Results
Over the summer Team Magneto worked hard and some of the preset goals were successfully accomplished. Here we show and explain you our main results.
Quick Overview
MamC-eGFP: the functionality of the eGFP part of the fusion was proven, regarding the MamC part only the expected size of the protein could be shown
MamC alone couldn’t be further characterized
eGFP: the functionality and autenticity of the protein could be shown
eFbFP: the submitted BioBrick couldn’t be successfully characterized
MamC-eGFP
MamC (BBa_K1094001) from Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum (MS-1) was tagged with enhanced green fluorescent protein (eGFP, BBa_K1094400). Between the parts a glycine linker (10 glycine residues) is added. The gene product can be used to detect localization of MamC in MS-1. The two parts were cloned together using classical cloning into pJAM1786 in E. coli. Colony PCR and gel electrophoresis was performed to ensure the insert was in the vector (Fig.1).
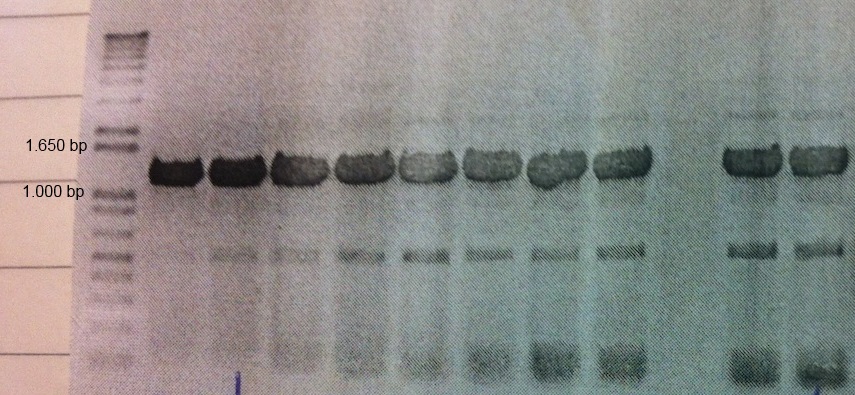
 "
"


