>Finding the right conditions for distinct phenotypes</h3> | <h3>Finding the right conditions for distinct phenotypes</h3> | ||
<p class="date">22.06.2013</p> | <p class="date">22.06.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> As described in literature, N593 formed giant cells after 24h at 44C. Since transcriptome data on N400 from multiple stages in its life cycle is available, this strain is chosen such that this research complements the current RNA landscape profile of A. niger and allows for comparison of data from different life stages. However, unlike N400, N593 repeatedly formed mycelium at 44C. To overcome this effect the temperature was increased to 45C, at which a single cell phenotype was obtained for N593. | + | <p> As described in literature, N593 formed giant cells after 24h at 44C. Since transcriptome data on N400 from multiple stages in its life cycle is available, this strain is chosen such that this research complements the current RNA landscape profile of <i>A. niger</i> and allows for comparison of data from different life stages. However, unlike N400, N593 repeatedly formed mycelium at 44C. To overcome this effect the temperature was increased to 45C, at which a single cell phenotype was obtained for N593. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item human"> | <div class="item human"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e3/Biohacker.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon human"></div> | <div class="icon human"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 782: | Line 771: | ||
<div class="item human"> | <div class="item human"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/76/Potato.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon human"></div> | <div class="icon human"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 801: | Line 790: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f5/7_people.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 811: | Line 800: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/d2/Dinner-is-served-peas-on-plate.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 825: | Line 814: | ||
<h3>Host Engineering: Research plan</h3> | <h3>Host Engineering: Research plan</h3> | ||
<p class="date">13.06.2013</p> | <p class="date">13.06.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> Different environmental conditions induce changes in phenotypic cellularity of Aspergillus niger. Mapping reads onto the reference genome allows for discovery of patterns in gene expression that are unique to the single cell phenotype. | + | <p> Different environmental conditions induce changes in phenotypic cellularity of <i>Aspergillus niger</i>. Mapping reads onto the reference genome allows for discovery of patterns in gene expression that are unique to the single cell phenotype. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 841: | Line 830: | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e7/Tinkercell.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 851: | Line 840: | ||
<div class="item wetlab"> | <div class="item wetlab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/85/975.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon wetlab"></div> | <div class="icon wetlab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 861: | Line 850: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/ | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/59/Cornell_iGEMLogo.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 905: | Line 894: | ||
<p> | <p> | ||
Research question: <br /> | Research question: <br /> | ||
| - | Finding sets of candidate genes causative to the single cell phenotype in Aspergillus niger by transcriptome analysis. <br /> <br /> | + | Finding sets of candidate genes causative to the single cell phenotype in <i>Aspergillus niger</i> by transcriptome analysis. <br /> <br /> |
Subquestions: <br /> | Subquestions: <br /> | ||
| - | - is A. niger metabolically active at 44C? <br /> | + | - is <i>A. niger</i> metabolically active at 44C? <br /> |
| - | - does A. niger divide at 44C? | + | - does <i>A. niger</i> divide at 44C? |
</p> | </p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 919: | Line 908: | ||
<div class="item modeling"> | <div class="item modeling"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/2/25/Kegg-Pathway.png"/> |
<div class="icon modeling"></div> | <div class="icon modeling"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Metabolic model <i> A. niger </i></h3> | <h3>Metabolic model <i> A. niger </i></h3> | ||
<p class="date">30.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">30.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p> The current metabolic model of A. niger needs to be expanded to include the lovastatin pathway as known from literature. First the model has to be checked: is it balanced? can we perform a FBA on the current model? <br /> <br /> | + | <p> The current metabolic model of <i>A. niger</i> needs to be expanded to include the lovastatin pathway as known from literature. First the model has to be checked: is it balanced? can we perform a FBA on the current model? <br /> <br /> |
- M.R. Anderson et al., 2008. <i> Metabolic model integration of the bibliome, genome, metabolome and reactome of Aspergillus niger. </i> Molecular Systems Biology, Vol. 4, Article number 178; doi:10.1038/msb.2008.12 | - M.R. Anderson et al., 2008. <i> Metabolic model integration of the bibliome, genome, metabolome and reactome of Aspergillus niger. </i> Molecular Systems Biology, Vol. 4, Article number 178; doi:10.1038/msb.2008.12 | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 931: | Line 920: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/87/This-is-where-the-magic-happens-limited-edition-silkscreen-print-with-diamond-dust-14176-p.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Meeting room</h3> | <h3>Meeting room</h3> | ||
<p class="date">26.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">26.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We reserved a room for all future Monday and Thursday lunch meetings in the Forum</p> | + | <p>We reserved a room for all future Monday and Thursday lunch meetings in the Forum.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 945: | Line 934: | ||
<h3>Visualization of the actin cytoskeleton</h3> | <h3>Visualization of the actin cytoskeleton</h3> | ||
<p class="date">27.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">27.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>Finally the labwork for the visualization of the septa and actin cytoskeleton started. And the first thing to do was order primers and isolate genomic DNA from A. niger.</p> | + | <p>Finally the labwork for the visualization of the septa and actin cytoskeleton started. And the first thing to do was order primers and isolate genomic DNA from <i>A. niger</i>.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 964: | Line 953: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/cb/Super_Gmail_Logo1.png"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Created a Gmail account</h3> | <h3>Created a Gmail account</h3> | ||
<p class="date">23.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">23.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We created a Gmail account. Let the spam begin</p> | + | <p>We created a Gmail account. Let the spam begin!</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/c6/Uppamarit.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Meeting iGem Uppsala</h3> | <h3>Meeting iGem Uppsala</h3> | ||
<p class="date">18.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">18.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We met with the iGem Uppsala 2013 team in Uppsala</p> | + | <p>We met with the iGem Uppsala 2013 team in Uppsala.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 987: | Line 976: | ||
<h3>Glycerol stocks made</h3> | <h3>Glycerol stocks made</h3> | ||
<p class="date">16.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">16.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>All the < | + | <p>All the <i>E. coli</i> stabs with constructs from Addgene and the Imamura lab were revived and glycerol stocks were made and preserved at -80'C.</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/a/a2/Twitter_bird.png"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Created a Twitter account</h3> | <h3>Created a Twitter account</h3> | ||
<p class="date">15.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">15.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We created a Twitter account. Hello world! Meet iGem Wageningen 2013</p> | + | <p>We created a Twitter account. Hello world! Meet iGem Wageningen 2013~</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item drylab"> | <div class="item drylab"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/6f/GBlocks-Even-Longer.png"/> |
<div class="icon drylab"></div> | <div class="icon drylab"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Chromoprotein sequencing</h3> | <h3>Chromoprotein sequencing</h3> | ||
<p class="date">13.05.2013</p> | <p class="date">13.05.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>Looked into sequencing options: codon optimization to Aspergillus Niger, suffix/prefix, (illegal) restrictionsites. Let’s order some g-blocks!</p> | + | <p>Looked into sequencing options: codon optimization to <i>Aspergillus Niger</i>, suffix/prefix, (illegal) restrictionsites. Let’s order some g-blocks!</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 1,022: | Line 1,011: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src="https:// | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f8/First_floor_lab.jpg"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 1,051: | Line 1,040: | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/8/8a/Glp.gif"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
<h3>Good Lab Practice</h3> | <h3>Good Lab Practice</h3> | ||
<p class="date">24.04.2013</p> | <p class="date">24.04.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>We had a lecture on good lab practice and safety in the lab</p> | + | <p>We had a lecture on good lab practice and safety in the lab, awesome! ;)</p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="item other"> | <div class="item other"> | ||
| - | <img src=" | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/32/StemCellDiff.gif"/> |
<div class="icon other"></div> | <div class="icon other"></div> | ||
<div class="content"> | <div class="content"> | ||
| Line 1,085: | Line 1,074: | ||
<h3>Influence of temperature on germination</h3> | <h3>Influence of temperature on germination</h3> | ||
<p class="date">15.04.2013</p> | <p class="date">15.04.2013</p> | ||
| - | <p>A paper from 1970 shows that at 44C Aspergillus niger does not germinate, but rather forms giant cells. This dimorphism is not unfamiliar within the fungal world, where at lower temperatures the mycelium is formed and at higher temperatures the yeast-like form is found. <br /> <br /> | + | <p>A paper from 1970 shows that at 44C <i>Aspergillus niger</i> does not germinate, but rather forms giant cells. This dimorphism is not unfamiliar within the fungal world, where at lower temperatures the mycelium is formed and at higher temperatures the yeast-like form is found. <br /> <br /> |
Anderson, J. G. and J. E. Smith (1972). <i> "Effects of Elevated-Temperatures on Spore Swelling and Germination in Aspergillus Niger." </i> Canadian Journal of Microbiology 18(3): 289-297. | Anderson, J. G. and J. E. Smith (1972). <i> "Effects of Elevated-Temperatures on Spore Swelling and Germination in Aspergillus Niger." </i> Canadian Journal of Microbiology 18(3): 289-297. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| Line 1,096: | Line 1,085: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:16, 5 October 2013
- Safety introduction
- General safety
- Fungi-related safety
- Biosafety Regulation
- Safety Improvement Suggestions
- Safety of the Application
- Lablog
- Experimental protocols
notebook entries
Week 18
September (30.09 - 06.10)

Magic hand works again for ligation
02.10.2013
The ligation for KS domain in vector works finally. PS: This breaking news came out after 9PM. Hard working now return back!
Week 17
September (23.09 - 29.09)

Transformation protoplast with shuttle vectors containing constructs from Cornell UR iGEM team
24.09.2013
As collaborating with Cornell iGEM team, they sent us the Cre recombinase, as well as hygromycin and geneticin resistances behind the Aspergillus promoter and a sample of geneticin. We transformed protoplast with shuttle vectors containing those constructs to test in our A. Niger host.
Week 16
September (16.09 - 22.09)

The invaluable painting Sunflower in our lab
20.09.2013
Marjan made a counterfeit of Van Gogh's sunflower using agar plates and some mysterious microorganism by her magic hand. What a masterpiece and makes our lab more colorful.

Transformation protoplast with codon optimized eforRed constructs
18.09.2013
We transformed protoplasts Aspergillus niger N593 with plasmids containing codon-optimized chromoprotein encoding genes. Since the in-house shuttle vectors contained the pyrA gene, allowing them to grow without uridine, we selected successful transformants via uridine-dependence.

Science Cafe Wageningen
16.09.2013
On 16th of September, there was an awesome gathering for all biologists in café Loburg. It was organized by iGEM team with some tipps and advices from the science café team. This edition was about “synthetic biology, towards the creation of life?” and the speakers were Prof dr. Arnold Driessen (University of Groningen) and dr. Dirk Stemerding (Rathenau institute) and as the side-kick Pieter van Boheemen , who is a DIY biohacker. It turned to be a really success!
Week 15
September (09.09 - 15.09)

New primers to clone GFP+Actin construct for parts registry
13.09.2013 – 15.09.2013
We ordered primers with standard 10 restriction sites for cloning our GFP+Actin construct into the recommended plasmid for parts registry. With these primers, actin-GFP constructs were amplified by PCR. Then PCR products and parts registry plasmids were digest to obtain the compatible restriction sites and ligated to each other.

Alignment of Chromoprotein sequencing results
10.09.2013
We checked whether the sequence of the chromoprotein encoding genes had remained unchanged by sending it out for sequencing. Then the results were compared with the original sequence from parts registry. For aeBlue, mRFP and amilGFP chromoprotein gene, the identity was almost 100%.
Week 14
September (02.09 - 08.09)

Extraction of fungus genome DNA and validation insertion via PCR
06.09.2013
The aeBlur, eforRed, mRFP and amilGFP transformants were culture in the CM- medium. After 2 days, their mycelium was harvested and used to extract fungus genome DNA. With the genome DNA as templates and corresponding chromoprotein primers, we did PCR to validate insertion of the chromoprotein encoding gene.

Sequencing result of QC-PCR products
05.09.2013
With Quick-change PCR, actin gene was mutated to get rid of the xba1 restriction site. The site-directed mutagenesis was confirmed by sequencing result. Comparing with the original sequence, T was changed into G. Then it will be double checked by restriction analysis with double digestion “XbaI + NsiI”.
Week 13
August (26.08 - 1.09)

Site-directed mutagenesis of actin gene
27.08.2013
We designed special primers that induced a point mutation to remove the xba1 restriction site. Quick Change Lightning kit was used to QC-PCR of p-Jet with actin gene. Then the PCR products was digested with Dpn1 to cut off methylated sites.

Work in progress
26.08.2013
Performed some more Gibson assemblies and tried to ligate DH and MT together in the same vector. Made chemically competent cells and the primers for our mini-genes arrived.
Week 12
August (19.08 - 25.08)

iGEM Netherlands
24.08.2013
We works really hard to participate and organize iGEM activities and now deserve a rainy BBQ as the end of a busy communication day. It is not only about eating, we are actually talking about science mainly.

Microscopic pictures of actin cytoskeleton
23.08.2013
From the actin GFP fusion pictures were made under a fluorescent microscope. Beforehand the A.niger transformantss were grown under different conditions in an 8-well plate specially designed for microscopy.

Gibson assembly
22.08.2013
The colony PCR’s of DH, MT, ACP and eforRed are successful. Performed another Gibson assembly with KS.

Ligation of proton-ATPase gene into in-house brick
22.08.2013
Finally we managed to ligate the proton-ATPase used for the visualization of the septa into an in-house brick containing an n-terminal GP fusion.

Improving the A. terreus model
21.08.2013
As it turns out, the lovastatin pathway in the published A. terreus model is not balanced and optimization for its production is therefore impossible. This is actually an interesting finding, since it implies that we can now improve the current model by adding the detailed lovastatin biosynthesis pathway that is balanced and allows for optimization of lovastatin production.

Gibson assembly
21.08.2013
Today we did our first Gibson assemblies of DH, MT, ACP, eforRed and ATP. Including transformations.

Working on the Wiki
20.08.2013
The wiki is making good progress, everybody should be able to work with the system now. Objectives are to upload content, look for icons that can be used in the menu bar and to finish the team page

Transformations
19.08.2013
We have two kinds of competent E.coli cells to do the transformation. Both of the Electro-competent cells and chemical-competent work.

G-blocks from IDT arrived today
19.08.2013
Today the G-blocks we ordered finally arrived! This is great news, because now we can start on the gibson assembly and transformations.
Week 11
August (12.08 - 18.08)

iGem Olympics: Second round
18.08.2013
We played pool during the second round of the iGem Olympics. Also to celebrate Shreyans Birthday!

Sequencing results arrived
15.08.2013
The sequencing results from the proton-ATPase arrived and it appeared that one of the two samples was correct and work could be continued.

A. terreus model
14.08.2013
Recently an A. terreus model has been published. This is quite interesting, since A. terreus is the organisms that naturally produces lovastatin. A quick scan for metabolites shows that both dihydromolacolin L and lovastatin are included in the model. Altough reactions have been lumped, now we can also investigate the potential differences between the lovastatin pathway present and the one we constructed ourselves.
- J. Lui et al., 2013. Genome-scale reconstruction and in silico analysis of Aspergillus terreus metabolism. . Molecular Biosystems, Vol. 9, p. 1939-1948.

Molecular Interactions Symposium Berlin
14.08.2013
We went to the Molecular Interactions symposium in Berlin to present a poster about our project! We were kind of surprised that there were no other iGem teams. The interaction we had with the interested people lead to a couple of nice suggestions to the poster and the project. We even had a good discussion about Gibson Assembly. The interesting speakers there, nice ambience and good dinner in the evenings these 2 days totally made up for the 2 times 7 hours of midnight driving!
Week 10
August (05.08 - 11.08)

Vitruvian man stamp
11.08.2013
We looked into using Vitruvian man metal stamps to make imprints in the agar.

pH
10.08.2013
Finally gibson assembly worked for ph-sensor into pJet1.2. Here's a picture showing the digestion analysis using; nsiI and notI; pstI and notI

Workshop by Paulien Poelarends
09.08.2013
Paulien did her master thesis on last year’s iGEM teams and their way of communicating with the public and politicians. We have a wonderful afternoon with her, obtaining a lot by her workshop.

Protoplasts
08.08.2013
During this week we have prepared media and spores to make protoplasts. The protoplasts will be used for transformations. Until recently Novozym has been used to make protoplasts, this is not available anymore and some new protocols have to be used.

Lovastatin
06.08.2013
The restriction enzymes that we ordered last week have arrived. After a few attempts the sequences have been optimized and the G-blocks can be ordered. Also some Lovastatin has been ordered to perform some experiments with A. niger. Lovastatin may be fatal to cell growth of A. niger therefore experiments have to indicate whether A. niger is resistant to Lovastatin. Otherwise A. niger has to be transformed with the resistance gene from A. terreus.

Plasmids extraction with Kit
06.08.2013
Using GeneJET Plasmid Miniprep Kit, we extracted the plasmids containing chromoprotein genes from DH5α E.coli and checked their concentration with Nanodrop 1000.

Expanding the database
05.08.2013
In order to expand the database, more information on secondary metabolite backbone enzymes from Aspergilli needs to be added. Luckily there is a recent publication on secondary metabolites from A. nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae.
- D.O. Inglis et al., 2013. Comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of Aspergillus nidulans, A. fumigatus, A. niger and A. oryzae. BMC Microbiology, Vol. 13, p. 1-23.

Chemical transformation
05.08.2013
The plasmids containing chromoprotein genes were transformed into DH5α E.coli competent cells and we set up the same background within the DH5α E.coli strains .
Week 9
July (29.07 - 04.08)

iGem BBQ
02.08.2013
We finally had our first group BBQ! Together with all people that are involved with our team! It was a really nice day.

Design the primers for Chromoprotein
02.08.2013
The primers for aeBlue, eforRed, amilGFP and mRFP chromoprotein genes were designed with Clone Manager.

First transformation of A. niger
01.08.2013
Finally it was time to transform A. niger with the first construct we got. This would be the actin GFP fusion. This was introduced into A. niger and transormation worked as it appeared 4 days later.

Shopping
30.07.2013
This week we ordered the restriction enzymes for the assembly strategy. Also other stuff should be ordered like pJET, lovastatin, A. niger & A. terrus strain, Gibson assembly kit...
Week 8
July (22.07 - 28.07)

Obtained E.coli expressing chromoproteins from Braunschweig
26.07.2013
We obtained the E.coli from Braunschweig that have plasmids with an chromoprotein encoding gene insert. Lets start introducing it into Aspergillus Niger!

Actin gene was ligated in in-house vector
24.07.2013
It was time to ligate the actine gene into the in-house vector containing an n-terminal GFP fusion and transform E. coli with this vector.

Setting a standard
23.07.2013
Metanetx.org uses its own namespace to standardize the entities that are used within the models, such as metabolites and the reactions. Standardization makes working with different models from different origins much more feasible. However, Metanetx is a project in the making, which means that even though it facilitates the process, manual curation is required.

Metabolic activity: GFP
22.07.2013
In a similar way that the DAPI stained cells give an indication of metabolic activity by showing an increase in nuclei, GFP-transformed A. niger also give an indication of metabolic activity by giving an indication on whether transcription and translation occur.

Splitting up the domains
22.07.2013
Luckily, we got some help from Kal, a really nice guy who offered a lot of help. Several very useful websites he suggested could analyse the AA sequence and give some advice on where is the possible site to split the whole protein. We combined the analysis result with references, we finally got a clear idea (or at least we believe) about the boundary of the domains.
Week 7
July (15.07 - 21.07)

Working on the Wiki
19.07.2013
The design of the wiki is making good progress. Basic layout has been determined and we created icon to indicate different parts of the project.

Article searching
18.07.2013
Totally lost in how to divide each single domain in the lovB gene. By searching the articles, we could find information and experimental details about ACP, KS, MAT and CON domain. While for the others, still virgin land. KR seems to have two subdomains, what the hell~

Database design
16.07.2013
MySQL the world's most widely used open-source relational database management system. Now we will also check the possibility to use it as our method.
Week 6
July (08.07 - 14.07)
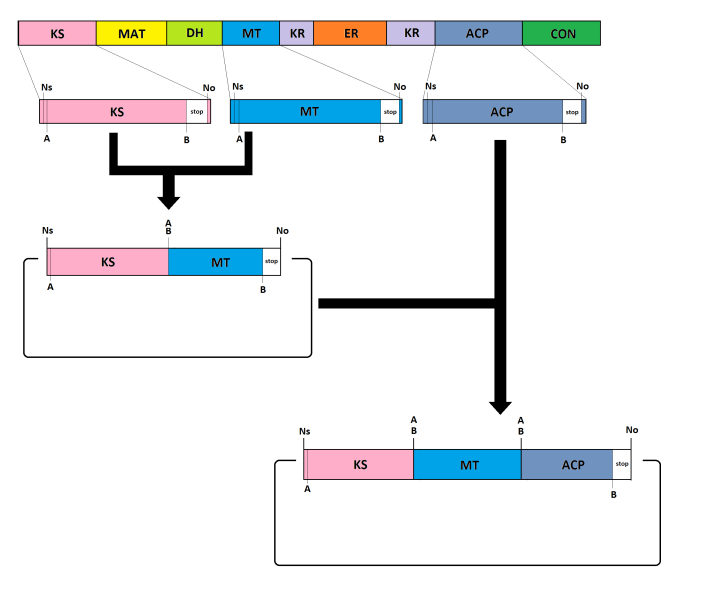
Lovastatin strategy
12.07.2013
Now that we have the general idea the details need to be worked out. Therefore we came up with a strategy to assemble the modules using compatible restriction enzymes. The strategy will enable us to assemble several modules and to have a stop codon at the end of the assembled gene without a frame shift. Also the general planning of the project was worked out this week.

Expanding the scope
12.07.2013
To expand the scope of the modeling and create a larger overlap with the secondary metabolite backbone enzyme database we have chosen to expand the number of models. A. oryzae and A. nidulans have been added to the scope of this project. Expansion of the modeling with these three additional Aspergilli allows for a comparative approach in which results can be compared.

DAPI staining
11.07.2013
It has been found that dormant conidia are predominantly bi-nucleate (85%), the remainder being uni-nucleate. Therefore, if one stains the giant cells with DAPI, which colours the nuclei, one can assess whether the nuclei within the cells are actively dividing. This appears to be the the case and thus indicates that the cells are not in a vegetative state.
Week 5
July (01.07 - 07.07)

BioKe meeting in Wageningen
05.07.2013
A BioKe spokesperson came over to Wageningen. We gave her a tour and presentation. We obtained the Q5 PCR kit!

Lovastatin
05.07.2013
Finally the search has begun, this week we have started with literature research for the Lovastatin project. Some topics were for example what is Lovastatin, which genes are involved in Lovastatin production in Aspergillus terreus, and how to measure Lovastatin production. The first idea was to introduce the Lovastatin pathway of A. terreus into A.niger. During the research we found that one of the bigger genes involved is composed of several domains. Our new idea now is to synthesize these domains, making several modules that we can assemble as we wish.

Science Café
04.07.2013
We met with the Science Café organisation to discuss the possibilities towards our team organising an evening there with a Biohacker theme.

Database planning
03.07.2013
A database of Aspergillus niger is planned to set. Thus we can get insight to comprehensive annotation of secondary metabolite biosynthetic genes and gene clusters of it.

Primers for septa visualizition arrived
02.07.2013
After some waiting time the primers needed for the visualization of the septa using a proton-ATPase finally arrived and this part of the project could also get started by isolating the gene from genomic A. niger DNA.

Sequensing results arrived
01.07.2013
The sequencing results from the actin gene arrived and everything looked fine. We had the right gene without mistakes and could go on with the actin cytoskeleton project.

Actin gene in house internal brick system
01.07.2013
The actin gene for cytoskeleton visualization purposes was ligated into a house internal brick system with a n-terminal GFP fusion. This construct was then introduced into E. coli for amplification purposes.
Week 4
June (24.06 - 30.06)

Complimentary Supplies from BIOKE
26.06.2013
Complimentary cloning kits arrived today from one of our sponsors, BIOKE.

Lovastatin Pathway
25.06.2013
The lovastatin pathway has been added to the metabolic model of Aspergillus niger. Because the medium composition of the model is not yet properly defined, the maximum flux towards lovastatin can be achieved. This however is not realistic and therefore the next thing is to redefined the medium composition.
- B.D. Ames et al., 2011. Crystal structure and biochemical studies of the trans-acting polyketide enoyl reductase LovC from lovastatin biosynthesis. PNAS, doi/10.1073/pnas.1113029109

Calcofluor staining
24.06.2013
Calcofluor is known to stain cellulose and chitin. In A.niger, chitin is found in the cell wall, thus if we find cells in this specific stage of mitosis, just before division is completed and when the cytoplasm is connected, we might be able to visualize this with the use of this staining method.
Week 3
June (17.06 - 23.06)

Finding the right conditions for distinct phenotypes
22.06.2013
As described in literature, N593 formed giant cells after 24h at 44C. Since transcriptome data on N400 from multiple stages in its life cycle is available, this strain is chosen such that this research complements the current RNA landscape profile of A. niger and allows for comparison of data from different life stages. However, unlike N400, N593 repeatedly formed mycelium at 44C. To overcome this effect the temperature was increased to 45C, at which a single cell phenotype was obtained for N593.

Do It Yourself Biohacker Meeting 2
20.06.2013
We had a DIY Biohacker Meeting in the Waag, Amsterdam. The Waag had its grand opening and there was a exposition and party afterwards

Do It Yourself Biohacker Meeting 1
18.06.2013
We had a DIY Biohacker Meeting in the Waag, Amsterdam. Learned how to make your own potato-agar
Week 2
June (10.06 - 16.06)

Funny group picture
15.06.2013
Opportunity was presented to take a few fun group pictures... we obviously took it

Dinner and discussion
14.06.2013
We met at Mark’s place for dinner and evaluation of possibilities in using secondary metabolites for our project

Host Engineering: Research plan
13.06.2013
Different environmental conditions induce changes in phenotypic cellularity of Aspergillus niger. Mapping reads onto the reference genome allows for discovery of patterns in gene expression that are unique to the single cell phenotype.

Last and 8th recruit
13.06.2013
Yeng Ding AKA Danny joind our team. We are now 8 members strong!

ThinkerCell & CloneManager meeting
12.06.2013
The ones from our team who had learned to work with these software tools, during one of the iGem Netherlands courses, taught the others how use it.

Lab supplies
11.06.2013
We ordered reagents for cloning and PCR.

Collaboration
11.06.2013
We contacted the Cornell University iGem 2013 team to talk about possibilities for collaboration. They also work with fungus.
Week 1
June (03.06 - 09.06)

Actin primers arrived
06.06.2013
Finally the improved pair of actin primers arrived and after not getting good PCR results for some time I could finally get started and optimize PCR conditions for gene amplification of the actin gene.

House internal brick system
05.06.2013
The house internal brick system with a n-terminal GFP fusion was proven to be ok by restriction digestion and was ready to be worked with.

Host Engineering: Research Question
04.06.2013
Research question:
Finding sets of candidate genes causative to the single cell phenotype in Aspergillus niger by transcriptome analysis.
Subquestions:
- is A. niger metabolically active at 44C?
- does A. niger divide at 44C?
May

Metabolic model A. niger
30.05.2013
The current metabolic model of A. niger needs to be expanded to include the lovastatin pathway as known from literature. First the model has to be checked: is it balanced? can we perform a FBA on the current model?
- M.R. Anderson et al., 2008. Metabolic model integration of the bibliome, genome, metabolome and reactome of Aspergillus niger. Molecular Systems Biology, Vol. 4, Article number 178; doi:10.1038/msb.2008.12

Meeting room
26.05.2013
We reserved a room for all future Monday and Thursday lunch meetings in the Forum.
Visualization of the actin cytoskeleton
27.05.2013
Finally the labwork for the visualization of the septa and actin cytoskeleton started. And the first thing to do was order primers and isolate genomic DNA from A. niger.

Plasmid isolation and DNA quantification
24.05.2013
Plasmid DNA containing the ATP and pH constructs was isolated by midi preparation and quantified by Nanodrop measurement.

Created a Gmail account
23.05.2013
We created a Gmail account. Let the spam begin!

Meeting iGem Uppsala
18.05.2013
We met with the iGem Uppsala 2013 team in Uppsala.

Glycerol stocks made
16.05.2013
All the E. coli stabs with constructs from Addgene and the Imamura lab were revived and glycerol stocks were made and preserved at -80'C.

Created a Twitter account
15.05.2013
We created a Twitter account. Hello world! Meet iGem Wageningen 2013~

Chromoprotein sequencing
13.05.2013
Looked into sequencing options: codon optimization to Aspergillus Niger, suffix/prefix, (illegal) restrictionsites. Let’s order some g-blocks!

ATP,pH bio-sensor constructs delivered
13.05.2013
The constructs ordered from Addgene, Boston and from the Imamura lab, Japan reached us today.

Lab space
08.05.2013
We arranged our very own lab space!

Host Engineering: why?
05.05.2013
The single-cell phenotype Aspergillus has a higher surface to volume ratio and results in a lower viscosity of the liquid broth, offering perspective on substantially increasing process yields when used in liquid fermentations. Besides from an industrial point of view it is also interesting from an evolutionary perspective, which couples application-oriented research using a directed evolution approach to a more fundamental research topic: the evolution of multicellularity.
April

Good Lab Practice
24.04.2013
We had a lecture on good lab practice and safety in the lab, awesome! ;)

Task division
18.04.2013
Co-ordinator – Michiel
Secretary – Emiel
Sponsoring - Emiel
Safety - Jingjing
Lab manager – Shreyans
Strategy - Marit
Wiki – Michiel
Human Practice - Marjan

Influence of temperature on germination
15.04.2013
A paper from 1970 shows that at 44C Aspergillus niger does not germinate, but rather forms giant cells. This dimorphism is not unfamiliar within the fungal world, where at lower temperatures the mycelium is formed and at higher temperatures the yeast-like form is found.
Anderson, J. G. and J. E. Smith (1972). "Effects of Elevated-Temperatures on Spore Swelling and Germination in Aspergillus Niger." Canadian Journal of Microbiology 18(3): 289-297.
March
javascript
 "
"
