Team:DTU-Denmark/Project
From 2013.igem.org
(→Why?) |
|||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
Global demand for fixed nitrogen has increased to the point that half the human population now relies on chemical fertilizer to grow their food. While fertilizer is a requirement for modern life, runoff from overfertilized farmland can cause eutrophication. In the presence of abundant ammonia, algae overgrow and consume the much of the available oxygen in the water. This results in decreased biodiversity throughout the watershed. Within Europe, 53% of lakes are eutrophic. | Global demand for fixed nitrogen has increased to the point that half the human population now relies on chemical fertilizer to grow their food. While fertilizer is a requirement for modern life, runoff from overfertilized farmland can cause eutrophication. In the presence of abundant ammonia, algae overgrow and consume the much of the available oxygen in the water. This results in decreased biodiversity throughout the watershed. Within Europe, 53% of lakes are eutrophic. | ||
| - | In Europe the annual surplus of fixed nitrogen from crop production and livestock farming is 10 Tg (10 Teragrams = a million tonnes), 6 Tg leaches into ground and surface water. If that was to be converted into | + | In Europe the annual surplus of fixed nitrogen from crop production and livestock farming is 10 Tg (10 Teragrams = a million tonnes), 6 Tg leaches into ground and surface water. If that was to be converted into N<sub>2</sub>O, it could be decomposed for 4.87 Billion kW h or equivalent to the annual power consumption of 36,000 Avarage households. |
===How?=== | ===How?=== | ||
Revision as of 03:13, 4 October 2013
Project Description
What?
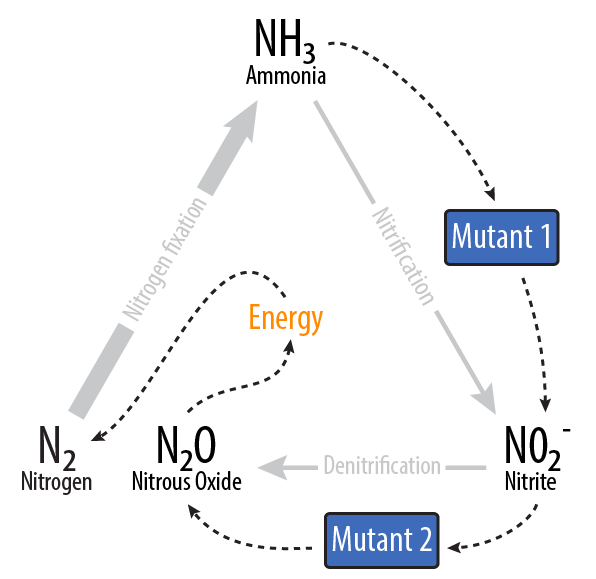
Our project removes ammonia from waste water, and via two E. coli mutants, turns it into nitrous oxide.
Why?
Global demand for fixed nitrogen has increased to the point that half the human population now relies on chemical fertilizer to grow their food. While fertilizer is a requirement for modern life, runoff from overfertilized farmland can cause eutrophication. In the presence of abundant ammonia, algae overgrow and consume the much of the available oxygen in the water. This results in decreased biodiversity throughout the watershed. Within Europe, 53% of lakes are eutrophic.
In Europe the annual surplus of fixed nitrogen from crop production and livestock farming is 10 Tg (10 Teragrams = a million tonnes), 6 Tg leaches into ground and surface water. If that was to be converted into N2O, it could be decomposed for 4.87 Billion kW h or equivalent to the annual power consumption of 36,000 Avarage households.
How?
Using two E. coli mutants built with genes from Nitrosomonas europaea and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we provide a system to reverse nitrogen fixation. Our mutants consume ammonia and produce nitrous oxide, releases a sustainable source of energy when decomposed into nitrogen and oxygen. We also provide a prototype of a bioreactor that could be scaled up and deployed in the field to simultaneously clean the water and produce energy.
Details
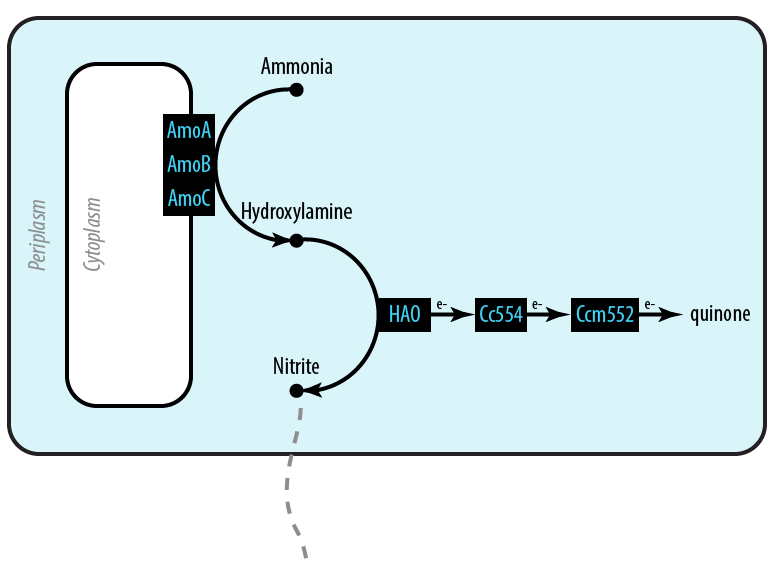
Mutant 1: Aerobic
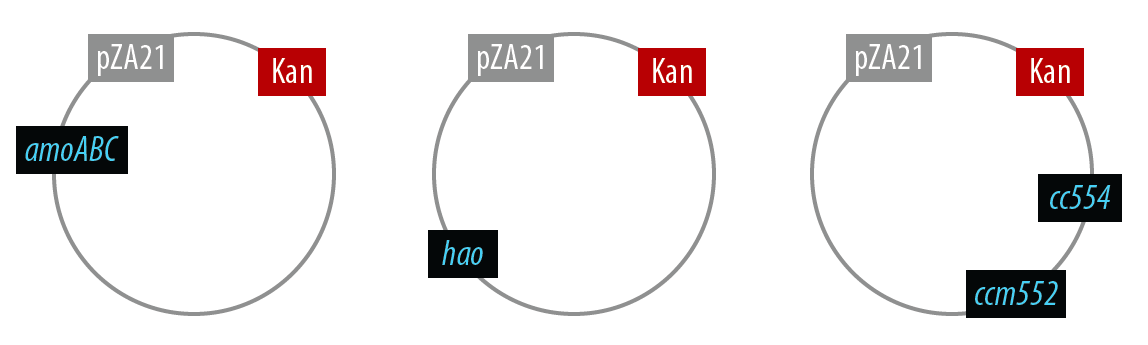
The first mutant incorporates AMO, HAO and two cytochromes c554 and cm552 from Nitrosomonas europaea (shown in blue). AMO is a 3 subunit protein which converts ammonia (NH4) to an intermediate called hydroxylamine (NH2OH). HAO then converts the hydroxylamine to nitrite (NO2-). During this conversion process, cytochrome c554 accepts an electron from HAO, and then passes this electron on to ccm552. The terminal electron acceptor in this chain is quinone. AMO and ccm552 are embedded in the cytoplasmic membrane, and all other proteins in this process are found in the periplasm.
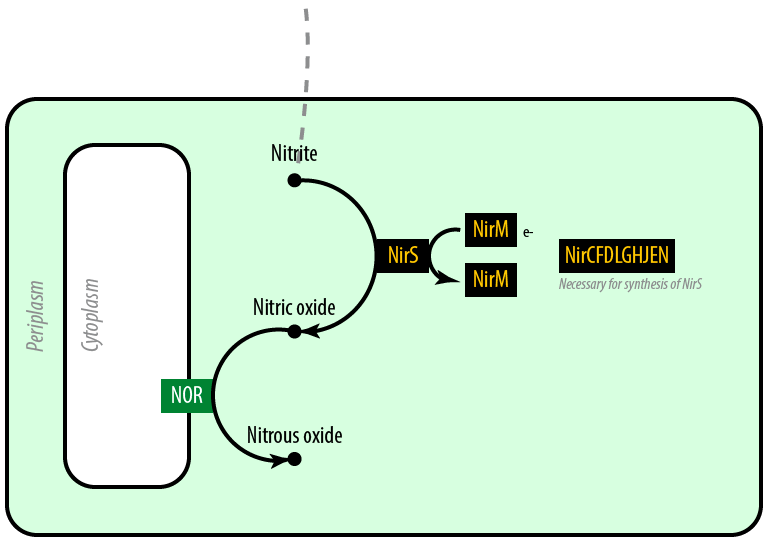
Mutant 2: Anaerobic
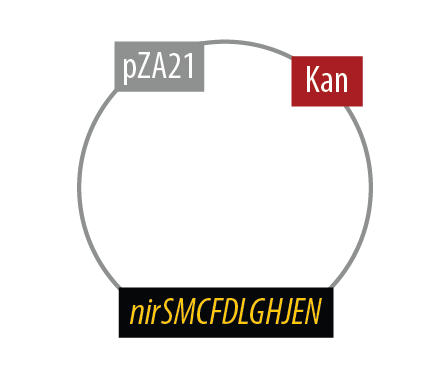
The second mutant incorporates the Nir region from Pseudomonas aeruginosa (shown in yellow). NirS converts nitrite to nitric oxide (NO), while removing an electron from NirM. The remainder of the Nir region is necessary for the synthesis of NirS, and so we have included these genes as well. NOR, which is present natively in E. coli, converts nitric oxide to nitrous oxide (N2O). In contrast to N. europaea, E. coli is not a nitrifying bacterium and so does not convert nitrous oxide into nitrogen to complete the denitrification process.
Plasmids
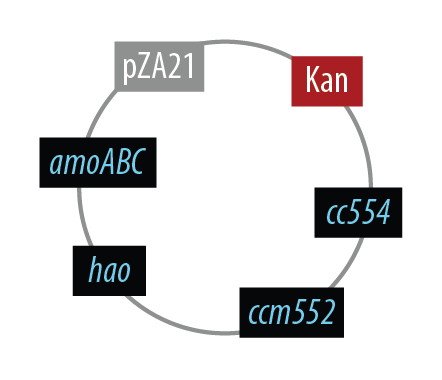
Mutant 1
The final plasmid for Mutant 1 should be the following which includes all genes on one plasmid:
In order to simplify and to be able to debug each part of this pathway separately, we first implemented the genes individually. Unfortunately, we did not have time to combine all the genes into the final plasmid, but we were able to verify that the AMO containing plasmid is working as designed.
Mutant 2
The final plasmid for Mutant 2 is the following:
Since we had difficulty extracting Nir from Pseudomonas aeruginosa in one piece, we split it into two pieces to be extracted seperately and then re-combined them with USER cloning.
USER Cloning
To assemble our plasmids we employ uracil-specific excision reagent (USER) cloning as described by Nour-Eldin et al. This technique enables us to speed up the cloning process, to clone seamlessly, and to assemble many fragments in one reaction. The steps are:
- PCR: The backbone and all fragments are amplified as linear products containing a uracil instead of a thymine at a specific position. This requires specifically designed primers with a tail that will become the overhang and a polymerase that is able to perform uracil-insertion.
- Optional - If circular DNA was used as PCR template a DpnI digestion can be performed to eliminate this DNA.
- USER-reaction: Digesting the linearized PCR fragment with the USER enzyme removes the uracil-insertions, which will produce the required overhangs.
- Transformation: The mix is immediately transformed into competent E. coli cells where the plasmid assembles itself by base pairing between the complementary overhangs.
See our "Bricks of Knowledge" video on USER cloning and the wiki of the 2011 DTU-2 iGEM team for more information.
References
- Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Sato, Y., Furumichi, M., and Tanabe, M.; KEGG for integration and interpretation of large-scale molecular datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D109-D114 (2012).
- Kanehisa, M. and Goto, S.; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27-30 (2000).
- Zumft, Walter G. (1997) Cell Biology and Molecular Basis of Denitrification. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, December 1997 p. 533–616
- Ingledew, WJ and Poole, RK (1984) The Respiratory Chains of Escherichia coli. Microbiological Reviews, Sept. 1984, p. 222-271
- Nour-Eldin, HH et al (2010). USER cloning and USER fusion: the ideal cloning techniques for small and big laboratories. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;643:185-200. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-723-5_13.
 "
"