Team:Yale/Project MAGE
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→MAGE Targets) |
m (→MAGE Targets) |
||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| - | + | == Pathway Engineering == | |
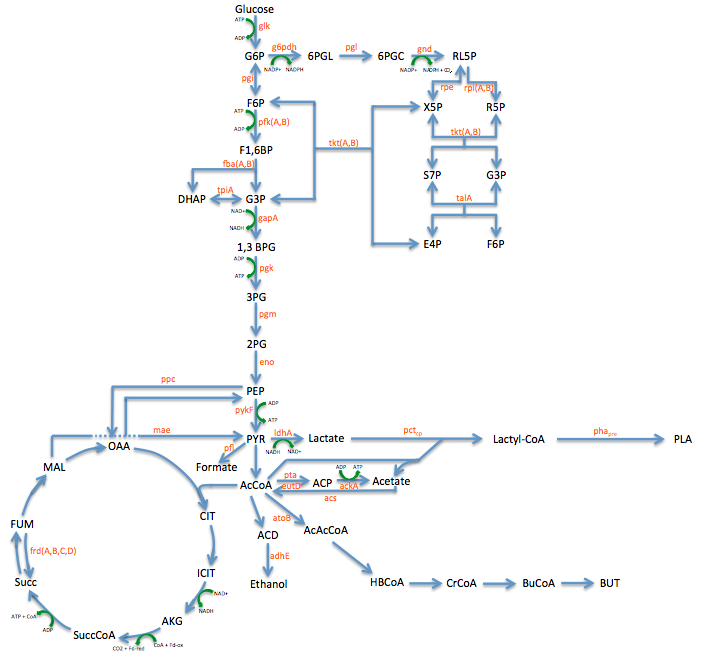
| + | *We wanted to divert resources toward our desired pathway | ||
| + | **This mainly consisted of increase the production of lactate | ||
| + | **In order to better understand the pathway we were tampering with we created this Metabolic engineering graphic (using the sources listed at the bottom of this page) <br> | ||
| + | [[File:Metabolic Engineering Graphic.png|800px]] | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
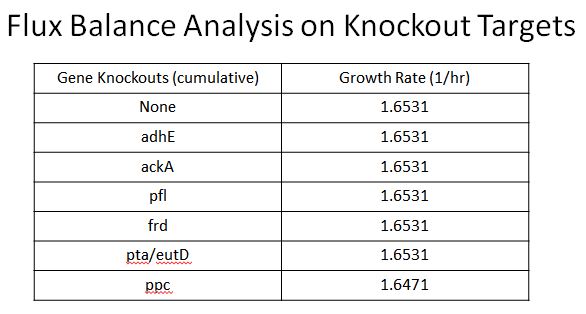
| + | ==== Enzyme KOs ==== | ||
| + | *This led us to find 8 targets for Knockouts (enzymes which would divert resources from our desired pathway) | ||
| + | **These include adhE, ackA, pfl(A,B), frd(A,B,C,D, ppc, atoB, pta, eutD | ||
| + | **Oligos were designed to introduce two nonsence mutation near the begining of these ezymes, so they would not be expressed | ||
| + | **Using Flux Balance Anylysis ([https://2013.igem.org/Team:Yale/Modeling Instructions here]) we were able to determine that none of these enzymes would cause a fitness hit except ppc | ||
| + | |style="padding-left: 20px; padding-right: 20px;"|[[File:FBAKO.JPG|400px]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 19:19, 31 August 2013
| Project Overview | Validate PLA synthesis | Develop bioassay | Apply MAGE | Introduce export system | Make a bioplastic |
|---|
Contents |
Aims for the Project
- Engineer strains of E. coli to validate PLA synthesis
- Develop bioassay to screen PLA production
- Apply MAGE to optimize PLA production, guided by FBA
- Introduce type 1 secretion system to export and extract PLA
- Make a bioplastic
MAGE Targets
- The first step in applying MAGE is finding MAGE targets. This involved reading numerous scientific papers learning as much as possible about the heterologous enzymes, and the pathway that was being used to create the PLA
Enzyme Targets
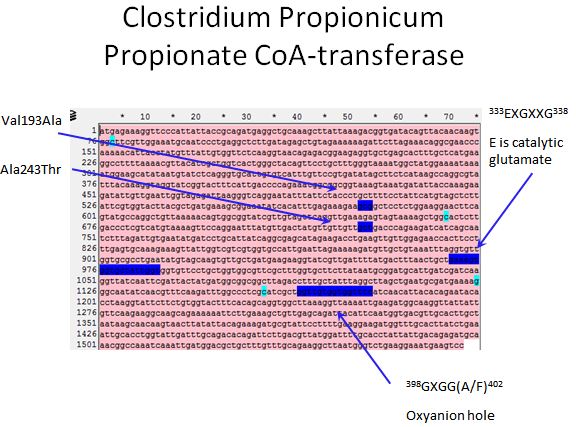
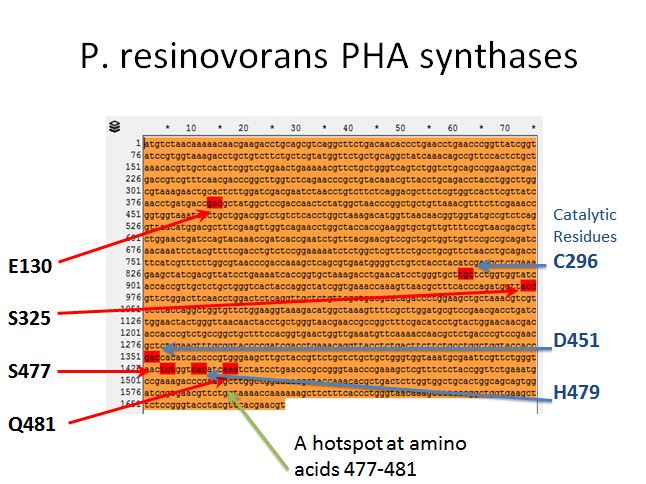
- Sadly there was no crystal structure of either enzyme we could use to locate the sites to introduce mutations
- However, we used the literature available to locate spots where we would want to introduce mutations
Propionate CoA-transferase
| 
|
P. resinovorans PHA synthases
| 
|
Pathway Engineering
- We wanted to divert resources toward our desired pathway
- This mainly consisted of increase the production of lactate
- In order to better understand the pathway we were tampering with we created this Metabolic engineering graphic (using the sources listed at the bottom of this page)
Enzyme KOs
| 
|

List of Papers:
Jacob et al. 1997
Matsuzaki et al. 1998
Sawers et al. 1998
Park et al. 2002
Selmer et al. 2002
Takase et al. 2002
Fong et al. 2005
Matsumoto et al. 2005
Rangarajan ES et al. 2005
Matsumoto et al. 2006
Jung et al. 2009
Matsumoto et al. 2009
Juang et al. 2010
Orth et al. 2010
Yang et al. 2011
Kandasamy et al. 2012
Yang et al. 2013
 "
"