Team:Groningen/Project/Coating
From 2013.igem.org
Coating
Overview
Coating the implant is one of the last steps of our plan. Here is an overview of what we would have up to this point:
- Backbone with IPTG inducable promoter for tranformation of Bacillus subtilis
- Spider silk genes put together with various components and separately put into backbones
- Our Bacillus subtilis immobilizes near heat
With our engineered B. subtilis possessing all the desired genes and modifications, we can put it to work in our coating setup.
Setup
Our setup consists of the following components:
- A large, deep and circular bath To contain enough volume for a large culture
- Suitable growth medium for our B. subtilis strain Perhaps with agar
- Fine bubble aeration Bacillus is a very aerobic bacterium. This system facilitates thorough and gentle aeration. The small bubbles will diffuse enough when released from below the deep bath.
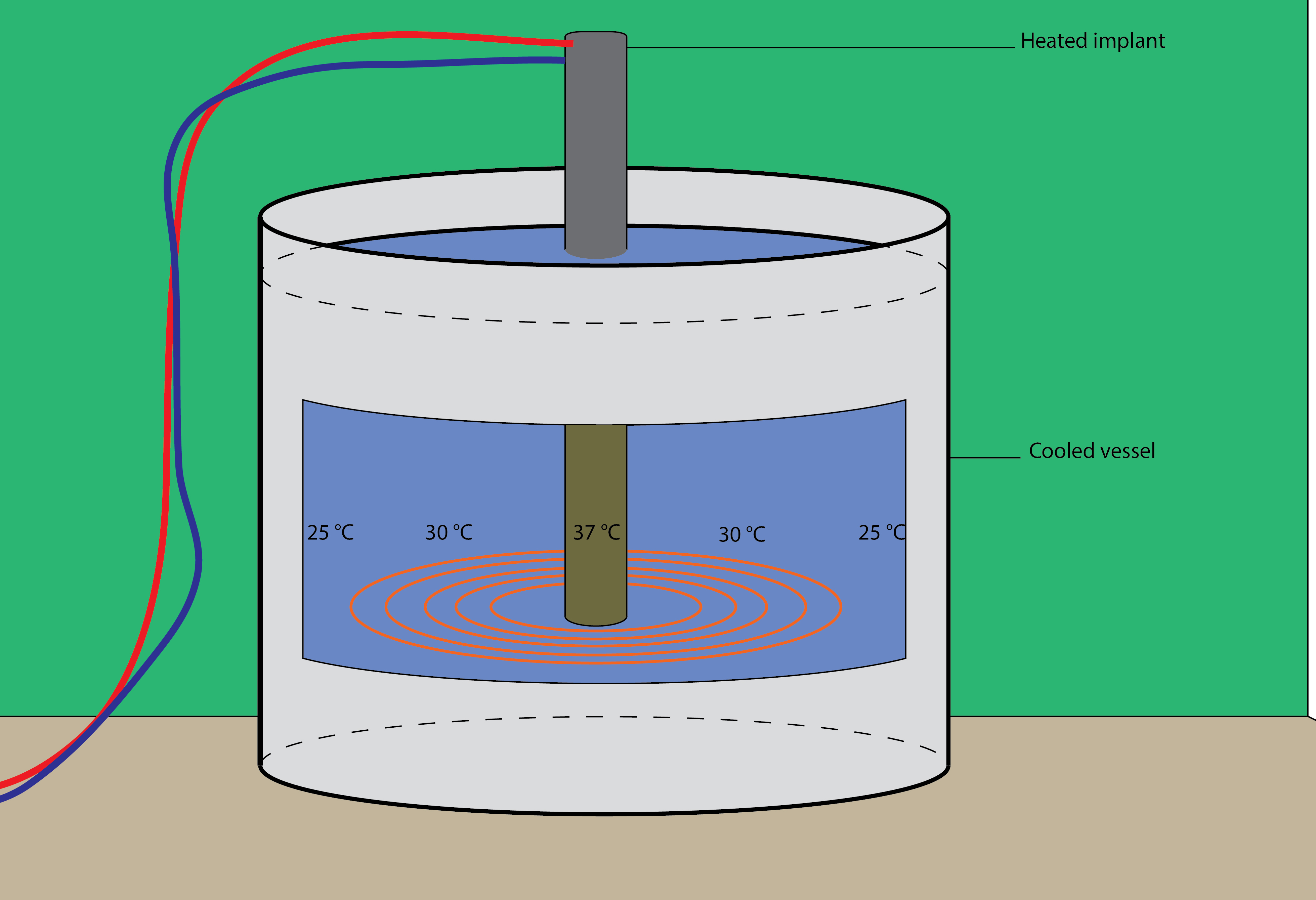
- A heated implant hanging inside and in the centre of the bath This is what we want to coat. As the implant is providing a temperature gradient, no heating of the medium is required, saving energy that would be spend on heating the enitre bath.
Remarks
Before going into the proposed procedures, it should be noted that this page covers aspects of our hypothetical situation. It is how we planned to proceed if the engineering of our B. subtilis would have been achieved earlier in our project. However, instead of assuming everything works as we intended, which would be the ideal situation, we have designed alternative procedures. These alternative procedures are adapted to the lack of a certain component, an assumption we make in our ideal situation, such as secretion of the spider silk protein.
Procedure 1 - Ideal situation
Step 1
Initially the B. subtilis cells are grown in liquid medium (LB) at 37 °C until the culture is in the early exponential phase.
This can be detected as the culture is rapidly increasing in number of cells, while the total number of cells is still relatively low.
Step 2
The cells are moved to the big volume of our setup, where The cells move around and grow further, though should still be in the exponential phase.
Influenced by the temperature gradient most cells should lose their ability to move near the implant.
This results in accumulation of cells in the heated area close to the implant.
Step 3
Expression of the spider silk protein is stimulated by addition of IPTG to the medium.
The secreted spider silk will attach to the implant.
Step 4
...
Procedure 2 - No silk secretion
Step 1
Initially the B. subtilis cells are grown in liquid medium (LB) at 37 °C until the culture is in the early exponential phase.
This can be detected as the culture is rapidly increasing in number of cells, while the total number of cells is still relatively low.
Step 2
The cells are moved to the big volume of our setup, where the cells move around and grow further, though should still be in the exponential phase.
Influenced by the temperature gradient most cells should lose their ability to move near the implant.
This results in accumulation of cells in the heated area close to the implant.
Step 3
Expression of the spider silk protein is stimulated by addition of IPTG to the medium.
The secreted spider silk will attach to the implant.
Step 4
...
Whole setup:(FRISO)
Spider Silk
Localizing the cells near the implant
Secretion or lysis approaches
Binding to streptavidin coated implant
Polymerization and sterilization
Old page silk secretion
 "
"