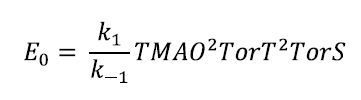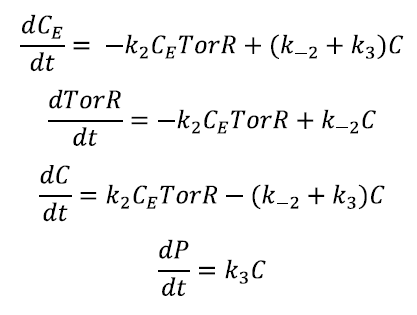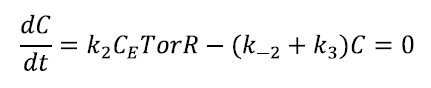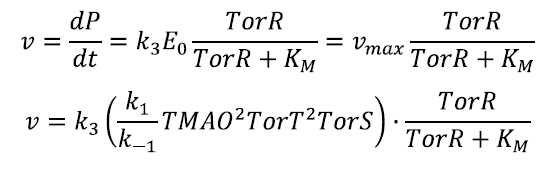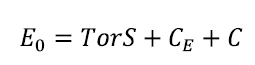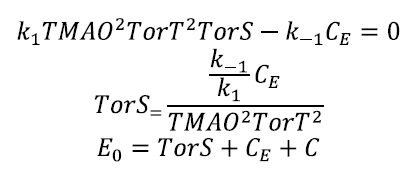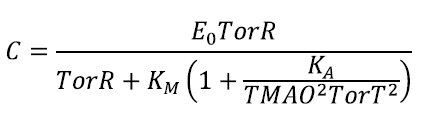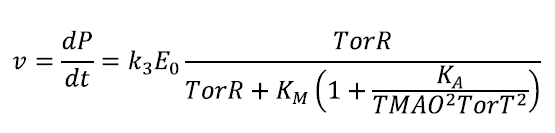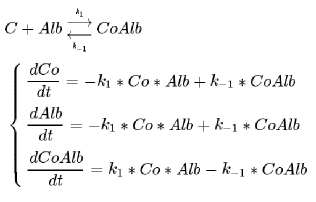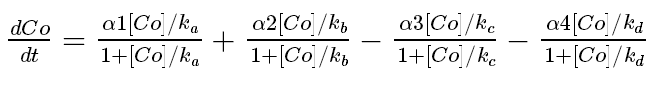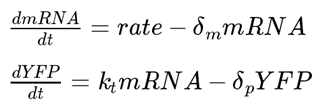Modelagem
From 2013.igem.org
(Created page with "{{Team:UFMG Brazil/barra_pt}} {{carlos_teste}} Modelagem =Modeling TMAO system= ==Labels and conventions== <html><b>C<sub>E</sub></b></html>: The enzymatic complex formed ...")
Newer edit →
Revision as of 18:06, 13 October 2013
Modelagem
Contents |
Modeling TMAO system
Labels and conventions
CE: The enzymatic complex formed by TorT+TorS+TMAO, which reacts with TorR
C: intermediate component of the final enzymatic process
P: Product of the enzymatic reaction
CTS: Complex formed by TorT and TorS
CTSM: Complex formed by TorT+TorS and one molecule of TMAO
CTSM: Complex formed by TorT and TMAO
First Modeling
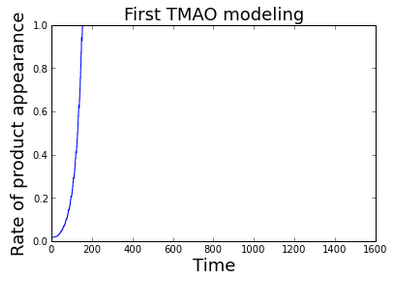
This is the simplest modeling process to be considered in our study. The product of the enzymatic process is collapsed in only one reaction that was placed at equilibrium.
Imposing the equilibrium in the first reaction we have:
The value of CE is the initial enzyme concentration for the subsequent enzymatic reactions.
Regarding the enzymatic reaction:
The following relation holds E0 = CE + C. And as usual imposing the steady state condition:
With CE = E0 - C
Solving for C:
withIn conclusion, we find:
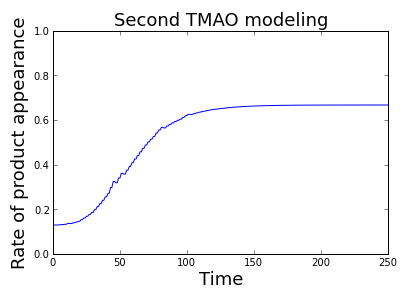
Second Modeling
It was used the same pattern of reactions as before, but with a standpoint of "essential activation" (the first reaction is no longer considered to equilibrium). Some enzymes need to be activated to bind the substrate. In our case, the enzyme is activated by TorS and activators are TMAO and TorT. The rate of product P appearance depends on the activators concentration. The equation that varies with respect to the previous case is:
The total concentration of the enzyme is:
Then we considered ![]() and imposed
and imposed 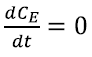 and
and 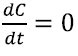
The system of equations also comes from:
Defining 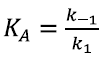 and replacing we have:
and replacing we have:
In conclusion the rate of product appearance results
Modeling IMA System
First Reaction - Cobalt ions bind to albumin
The cobalt ion binds to albumin protein, originating the cobalt-albumin complex. If the albumin is derived from a healthy patient, it will bind more cobalt ions than a albumin derived from a patient with heart disease. It happens because patients with heart conditions will have a isquemic modified albumin (IMA), which has less capability of binding to cobalt. Thus, the amount of free cobalt in the system will be determined by the presence of a normal or ischemic albumin in the sample.
Second Reaction - The entry of cobalt in the cell
There are four cobalt transporters in the cell. The rcnA (Uniprot code: P76425) and zntA (Uniprot code: P37617) transport the cobalt to outside the cell. The corA (Uniprot code: P0ABI4) and zupT (Uniprot code: P0A8H3) transport the cobalt to inside the cell.
The equation for the cobalt flux through these transporters is:
Third Reaction - Transcription
In our modeling, we considered the cobalt acting as a transcriptional activator in order to simplify our model.
The transcriptional activation are accessed by the equation:
The transcription and translation are accesed by the equations:
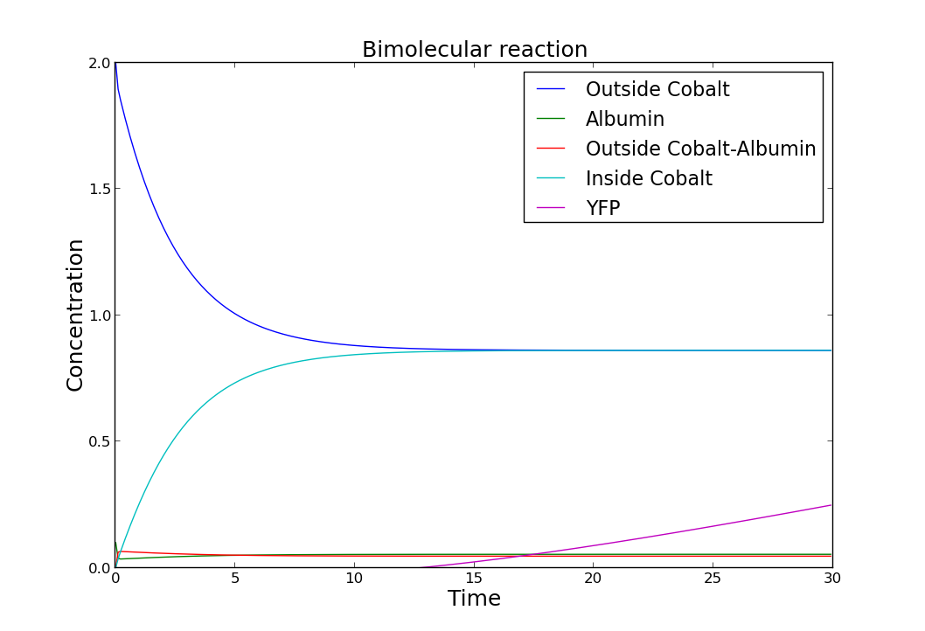
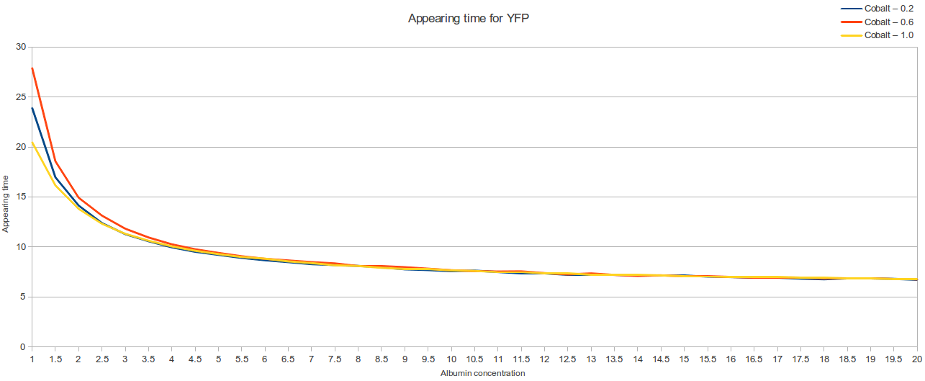
Model simulations
The simulation showed that for lower concentrations of albumin, the initial concentration of cobalt has an influence in the time of reporter protein appearance and it will be detected faster. Nevertheless, for higher concentrations of albumin, the initial concentration of cobalt doesn't have effect in the time of reporter protein appearance, and it will take more time to be detected.
Our Sponsors


 "
"