Team:Carnegie Mellon/Parts
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Enpederson (Talk | contribs) |
Enpederson (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{:Team:Carnegie_Mellon/Templates/header}} | {{:Team:Carnegie_Mellon/Templates/header}} | ||
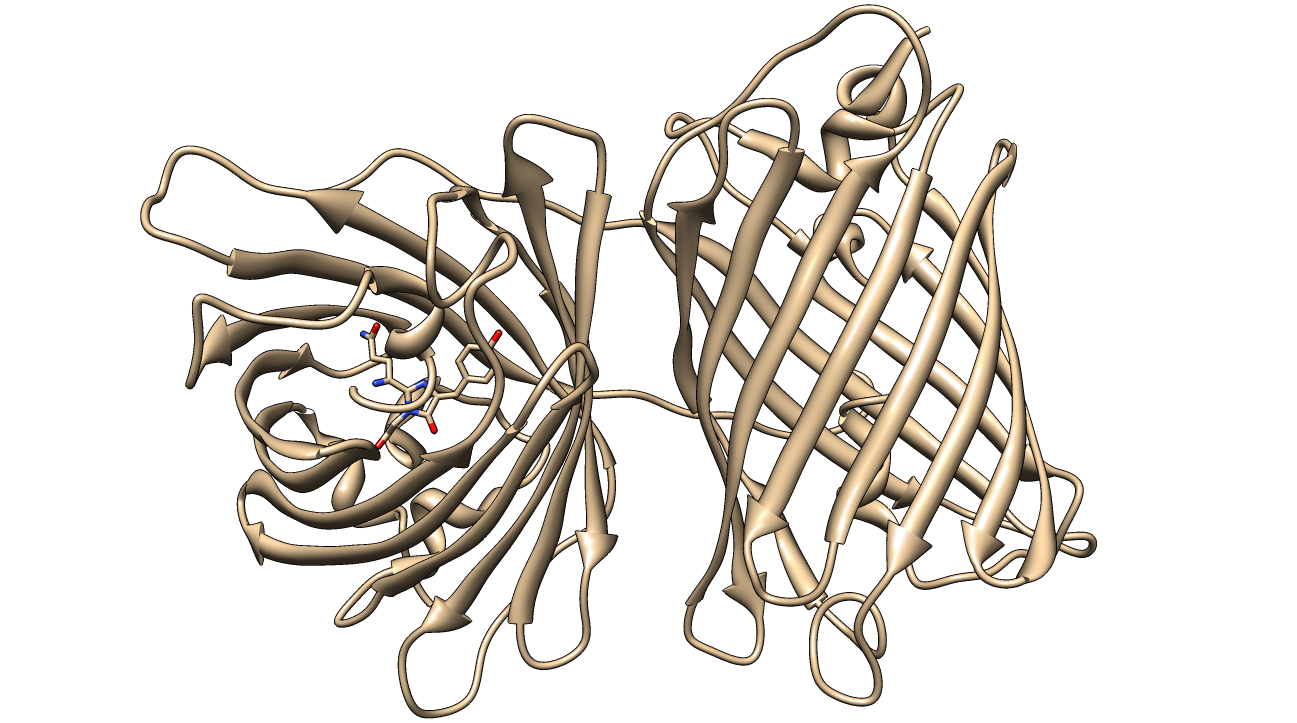
[[image:KillerRed.png|600px|thumb|center|Crystal Structure of KillerRed (PDB ID: 3GB3) with the QYG chromophore shown<sup>2,3,4</sup>]] | [[image:KillerRed.png|600px|thumb|center|Crystal Structure of KillerRed (PDB ID: 3GB3) with the QYG chromophore shown<sup>2,3,4</sup>]] | ||
| - | <html><p>KillerRed (<partinfo> | + | <html><p>KillerRed (<partinfo>K1184000</partinfo>) is a red fluorescent protein that produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of yellow-orange light (540-585 nm). KillerRed is engineered from anm2CP to be phototoxic. It has been shown that KillerRed produces superoxide radical anions by reacting with water. Superoxide reacts with the chromophore of KillerRed, causing it to become dark, which ultimately gives rise to a bleaching effect. KillerRed is spectrally similar to mRFP1 with a similar brightness. KillerRed is oligomeric and may form large aggregates in cells. Expression of KillerRed and irradiation with light may act a kill-switch for biosafety applications. |
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </html>The parts we used this year to characterize KillerRed involve the mRFP1 protein (<partinfo>BBa_E1010</partinfo>), which acts as a negative control for phototoxicity due their spectral similarity. For expression, we used a wild-type <i>lac</i> promoter (<partinfo>BBa_R0010</partinfo>) and an RBS (<partinfo>BBa_B0034</partinfo>)<html> | ||
<a href="/Team:Carnegie_Mellon/KillerRed">More Information about KillerRed</a><br /> | <a href="/Team:Carnegie_Mellon/KillerRed">More Information about KillerRed</a><br /> | ||
Revision as of 17:14, 26 September 2013
KillerRed (
More Information about RFP <groupparts>iGEM013 Carnegie_Mellon</groupparts>
 "
"