Team:Heidelberg/Templates/NRPS-W-20a
From 2013.igem.org
JuliaS1992 (Talk | contribs) |
JuliaS1992 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | |||
== Tool selection for domain prediciton == | == Tool selection for domain prediciton == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 58: | ||
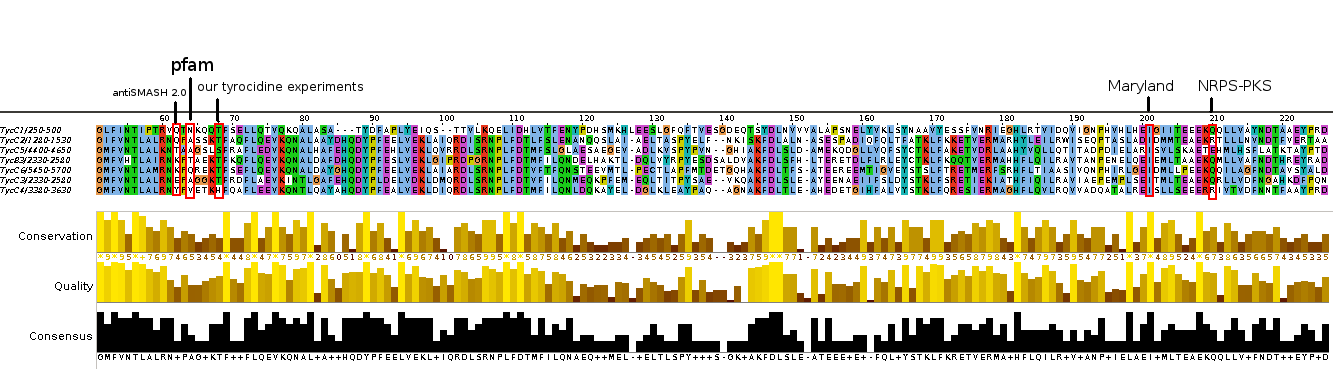
TycB3 C-A domain | TycB3 C-A domain | ||
| - | [[File: | + | [[File:Heidelberg2013_TycCAclustalComparison.png|thumbnail|Clustal Omega MSA of different C-A domain borders of Tyrocidine cluster with annotation (prediction) of the start of the A domain according to different tools.]] |
[[File:TycCdomainBorderTools.png|thumbnail|Clustal Omega MSA of different C-A domain borders of Tyrocidine cluster with annotation (prediction) of the end of the C domain according to different tools.]] | [[File:TycCdomainBorderTools.png|thumbnail|Clustal Omega MSA of different C-A domain borders of Tyrocidine cluster with annotation (prediction) of the end of the C domain according to different tools.]] | ||
Revision as of 02:39, 29 October 2013
Tool selection for domain prediciton
We tried to determine, which tool would be most appropriate for automated determination of domains. Thus we used the first CDS of the teicoplanin NRPS, as curated in the NRPS-PKS (SBSPKS) database. We then compared the automated prediction with the tool of Maryland, as well as antiSMASH2.
| A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | E domain | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | |
| NRPS-PKS | 1 | 491 | 505 | 564 | 604 | 1021 | 1015 | 1511 | 1526 | 1584 | 1608 | 2053 |
| Maryland | 18 | 503 | 504 | 567 | 599 | 1012 | 1008 | 1524 | 1524 | 1587 | 1604 | 2063 |
| antiSMASH | 35 | 426 | 502 | 567 | 598 | 891 | 1056 | 1447 | 1522 | 1589 | 1602 | 1896 |
| pfam | 15 | 478 | 504 | 566 | 598 | 891 | 1036 | 1498 | 1524 | 1586 | 1620 (as C) | 1896 (as C) |
Note that Pfam can't differentiate between C and E domains. Pfam also does not return any predictions in regard to A-domain specificity. antiSMASH is able to predict the A-domain specificities as annotated in NRPS-PKS, while Maryland's tool can only predict the second A-domain (Tyrosine), while the first is incorrectly predicted to be specific for Leucine (curated: HpG, 4-hydroxyphenyl glycine).
The same analysis was also repeated for thaxtomin.
| A domain | NM domain | T domain | C domain | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | |
| NRPS-PKS | 1 | 506 | 509 | 712 | 944 | 1005 | 1029 | 1458 |
| Maryland | 5 | 521 | 468 | 879 | 942 | 1006 | 1028 | 1455 |
| antiSMASH | 42 | 445 | 511 | 732 | 940 | 1007 | 1025 | 1325 |
| pfam | 22 | 486 | 538 | 638 | 942 | 1006 | 1023 | 1326 |
In this case, both tools correctly predict the L-Phenylalanine specificity of the A-domain.
Analysis of tycC from the tyrocidine-cluster.
| C domain | A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | C domain | A domain | T domain | TE domain | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | Start | End | ||
| Marahiel (C-T), Ilia (A-T), Philipp (C-A) | 953 | 963 | 1033 | 1050 | 1345 | 1990 | 2000 | 2070 | 2087 | 3028 | 3038 | 3108 | 3125 | 3571 | 4063 | 4073 | 4143 | 4160 | 5107 | 5117 | 5187 | 5204 | 6150 | 6160 | 6230 | 6247 | |||||||||||||
| NRPS-PKS | 13 | 447 | 442 | 957 | 972 | 1036 | 1058 | 1483 | 1478 | 1994 | 2009 | 2073 | 2095 | 2520 | 2515 | 3032 | 3048 | 3111 | 3133 | 3558 | 3553 | 4066 | 4082 | 4146 | 4168 | 4593 | 4588 | 5111 | 5126 | 5190 | 5212 | 5639 | 5636 | 6151 | 6169 | 6233 | 6256 | 6466 | |
| Maryland | 8 | 438 | 441 | 964 | 972 | 1036 | 1053 | 1474 | 1477 | 2001 | 2009 | 2073 | 2090 | 2511 | 2516 | 3039 | 3047 | 3111 | 3128 | 3549 | 3552 | 4074 | 4082 | 4146 | 4163 | 4584 | 4587 | 5118 | 5126 | 5190 | 5207 | 5630 | 5637 | 6160 | 6169 | 6233 | 6254 | 6482 | |
| antiSMASH | 8 | 305 | 490 | 887 | 970 | 1039 | 1054 | 1339 | 1526 | 1924 | 2007 | 2075 | 2090 | 2376 | 2563 | 2962 | 3045 | 3113 | 3128 | 3413 | 3601 | 3997 | 4080 | 4149 | 4165 | 4449 | 4636 | 5041 | 5124 | 5193 | 5208 | 5494 | 5682 | 6083 | 6167 | 6236 | 6253 | 6482 | |
| pfam | 7 | 306 | 470 | 944 | 972 | 1036 | 1052 | 1341 | 1506 | 1981 | 2009 | 2073 | 2089 | 2378 | 2543 | 3019 | 3047 | 3111 | 3127 | 3416 | 3581 | 4054 | 4082 | 4146 | 4162 | 4450 | 4616 | 5098 | 5126 | 5190 | 5206 | 5495 | 5662 | 6141 | 6169 | 6233 | 6254 | 6482 | |
In regards to prediction of A-domain specificity, antiSMASH predictions and the curated NRPS-PKS amino acids were the same. On the other hand, Maryland predicted did not get any hit for A6 (Leu) and for A1/A3 respectively it predicted to possible amino acids (Asn+Asp compared to Asn / Tyr + Trp compared to Tyr in antiSMASH and NRPS-PKS).
TycB3 C-A domain
| C domain | A domain | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Start | End | |
| paper primer position | 2520 (MLTAA..) | |||
| NRPS-PKS | 2100 | 2527 | 2540 | 3029 |
| Maryland | 2095 | 2518 | 2521 | 3039 |
| antiSMASH | 2096 | 2381 | 2570 | 2961 |
| pfam | 2094 | 2383 | 2550 | 3019 |
 "
"