Team:Yale/Project Export
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Introduce type 1 secretion system to export and extract PLA) |
|||
| Line 180: | Line 180: | ||
**We found the paper by Linton 2010 where she focused on exporting PHA from engineered ''E. coli'' | **We found the paper by Linton 2010 where she focused on exporting PHA from engineered ''E. coli'' | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | * | + | *Ms. Linton used Phasin, a PHA granule associated protein that plays a role in granule formation, with a hlyA tag. |
**This allowed the cells to export the PLA since the hlyA tag was attached to the granule | **This allowed the cells to export the PLA since the hlyA tag was attached to the granule | ||
<center>[[File:PHA_export_system.jpg|400px]]</center> | <center>[[File:PHA_export_system.jpg|400px]]</center> | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 26 September 2013
Introduce type 1 secretion system to export and extract PLA
- We needed a way to export the PLA once it was synthesized by the E. coli
- We found the paper by Linton 2010 where she focused on exporting PHA from engineered E. coli
- Ms. Linton used Phasin, a PHA granule associated protein that plays a role in granule formation, with a hlyA tag.
- This allowed the cells to export the PLA since the hlyA tag was attached to the granule
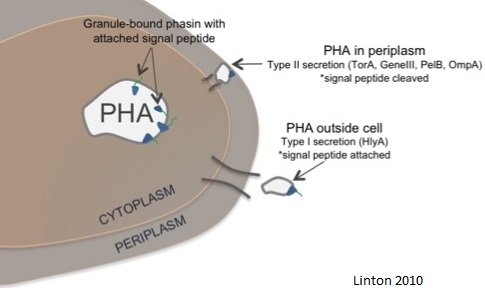
- Due to the similarity between PHA granules and PLA granules we hypothesized that this same export system would allow us to export PLA from our cells.
 "
"
