Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Inhibition/Sensor
From 2013.igem.org


Contents |
Introduction
- After Nosema ceranae enter midgut of bee, we have to make E. coli sense this pathogen. E. coli with ROS-sensing promoters will response to Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), which is produced by infected midgut cells. The following circuit behind ROS-sensing promoters will be turned on and fight against N.cerenae.
- As for circuit design, we add a new part with a constitutive promoter [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23102 Part:BBa_J23102] and a transcription factor(OxyR or SoxR) which can activate ROS-sensing promoters, making the quantity of inactivated transcription factors more in E. coli, in order to enhance the strength of promoters.
- We improve the function of a BioBrick Part: AhpC([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 Part:BBa_K362001])designed by 2010 KIT-Tokyo team.
Background
Nosema Ceranae Induces Oxidative Stress in the Midgut.
ROS(Reactive Oxygen Species)are efficient antimicrobial molecules. Genes involved in oxidation-reduction were significantly overrepresented in the gene set upregulated upon spore infection. In response to the infection, the increase of oxidoreduction in the midgut epithelia of bees infected by N. ceranae would therefore indicate an enhanced generation of ROS. It is suggested that ROS production is a general immune response in bees' midgut to microorganism infection. There are promoters in the genome of E. coli that can be regulated by ROS. After Nosema ceranae enter midgut of bee, the regulator of promoters will be activated by ROS, trigger the following circuit fighting against Nosema ceranae.
Literature Study of ROS-induced Promoters
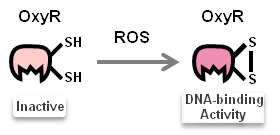
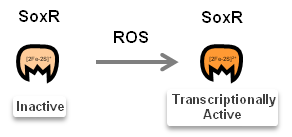
Once N.cerenae infect the midgut of bee, midgut cells of bee will secret Reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS have been shown to be toxic but also function as signalling molecules which can transcriptionally activate transcription factors: OxyR and SoxR. We focus on ROS-induced promoters regulated by either OxyR or SoxR.
Activated transcription factors, such as OxyR and SoxR, then bind to TFBS of promoters(sensor), as figures show below.
We did a study about promoters that can sense OxyR, or SoxR. Several promoters on part registry can be induced by ROS: OxyR-activated promoters such as [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 Part:BBa_K362001](AhpC promoter)and [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 Part:BBa_K362005](SufA promoter)were designed and used as favorite parts by 2010 KIT-Tokyo team. They can be controlled by OxyR. SoxR-activated part like [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K554000 Part:BBa_K554000](SoxS promoter)was designed and used as favorite parts by 2011 UNICAMP-EMSE Brazil team, which can be controlled by SoxR.
We also got the sequence and tested promoters: [http://biocyc.org/ECOLI/NEW-IMAGE?type=OPERON&object=TU0-12951&orgids=ECOLI hemH] (Figure. 1)and [http://biocyc.org/ECOLI/NEW-IMAGE?type=OPERON&object=TU0-3104&detail-level=1 trxC] (Figure. 2) ) on [http://www.ecocyc.org/ EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of Escherichia coli K-12 Genes and Metabolism]. Both of them have dual binding site only interact with OxyR, cooperate with sigma factor 70, and have no EXSP cutting site. We have designedand sent them to partregistry as new parts: [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104202 Part:BBa_K1104202]、[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104201 Part:BBa_K1104201].
Method
How Can Bee. coli Sense Nosema?
After Nosema ceranae infected midgut cells of bees, and , Bee. coli should sense the pathogen first before the following circuit(fighting against Nosema ceranae)is triggered. After Nosema ceranae infected midgut cells of bees, ROS(Reactive Oxygen Species) will be produced by midgut cells of bee and released to the cavity. As we can see, there are many kinds of promoters (and their transcription factors) responding to ROS naturally exist in E. coli MG1655 genome. We choose proper and strength enough ones from them, basing on reporting assays we made about promoetr testing. Besides, in order to enhance the strength, we designed an upstream device to enlarge the expression of the activators, so the sensitivity of Bee. coli to ROS will be sharper, and the probability of downstream circuit(fighting against Nosema ceranae) being turned on.
Circuit Design
There are two kinds of circuit: OxyR-included circuit and SoxR-included circuit, depending on the categories of promoters controled by different transcription factor. In order to enhance the strength and sensitivity of ROS-sensing promoters, we make E. coli continuously produce inactivated OxyR or SoxR, so that ROS can affect promoters more easily.
OxyR-included circuit
This is one kind of the two circuits--OxyR-included circuit. Device1 is composed of a sensor (OxyR-induced promoter, including TrxC, HemH, SufA, AhpC(mutated), AhpC2D1, AhpC2, AhpCD1, AhpC1, DsbG) plus reporter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0840 Part:BBa_E0840]). Device2 in order to enhance the effect of ROS on E. coli is added ahead: a constitutive promoter([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23102 Part:BBa_J23102]), RBS([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034 Part:BBa_B0034]), activator OxyR([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104200 Part:BBa_K1104200]),and double terminator [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015 Part:BBa_B0015].Parts
OxyR-activated promoters
SoxR-included circuit
This is the other kind of the two circuits--SoxR-included circuit. The deference is activator: in this circuit OxyR is replaced with SoxR. The construct is initially built by 2011 UNICAMP-EMSE Brazil team. We made some replacement to the original circuit: the constitutive promoter, double terminator, and a reporter[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0840 Part:BBa_E0840] downstream the promoter. It is also composed of 2 devices:One is a sensor SoxS([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K554003 Part:BBa_K554003]) plus reporter ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_E0840 Part:BBa_E0840]). The other device is a constitutive promoter([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23102 Part:BBa_J23102]), RBS([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034 Part:BBa_B0034]), activator SoxR([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K554003 Part:BBa_K554003]),and double terminator [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015 Part:BBa_B0015].Disscussion
We test only Device2, as well as Device1+Device2. And the results of OxyR-induced promoters testing on PartRegistry are linked below:
- TrxC ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104201:Experience Part:BBa_K1104201:Experience])
- HemH ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104202:Experience Part:BBa_K1104202:Experience])
- SufA ([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience])
- AhpC(mutated)([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104203:Experience Part:BBa_K1104203:Experience])
- AhpC2D1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104204:Experience Part:BBa_K1104204:Experience])
- AhpC2([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience])
- AhpCD1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104206:Experience Part:BBa_K1104206:Experience])
- AhpC1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104207:Experience Part:BBa_K1104207:Experience])
- DsbG([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104208:Experience Part:BBa_K1104208:Experience])
The same as SoxR-induced promoter testing, we test Device2 and Device1+Device2. The construct is initially built by 2011 UNICAMP-EMSE Brazil team. We tested the Device with hydrogen peroxide instead of Paraquat(both of them are ROS). Besides, we made some replacement to the original circuit. The edited results of SoxR-induced promoters testing on PartRegistry: SoxS([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K554000:Experience Part:BBa_K554000:Experience]).
Part Improvement
We improve the function of a BioBrick Part: AhpC promoter([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 K362001])designed by 2010 KIT-Tokyo team into four versions.On PartRegistry, the complex part(Figure. 3) according to [http://ecocyc.org/ECOLI/new-image?object=EG11384 Ecocyc]composition contains hybrid promoters, shared TFBS (Transcription Factor Binding Site), and reverse promoter DsbG. The intergenic region between dsbG and ahpC carries two binding sites for OxyR, a dsbG-proximal site, located 54 bp upstream of the dsbG start codon, and an ahpC-proximal site, located 290 bp upstream of the dsbG start codon.

OxyR binding to the ahpC-proximal site leads to the induction of both dsbG and ahpC transcripts, while OxyR binding to the dsbG-proximal site leads to the induction of a second ahpC transcript. This transcript of ahpC and the transcript of dsbG overlap by over 100 nucleotides.
Because AhpC promoter([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 Part:BBa_K362001]) on PartRegistry is a hybrid promoter containing AhpC1, AhpC2, and DsbG promoter in its 1000bp, we create the new part and test it apart.
Disscussion
As the results shows, we successfully improved AhpC promoter([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K362001 Part:BBa_K362001]). And the results and disscussion on PartRegistry are linked below:
- AhpC(mutated)([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104203:Experience Part:BBa_K1104203:Experience])
- AhpC2D1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104204:Experience Part:BBa_K1104204:Experience])
- AhpC2([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience Part:BBa_K1104205:Experience])
- AhpCD1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104206:Experience Part:BBa_K1104206:Experience])
- AhpC1([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104207:Experience Part:BBa_K1104207:Experience])
- DsbG([http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104208:Experience Part:BBa_K1104208:Experience])
Reference
- Dussaubat, Claudia, Brunet, Jean-Luc, Higes, Mariano, Colbourne, John K., Lopez, Jacqueline, Choi, Jeong-Hyeon, Martín-Hernández, Raquel, ... Alaux, Cédric. (n.d.). Gut Pathology and Responses to the Microsporidium Nosema ceranae in the Honey Bee Apis mellifera. Public Library of Science.
- D'Autréaux, B., & Toledano, M. B. (January 01, 2007). ROS as signalling molecules: mechanisms that generate specificity in ROS homeostasis. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 8, 10, 813-24.2[http://www.nature.com/nrm/journal/v8/n10/fig_tab/nrm2256_F1.html]
- Ryu, S. E. (June 01, 2012). Structural mechanism of disulphide bond-mediated redox switches. Journal of Biochemistry, 151, 6, 579-588.[http://jb.oxfordjournals.org/content/early/2012/05/02/jb.mvs046.full.pdf]
 "
"