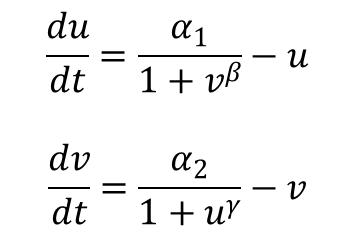Team:Duke/Modeling/3
From 2013.igem.org
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→Following Gardner's Work...) |
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→Following Gardner's Work...) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:Gardner_variables.png|300px|center]] |
<div align="center"> Figure 2. Equation Used in Gardner's Model</div> <br><br> | <div align="center"> Figure 2. Equation Used in Gardner's Model</div> <br><br> | ||
Revision as of 05:41, 22 September 2013
Contents |
Mathematical Modeling of Bistable Toggle Switch
Kinetic Model of Bistable System
Following Gardner's Work...
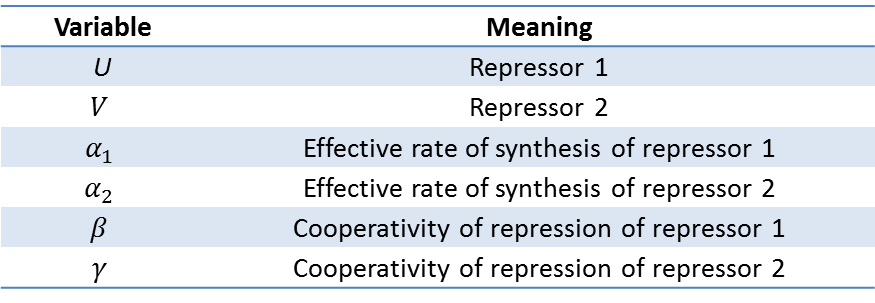
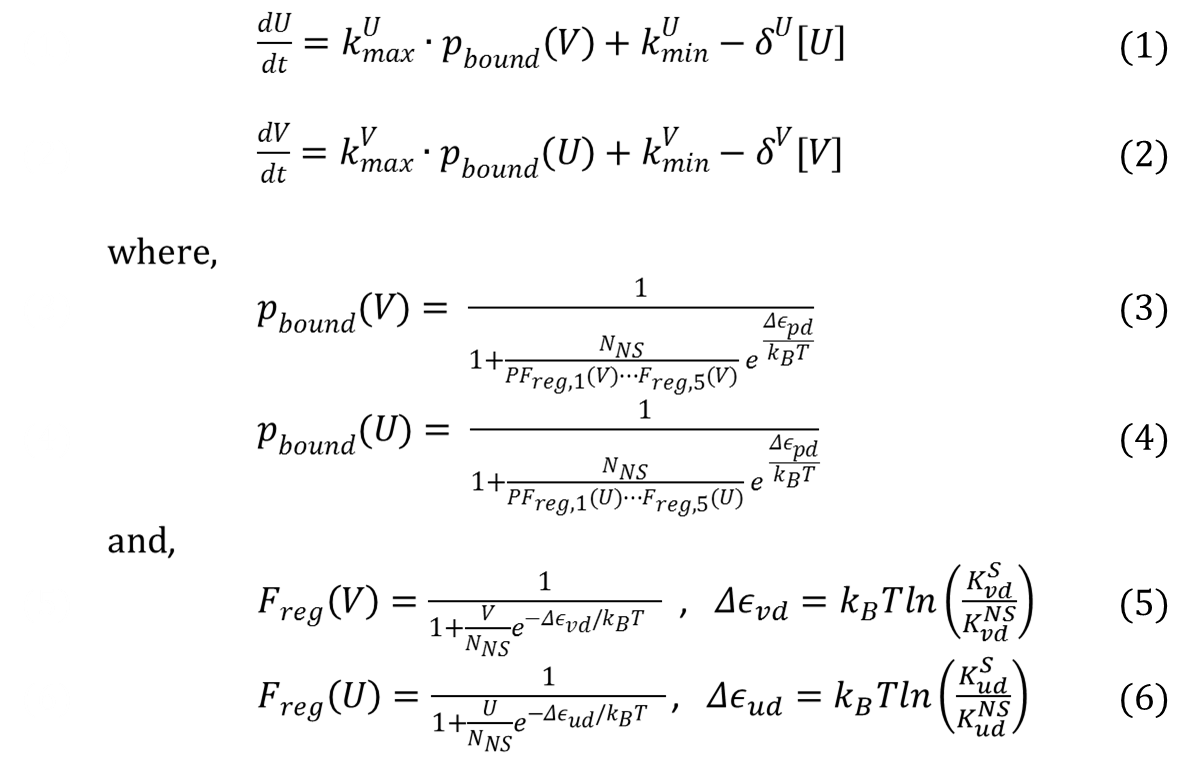
Tim Gardner from Jim Collins' Lab of Boston Univeristy published one of the first major papers on genetic toggle switch. In his work, he used a kinetic approach to model the stability of a genetic toggle switch. His equations involved two equations expressing the change in the level of two mutually repressive repressors with respect to time.
explain bifurcation
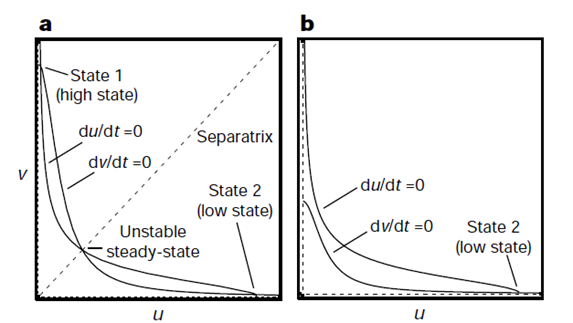
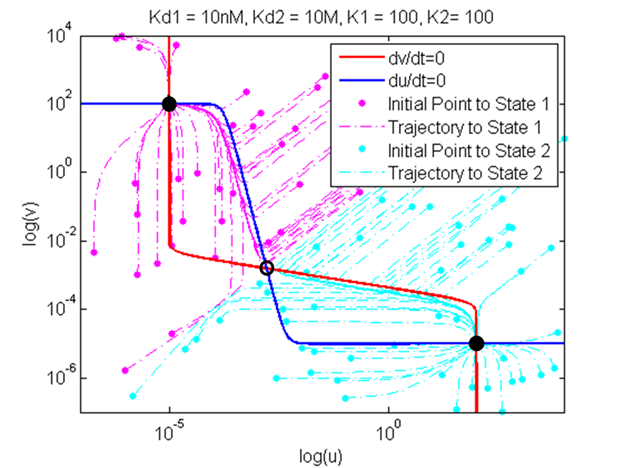
figure (trajectory)
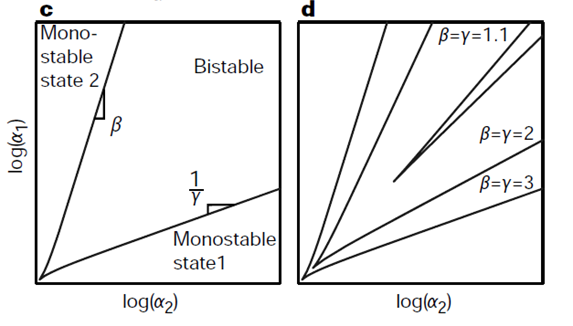
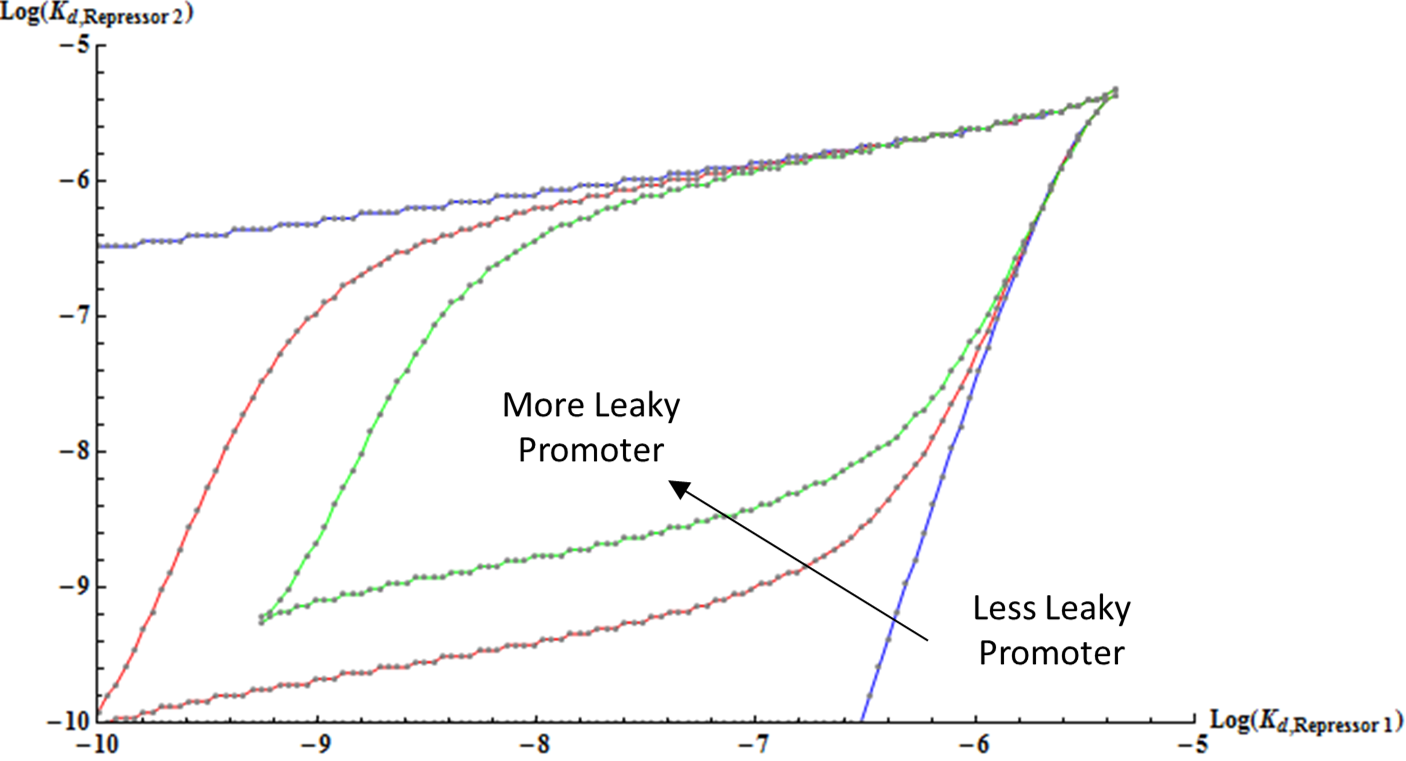
figure (bifurcation)
explain the effect of changing hill coeff on bifurcation region. explain nullcline
reproduce nullcline and trajectory (explain trajectory)
Development of Our Kinetic Model
moving on, we have developed another kinetic model using the results of the thermodynamic model. gardner = effect of hill coeff on bistability of a system (bifurcation region) new model = effect of various parameters on bistability (highlight and number Kd, pr_Str, basal rate.
as mentioned before, key assumption is is (du/dt , dv/dt = proportional to p_bound)
show equation
explain
show values for variables like degradation rate
Results from Our Kinetic Model
show graph
explain
show nullcline
confirm bistability of the system (thermodynamic model incorporated into kinetic model)
References
- Gardener, T. et al. Construction of a genetic toggle switch in Escherichia coli. Nature. 403, 339-342 (2000).
 "
"