Team:Greensboro-Austin/MAPs
From 2013.igem.org
(→The mussel and its glue) |
|||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
Additionally, in current systems there is no guarantee that a tyrosine placed at your desired location will even end up as an L-DOPA, so we would also want the ability to know for certain that the residues of interest are in fact L-DOPA and not tyrosine. | Additionally, in current systems there is no guarantee that a tyrosine placed at your desired location will even end up as an L-DOPA, so we would also want the ability to know for certain that the residues of interest are in fact L-DOPA and not tyrosine. | ||
| - | == Our solution: direct | + | == Our solution: direct non-canonical amino acid incorporation == |
| - | Incorporating the | + | Incorporating the non-canonical amino acid L-DOPA '''directly''' would solve these problems of control and predictability. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, the enzymes that charge tRNAs with amino acids, can be evolved to recognize non-canonical amino acids by sequential rounds of positive and negative selection. The tRNA’s anticodon loop can be engineered to recognize any codon. So, a stop codon (such as UAG, also known as the Amber codon) can be repurposed to code for a 21st amino acid. |
| - | In addition, release factor 1, which normally recognizes this Amber codon, can be knocked out, ensuring no competition between the stop codon’s old effect (termination) and its new effect ( | + | In addition, release factor 1, which normally recognizes this Amber codon, can be knocked out, ensuring no competition between the stop codon’s old effect (termination) and its new effect (non-canonical amino acid incorporation). The result of this system is an expansion of the cell’s genetic code to 21 amino acids, allowing precise control of targeted L-DOPA incorporation. |
== ''E. coli'' as a self-sufficient "black box" == | == ''E. coli'' as a self-sufficient "black box" == | ||
| Line 85: | Line 85: | ||
[[File:E._coli_as_biosynthetic_factory_for_MAPs.png | center]] | [[File:E._coli_as_biosynthetic_factory_for_MAPs.png | center]] | ||
| - | Our vision is of ''E. coli'' as biosynthetic "factory" able to make complicated products with simple inputs. By giving it the machinery to charge tRNA with L-DOPA, and expanding the genetic code to include L-DOPA, this | + | Our vision is of ''E. coli'' as biosynthetic "factory" able to make complicated products with simple inputs. By giving it the machinery to charge tRNA with L-DOPA, and expanding the genetic code to include L-DOPA, this non-canonical amino acid can be incorporated at rationally targetted locations, generating a library of foot protein variants. |
Appropriate with this characterization of self-sufficiency and synthetic capability, these E. coli would not even need to be supplemented with exogenous L-DOPA, as they could continually generate it from intracellular free tyrosine. | Appropriate with this characterization of self-sufficiency and synthetic capability, these E. coli would not even need to be supplemented with exogenous L-DOPA, as they could continually generate it from intracellular free tyrosine. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
A two-plasmid system would be appropriate for our aims. One plasmid would code for a library of fp-151 variants, each containing Amber codons in unique locations and quantities, yielding a diverse set of foot proteins with characteristic locations and numbers of L-DOPA residues. The adhesive properties of these variants would be compared against both in vitro and in vivo tyrosinase-treated foot proteins, which would serve as positive controls. | A two-plasmid system would be appropriate for our aims. One plasmid would code for a library of fp-151 variants, each containing Amber codons in unique locations and quantities, yielding a diverse set of foot proteins with characteristic locations and numbers of L-DOPA residues. The adhesive properties of these variants would be compared against both in vitro and in vivo tyrosinase-treated foot proteins, which would serve as positive controls. | ||
| - | This plasmid would also contain our L-DOPA biosynthesis cassette, ensuring a continual source of | + | This plasmid would also contain our L-DOPA biosynthesis cassette, ensuring a continual source of non-canonical amino acid without supplementation. |
The second plasmid would code for the synthetase/tRNA pair that is responsible for adding L-DOPA to the genetic vocabulary. | The second plasmid would code for the synthetase/tRNA pair that is responsible for adding L-DOPA to the genetic vocabulary. | ||
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
Make mussel adhesive proteins (MAPs) using ''E. coli'' | Make mussel adhesive proteins (MAPs) using ''E. coli'' | ||
| - | Incorporate | + | Incorporate non-canonical amino acids |
(How? Expand in Introduction. Stress novelty of idea.) | (How? Expand in Introduction. Stress novelty of idea.) | ||
| Line 187: | Line 187: | ||
== Strategy == | == Strategy == | ||
| - | == | + | ==Non-canonical Amino Acid Incorporation== |
[[File:Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase.png| A tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from ''Thermus thermophilus'' (PDB: 1H3E) | right|thumb|300px]] | [[File:Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase.png| A tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase from ''Thermus thermophilus'' (PDB: 1H3E) | right|thumb|300px]] | ||
| - | Previous studies have generated L-DOPA residues through post-translational modification (Choi et al. 2012, Hwang et al. 2007). However, this method has the disadvantage of less control of where L-DOPAs are incorporated and how efficient the process is. We will directly incorporate L-DOPA as an | + | Previous studies have generated L-DOPA residues through post-translational modification (Choi et al. 2012, Hwang et al. 2007). However, this method has the disadvantage of less control of where L-DOPAs are incorporated and how efficient the process is. We will directly incorporate L-DOPA as an non-canonical amino acid (UAA) into the MAP. |
Successful UAA incorporation requires the addition of two components: a new tRNA synthetase and its corresponding tRNA. This pair must be orthogonal, meaning that they must be highly specific for each other and the UAA. The tRNA should also be complementary to the UAG stop codon (also known as the “amber” stop codon), which will be reprogrammed to code for the new UAA instead of termination. | Successful UAA incorporation requires the addition of two components: a new tRNA synthetase and its corresponding tRNA. This pair must be orthogonal, meaning that they must be highly specific for each other and the UAA. The tRNA should also be complementary to the UAG stop codon (also known as the “amber” stop codon), which will be reprogrammed to code for the new UAA instead of termination. | ||
Revision as of 22:07, 26 September 2013
Contents |
The mussel and its glue
The mussel is a marine mollusk that lives in the inter-tidal zone on wave washed rocks. To stand the tidal forces, they must bind themselves to these rocks with their endogenous glue. Mussels have an organ called the foot, which is used to both pull the mussel through terrain and to excrete a structure called the byssus. These byssal threads are made up of collagen and other proteins and are what allow the mussel to attach to surfaces.
So why is mussel "glue" more useful over traditional glues?
The properties of mussel glue make it an attractive target for synthetic improvement; mussel glue allows attachment to many different types of surfaces, both organic and inorganic. It is strong and durable as it is able to withstand the harsh ocean environment. It is made of protein, so it can be easily degraded and is environmentally friendly.
Most importantly, however, it is biocompatible (non-immunogenic) and—unlike most glues—it works in aqueous environments.
Mussel adhesion proteins
There are several different proteins that make up the byssal threads, but the ones we’re most interested in are the ones that lie at the interface with the surface to which the mussel adheres. These proteins are responsible for the binding to the substrates and therefore have the most potential for use as a glue.
Adhesion relies on post-translational modifications
All of the different mussel foot proteins have a percentage of their tyrosines post-translationally modified to a molecule called L-DOPA. It turns out that the proteins closer to the adhesion surface have a much higher L-DOPA content, and in fact the L-DOPA content is linearly correlated with adhesiveness.
How MAPs adhere to surfaces
To the right is the sequence of a recombinant mussel adhesion protein, fp-151, that has good adhesive properties. Notably, it has high tyrosine content, denoted by the letter Y.
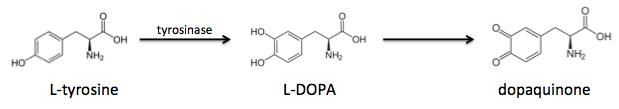
It turns out that tyrosines are critical for adhesion, but first they must undergo tyrosinase-mediated hydroxylation to L-DOPA, which can be further oxidized to dopaquinone:
These modified amino acids contribute to adhesion via two separate mechanisms: L-DOPA interacts non-covalently with inorganic surfaces by chelating metal ions, whereas dopaquinone interacts with organic surfaces through the formation of covalent bonds.
Previous work
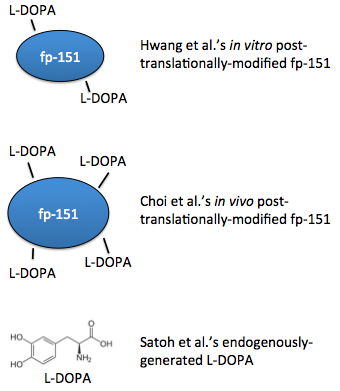
Hwang et al.: in vitro post-translational hydroxylation of fp-151
In 2007, a recombinant protein called fp-151 was first produced, which was notable for its lower cytotoxicity than previous recombinant foot proteins. After purifying the protein, tyrosine residues were hydroxylated in vitro with tyrosinase, so the protein was already folded before this modification could occur, possibly limiting access to the tyrosines [1].
Choi et al.: in vivo post-translational hydroxylation of fp-151
Choi, et al. extended this work with a coexpression system, such that the residues were modified in vivo, simultaneously along with translation. These foot proteins had better adhesive properties [2].
Satoh et al.: endogenous L-DOPA generation
Also in 2012, a system to generate L-DOPA from free tyrosine was engineered [3].
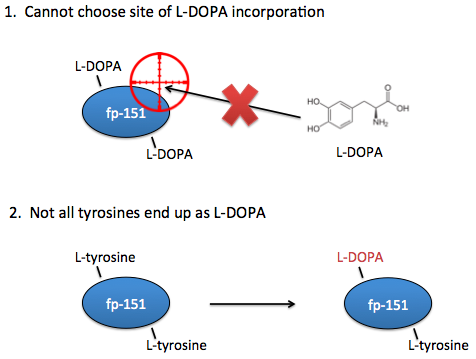
Limitations of previous work
However, these systems are not yet optimal for studying the effects of L-DOPA content on adhesive properties. Ideally, you need the ability to choose exactly which sites that L-DOPA should be incorporated. In current systems, you can only choose where there should be tyrosines.
Additionally, in current systems there is no guarantee that a tyrosine placed at your desired location will even end up as an L-DOPA, so we would also want the ability to know for certain that the residues of interest are in fact L-DOPA and not tyrosine.
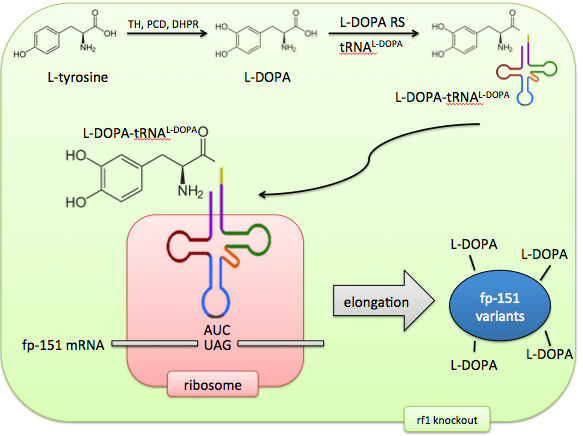
Our solution: direct non-canonical amino acid incorporation
Incorporating the non-canonical amino acid L-DOPA directly would solve these problems of control and predictability. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, the enzymes that charge tRNAs with amino acids, can be evolved to recognize non-canonical amino acids by sequential rounds of positive and negative selection. The tRNA’s anticodon loop can be engineered to recognize any codon. So, a stop codon (such as UAG, also known as the Amber codon) can be repurposed to code for a 21st amino acid.
In addition, release factor 1, which normally recognizes this Amber codon, can be knocked out, ensuring no competition between the stop codon’s old effect (termination) and its new effect (non-canonical amino acid incorporation). The result of this system is an expansion of the cell’s genetic code to 21 amino acids, allowing precise control of targeted L-DOPA incorporation.
E. coli as a self-sufficient "black box"
Our vision is of E. coli as biosynthetic "factory" able to make complicated products with simple inputs. By giving it the machinery to charge tRNA with L-DOPA, and expanding the genetic code to include L-DOPA, this non-canonical amino acid can be incorporated at rationally targetted locations, generating a library of foot protein variants.
Appropriate with this characterization of self-sufficiency and synthetic capability, these E. coli would not even need to be supplemented with exogenous L-DOPA, as they could continually generate it from intracellular free tyrosine.
Experimental design
A two-plasmid system would be appropriate for our aims. One plasmid would code for a library of fp-151 variants, each containing Amber codons in unique locations and quantities, yielding a diverse set of foot proteins with characteristic locations and numbers of L-DOPA residues. The adhesive properties of these variants would be compared against both in vitro and in vivo tyrosinase-treated foot proteins, which would serve as positive controls.
This plasmid would also contain our L-DOPA biosynthesis cassette, ensuring a continual source of non-canonical amino acid without supplementation.
The second plasmid would code for the synthetase/tRNA pair that is responsible for adding L-DOPA to the genetic vocabulary.
A side note: diversity of parts
The individual components of this system are derived from a variety of organisms. The foot proteins come from mussels, the genes in the L-DOPA biosynthesis cassette come from mice and humans, and the synthetase/tRNA pair is derived from archaea, and all these components are put in bacteria.
This covers 5 different organisms from all three domains of life, and as such would be a remarkable illustration of synthetic biology!
References
- Hwang DS, Gim Y, Yoo HJ, Cha HJ. Practical recombinant hybrid mussel bioadhesive fp-151. Biomaterials. 2007 Aug;28(24):3560-8. Epub 2007 May 3. PubMed PMID: 17507090.
- Choi YS, Yang YJ, Yang B, Cha HJ. In vivo modification of tyrosine residues in recombinant mussel adhesive protein by tyrosinase co-expression in Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact. 2012 Oct 24;11:139. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-11-139. PubMed PMID: 23095646; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3533756.
- Satoh Y, Tajima K, Munekata M, Keasling JD, Lee TS. Engineering of L-tyrosine oxidation in Escherichia coli and microbial production of hydroxytyrosol. Metab Eng. 2012 Nov;14(6):603-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2012.08.002. Epub 2012 Aug 29. PubMed PMID: 22948011.
 "
"