Team:NCTU Formosa/modeling
From 2013.igem.org
(→Temperature-regulated system) |
(→Plux efficiency) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
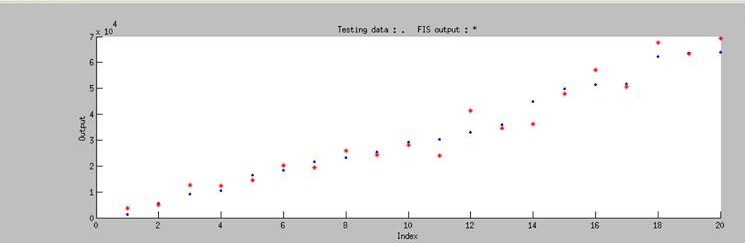
it showed the testing data could match the training data.</p> | it showed the testing data could match the training data.</p> | ||
[[File:Nctu_Plux_train_wikifig.jpg|745px|center|Figure 3. The training and testing data using ANFIS system]] | [[File:Nctu_Plux_train_wikifig.jpg|745px|center|Figure 3. The training and testing data using ANFIS system]] | ||
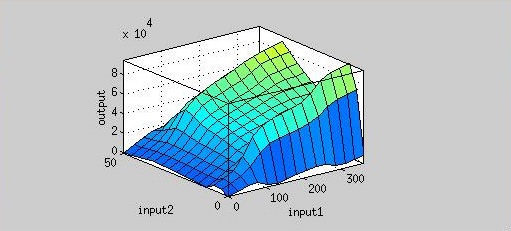
| - | The Figure 4 is the result graph from input 1(time) and input 2(AHL concentration). According this graph, we can observe the fluorescence has two peaks about AHL concentration(at concentration of | + | The Figure 4 is the result graph from input 1(time) and input 2(AHL concentration). According this graph, we can observe the fluorescence has two peaks about AHL concentration(at concentration of 4 nM and 40 nM). |
That means we could achieve our regulation goal with little AHL. | That means we could achieve our regulation goal with little AHL. | ||
[[file:Nctu_Plux_ahl_time_wikifig.jpg|500px|center|Figure 4. Input 1 is time(min), input 2 is AHL concentration and output is fluorescence.]] | [[file:Nctu_Plux_ahl_time_wikifig.jpg|500px|center|Figure 4. Input 1 is time(min), input 2 is AHL concentration and output is fluorescence.]] | ||
Revision as of 03:59, 27 October 2013
Modeling was our first step forward. When validated with our experimental data, modeling is also a verification of the accuracy of our experiments.
Contents |
MATLAB Introduction
MATLAB (matrix laboratory) is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. It is developed by MathWorks, a company in United States. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages, including C, C++, Java, and Fortran. Although MATLAB is intended primarily for numerical computing, an optional toolbox uses the MuPAD symbolic engine, allowing access to symbolic computing capabilities. An additional package, Simulink, adds graphical multi-domain simulation and Model-Based Design for dynamic and embedded systems.
ANFIS Introduction
Adaptive-Network-Based Fuzzy Inference System, in short ANFIS, is a power tool for constructing a set of fuzzy if-then rules to generate stipulated output and input pairs. Unlike system modeling using mathematical rules that lacks the ability to deal with ill-defined and uncertain system, ANFIS can transform human knowledge into rule base, and therefore, ANFIS can effectively tune membership functions, minimizing the output error.
Light-regulated System
Red Promoter
Temperature-regulated system
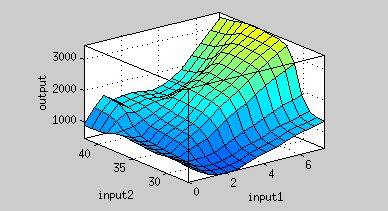
From Figure 1, the maximum output is obtained at 37 oC. Under the same time frame, the output (the normalized expression of the reporter gene) is maximized at 37oC while minimized at 25 oC. There is a dramatic decrease in the output near 30 o and the outputs around 37oC are much higher. This modeling demonstrates that using 37 oC RBS is a plausible approach for achieving gene expression through temperature.
Small RNA-regulated System
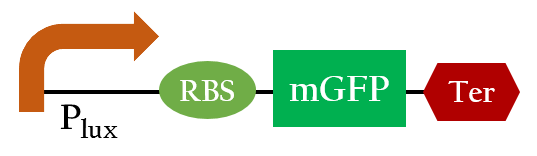
Plux efficiency
We searched the biobrick like Figure 2 and got the data from Imperial 2007 iGEM team. The data is about Plux under different concentration of AHL and different time.
Using ANFIS to train 76 sets of data and test 20 sets of data, we got the output Figure 3 and it showed the testing data could match the training data.
The Figure 4 is the result graph from input 1(time) and input 2(AHL concentration). According this graph, we can observe the fluorescence has two peaks about AHL concentration(at concentration of 4 nM and 40 nM). That means we could achieve our regulation goal with little AHL.
Reference
- iGEM 2007 Imperial https://2007.igem.org/Imperial
 "
"