Team:Carnegie Mellon/KillerRed
From 2013.igem.org
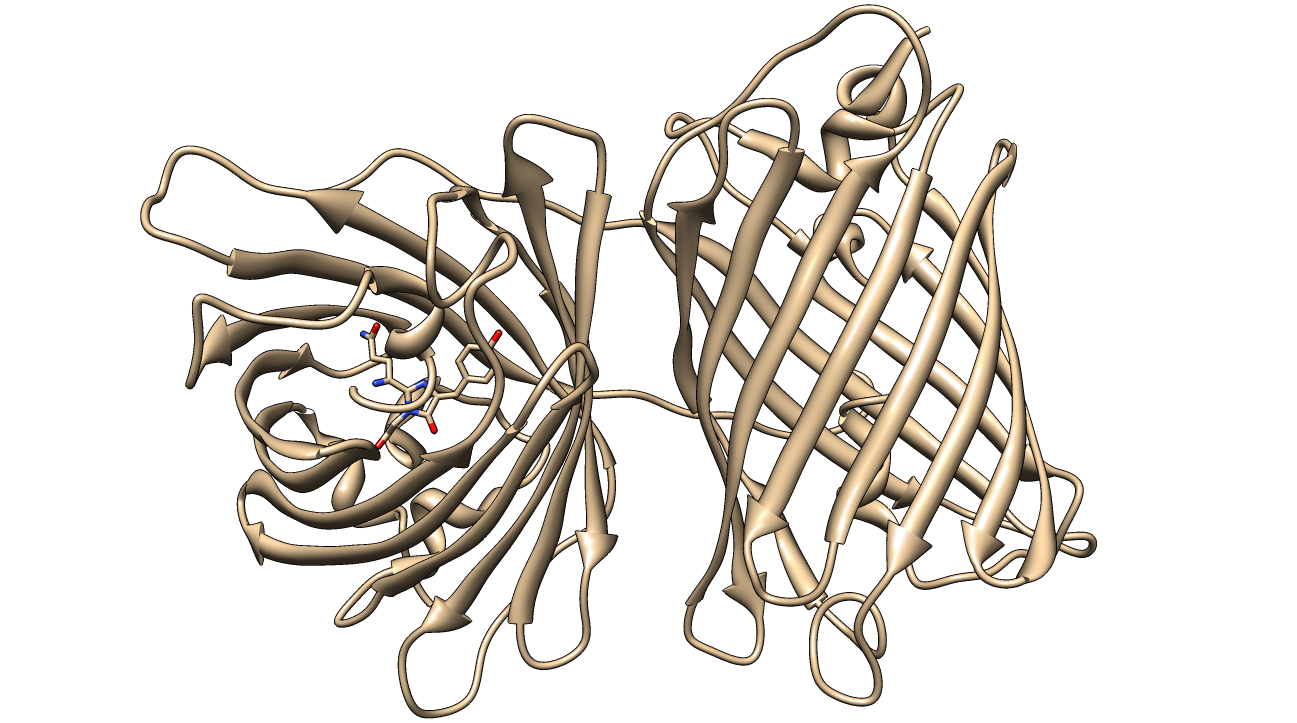
KillerRed is a red fluorescent protein that produces reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the presence of yellow-orange light (540-585 nm). KillerRed is engineered from anm2CP to be phototoxic. It has been shown that KillerRed produces superoxide radical anions by reacting with water. Superoxide reacts with the chromophore of KillerRed, causing it to become dark, which ultimately gives rise to a bleaching effect. KillerRed is spectrally similar to mRFP1 with a similar brightness. KillerRed is oligomeric and may form large aggregates in cells. Expression of KillerRed and irradiation with light may act a kill-switch for biosafety applications.
The structure of KillerRed has been analyzed and the structural basis for its toxicity has been explored. The relevant PDB IDs are 2WIQ and 2WIS for the fluorescent and dark states, respectively.
The surface of KillerRed is predominantly negatively charged. As shown in figures 3-6
[[Image:KillerRed ES1.jpg|thumb|600px|Figure 3: Electrostatic surface at 1.4 Å of KillerRed dimer (from -10 kcal/(mol*e) in red to +10 kcal(mol*e) in blue). PDB ID: 2WIQ]] [[Image:KillerRed ES2.jpg|thumb|600px|Figure 4: Electrostatic surface at 1.4 Å of KillerRed dimer (from -10 kcal/(mol*e) in red to +10 kcal(mol*e) in blue). PDB ID: 2WIQ]] [[Image:KillerRed ES3.jpg|thumb|600px|Figure 5: Electrostatic surface at 1.4 Å of KillerRed dimer (from -10 kcal/(mol*e) in red to +10 kcal(mol*e) in blue). PDB ID: 2WIQ]] [[Image:KillerRed ES4.jpg|thumb|600px|Figure 6: Electrostatic surface at 1.4 Å of KillerRed dimer (from -10 kcal/(mol*e) in red to +10 kcal(mol*e) in blue). PDB ID: 2WIQ]]
 "
"