Team:Kyoto/Humanpractice
From 2013.igem.org
(→アンケート調査) |
(→アンケート調査) |
||
| Line 108: | Line 108: | ||
問4 信仰の有無で <br><br><br> | 問4 信仰の有無で <br><br><br> | ||
| - | + | [[File:Q4 religion(chi-square).jpg]][[File:Q4 religion.jpg]]<br> | |
Yes p=0.238593 Partly yes p=0.377508 No p=0.011818 <br> | Yes p=0.238593 Partly yes p=0.377508 No p=0.011818 <br> | ||
Yes,Partly yes は有意差がない<br> | Yes,Partly yes は有意差がない<br> | ||
Revision as of 21:56, 27 September 2013
count down
Contents |
Human Practices
-To spread LIFESCIENCE throughout the world
This year,iGEM Kyoto carried out activities to enrich people's knowledge on biotechnology because in 2010 we and other iGEM teams in Japan carried out an attitude survey towards genetically modifying and genetically engineering. From this survey, we concluded that it is important to enrich the people's knowledge on biotechnology when we want public people to accept biotechnology more. Therefore, we carried out these activities as below.
Life Science Seminar in High School
Toyonaka high school is one of the Super Science High Schools (SSH) and conducts some programs to increase the number of students who learn university-level biology. As one of the programs, we held a seminar in Toyonaka high school at (2013/1/12-13). In this seminar, we lectured molecular biology and experiments to the students. Through this activity, students seemed to feel a familiarity with life science and we were able to give essential knowledge. We believe that this activity can lead to their future understanding of biotechnology
Poster session at the school festival
Our University has a school festival called November Festival (NF) every year. This is one of the biggest events in our university and many people from all around Japan visit it. This year, iGEM Kyoto presented our project to these visitors by poster session, and this was actually broadcasted by a popular Japanese TV news program (Mezamashi TV). Through this TV program, we were able to spread our activity to the general public, and succeeded in increasing general knowledge towards biotechnology and life science.
The 4th international symposium on liberal arts and general education in Kyoto University
The 4th international symposium on liberal arts and general education is a large scale symposium where many students and public people visit. Therefore, it is a good opportunity to enrich their knowledge on biotechnology and life science. Through presenting our project, we helped people understand life science. Additionally, we received the "Einstein" prize.
International Student Seminar
iGEM Kyoto participated in the International Student Seminar(ISS). This is a seminar for young scientist from all over the world. Men and women of all ages including many foreigners visited this seminar. We made a presentation about our project in English. In this event, we spread our activity about life science to many people
Join "START"
iGEM Kyoto joined “START”, a party held in April and welcomed new students to make iGEM’s activities more common. START is a union which consists of 25 students’ organizations, and those 25 organizations encourage students to contribute to global society. For example, help students who want to study abroad, practice English to work in global society, and communicate with foreign universities. Additionally, most of these organizations perform international scene or positively contribute to the society. Therefore, some famous companies or volunteer organizations visited this party. We advertised iGEM and succeeded in making synthetic biology more popular.
アンケート調査
We had been carrying out these activities shown above in order to spread the basic ideas of biotechnology. However, we thought that there might be other reasons towards the fact that people are not positive to the achievements of them. Therefore, in order to determine the cause, we conducted a questionnaire.
- Methods
- Methods
In the beginning of this questionnaire, we asked answerers about their sex, country, age, religion, and profession. And, we investigated how these elements influence the answers of this questionnaire about gene modification. We conducted this survey to Japanese and non-japanese people. The countries where we conducted the questionnaire is listed below.
U.S.A.: Stanford, Davis/ Germany: Goettingen/ Japan: Kyoto, Nara, Shiga, Okinawa/
- Content
- Content
Questionnaire!!!!
Q1 Have you ever thought about experiments using living things?
1 Yes
2 No
Q2 Do you think these experiments using living-creatures are permissible? Please give X as many as you think it is permissible.
1 check
2 no check
Q2.1 Subjects are killed in the experiment, but it can save people in disease.
Q2.2 Subjects can be killed in the experiment, but it can save people in disease.
Q2.3 Subjects are not killed in the experiment but they never go back in nature. However, it can save people in disease.
Q2.4 Subjects are only observed in nature and it can save people in disease.
Q2.5 Subjects are killed in the experiment, but it can improve our life.
Q2.6 Subjects can be killed in the experiment, but it can improve our life.
Q2.7 Subjects are not killed in the experiment but they never go back in nature. However, it can improve our life.
Q2.8 Subjects are only observed in nature and it can improve our life.
Q2.9 Subjects are killed in the experiment, but it can advance science.
Q2.10 Subjects can be killed in the experiment, but it can advance science.
Q2.11 Subjects are not killed in the experiment but they never go back in nature. However, it can advance science.
Q2.12 Subjects are only observed in nature and it can advance science.
Q3 How much do you know about genetically modifying (GM) technology?
1 I know well.
2 I know only its name.
3 I do not know at all.
Q4 Do you think modifying creature’s gene is ethically permissible or not?
1 Yes, we can modify every creatures’ gene.
2 Partly yes, some can be but others are not.
3 No, any living things’ gene cannot be modified.
Q5 Who answered ‘partly yes’ to the fifth question, please answer this question. Which of these creatures’ gene can be modified? Please give X as many as you think it is permissible.
1 check
2 no check
Q5.1 Bacteria Q5.2 wheat Q5.3 honeybee Q5.4 killifish Q5.5 frog
Q5.6 chickens Q5.7 mouse Q5.8 dog Q5.9 monkey Q5.10 human beings
- Results
- Results
Q2 The standard of the answer to this question is whether the answer places an importance on the profit they may gain through animal experiments, or the agony the animals feel through these experiments. We asked whether animal experiments can be allowed from three points, “saving human beings”, “useful to our life”, “contribution to the development of science” As a result, people who answered that animal experiment can be performed if it is for saving human beings was obviously larger than the other two points. As for the difference by sex, male seems to be more generous to animal experiment, and place an importance on the profit of the human beings while female seem to place an importance on the animals’ pain. When we compared by the salary or age, there seemed to be no significant difference.
問4 信仰の有無で
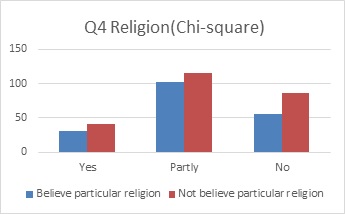
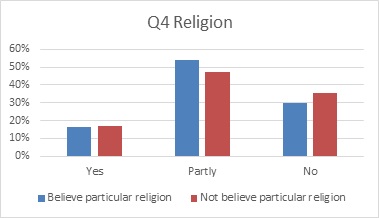
Yes p=0.238593 Partly yes p=0.377508 No p=0.011818
Yes,Partly yes は有意差がない
No は有意差があるといえる
よって信仰の有無が許容度に影響を与えている可能性がある
<X^2検定の説明> X²検定:実測度数と期待度数との差を統計的に検定する
算出した確率(p-value)が0.05未満であると、統計的に有意性が確認される。
Chi-square test: To test statistically the difference between the expected frequency with the measured frequency
If calculated probability (p-value) is less than 0.05, significance is confirmed statistically.
Q5
Significant difference is observed in the results by different sex, region, religion. According to the difference of gender, men tend to allow genetically modification than women.
According to the regional differences, half of the people of Asia have allowed the experiment of wheat and E. coli. Subsequently, the rat is about 35%, monkeys and dogs is about 20%. In comparison, people of Europe are generally allowed experiments wheat and E. coli. However, 15% people of them have allowed the other animals. This trend is similar to the results of the graph were compared Buddhism and Christianity. The parameter is small, but the graph of the Christians of Asia is similar to the graph of Christians in the world. From this date, we think this difference is a thing by religion.
英訳案2
Significant difference was observed in the results by different sex, region, religion. According to the difference of sex, men tended to allow genetically modification than women.According to the regional differences, half of the people in tnis survey in Asia admiited using wheat and E. coli for experiments. About 35% of them admited using mice and about 20% admited using dogs and monkeys. On the other hand, many people in Europe are admited using wheat and E. coli. However, no more than 15% of them admited using other animals. This was similar to the results of the graph which were compared Buddhism and Christianity. The parameter is small, but the graph of the Christians in Asia is similar to the graph of Christians in the world. From this date, we think this difference is a thing by religion.
- Conclusion
- Conclusion
2013年のアンケートでは知識での差は出ず、宗教の差が出た。
しかし2010年のアンケートは知識の差が出ている。
今回は合成生物学を受け入れる知識以外の理由を探る目的で、知識に関する問いを少なくしたので、知識の差が出なかった。
2010と2013を踏まえて、私たちは誰かの信仰に干渉したり、私たちの考えを誰かに押し付けられないので、個人の信仰について配慮しながら、合成生物学についての知識を広めていくべきだ
In the result of the questionnaire we conducted in 2013, we can see the influence of religion. To the contrary, the effect of knowledge level is not observed. However, in the questionnaire in 2010, people’s attitude vary according to knowledge level. In this time, since the aim is shed light on effect except for knowledge, we made fewer question to measure knowledge level. This is why knowledge level made next to no affection in this survey. Learning from the result of the two survey, because we should not interfere with others’ religion and opinion, we must disseminate information about biotechnology considering each individual person’s religion.
- Future Work
- Future Work
In these questionnaires, we found differences of tolerance limits on genetically modification among religions. Moreover, it is possible that region or culture affect it. In the future, we want to make questionnaires which can determine which elements affect tolerance limits on genetically modification such as region, culture and development of economy.
From the questionnaire we conducted, there seemed to be a difference in the tolerance of genetically modification, depending on the answers’ religion. However, this difference may have generated not only from religion but also from the difference between region and culture. We would like to conduct surveys on factors such as region, culture, economic development, and so on, in order to find out which factor influence the tolerance.

 "
"



