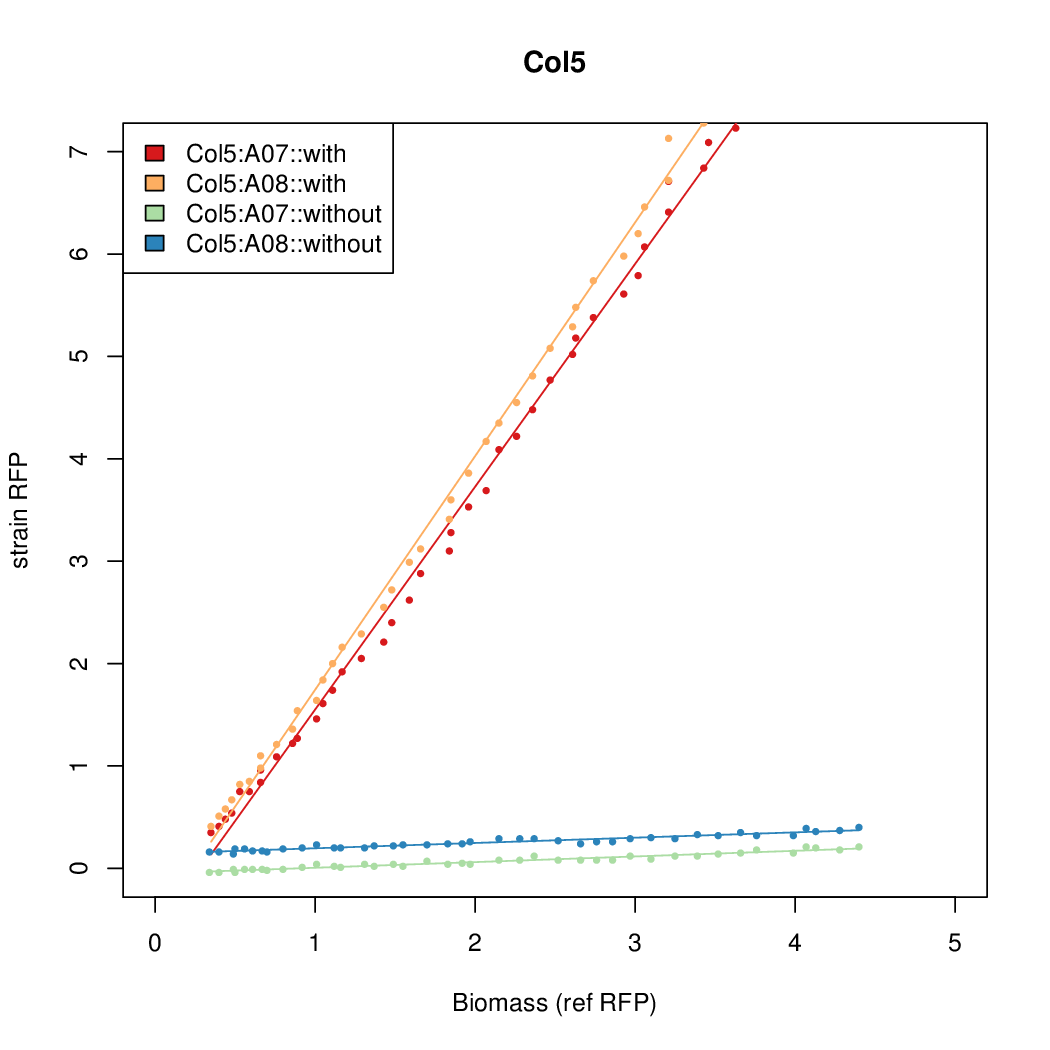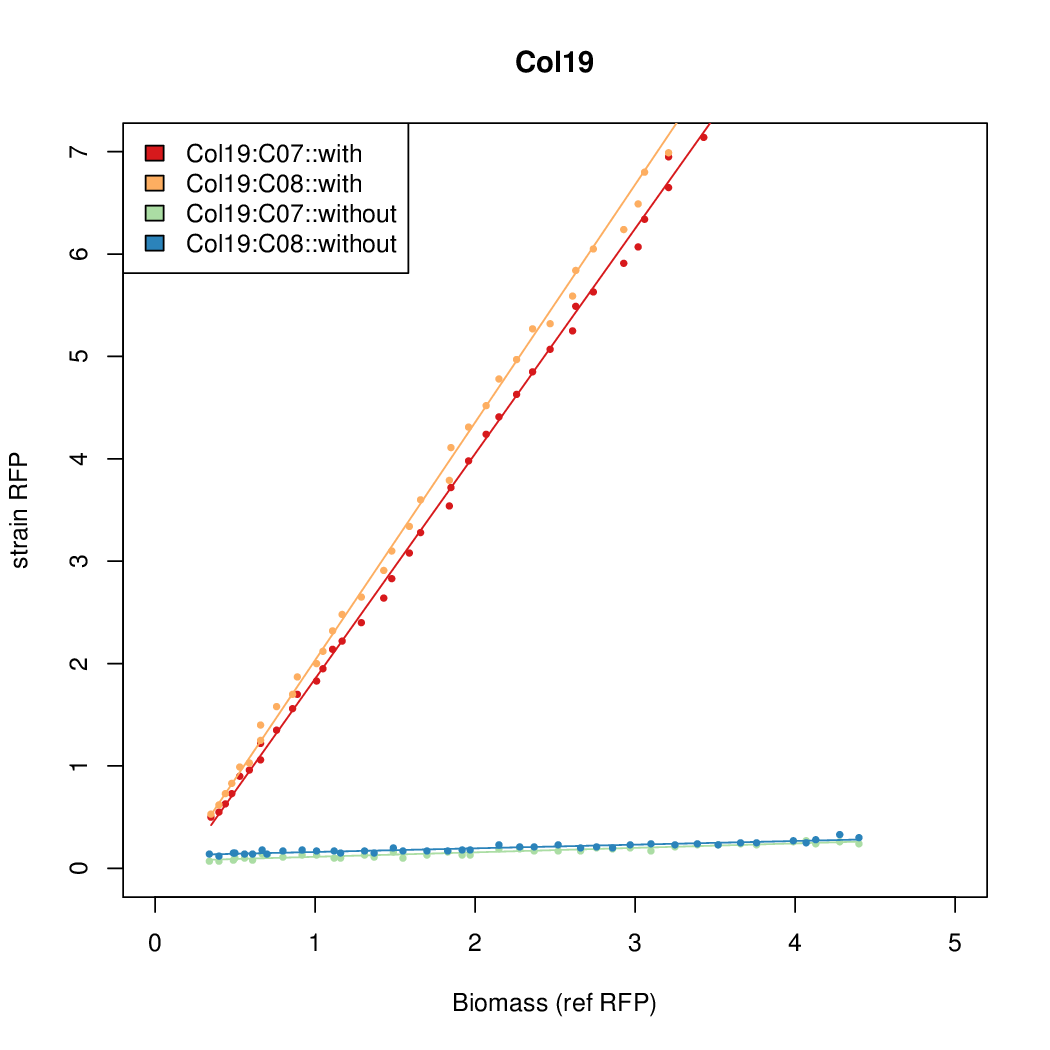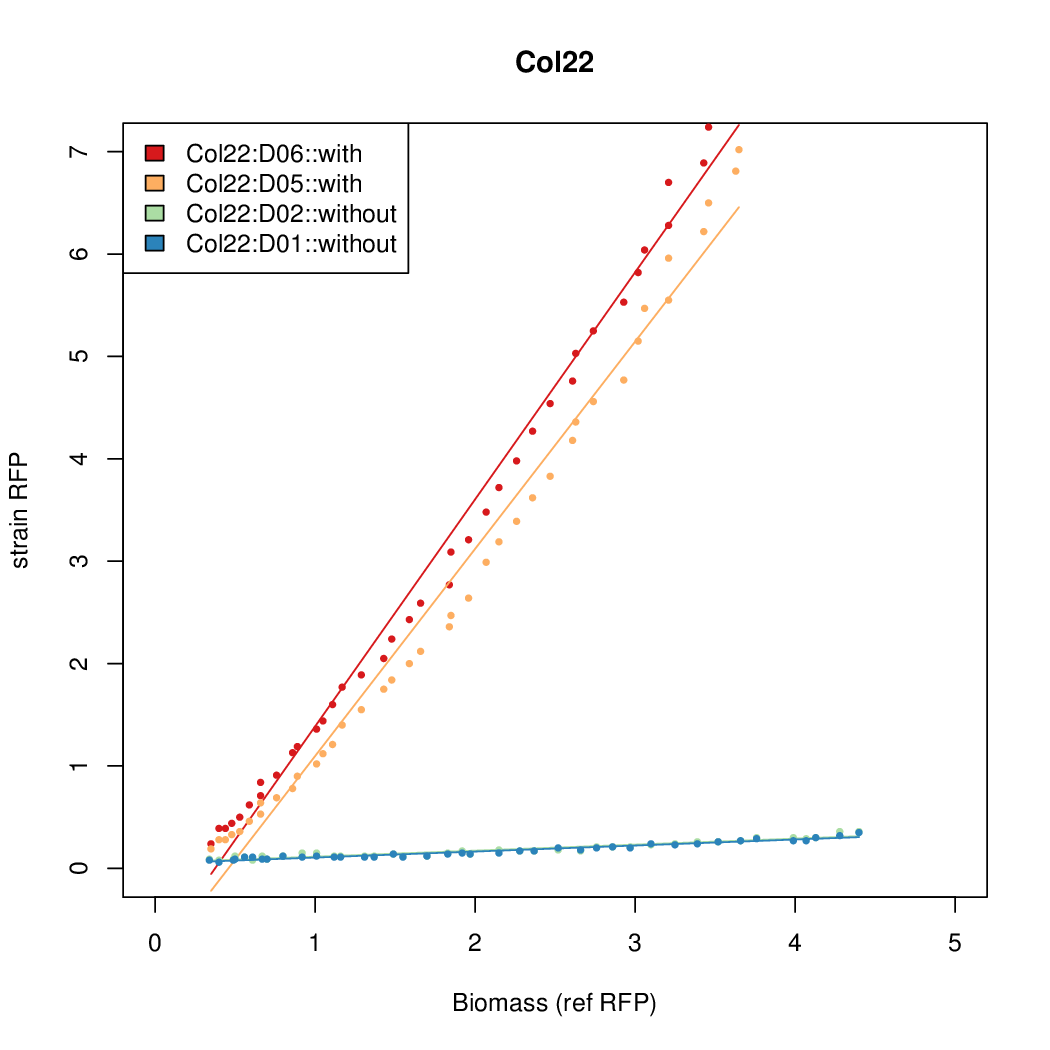Team:DTU-Denmark/pBAD SPL
From 2013.igem.org
(→Details) |
(→pBAD synthetic promoter library) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== pBAD synthetic promoter library == | == pBAD synthetic promoter library == | ||
| - | A synthetic promoter library (SPL) is a library of cells | + | A synthetic promoter library (SPL) is a library of cells which contain a promoter that has been randomly mutated to give different expression levels. This promoter upstream of a fluorescent protein like GFP/RFP. The term was first coined in 1998 and used in ''Lactococcus lactis'' [1]. The method was adapted by [https://2010.igem.org/Team:DTU-Denmark/SPL 2010 DTU iGEM team] to make a SPL for ''E.coli'' that enabled the modulation of constitutive gene expression with great precision. They even made a new standard for this method with the use of biobricks ([http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/60080 RFC 63]). |
| - | We used the method to build a non-leaky arabinose inducible promoter as a tool for expressing lethal proteins in ''E. coli''. The reason | + | We used the method to build a non-leaky arabinose inducible promoter as a tool for expressing lethal proteins in ''E. coli''. The reason we did this is that many of the proteins we are working with are membrane bound or integral membrane proteins and will be lethal if expressed in high quantities. |
| - | For testing our pathways we needed to grow the transformed | + | For testing our pathways we needed to grow the transformed cells to a certain concentration, and attempting this with the genes constitutively expressed was often not yielding viable colonies. We needed a inducible system, but the standard arabinose inducible system was way too leaky and we with this promoter we can into the same problem as before. Therefore we needed to either build or buy (if possible) an inducible system with great tightness that is able to be induced easily. We choose to build such a system. |
== Methods == | == Methods == | ||
Revision as of 17:36, 4 October 2013
pBAD SPL
Contents |
pBAD synthetic promoter library
A synthetic promoter library (SPL) is a library of cells which contain a promoter that has been randomly mutated to give different expression levels. This promoter upstream of a fluorescent protein like GFP/RFP. The term was first coined in 1998 and used in Lactococcus lactis [1]. The method was adapted by 2010 DTU iGEM team to make a SPL for E.coli that enabled the modulation of constitutive gene expression with great precision. They even made a new standard for this method with the use of biobricks ([http://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/60080 RFC 63]).
We used the method to build a non-leaky arabinose inducible promoter as a tool for expressing lethal proteins in E. coli. The reason we did this is that many of the proteins we are working with are membrane bound or integral membrane proteins and will be lethal if expressed in high quantities.
For testing our pathways we needed to grow the transformed cells to a certain concentration, and attempting this with the genes constitutively expressed was often not yielding viable colonies. We needed a inducible system, but the standard arabinose inducible system was way too leaky and we with this promoter we can into the same problem as before. Therefore we needed to either build or buy (if possible) an inducible system with great tightness that is able to be induced easily. We choose to build such a system.
Methods
Experimental procedure
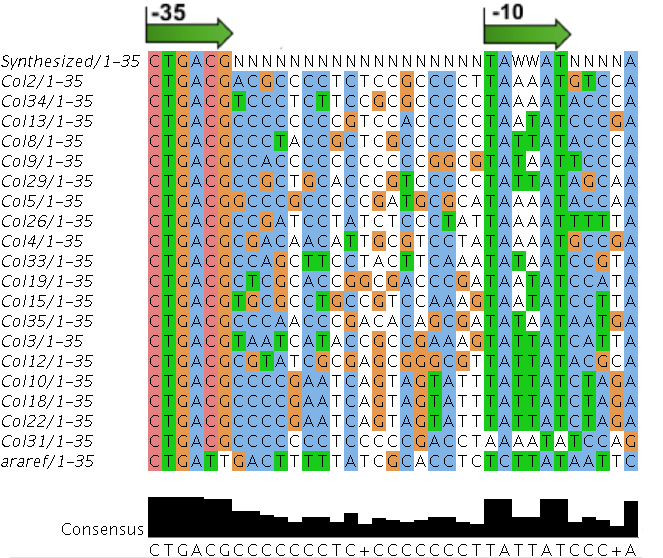
- Random promoter sequences were ordered matching the sequence CTGACGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNTAWWATNNNNA.
- USER cloning to add RFP downstream of promoter.
- Colonies were plated.
- After inspection under UV-light the visually non RFP containing colonies where picked.
- Plates were induced by spraying them with an 5% w/v aqueous arabinose solution.
- The plates were again inspected under UV-light and this time the most red florescent cells were picked.
- Colonies were grown in culture tubes and screened in parallel on BioLector. Wells on BioLector plate were loaded with culture by transferring a toothpick from each overnight culture selected and into the wells of the plate. All wells were run in duplicate.
- All duplicate colonies were run twice -- once with arabinose added at t=0, and again without arabinose.
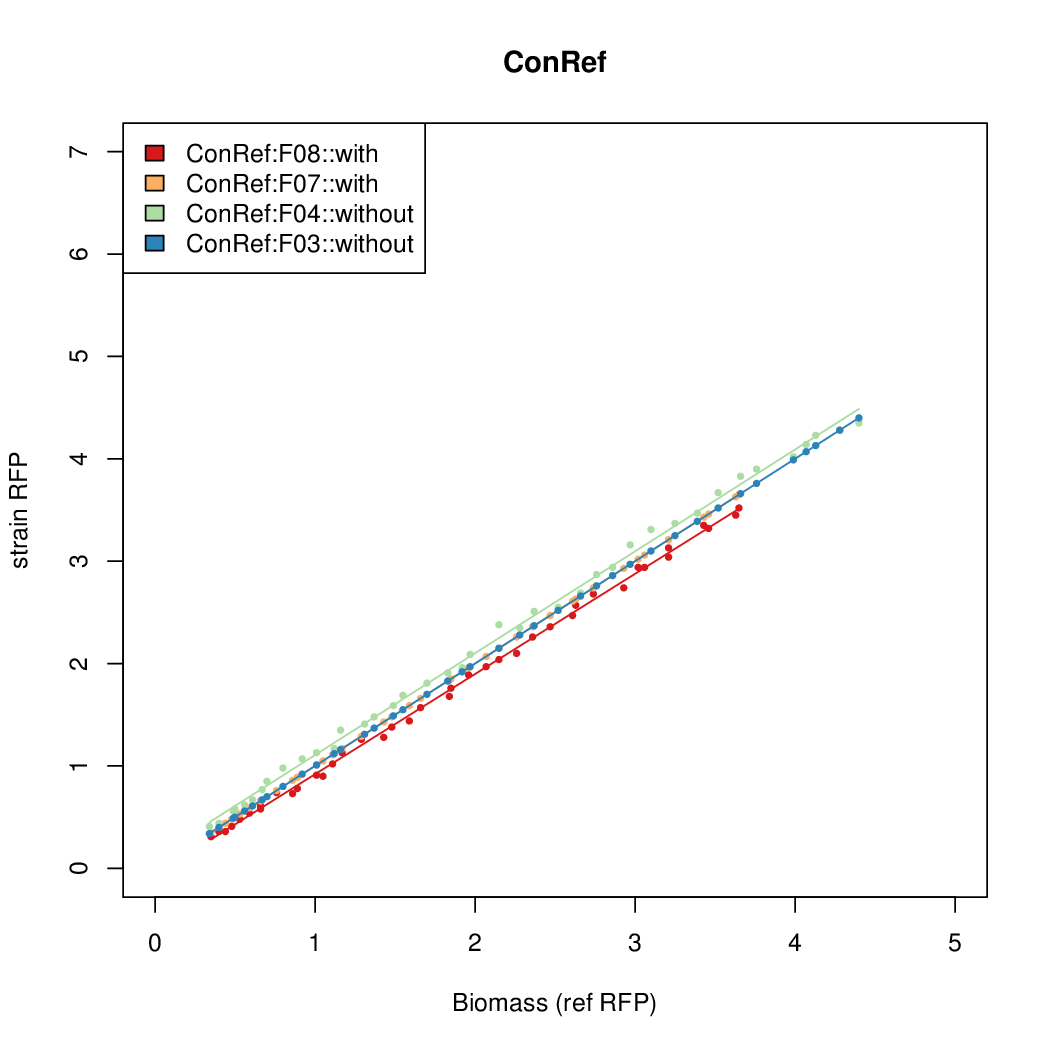
- The pBAD system [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K808000 BBa_K808000] was used as a reference.
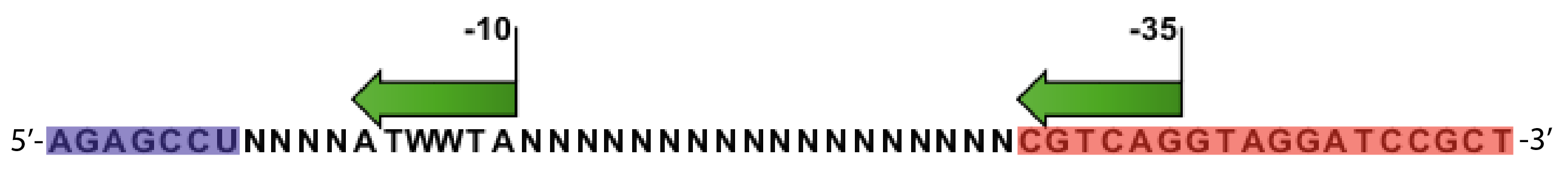
Data analysis
- Data was collected from the Biolector, and analyzed using a series of R scripts written by Chris Workman (unpublished).
- The maturation and degradation times for mCherry were both assumed to be 40 min.
- The growth rate, mu, was estimated to be 1.28 (from an average of all wells on all plates) since we expect each strain to grow at the same rate.
- A time window representing exponential growth was selected (between 1 and 4.5 hours).
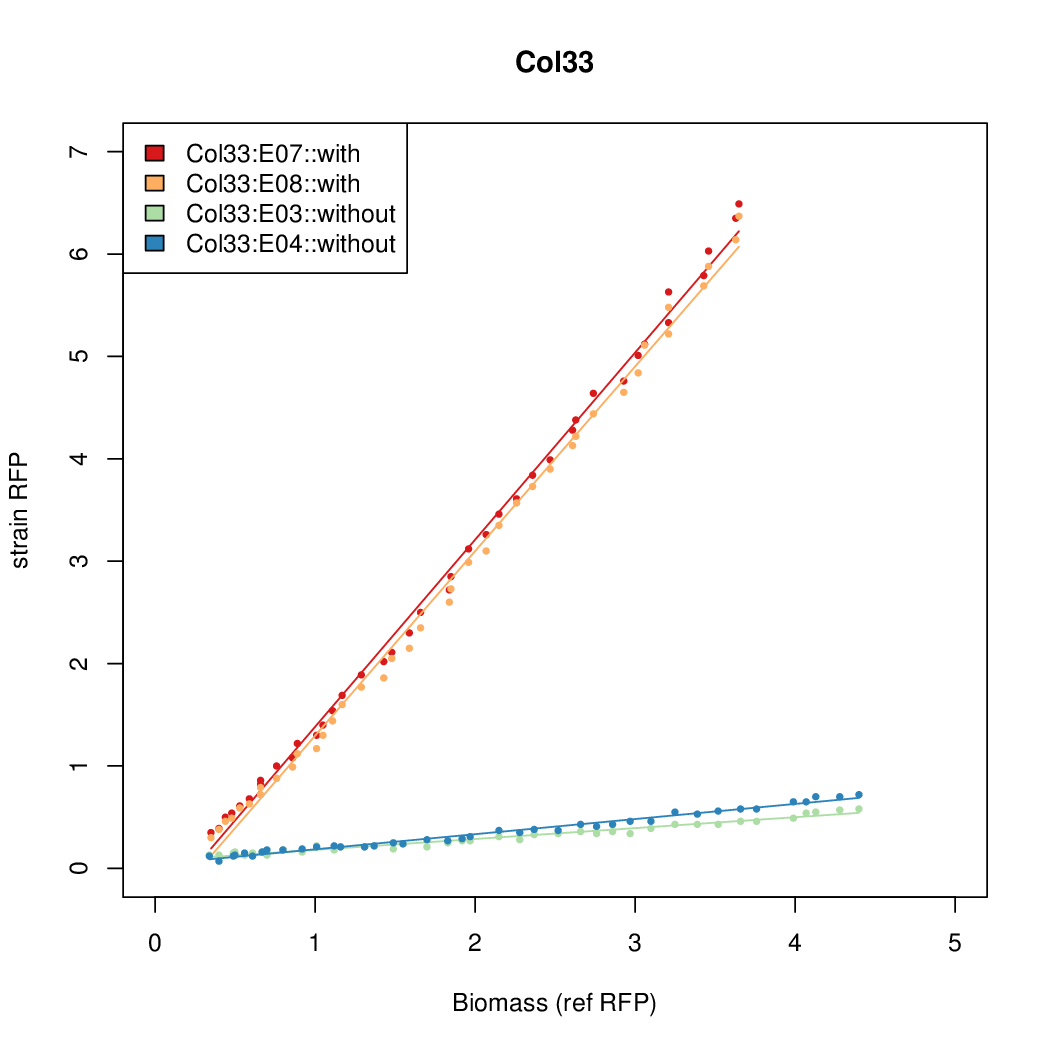
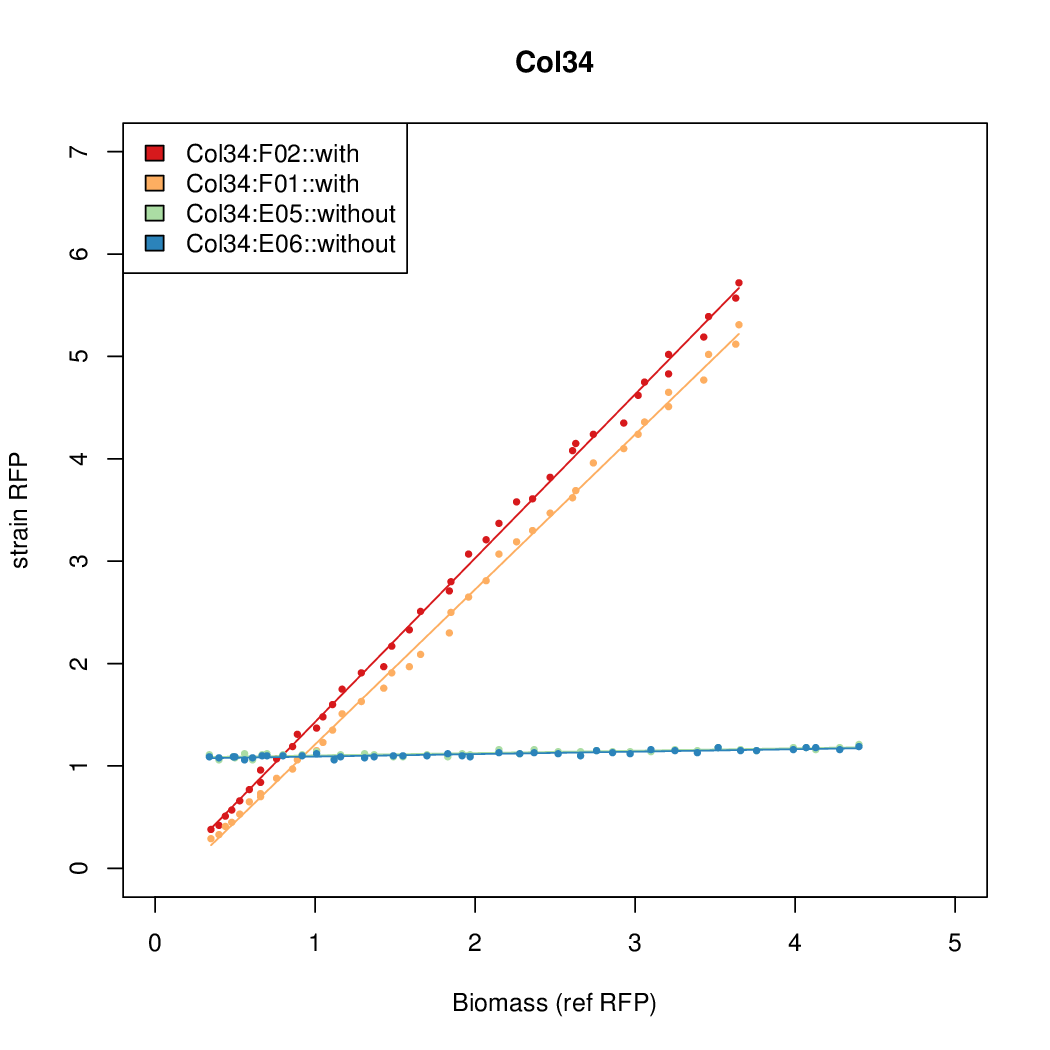
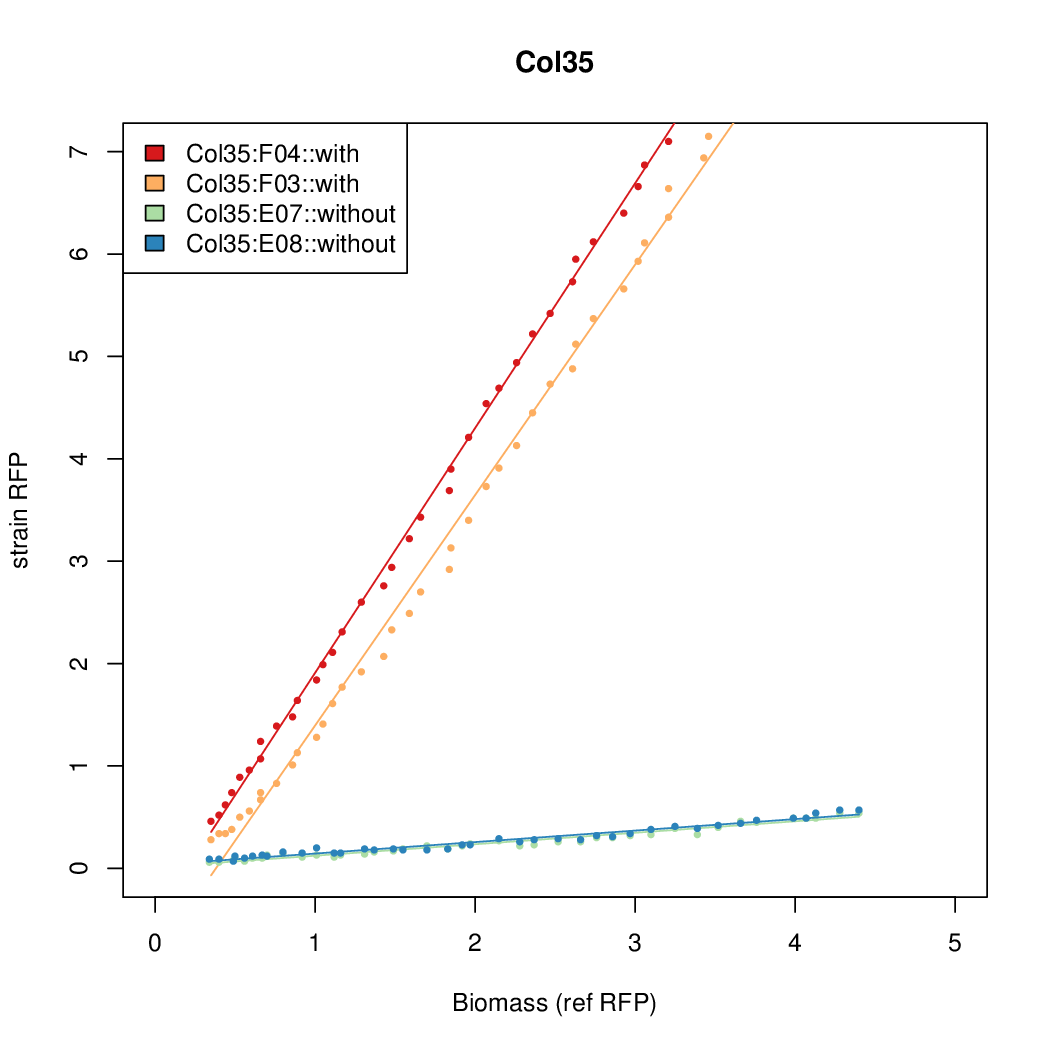
- The RFP measurement for a constitutively expressed strain was used as a standard measure of growth. This is plotted on the x-axis in the detailed plots per colony below.
- Figures were plotted using R.
Results
Summary
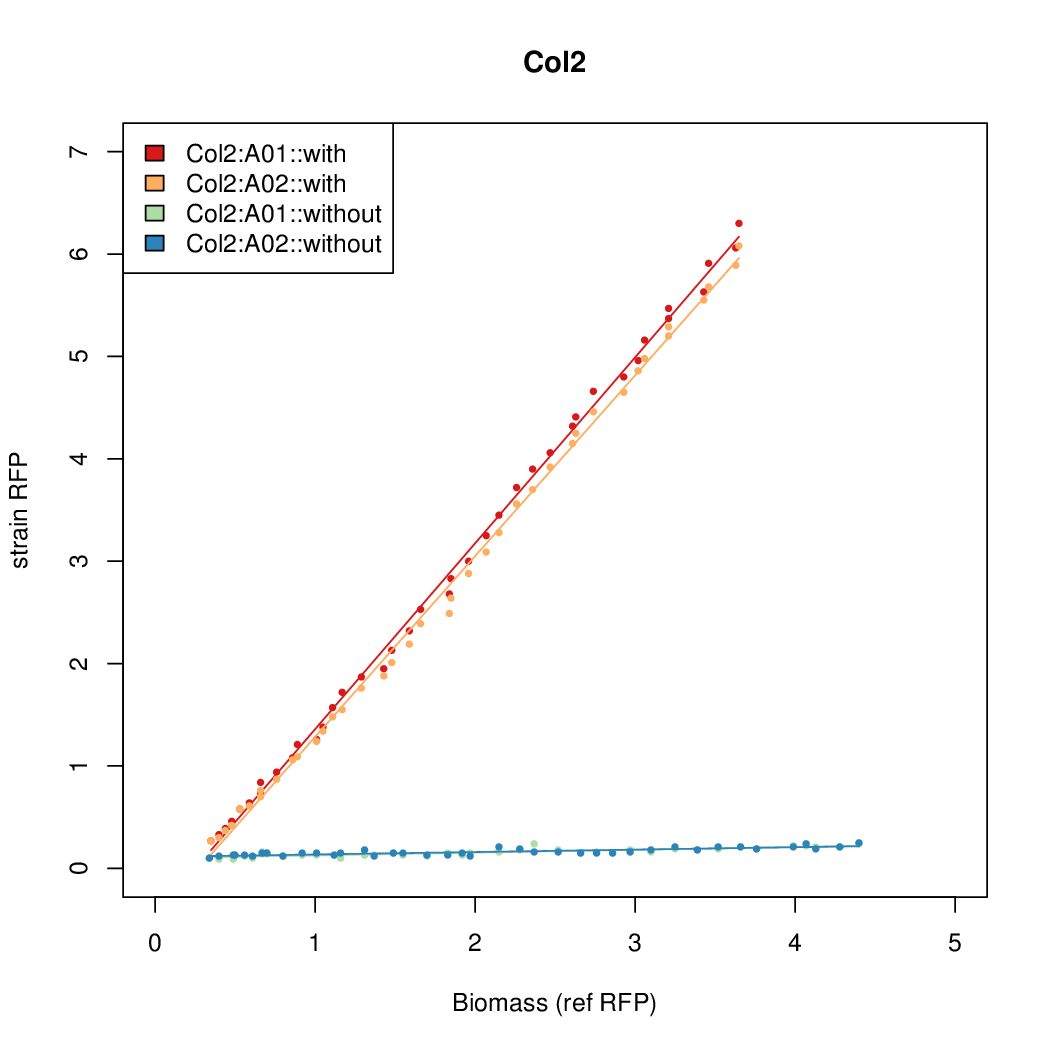
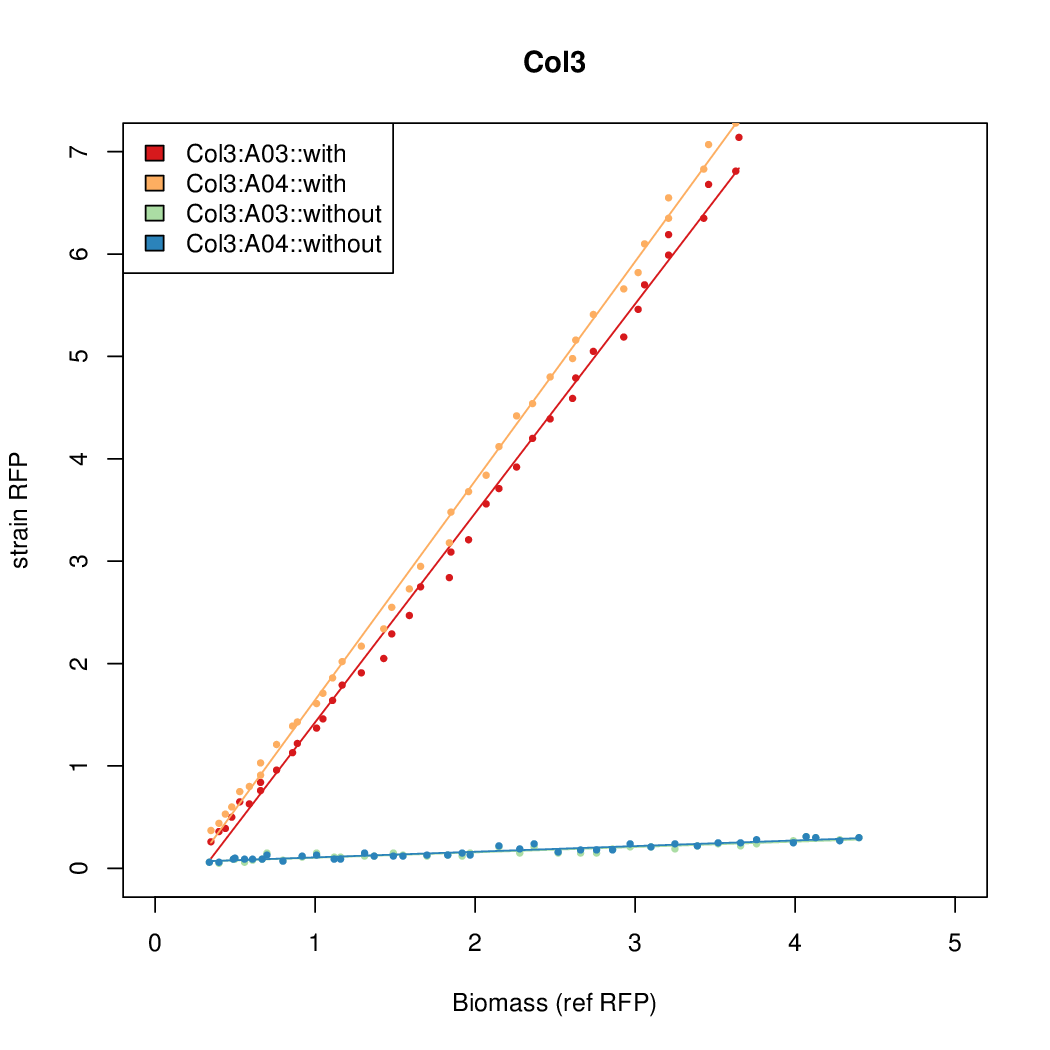
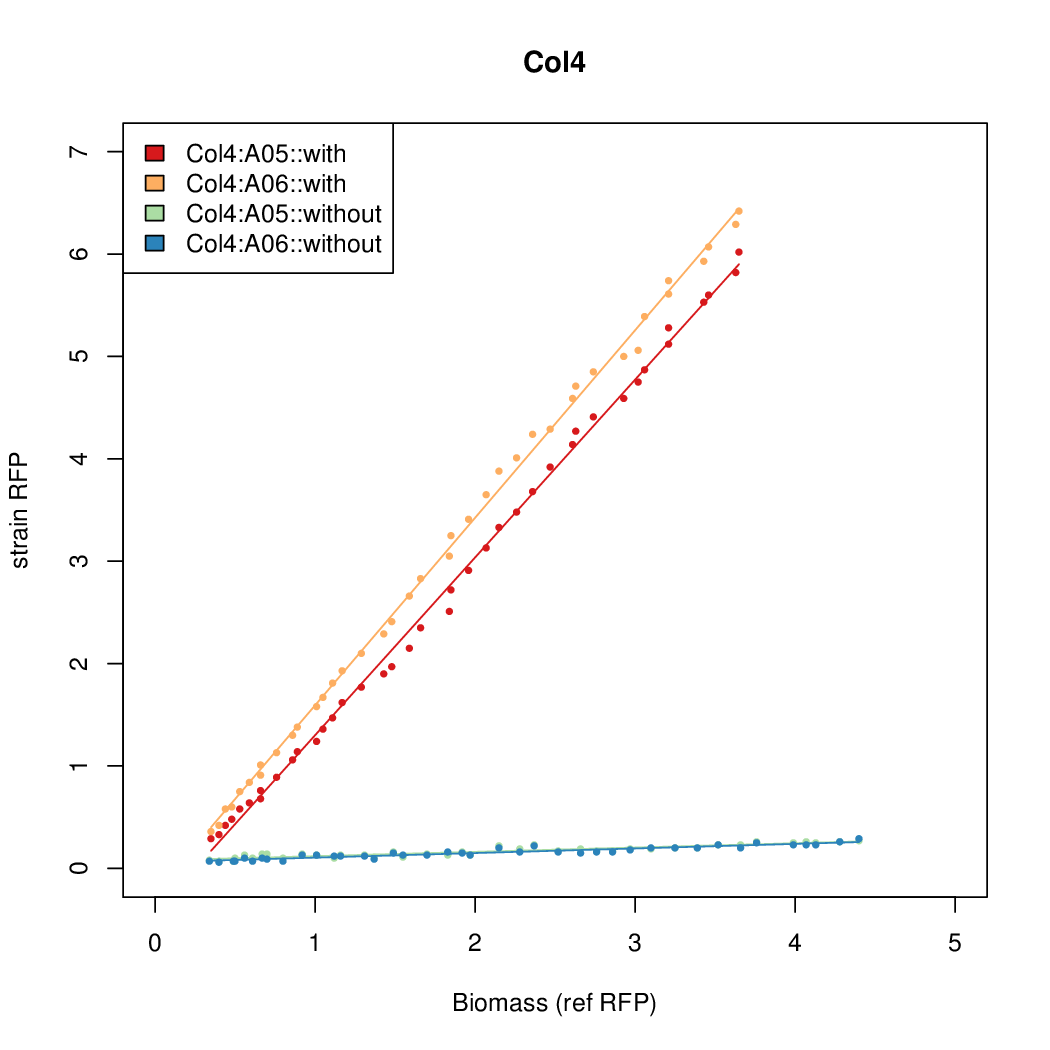
Promoter activity when induced (with arabinose added) plotted vs basal activity (without arabinose; ie leakiness of the promoter). The colonies that we selected all show less activity than the the constitutive promoter, and when induced, show higher activity than the constitutive promoter. The induced activity of the arabinose reference promoter is shown as a band representing two replicates.
Details
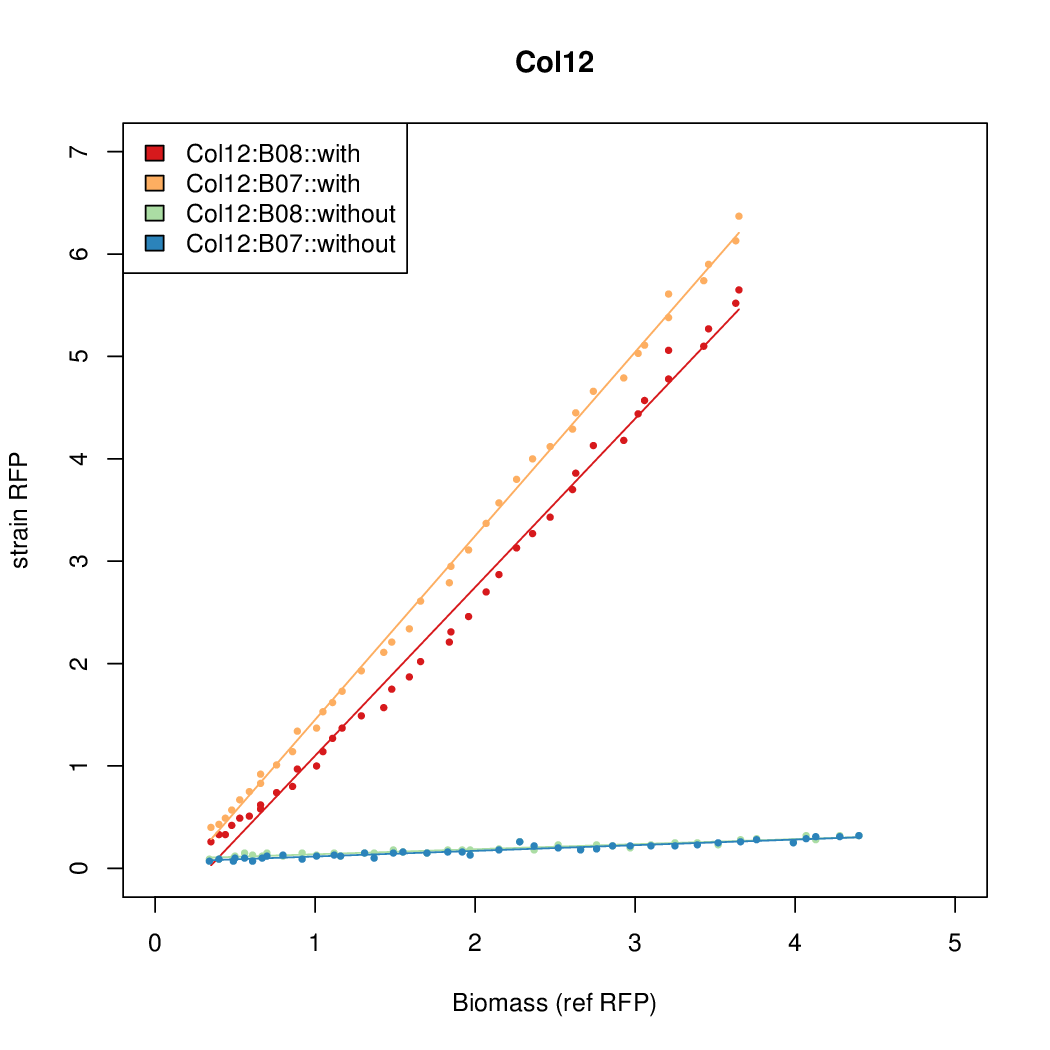
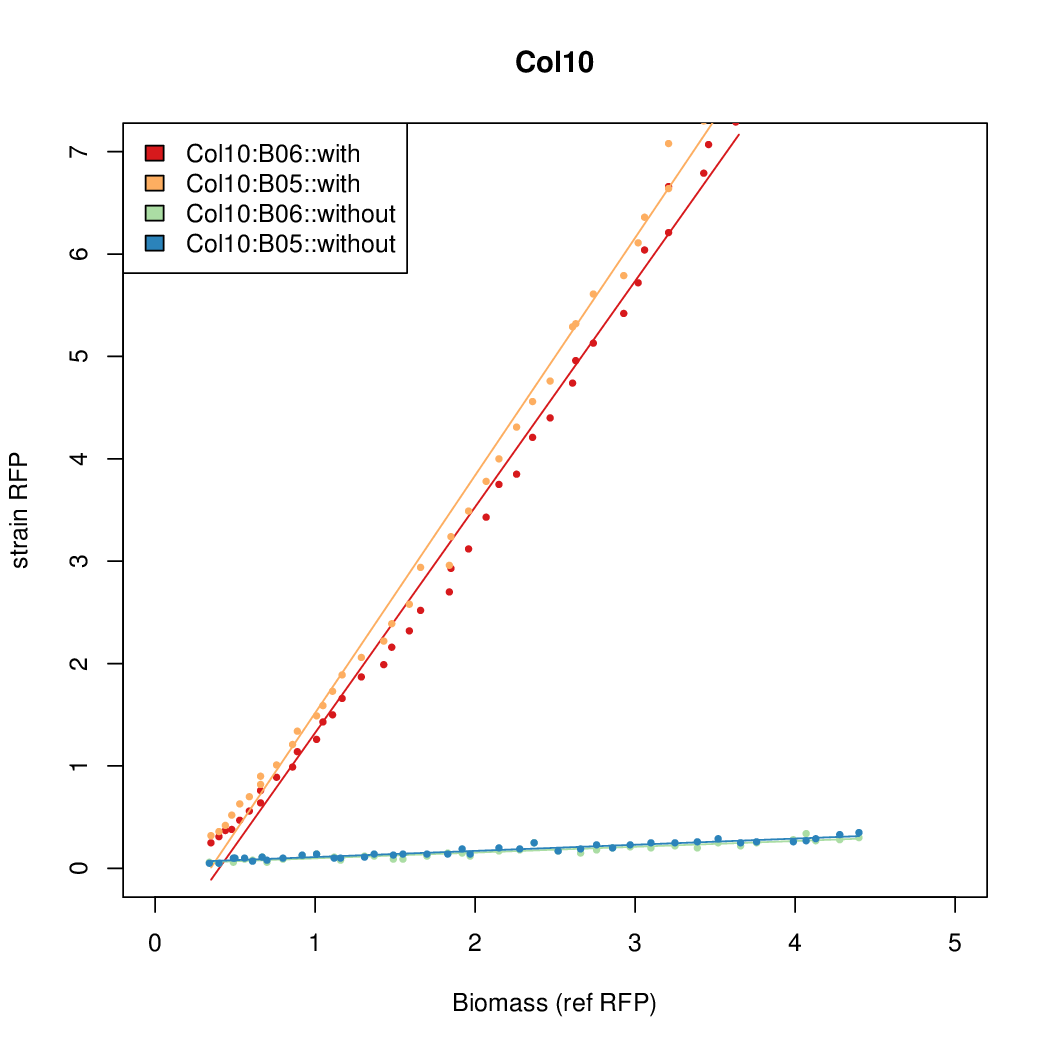
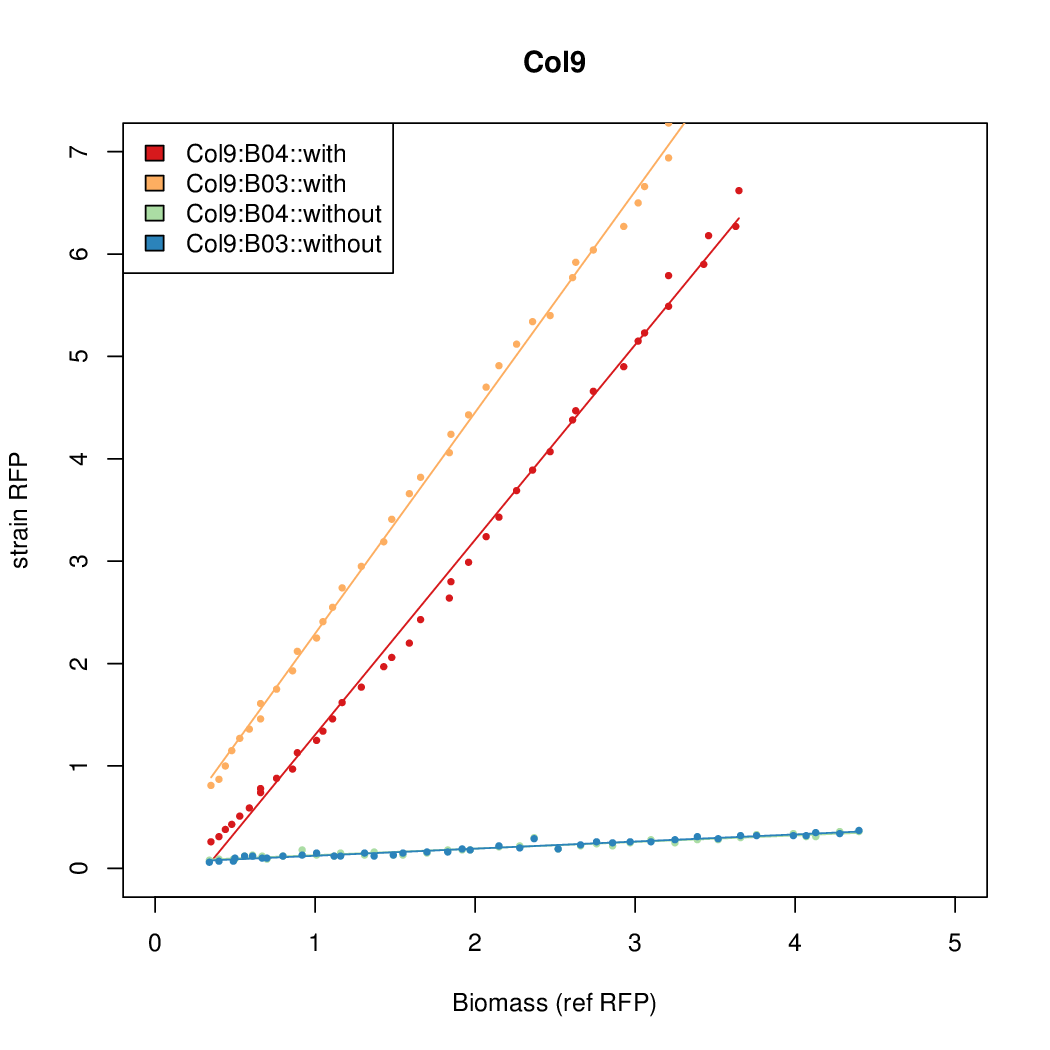
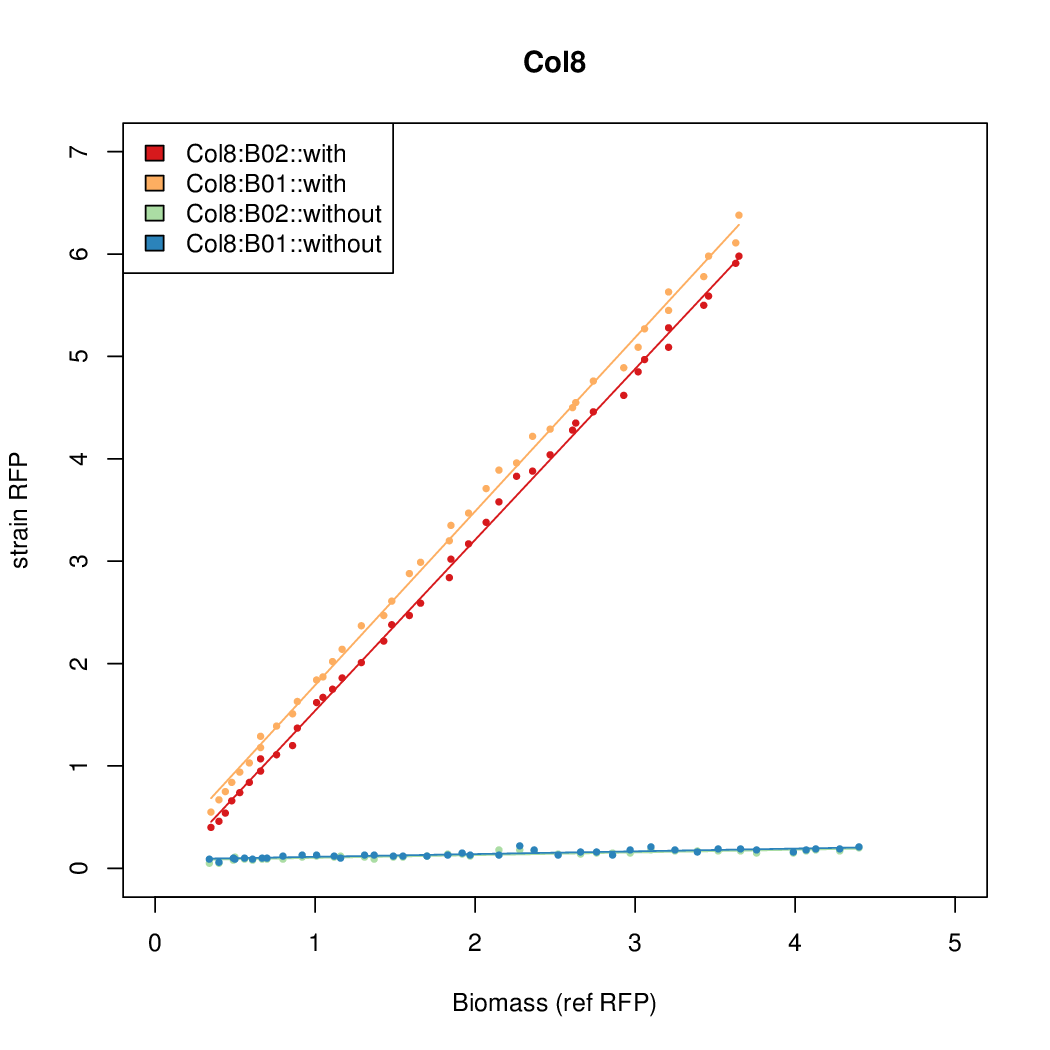
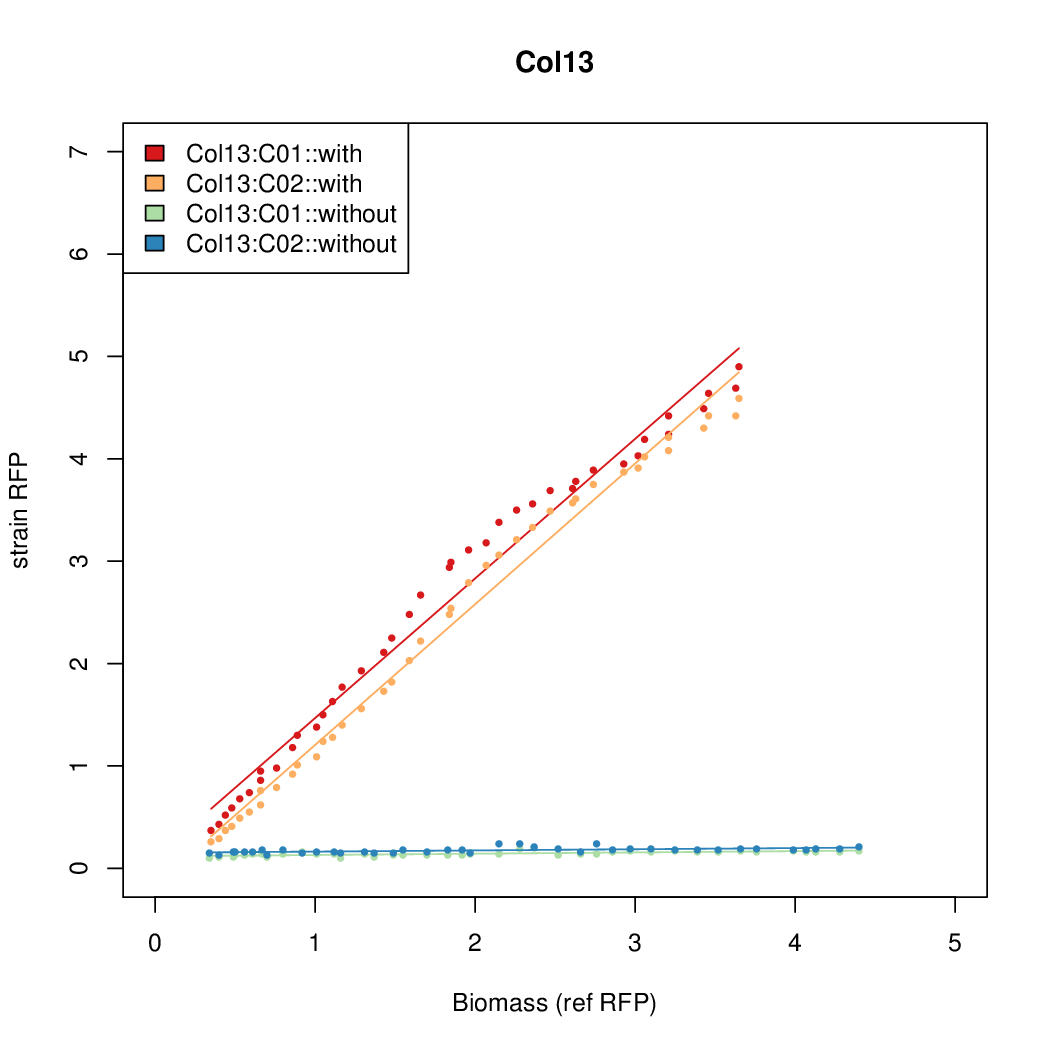
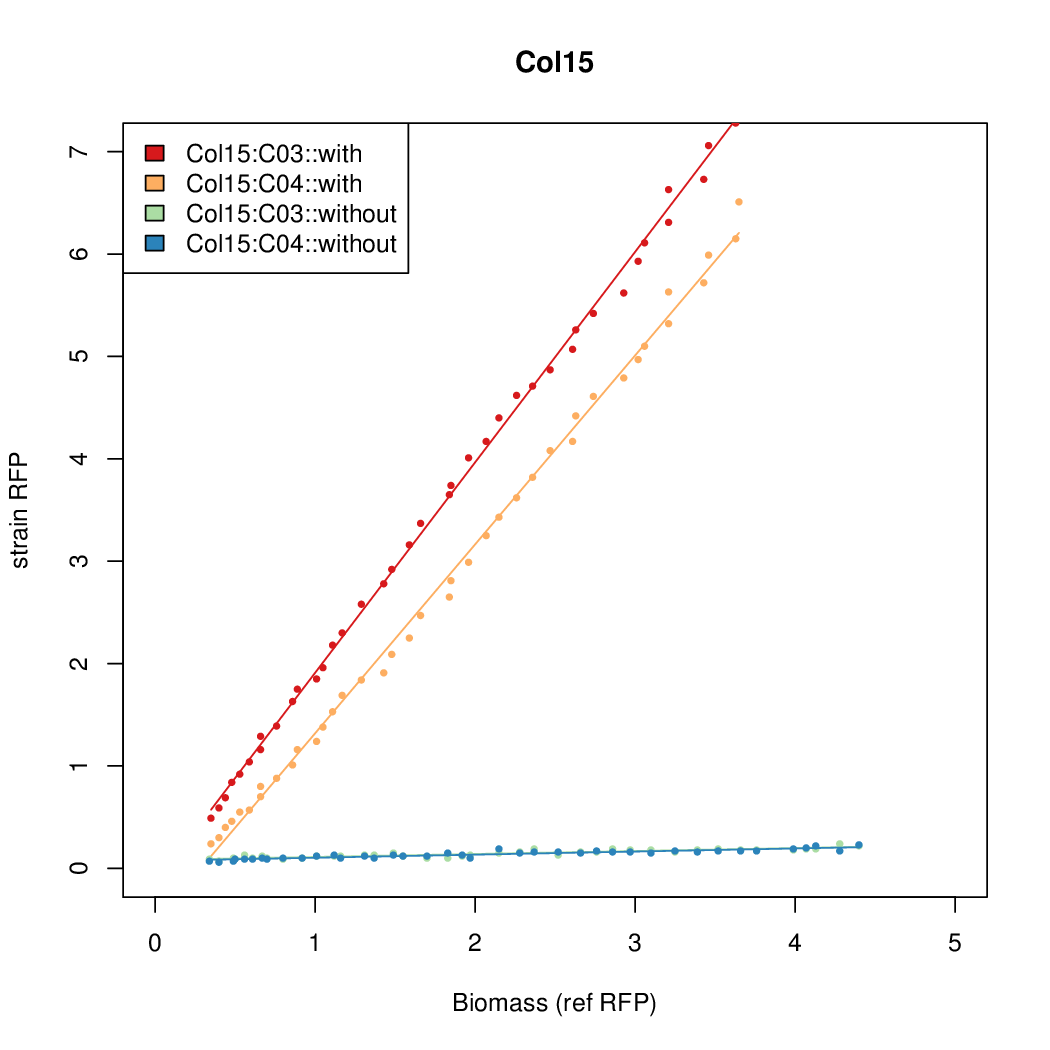
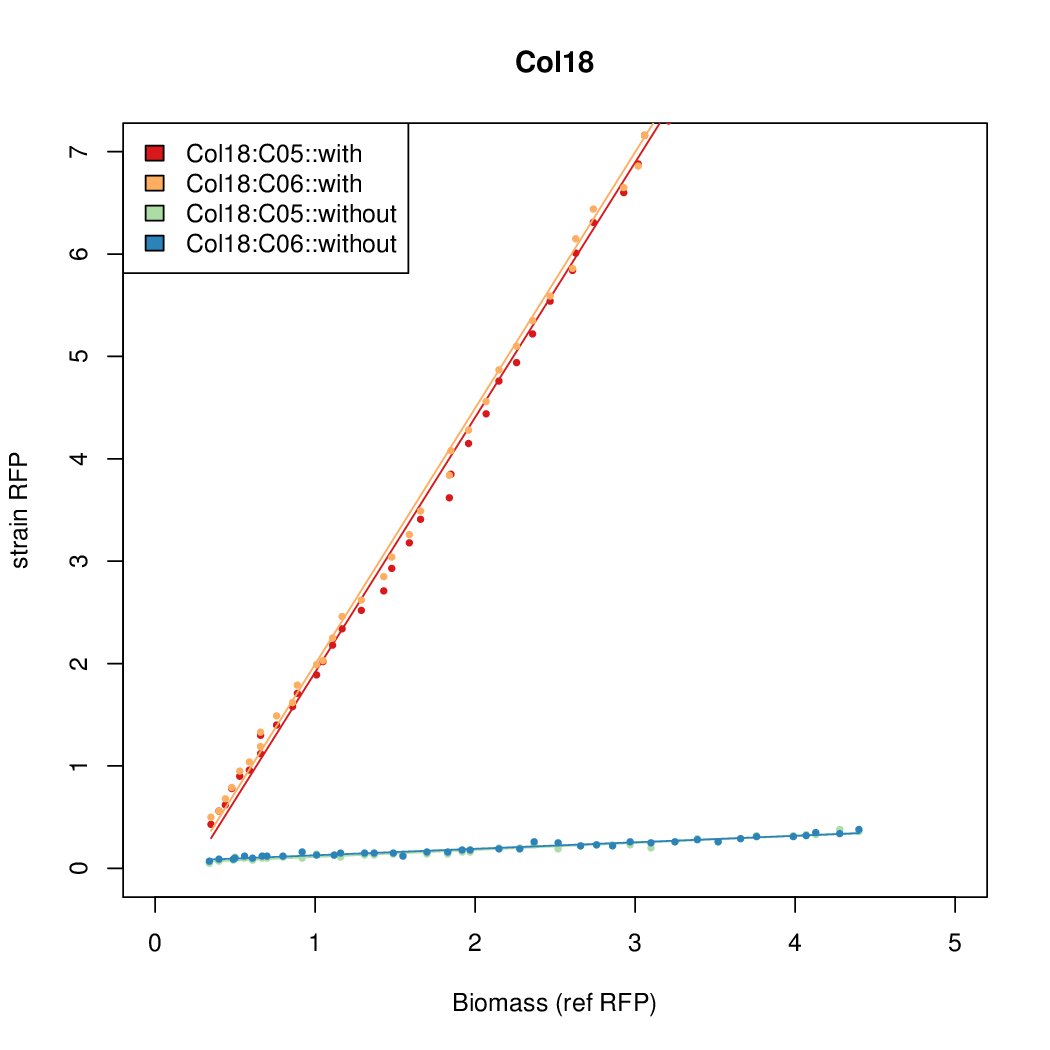
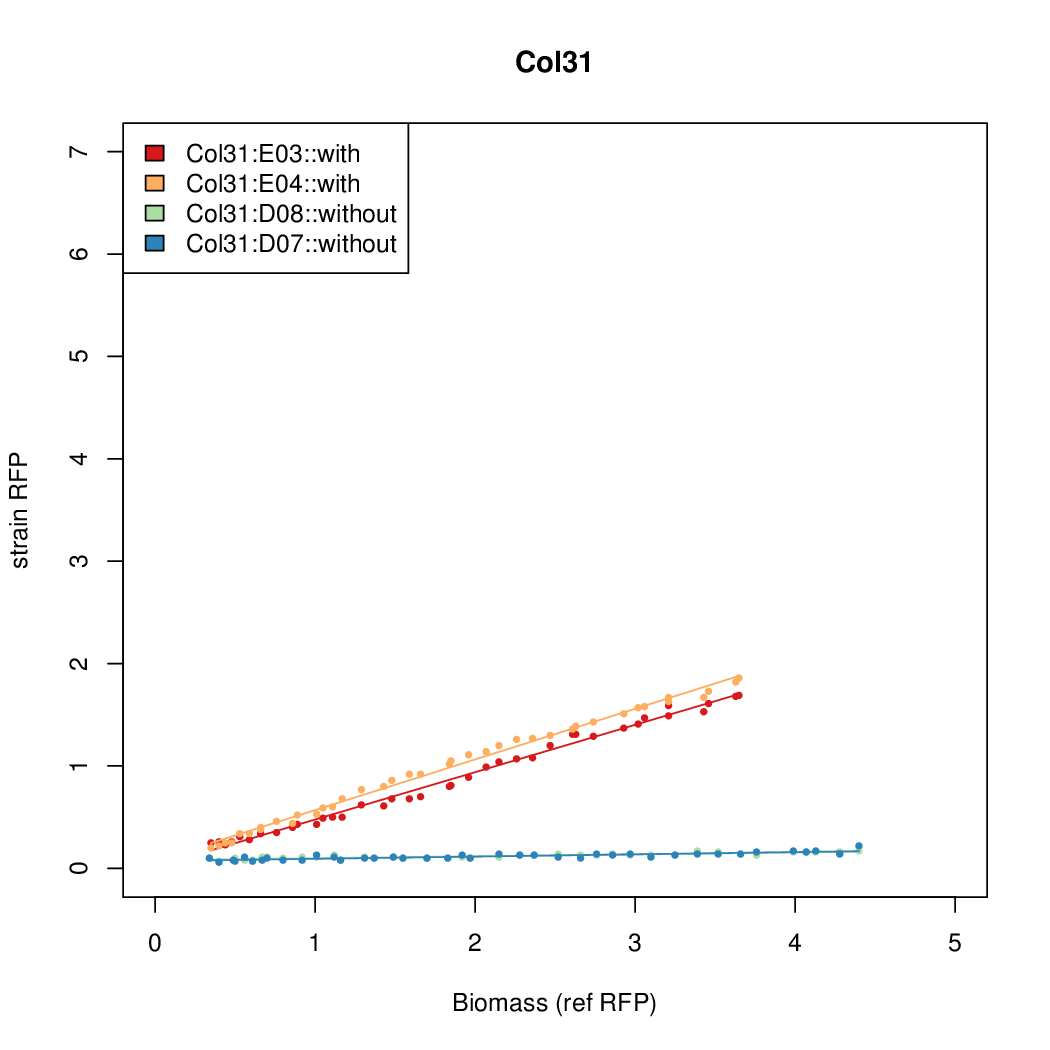
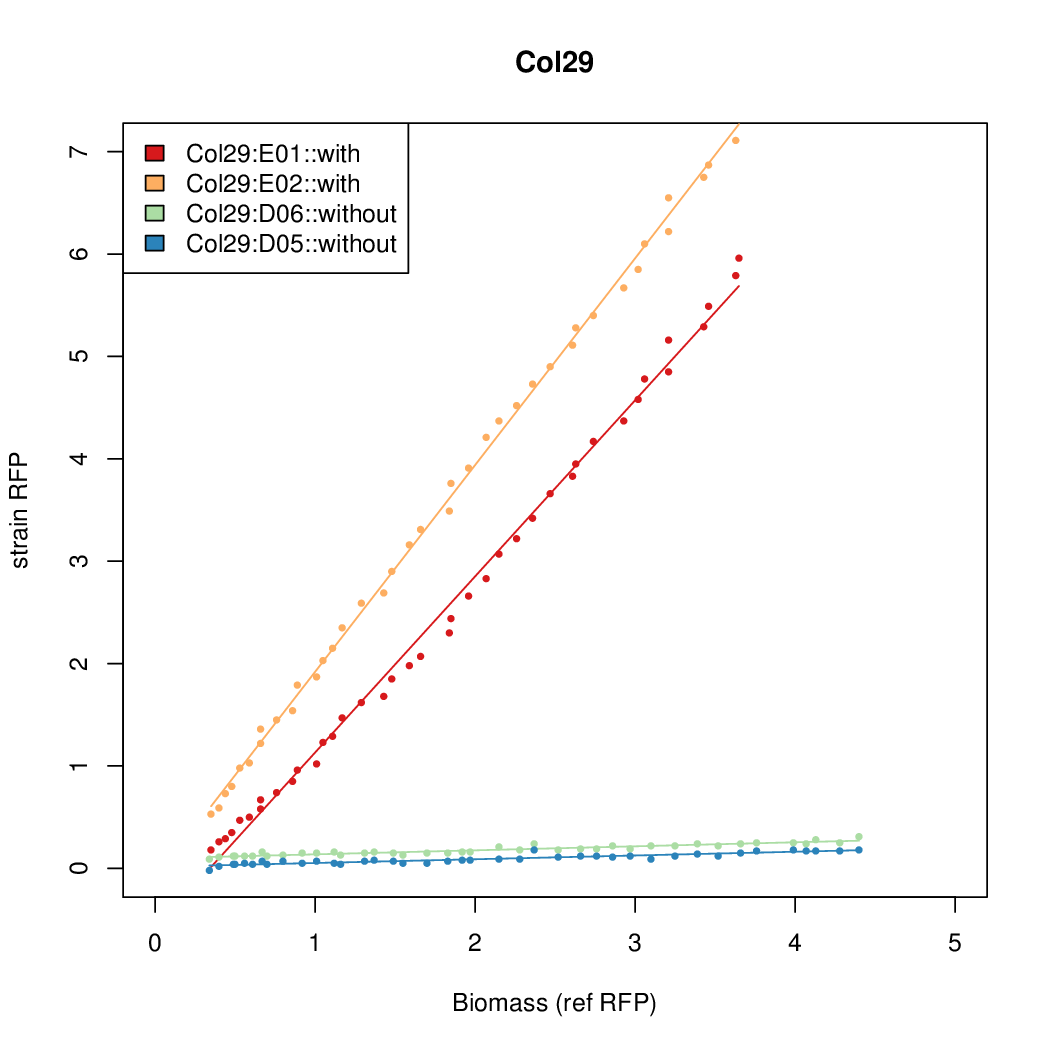
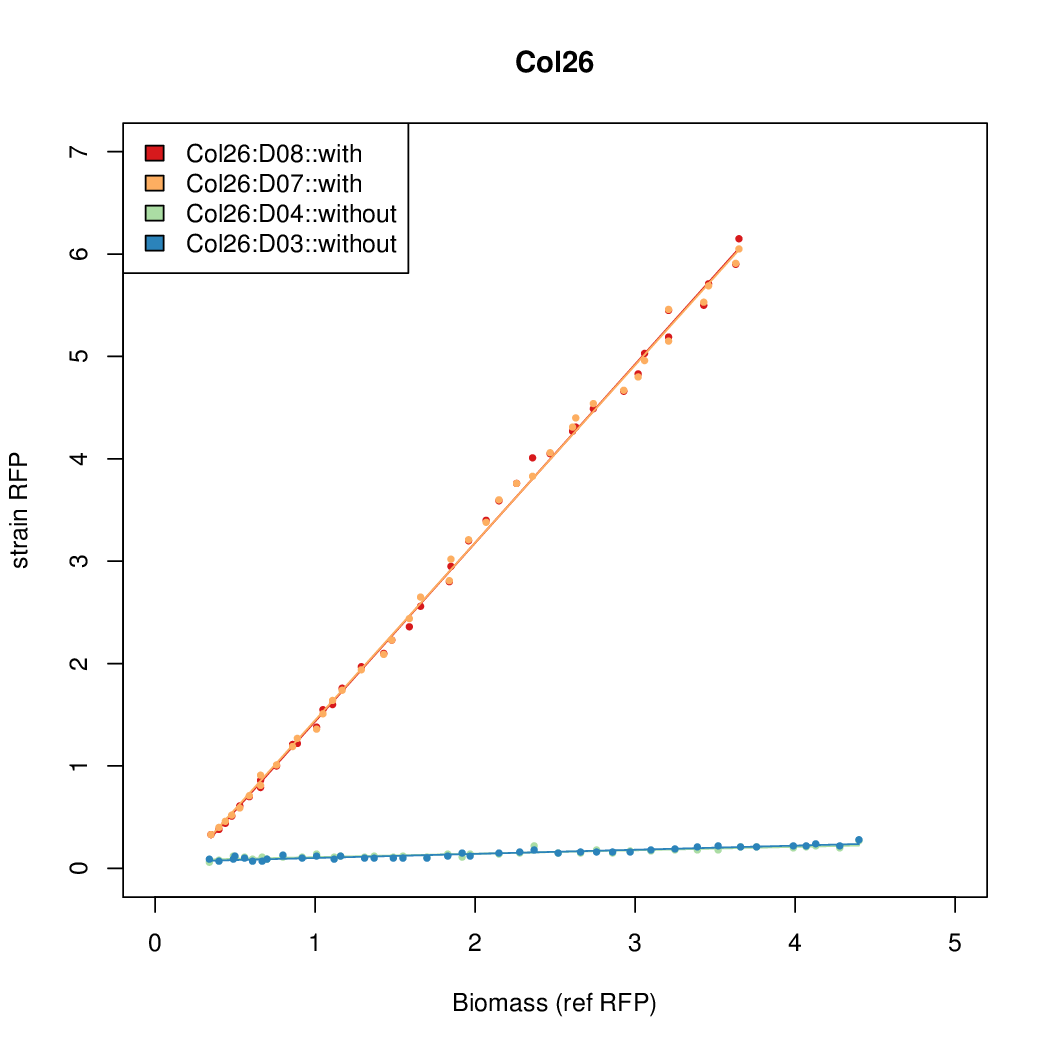
Promoter strengths for two trials of each colony with and without arabinose.
| Identifier | Sequencea | Induced Strength | Leakiness | Inducibilityb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Col. 2 | CTGACGACGCCCCTCTCCGCCCCTTAAAATGTCCA | 14.2 | 0.203 | 69.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 3 | CTGACGTAATCATACCGCCGAAAGTATTATCATTA | 16.6 | 0.426 | 39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 4 | CTGACGCGACAACATTGCGTCCTATAAAATGCCGA | 14.2 | 0.345 | 41 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 5 | CTGACGGCCCGCCCCCGATGCGCATAAAATACCAA | 17.7 | 0.424 | 41.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 12 | CTGACGCGTATCGCGAGCGGGCGTTATTATACGCA | 13.6 | 0.414 | 32.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 10 | CTGACGCCCCGAATCAGTAGTATTTATTATCTAGA | 18 | 0.462 | 38.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 9 | CTGACGCCACCCCCCCCCCCGGCGTATAATTCCCA | 16.1 | 0.530 | 30.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 8 | CTGACGCCCTACCGCTCGCCCCCCTATTATACCCA | 13.4 | 0.211 | 63.4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 13 | CTGACGCCCCCCCCGTCCACCCCCTAATATCCCGA | 10.9 | 0.096 | 113.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 15 | CTGACGTGCGCCTGCCGTCCAAAGTAATATCCTTA | 15.5 | 0.235 | 65.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 18 | CTGACGCCCCGAATCAGTAGTATTTATTATCTAGA | 19.8 | 0.524 | 37.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 19 | CTGACGCTCGCACCGGCGACCCGATAATATCCATA | 18.0 | 0.315 | 57 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 31 | CTGACGCCCCCCCTCCCCCGACCTAAAATATCCAG | 3.8 | 0.161 | 23.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 29 | CTGACGCCGCTGCACCCGTCCCCCTATTATAGCAA | 14.8 | 0.301 | 49.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 26 | CTGACGCCGATCCTATCTCCCTATTAAAATTTTTA | 13.8 | 0.292 | 47.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 22 | CTGACGCCCCGAATCAGTAGTATTTATTATCTAGA | 16.8 | 0.466 | 36.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 33 | CTGACGCCAGCTTCCTACTTCAAATATAATCCGTA | 14.4 | 1.01 | 14.3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 34 | CTGACGTCCCTCTTCCGCGCCCCCTAAAATACCCA | 12.4 | 0.187 | 65.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Col. 35 | CTGACGCCCAACCCGACACAGCGATATAATAATGA | 18.4 | 0.89 | 20.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
a The sequence of each pBAD promoter characterized. To use this simply produce a primer with the promoter sequence you wish in a tail. Replace the old promoter in your system e.g. [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K808000 BBa_K808000] with the new and see the chance.
b Inducibility = Induced Strength divided by leakiness.
Sequences
We sequenced and aligned the promoters that are shown above. The sequences show conservation in the -10 and -35 regions by design. Within the -10 region, we allowed for two random weak (A or T) bases. We do not see a strong preference for A over T or vice versa. Within the regions where we allowed any base, we see a preference for C over the other bases. This could be due to bias during synthesis.
Example of use
The tight inducible pBAD promoter was used in our "Hello World project" to regulate the expression of GFP SF, which was tagged with a signal peptide to direct it into the periplasm. Production and folding of GFP SF is faster than the transport system of E. coli, which leads to undesired accumulation of GFP SF in the cytoplasm. Only when using a promoter with low leakiness it is possible to translocate a significant fraction of GFP SF after its production has been switched off. Thereby we get a clear signal from the periplasm with low interference from the cytoplasm.
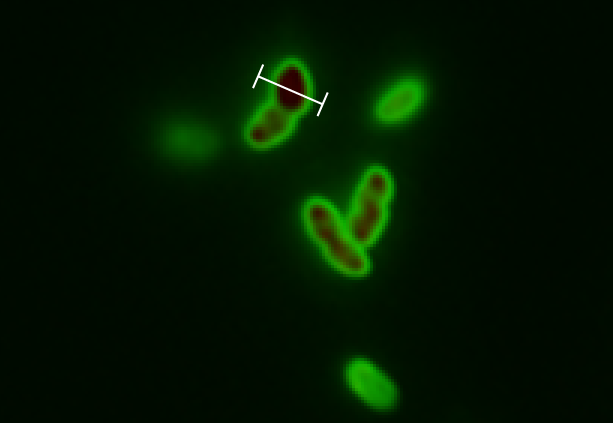
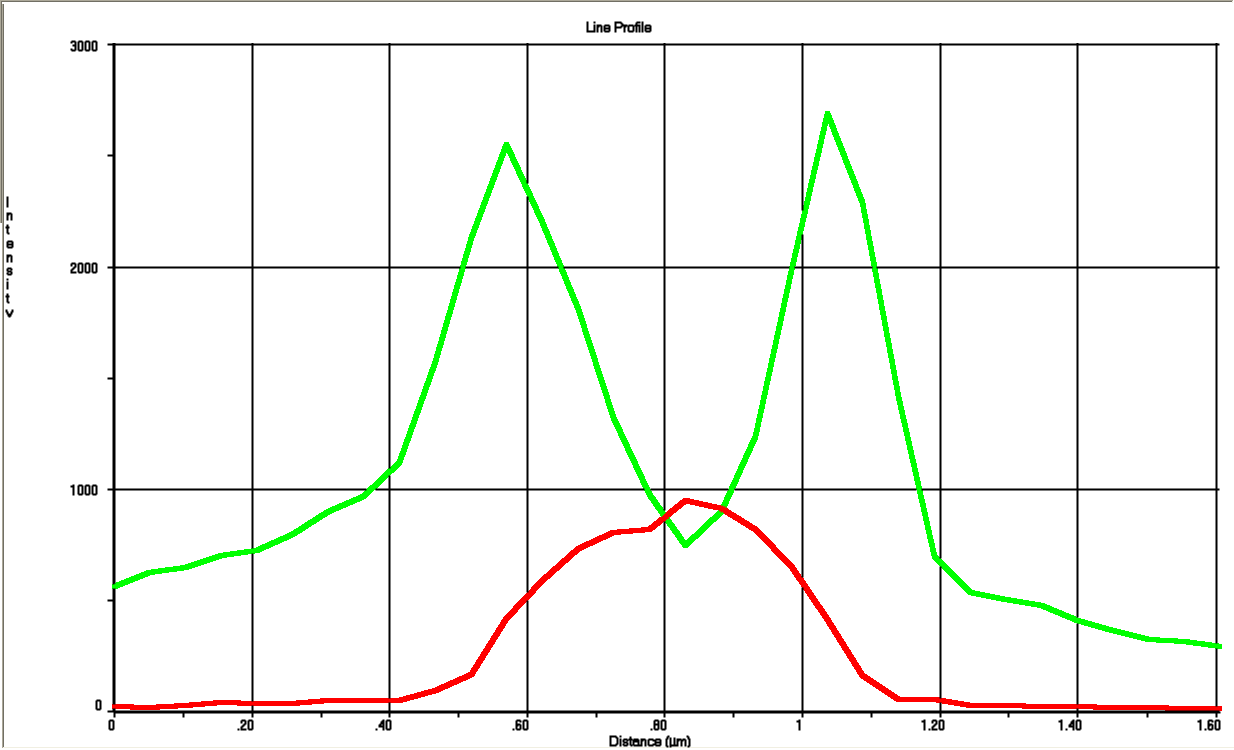
See also "Hello World project".
References
[1] Jensen, Peter Ruhdal, and Karin Hammer. "The sequence of spacers between the consensus sequences modulates the strength of prokaryotic promoters." Applied and environmental microbiology 64.1 (1998): 82-87.
 "
"