Team:DTU-Denmark/HelloWorld
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
Biobrick [[Team:DTU-Denmark/Parts|BBa_K1067009]] successfully directs proteins to the periplasm in ''E. coli''. | Biobrick [[Team:DTU-Denmark/Parts|BBa_K1067009]] successfully directs proteins to the periplasm in ''E. coli''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ul> | ||
| + | <li>Don, R. H et al. (1991). ‘Touchdown’ PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Research. 19 (14): 4008. | ||
| + | <li>Hammer, K., Mijakovic, I. and Jensen, P. R. (2006). Synthetic promoter libraries – tuning of gene expression. Trends in Biotechnology. 24(2): 53-55. | ||
| + | <li>Jensen, P. R. and Hammer, K. (1998). The Sequence of Spacers between the Consensus Sequences Modulates the Strength of Prokaryotic Promoters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 64(1): 82-87. | ||
| + | <li>Solem, C. and Jensen, P. R. (2002). Modulation of Gene Expression Made Easy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 68(5): 2397-2403. | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="163px" height="100%" valign="top"> | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </font> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Main content area --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
{{:Team:DTU-Denmark/Templates/EndPage}} | {{:Team:DTU-Denmark/Templates/EndPage}} | ||
Revision as of 14:12, 1 October 2013
Hello World Pilot Project
Contents |
Introduction
‘Hello World!’ are the first words a programmer prints when learning a new programming language. In analogy to this our team decided to do a ‘Hello World’ project in order to familiarize ourselves with lab techniques that we used later on to construct plasmids. Specifically we were performing PCR with uracil-containing primers, purifying PCR products and ligating them by means of USER cloning.
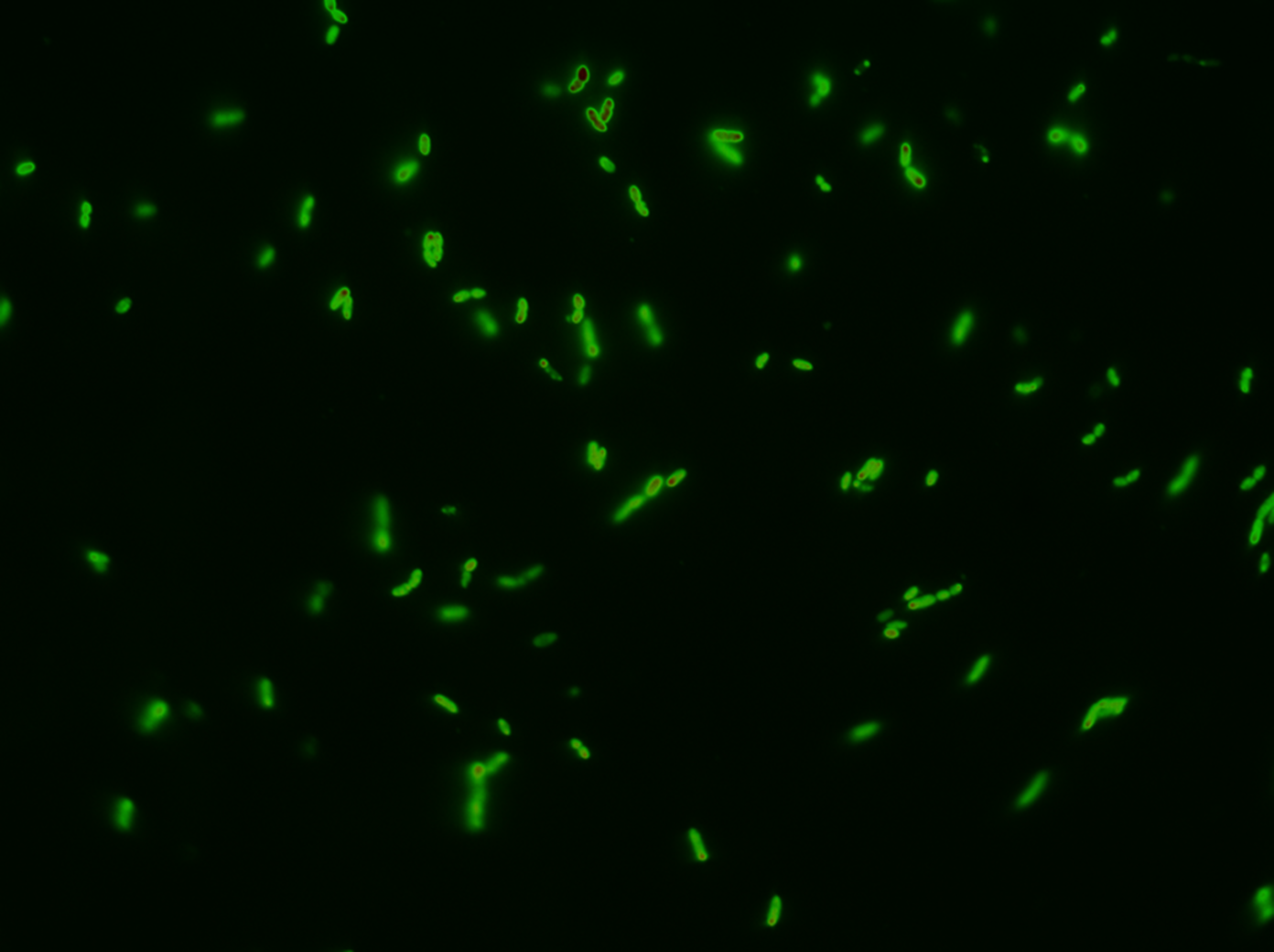
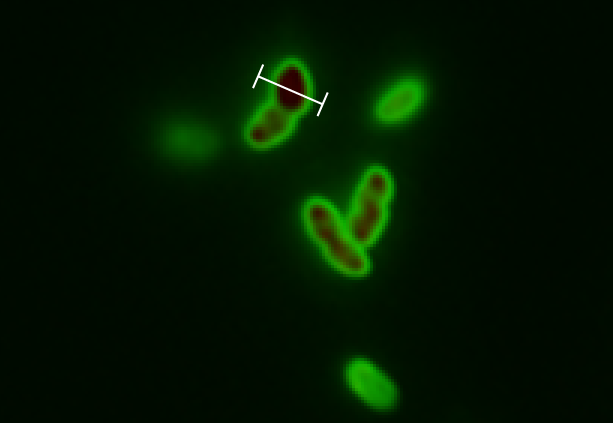
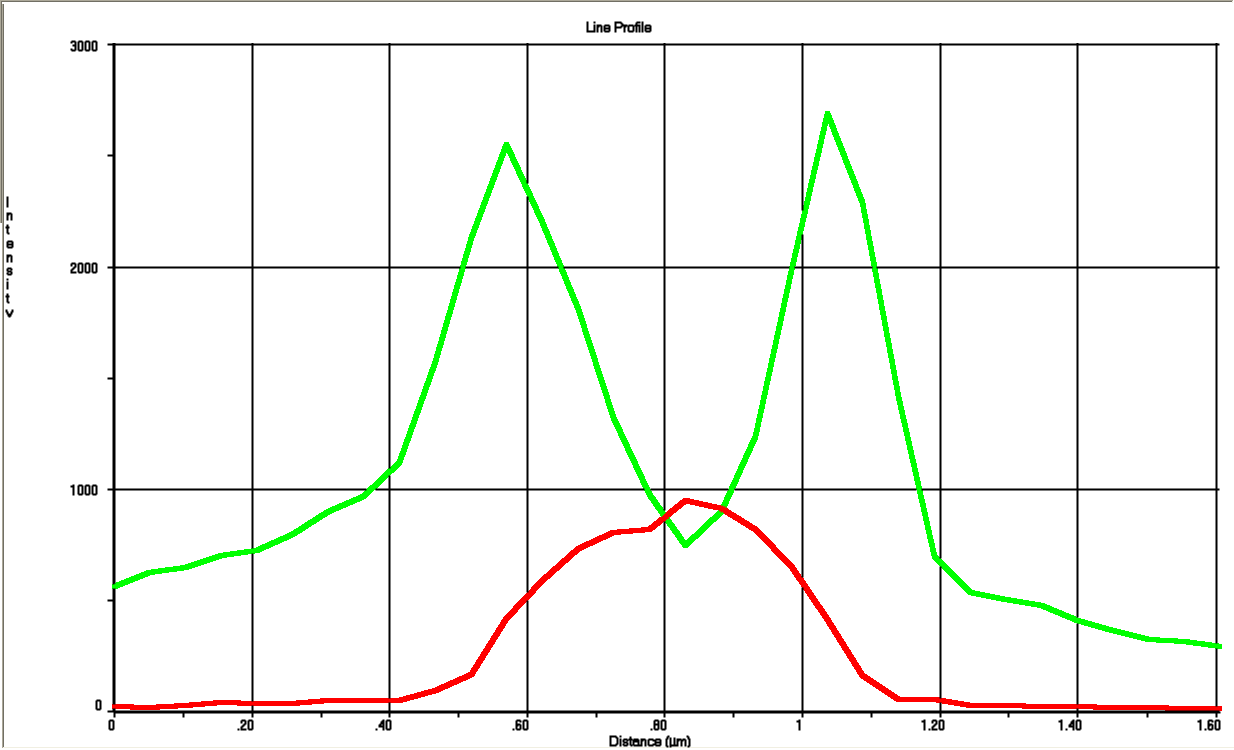
Since we are working with many periplasmic proteins, we wanted to try to target proteins to the periplasm. To do this, we used periplasmic signal peptides from the TAT and Sec pathways, and with a translational fusion of the signal peptide to GFP, we expressed GFP in the periplasm. Simultaneously, we expressed RFP in the cytoplasm.
Methods
We followed this protocol to visualize GFP in the periplasm.
Results
Conclusions
Biobrick BBa_K1067009 successfully directs proteins to the periplasm in E. coli.
- Don, R. H et al. (1991). ‘Touchdown’ PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Research. 19 (14): 4008.
- Hammer, K., Mijakovic, I. and Jensen, P. R. (2006). Synthetic promoter libraries – tuning of gene expression. Trends in Biotechnology. 24(2): 53-55.
- Jensen, P. R. and Hammer, K. (1998). The Sequence of Spacers between the Consensus Sequences Modulates the Strength of Prokaryotic Promoters. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 64(1): 82-87.
- Solem, C. and Jensen, P. R. (2002). Modulation of Gene Expression Made Easy. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 68(5): 2397-2403.
 "
"