Team:Paris Saclay/Project
From 2013.igem.org
(→Detection and degradation of PCB system in Escherichia coli) |
|||
| (74 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_menu_navigation}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_menu_navigation}} | ||
Project | Project | ||
| - | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/ | + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/PCBs|What are PCBs ?]] |
| - | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/ | + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/Project|Overview]] |
[[Team:Paris_Saclay/Modeling|Modeling]] | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/Modeling|Modeling]] | ||
| - | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/ | + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/PS-PCR|PS-PCR]] |
| + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/Achievements|Achievements]] | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin_menu_navigation}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin_menu_navigation}} | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_contenu}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_contenu}} | ||
| - | |||
| - | + | = '''Detection and degradation of PCB system in ''Escherichia coli''''' = | |
| - | |||
| - | + | Since the second half of the 20th century, scientists are fully aware that some bacterial species living in media with high concentration of PCBs are able to degrade PCBs into pyruvate and acetyl-CoA which are then easily metabolized by these organisms. | |
| - | |||
| + | These bacterial species structure in biofilm with regions that have variable concentrations of oxygen, high at the surface and decreasing with depth. Bacteria living in this habitat have, in most cases, different degradation pathways, which are aerobic or anaerobic depending on their spatial disposition in the biofilm. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | Bacteria in aerobic environment use PCB oxidative degradation pathways; those in anaerobic condition degrade PCBs via reductive dechlorination pathways. None of the bacteria seems to use both pathways. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | The reductive dechlorination reduces the number of chlorines of high chlorinated PCBs. The dechlorinated PCBs can be further degraded by an oxidative degradation which is efficient only with low chlorinated PCBs. That’s may explain why these different species coexist in biofilms. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | '''Our goal in this project is to desing an organism able to i) detect PCB and then ii) | ||
| + | '''employ a sequential degradation of the PCB using both combined pathways.''' | ||
| + | '''For our experiences, we used bacteria present in nature that are able to detect and degrade the''' | ||
| + | '''PCBs, namely [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Burkholderia_xenovorans ''Burkholderia xenovorans''], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22843571''Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes'' KF 707] and | ||
| + | [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rhodococcus'''''Rhodococcus jostii'' RHA1].''''' | ||
| - | + | [[File:Psnotenough.png|center|200px]] | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ==Construction of a system to detect the presence of PCBs== | |
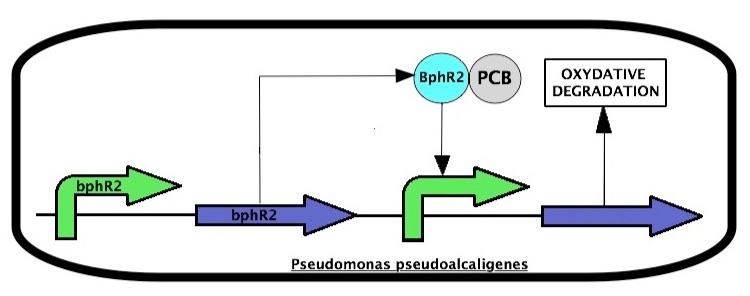
| - | ''' | + | ''Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes'' expresses enzymes that are responsible for an oxidative degradation of PCBs. The system is regulated two proteins, BphR2 and BphR1 coded by the ''bphR2'' and ''bphR1'' genes, respectively. PCBs induce a BphR2 conformational change to trigger BphR2 transcriptional activity leading to expression of the PCB oxidative degradation pathway. |
| - | + | ||
| - | ''' | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:PsR2degradation.jpg]] |
| + | BphR2 also induces the expression of ''bphR1''. | ||
| - | + | [[File:PsR2surR1.jpg]] | |
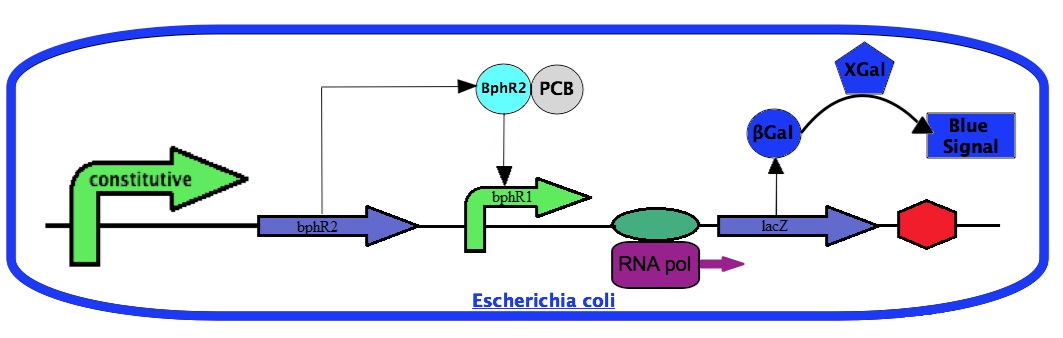
| - | + | For the project, we will use the ''bphR2'' gene and the ''bphR1'' promoter. We will place the ''bphR2'' coding sequence under a constitutive promoter. We will also construct a transcriptional fusion between the ''bphR1'' promoter with the ''lacZ'' gene coding for the β-galactosidase enzyme. The amount of β-galactosidase can be easily monitored by a chemical reaction using Xgal. With this system, the β-galactosidase activity will dependent on the ''bphR1'' promoter expression. Since the ''bphR1'' promoter is controlled by the PCB-activated BphR2, the β-galactosidase activity will correlate with the presence of PCBs. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | the | + | |
| + | [[File:PsavecPCB.jpg|800px]] | ||
| - | + | ==Combination of the aerobic and anaerobic PCB degradation pathways== | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
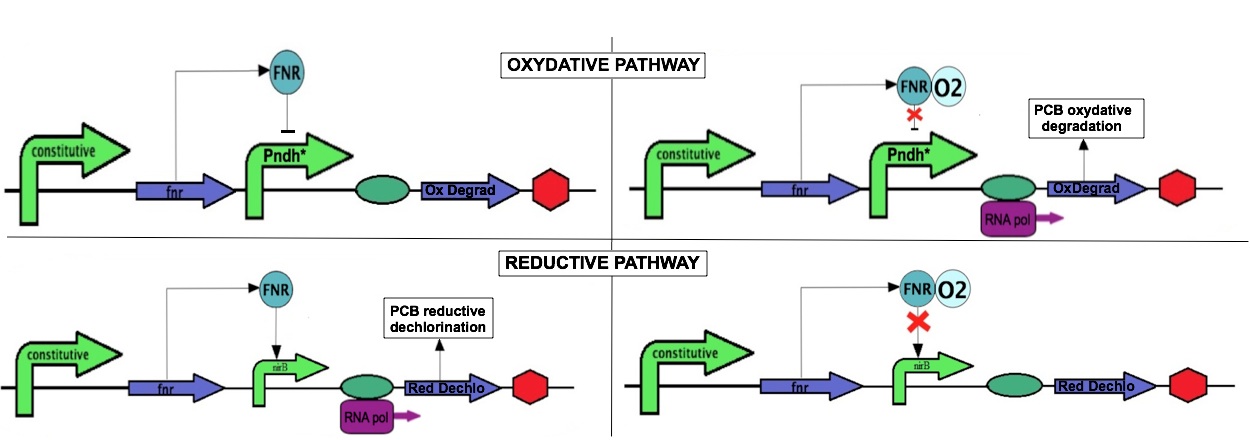
| + | To perform an efficient PCB degradation, two processes should be sequentially combined, the PCB reductive dechlorination followed by a PCB oxidative degradation pathway. Our goal is to engineer a bacterium expressing alternatively both pathways according to growth conditions, with first the reductive dechlorination in anaerobiosis followed by a PCB oxidative degradation in aerobiosis. | ||
| - | The | + | The bacterium ''E. coli'' has an aerobic and an anaerobic metabolism that will be used to combine of the two PCB degradation pathways. The switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism is partly regulated the transcriptional regulator FNR. This protein has a dual function: it activates genes involved in anaerobic metabolism and represses genes involved in aerobic metabolism. FNR expression is constitutive, but its activity is directly affected by the presence of oxygen which oxidizes of an essential [4Fe-4S] cluster. For the project, we use two promoters, PnrdH and PnifR which are repressed and activated by FNR, respectively |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | The reductive dechlorination pathway is not well characterized; only one enzyme, a dehalogenase, is mentioned as contributing to this pathway. We propose to clone the corresponding gene in ''E. coli'' under the control of the PnifR promoter. As a result, the reductive dechlorination enzyme should be expressed in anaerobiosis to perform the first PCB degradation step. The second step involves an oxidative degradation and is performed in aerobiosis. We propose to clone the operon PCB oxidative degradation under the PrndH promoter which is derepressed in anaerobiosis. This configuration should optimize the PCB degradation according to the environmental conditions. | ||
| + | [[File:Psbigschema.jpg|800px]] | ||
| - | + | ==References== | |
| + | Kensuke Furukawa, Hikaru Suenaga and Masatoshi Goto | ||
| + | Biphenyl Dioxygenases: Functional Versatilities and Directed Evolution | ||
| + | |||
| + | JOUNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, 2004 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Kazunari Taira, Jun Hirose, Shinsaku Hayashida, and Kensuke Furukawa | ||
| + | |||
| + | Analysis of bph Operon from the Polychlorynated Biphenyl-degrading Strain of ''Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes'' KF707 | ||
| + | |||
| + | THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, 1992 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Kensuke Furukawa and Hidehiko Fujihara | ||
| + | |||
| + | Microbial Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls: Biochemical and Molecular Features | ||
| + | |||
| + | JOURNAL OF BIOSCIENCE AND BIOENGINEERING, 2008 | ||
| - | |||
| + | Jim A. Field, Reyes Sierra-Alvarez | ||
| - | + | Microbial transformation and degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | Environmental Pollution, 2008 | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | Lorenz Adrian, Helmut Görisch | ||
| + | Microbial transformation of chlorinated benzenes under anaerobic conditions | ||
| + | Research in Microbiology, 2002 | ||
| - | |||
| + | Dean. A Tolla and Michael A. Savageau | ||
| + | Regulation of Aerobic-to-Anaerobic Transitions by the FNR Cycle in Escherichia coli | ||
| + | J. Mol. Biol. (2010) | ||
| + | Hidehiko Fujihara, Hideyuki Yoshida, Tetsuya Matsunaga, Masatoshi Goto, and Kensuke Furukawa | ||
| + | Cross-Regulation of Biphenyl- and Salicylate-Catabolic Genes by Two Regulatory Systems in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707 | ||
| - | + | JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 2006 | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| + | Article written by Eric and Nadia | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin}} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:50, 4 October 2013
Contents |
Detection and degradation of PCB system in Escherichia coli
Since the second half of the 20th century, scientists are fully aware that some bacterial species living in media with high concentration of PCBs are able to degrade PCBs into pyruvate and acetyl-CoA which are then easily metabolized by these organisms.
These bacterial species structure in biofilm with regions that have variable concentrations of oxygen, high at the surface and decreasing with depth. Bacteria living in this habitat have, in most cases, different degradation pathways, which are aerobic or anaerobic depending on their spatial disposition in the biofilm.
Bacteria in aerobic environment use PCB oxidative degradation pathways; those in anaerobic condition degrade PCBs via reductive dechlorination pathways. None of the bacteria seems to use both pathways.
The reductive dechlorination reduces the number of chlorines of high chlorinated PCBs. The dechlorinated PCBs can be further degraded by an oxidative degradation which is efficient only with low chlorinated PCBs. That’s may explain why these different species coexist in biofilms.
Our goal in this project is to desing an organism able to i) detect PCB and then ii)
employ a sequential degradation of the PCB using both combined pathways.
For our experiences, we used bacteria present in nature that are able to detect and degrade the
PCBs, namely [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Burkholderia_xenovorans Burkholderia xenovorans], [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22843571Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF 707] and
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RhodococcusRhodococcus jostii RHA1].
Construction of a system to detect the presence of PCBs
Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes expresses enzymes that are responsible for an oxidative degradation of PCBs. The system is regulated two proteins, BphR2 and BphR1 coded by the bphR2 and bphR1 genes, respectively. PCBs induce a BphR2 conformational change to trigger BphR2 transcriptional activity leading to expression of the PCB oxidative degradation pathway.
BphR2 also induces the expression of bphR1.
For the project, we will use the bphR2 gene and the bphR1 promoter. We will place the bphR2 coding sequence under a constitutive promoter. We will also construct a transcriptional fusion between the bphR1 promoter with the lacZ gene coding for the β-galactosidase enzyme. The amount of β-galactosidase can be easily monitored by a chemical reaction using Xgal. With this system, the β-galactosidase activity will dependent on the bphR1 promoter expression. Since the bphR1 promoter is controlled by the PCB-activated BphR2, the β-galactosidase activity will correlate with the presence of PCBs.
Combination of the aerobic and anaerobic PCB degradation pathways
To perform an efficient PCB degradation, two processes should be sequentially combined, the PCB reductive dechlorination followed by a PCB oxidative degradation pathway. Our goal is to engineer a bacterium expressing alternatively both pathways according to growth conditions, with first the reductive dechlorination in anaerobiosis followed by a PCB oxidative degradation in aerobiosis.
The bacterium E. coli has an aerobic and an anaerobic metabolism that will be used to combine of the two PCB degradation pathways. The switch between aerobic and anaerobic metabolism is partly regulated the transcriptional regulator FNR. This protein has a dual function: it activates genes involved in anaerobic metabolism and represses genes involved in aerobic metabolism. FNR expression is constitutive, but its activity is directly affected by the presence of oxygen which oxidizes of an essential [4Fe-4S] cluster. For the project, we use two promoters, PnrdH and PnifR which are repressed and activated by FNR, respectively
The reductive dechlorination pathway is not well characterized; only one enzyme, a dehalogenase, is mentioned as contributing to this pathway. We propose to clone the corresponding gene in E. coli under the control of the PnifR promoter. As a result, the reductive dechlorination enzyme should be expressed in anaerobiosis to perform the first PCB degradation step. The second step involves an oxidative degradation and is performed in aerobiosis. We propose to clone the operon PCB oxidative degradation under the PrndH promoter which is derepressed in anaerobiosis. This configuration should optimize the PCB degradation according to the environmental conditions.
References
Kensuke Furukawa, Hikaru Suenaga and Masatoshi Goto
Biphenyl Dioxygenases: Functional Versatilities and Directed Evolution
JOUNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, 2004
Kazunari Taira, Jun Hirose, Shinsaku Hayashida, and Kensuke Furukawa
Analysis of bph Operon from the Polychlorynated Biphenyl-degrading Strain of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY, 1992
Kensuke Furukawa and Hidehiko Fujihara
Microbial Degradation of Polychlorinated Biphenyls: Biochemical and Molecular Features
JOURNAL OF BIOSCIENCE AND BIOENGINEERING, 2008
Jim A. Field, Reyes Sierra-Alvarez
Microbial transformation and degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls
Environmental Pollution, 2008
Lorenz Adrian, Helmut Görisch
Microbial transformation of chlorinated benzenes under anaerobic conditions
Research in Microbiology, 2002
Dean. A Tolla and Michael A. Savageau
Regulation of Aerobic-to-Anaerobic Transitions by the FNR Cycle in Escherichia coli
J. Mol. Biol. (2010)
Hidehiko Fujihara, Hideyuki Yoshida, Tetsuya Matsunaga, Masatoshi Goto, and Kensuke Furukawa
Cross-Regulation of Biphenyl- and Salicylate-Catabolic Genes by Two Regulatory Systems in Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF707
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 2006
Article written by Eric and Nadia
 "
"