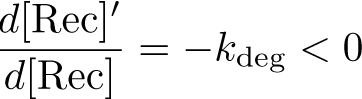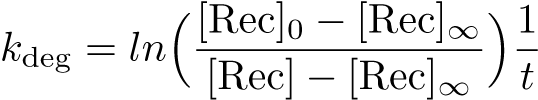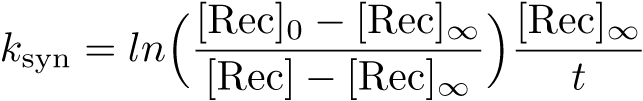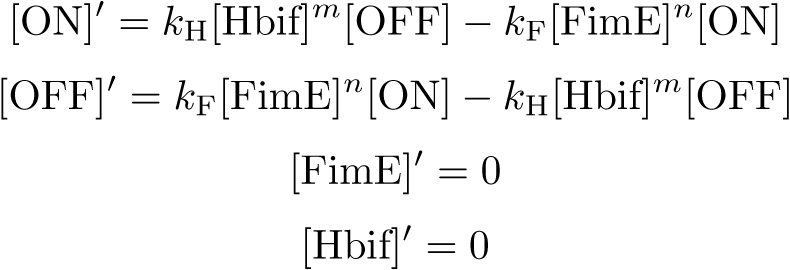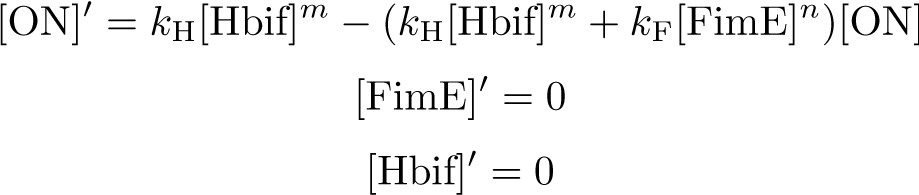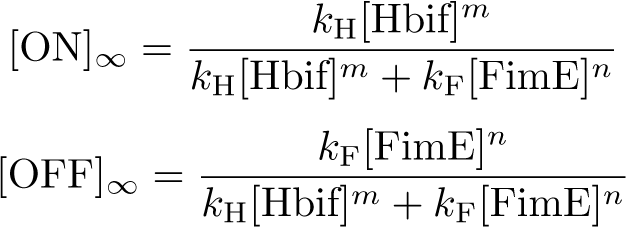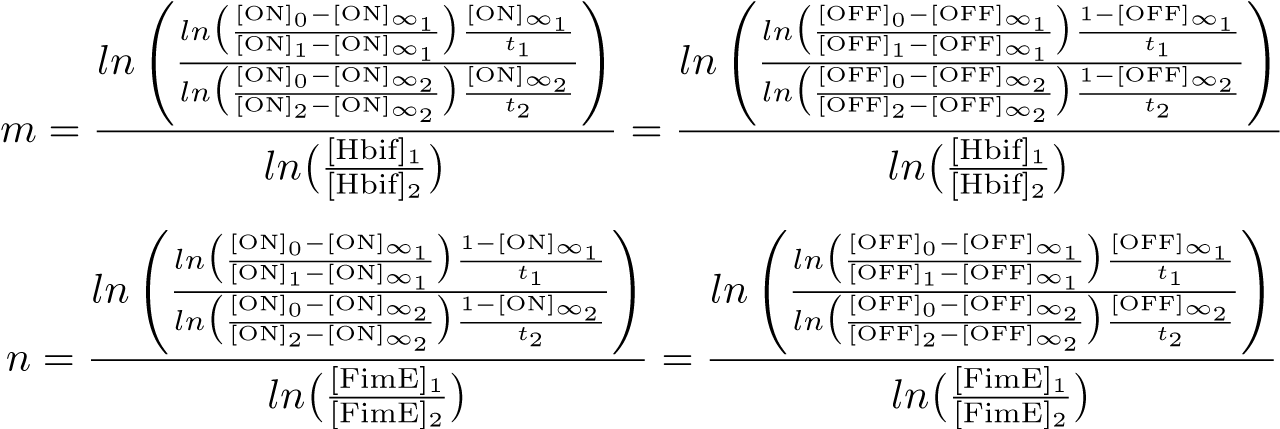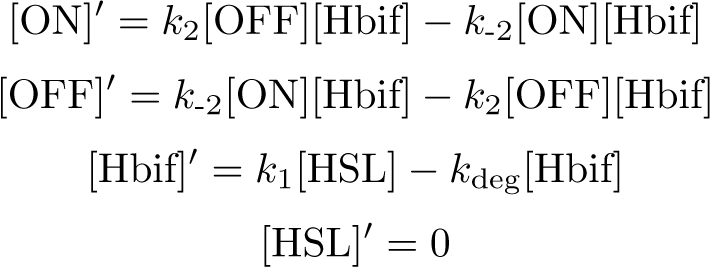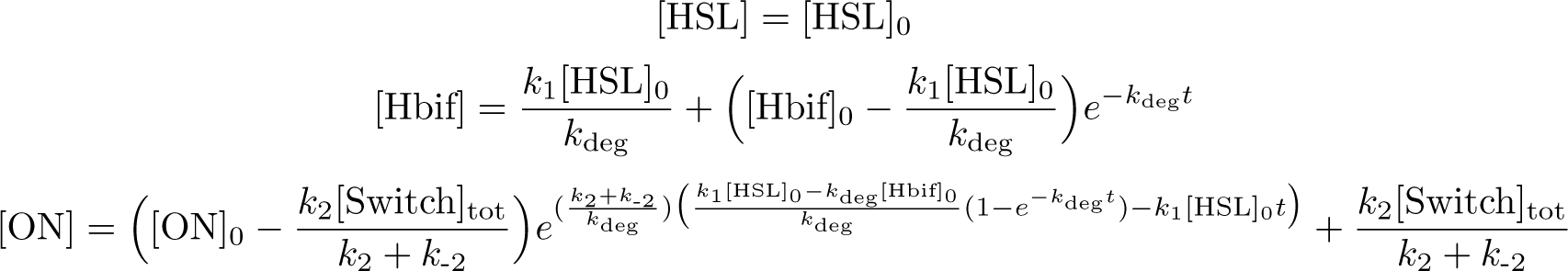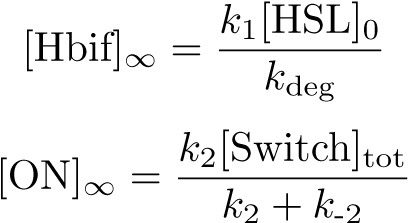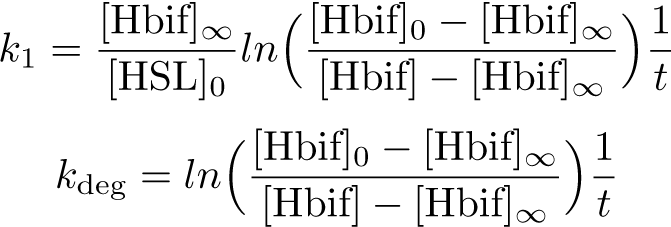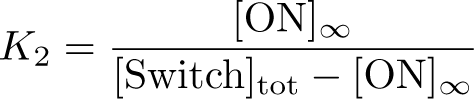Team:Michigan/Modeling
From 2013.igem.org
Contents |
Introduction
Switch modeling
• produce both states of switch
• use model to optimize switch
Mass action modeling
Definition
• differential equations
• each equation is a sum of rates
• each rate is proportional to each of its reactants
Benefits of mass action modeling, i.e. why we used it
• form of mass action models/solvability doc
Analytical modeling
• benefits
• naturally standardized • given parameters, it precisely predicts behavior
• accurately predicts the data needed to determine parameters
• allows avoidance of numerical errors like rounding
• ERSESCO
• equation
• reduction
• solution
• equilibration
• stabilization
• calibration
• optimization
SimBiology
• numerical approximation
• diagram / schematic
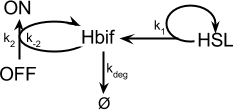
Model of Recombinase Expression
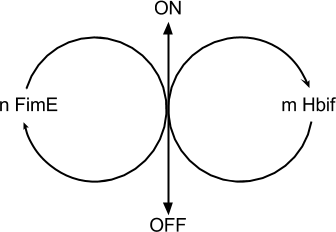
Model of the Switch
Model of Inducible Hbif
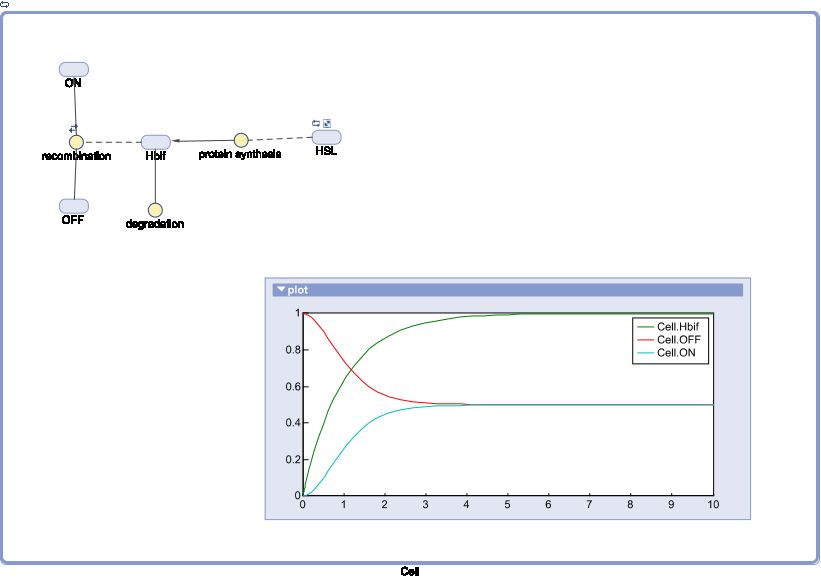
The Inducible Hbif Model describes how the switch flips when acted upon by the Lux/HSL-controlled expression of Hbif. In this model, [HSL] represents the concentration of the species HSL:pLux:LuxR, the complex that promotes the expression of Hbif. In this model [HSL] is a function of pLux and LuxR expression levels in the cell, the amount of HSL added, and the fractional occupancies at the complexation equilibrium. It can be assumed that this complexation reaction happens instantaneously with respect to the slow, rate-limiting translation step of Hbif.
Expression Model
Equation:
Reduction: None
Solution:
Equilibration:
Stabilization:
Calibration:
Optimization:
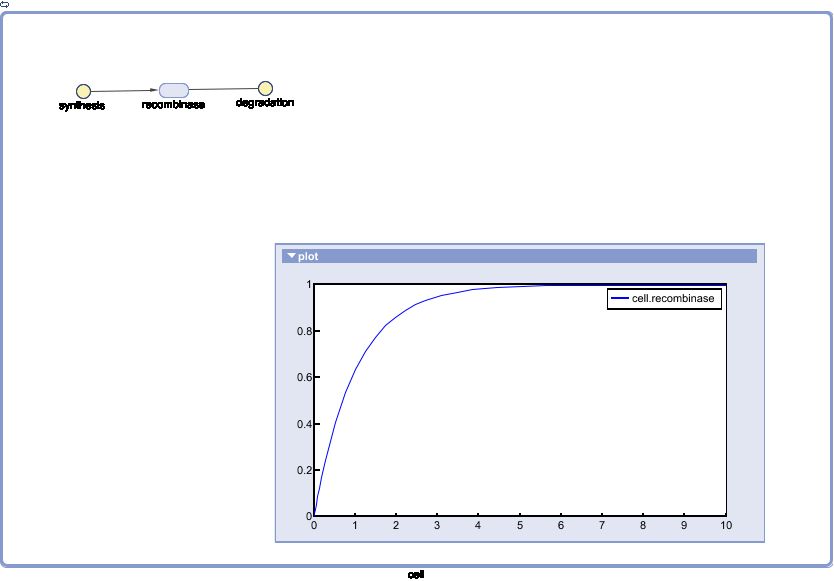
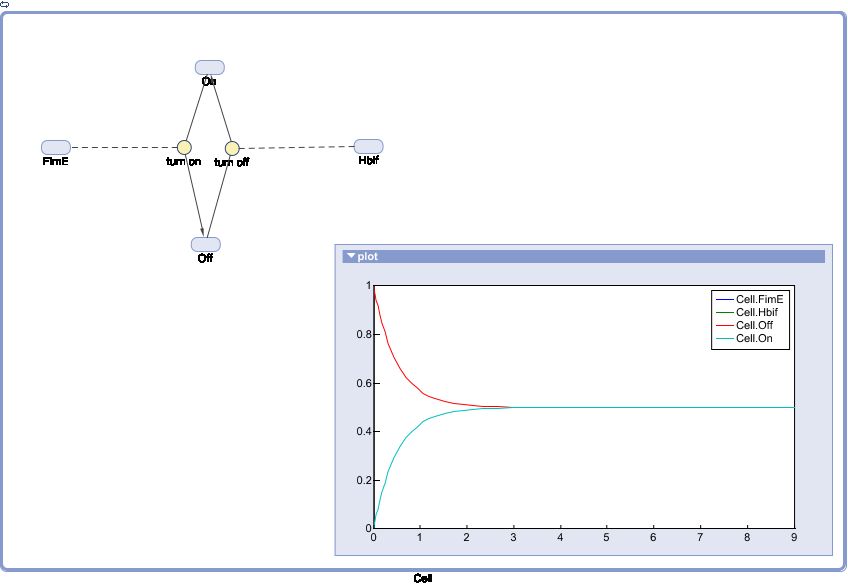
SimBiology:
Switch Model
Equation:
Reduction:
Solution:
Equilibration:
Stabilization:
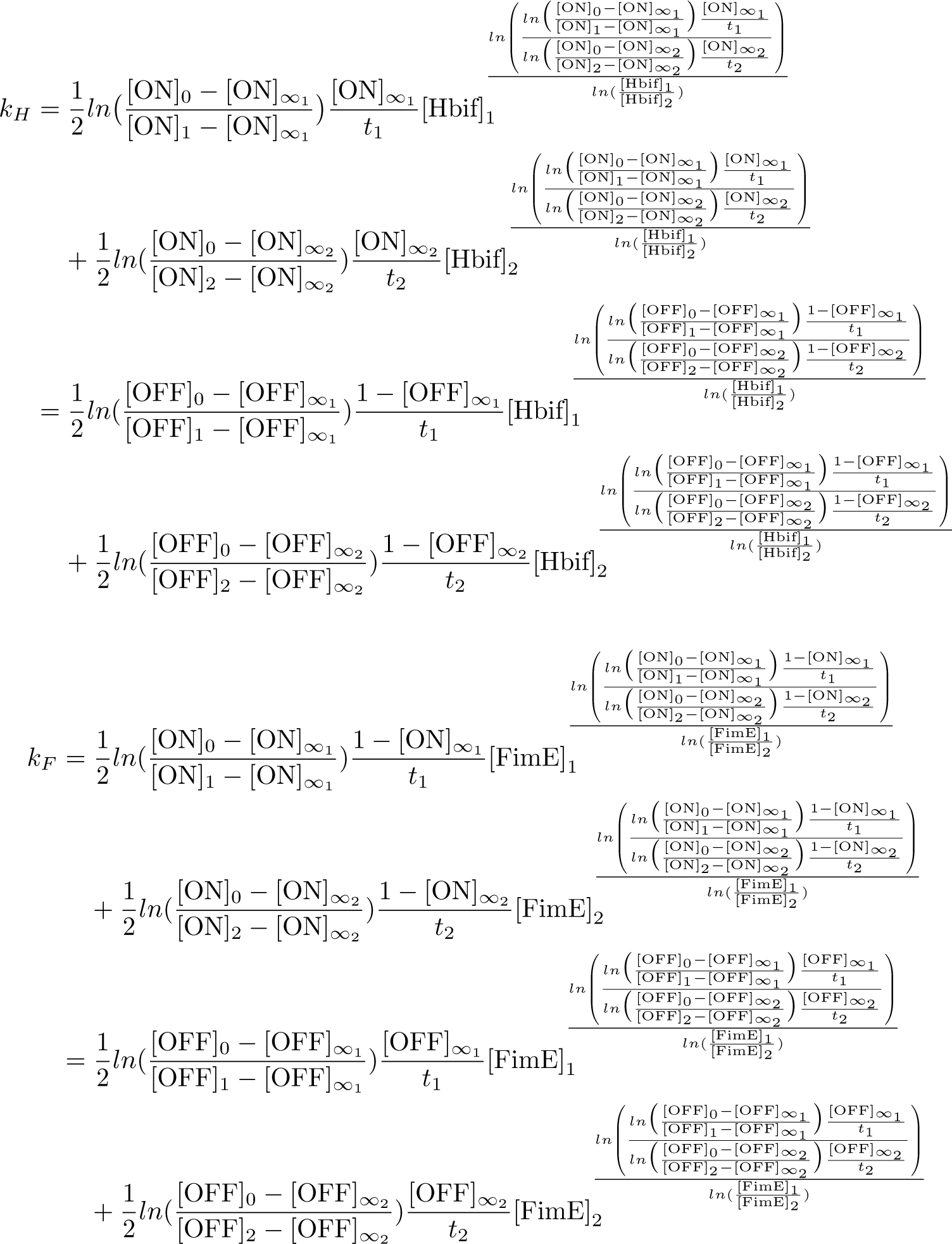
Calibration:
Optimization:
SimBiology:
Inducible Hbif Model
Equation:
Reduction:
Solution:
Equilibration:
Stabilization:
Calibration:
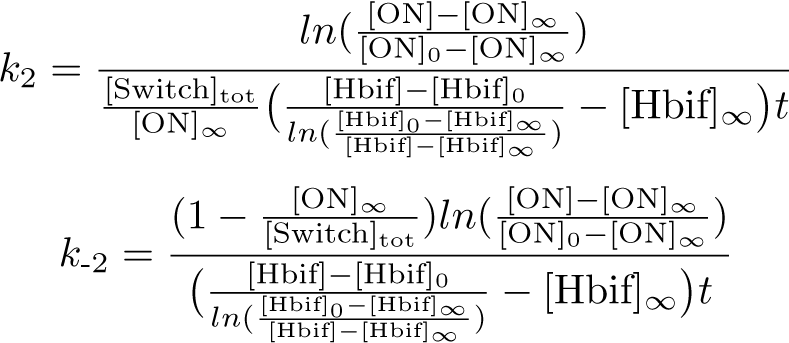
Optimization of Hbif:
Optimization of ON:
SimBiology:
Inducible Hbif Model Derivation
Future Directions
Data!
| Home | Team | Official Team Profile | Project | Parts Submitted to the Registry | Modeling | Notebook | Safety | Attributions |
|---|
 "
"