Team:Paris Saclay/Project
From 2013.igem.org
Contents |
What are PCBs?
Nowadays, although the manufacture of PCBs ceased many years ago, because of PCBs’ high stability they are still dangerous for both the environment and human health. This is the reason why we want to accelerate the processes of Biodegradation of PCBs by using Biosynthetic method.
Chronology of PCBs
| YEAR | EVENTS |
|---|---|
| 1881 | First PCBs synthesized |
| 1927 | PCBs were first manufactured commercially |
| 1968 | Yusho disease in Japan |
| 1973 | OCDE suggested of using PCBs in close system |
| 1975 | Ban of PCBs for open-air application in France |
| 1979 | Ban of PCBs production in U.S |
| 1987 | Ban of PCBs production and usage in France |
| 1992 | OSPAR COMMISSION, made decision of abandonment of PCBs |
| 2001 | The Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants signed |
Why are PCBs persistent in the environment?
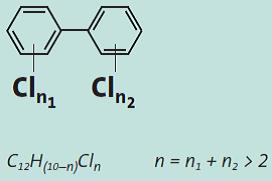
PCBs are chlorinated derivative of biphenyls which are distinguished by the number and the position of chlorines. Because of those substituted chlorines, the degradation of PCBs releases Cl- which is toxic for almost all organisms. Organisms should be capable to deal with these Cl- ion during degrading PCBs. However, some microbes are able to decompose PCBs by two series of processes: replacement of chlorine by hydrogen known as reductive dechlorination; then use these biphenyl or as a carbon source. But in a nature system, the degradation of PCBs needs a microbial community to eliminate all PCBs, these processes are extremely slow. So in our project, we try to combine these 2 processes in one cell of bacterial.
PCBs are either oily liquids or solids that are colorless to light yellow, have low solubility in water but highly soluble in organic solvents. This high lipophilicity causes PCBs to stay in animal fats and accumulate in food chain.
Where can PCBs be found today?
Chemically speaking PCBs are extremely stable with very high thermal conductivity, high boiling point (278-415 °C) and high flash points (170 to 380 °C). They were widely used in electrical equipment such as transformers and capacitors before the ban of PCBs. Nowadays, most of contaminated products and materials are sealed in special places like other dangerous chemicals. But the risk of release or exposure of PCBs always exists.
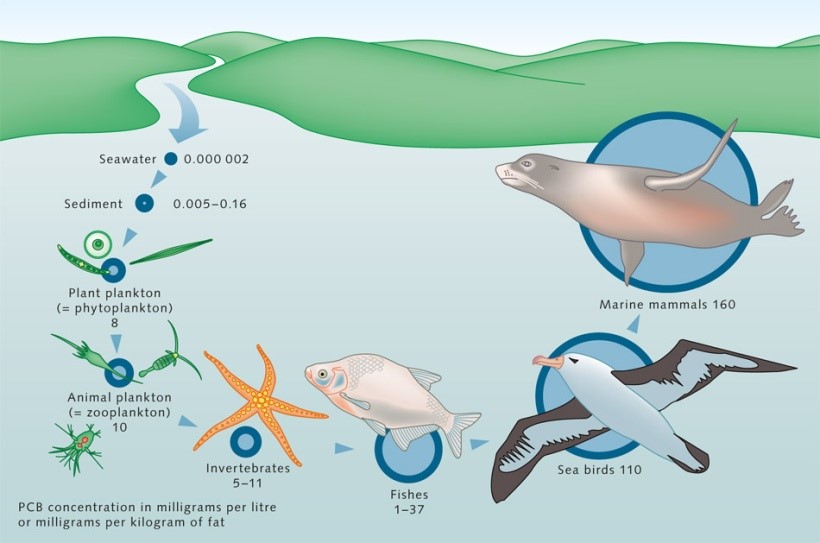
Although PCBs are no longer produced in France, but are still found in the environment. In water of Seine, PCBs are present in substantial quantities in sediments due to the high molecular weight, but they can also attach to the surface of organic matter, clay, and micro-particles so move to the overlying water when water current suspends those particles.
PCBs can also be found in organisms especially in the aquatic system. The lipophylicity of PCBs leads PCBs accumulate in animal fatty tissues, then the quantity of PCBs amplifies by the food chain. After this bioaccumulation of PCBs, the concentration of PCBs in animal or human’s body can be hundred times greater than in the food they eat.
How can PCBs affect my health?
Studies in humans provide supportive evidence for potential carcinogenic and non-carcinogenic effects of PCBs. The different health effects of PCBs may be interrelated, as alterations in one system may have significant implications for the other systems of the body.
Non-carcinogenic effects that have been associated with PCBs include acne-like skin conditions in adult and neurobehavioral and immunological changes in children. More precisely, they are:
- immune system (suppress the immune system);
- reproductive system (decrease in the number of human sperm, increase the rate of sperm deformity, increase the rate of female infertility, decrease the animal fertility, reduce the birth weight);
- nervous system (brain damage to human body, restrain brain cell synthesis, developmental delay, reduce the intelligence);
- endocrine system (decrease thyroid hormone levels, make the aquatic animals to feminization);
- Other health effects (dermal and ocular effects, liver toxicity).
PCBs can cause cancer in animals and humans. IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) has taken the polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) as a carcinogen to humans, carcinogenic effect is the major toxic effects represents by the PCBs after reaching a certain concentration in the human body.
Detection and degradation of PCB system in E.coli
Since the second half of the XXth century scientists are fully aware of the fact that some species of bacteria living in mediums with high concentrations of PCB are able to degrade the PCB in pyruvate and acetyl CoA easily metabolized by these organisms.
These species structure biofilms were there are regions with variables concentration of
oxygen, decreasing with depth to surface. The bacteria living in this habitat have in most of
case different degradation pathways namely aerobic or anaerobic depending on the spatial
disposition in the biofilm.
Bacteria in aerobic conditions use an aerobic degradation pathway, the PCB oxidative
degradation, and these in anaerobic condition the PCB reductive dechlorination; no one can
use both pathways so as to degrade the PCB.
The reductive dechlorination can reduce the number of chlorines in high chlorinated PCB
making them assimilable by the oxidative degradation, only efficient with low chlorinated
PCB. That’s the reason why these different species coexist in the biofilms.
So our goal in this project is the creation of an organism able to first detect PCB and after
employ a sequential degradation of the PCB using both combined pathways.
For our experiences we used bacteria present in nature that are able to detect and degrade the
'PCB namely Burkholderia xenovorans, Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes KF 707,
Rhodococcus jostii RHA1.'
Detection and report of the PCB
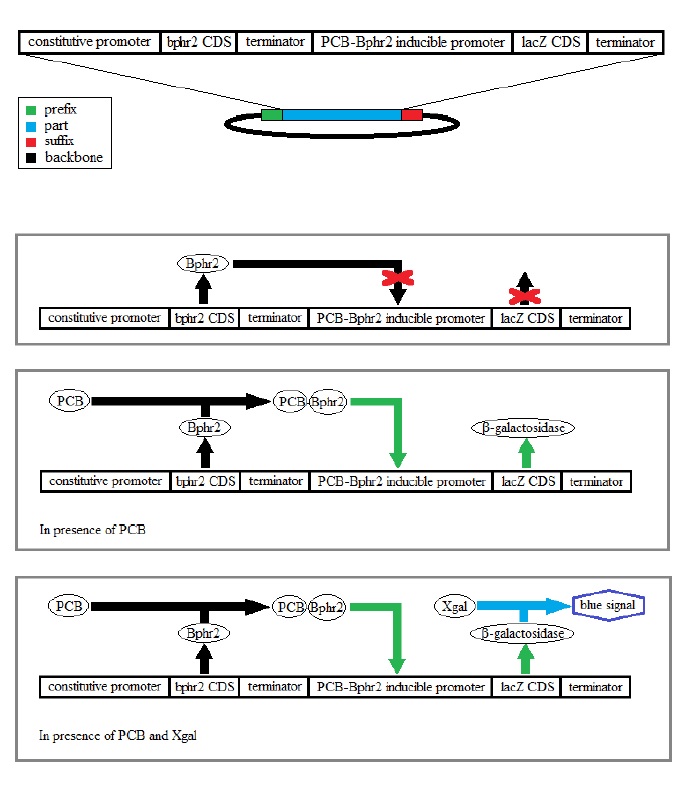
In nature these bacteria have a system for the regulation of the oxidative degradation of PCB. This one is based on two regulatory proteins namely Bphr2 and Bphr1 coded respectively by the genes of the same name bphr2 and bphr1.
Bphr2 is able to detect PCB that induces a modification of the protein conformation activating
the beginning of the gene cluster coding for the enzymes doing the oxidative degradation but
also the gene coding for the Bphr1 protein.
The Bphr1 protein can detect the HO-PCB a metabolite derived from PCB, a product of the
beginning of oxidation reactions. In presence of OH-PCB it induces his own transcription and
also the following genes from the cluster that will completely degrade the PCB.
For our construct we will pick out the bphr2 gene and the promoter of the bphr1 gene induced
by PCB-Bphr2 from our species. We will combine the bphr2 coding sequence with a
constitutive promoter that makes up the detection system and finally we will combine the
Bphr1 promoter with the lacZ gene coding for the β-galactosidase enzyme so as to do a
chemical dosing with Xgal and report the signal.
Combination of the aerobic and anaerobic PCB degradation pathways
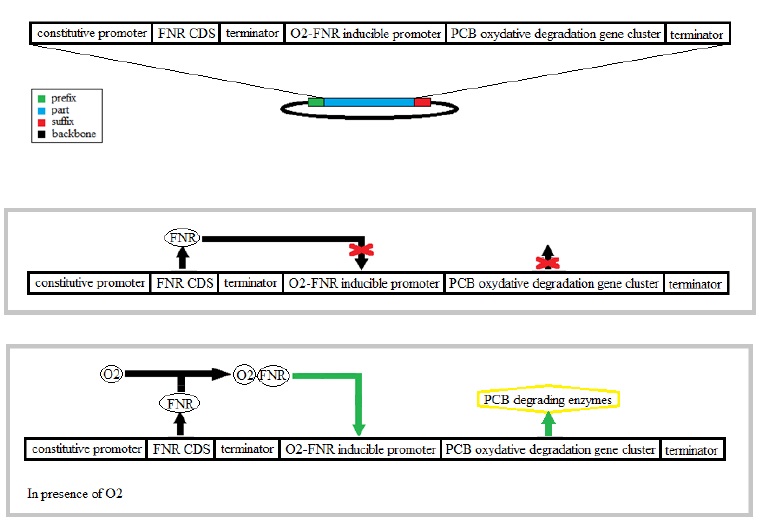
The bacteria E.coli has an aerobic and an anaerobic metabolism that’s why we used it for the combination of the two degradation pathways. The regulation between pathways in these two conditions is normally made by regulatory proteins like FNR. The FNR protein modifies its conformation in presence of oxygen having an activator or an inhibitor function.
The reductive dechlorination pathway is not well characterized only an enzyme, a
dehalogenase, is mentioned as contributing to this pathway. In these anaerobic conditions the
chlorine takes the place of the oxygen as the electron acceptor.
That’s why we have chosen an activator FNR in presence of oxygen in order to activate the
oxidative degradation.
Team project descriptions are due August 9. The description is only a preliminary description - it will not be used to judge your project. What you write will only serve to provide some background on what your team has been working on so far and what you hope to accomplish.
Description requirements:
- Describe your project on the front page of your team's wiki* or on another page that is easily reached.
- The description only needs to be a couple of paragraphs long.
*Note: The project description does not need to be emailed to iGEM HQ.
refrences:
Polycholorinated Biphenyls fact sheet, US EPA http://www.epa.gov/osw/wastemin/minimize/factshts/pcb-fs.pdf
Polychlorinated Biphenyls fact sheet 2001, ASDR(Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry)
The history of PCBs http://www.foxriverwatch.com/monsanto2a_pcb_pcbs.html#2
J.-M. BRIGNON, les PolyChloroBiphenyles 2012 INERIS( Données technico-économiques sur les substances chimiques en France)
greenFacts http://www.greenfacts.org
PCBs U.S EPA http://www.epa.gov
Amy Boate, Greg Deleersnyder, Jill Howarth, Anita Mirabelli, Leanne Peck, <Chemistry of PCBs>
http://wvlc.uwaterloo.ca/biology447/modules/intro/assignments/Introduction2a.htm
UK Marine Special Areas of Conservation Project http://www.ukmarinesac.org.uk/activities/water-quality/wq8_42.htm
The Present Situation and the Need for Solutions. http://tabemono.info/report/former/pcd/2/2_3_1/e_1.html
Heidelore Fiedler, Bavarian Institute for Waste Research - BIfA GmbH, Am Mittleren Moos 46a, D-86167 Augsburg, Germany 12. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs): Uses and Environmental Releases http://www.chem.unep.ch/pops/POPs_Inc/proceedings/bangkok/FIEDLER1.html
International Agency for Research on Cancer Agents Classified by the IARC Monographs, Volumes 1–107 http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification
Clearwater, News&Bulletins, Fact Sheet 12, <What Are The Human Health Effects Of PCBs?>
http://www.clearwater.org/news/pcbhealth.html
Criteria and Standards Division, Office of Water Planning and Standards, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Washington, B.C., Ambient Water Quality Criteria, < Polychlorinated Biphenyls>
http://nepis.epa.gov/Adobe/PDF/9100H6B7.PDF
 "
"