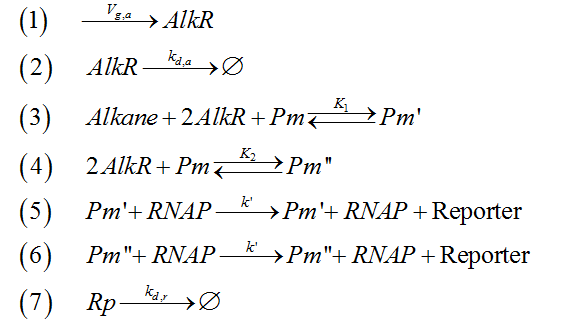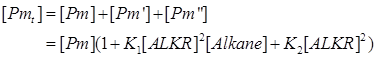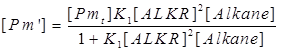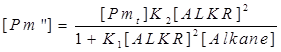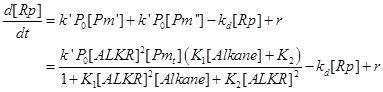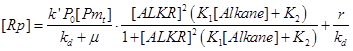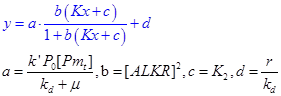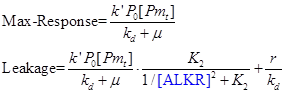Team:Tianjin/Modeling
From 2013.igem.org
(→Analysis & Discussion) |
|||
| (120 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| - | *{margin:0;padding:0;font-family:"微软雅黑"," | + | *{margin:0;padding:0;font-family:"微软雅黑","Times New Roman";} |
body{ | body{ | ||
| Line 18: | Line 13: | ||
font-size:12px; | font-size:12px; | ||
font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; | font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif; | ||
| + | background-color:#fff; | ||
} | } | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | h2,h3,h4,h5,h6{ | |
| - | + | border:none;} | |
| - | + | ||
p {margin:0.5em 0 !important; | p {margin:0.5em 0 !important; | ||
text-decoration:none; | text-decoration:none; | ||
| - | font-family: | + | font-family:Times New Roman, Helvetica, sans-serif; |
font-size:12px; | font-size:12px; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 31: | Line 27: | ||
width:960px; | width:960px; | ||
height:10px; | height:10px; | ||
| - | margin-top: | + | margin-top:0px; |
} | } | ||
.logo-section{ | .logo-section{ | ||
| - | + | height:220px; | |
| - | height: | + | |
width:960px; | width:960px; | ||
position:relative; | position:relative; | ||
float:left; | float:left; | ||
margin-top:5px; | margin-top:5px; | ||
| + | background:url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/igem.org/1/16/Tju-Project-banner.jpg) no-repeat; | ||
} | } | ||
.note{ | .note{ | ||
| Line 47: | Line 43: | ||
margin-top:10px; | margin-top:10px; | ||
position:relative; | position:relative; | ||
| - | background-color:# | + | background-color:#fff; |
padding:0; | padding:0; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 54: | Line 50: | ||
min-height:200px; | min-height:200px; | ||
float:left; | float:left; | ||
| - | + | background-color:#fff; | |
| - | background-color:# | + | |
margin-top:0px; | margin-top:0px; | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 66: | Line 61: | ||
padding:30px 10px 10px 30px; | padding:30px 10px 10px 30px; | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
#footer{ | #footer{ | ||
margin:0 auto; | margin:0 auto; | ||
| Line 74: | Line 70: | ||
float:left; | float:left; | ||
} | } | ||
| - | #goTopBtn | + | |
| - | + | #goTopBtn | |
| - | + | {POSITION: fixed;TEXT-ALIGN: center;LINE-HEIGHT: 30px;WIDTH: 100px;BOTTOM: 35px;HEIGHT: 100px;FONT-SIZE: 12px;RIGHT: 30px;} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | #globalWrapper{ | |
| - | + | width:960px; | |
| - | + | height:auto; | |
| - | + | background-color:#fff; | |
| - | + | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 89: | Line 84: | ||
.hidden {display:none;} | .hidden {display:none;} | ||
#p-logo,#footer-box {display:none;} | #p-logo,#footer-box {display:none;} | ||
| - | #top-section { | + | #top-section {border:none;height:15px;} |
.firstHeading {display:none;} | .firstHeading {display:none;} | ||
#bodyContent{display:none;} | #bodyContent{display:none;} | ||
| Line 96: | Line 91: | ||
#search-controls{display:none;} | #search-controls{display:none;} | ||
.printfooter{display:none;} | .printfooter{display:none;} | ||
| - | + | #catlinks{display:none;} | |
| + | #content{background:none;padding:0px;margin-top:0px;border:none;} | ||
| + | #toc{display:none;} | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| - | |||
<!--content section--> | <!--content section--> | ||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| - | + | .sddm{z-index: 30;width: 960px;height:65px;position:relative;float:left;background-color:#FFF;position:raletive;margin-left:0px;} | |
| - | { margin-left: | + | .sddm ul{margin-left:0px;} |
| - | + | .sddm li{margin: 0;list-style: none;float: left;font: bold 14px arial;height:25px;background-color:#FFF;} | |
| - | + | .sddm li a{display: block;margin:0;padding: 15px 0px 15px 0px;width: 96px;background: #FFF;color: #000;text-align: center;text-decoration: none;border-top:#ececec 5px solid;} | |
| - | + | .sddm li a:hover{background:#FCFCFC;color:#0babe7;border-top:#0babe7 5px solid;} | |
| - | + | .sddm div{position: absolute;width:96px;z-index:999;visibility: hidden;margin: 0;padding: 0;} | |
| - | + | .sddm div a{position: relative;display: block;margin: 0;padding: 5px 5px;width: auto;white-space: nowrap;text-align:center;text-decoration: none;color: #000;font: 12px arial} | |
| - | + | .sddm div a:hover{background:#FAFAFA;color: #0babe7;} | |
| - | + | </style> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | + | <div class="cont1"> | |
| - | + | <ul class="sddm"> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <style type="text/css"> | |
| - | { | + | .A-C{font-size:12px !important;padding-top:0 !important;text-align:center;line-height:100%} |
| - | + | .HP{font-size:14px !important;padding-top:0 !important;text-align:center;} | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Home</a> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Project" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Project</a> | |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Safety " style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Safety</a> | |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Modeling" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Modeling</a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Protocol" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Protocol</a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li class="HP"><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Human Practice" style="padding:14px 0px 13px 0px;">Human Practice</a> |
| + | </li> | ||
| + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Data" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Data</a> | ||
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Notebook" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Notebook</a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
| - | <li><a href=" | + | <li><a href=" https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Team" style="padding:20px 0px 15px 0px;height:30px;">Team</a> |
</li> | </li> | ||
| + | <li class="A-C"><a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:Tianjin/Attributions" style="padding:7px 0px 7px 0px;">Attributions<br/>&<br/>Contributions</a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="content-section"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="logo-section"> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="note1"> | ||
| + | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| + | .box{ width:960px; margin:0 auto; overflow:hidden;} | ||
| + | .main{ width:720px; height:auto; float:right;position:relative;padding:10px 10px 10px 10px;} | ||
| + | .fixed{ width:220px; height:400px; font:normal; text-align:center;float:left;word-spacing:0.1em;top:10px;margin-top:10px;} | ||
| + | .main img{border:hidden;margin-bottom:5px;} | ||
| + | .main div,li,p{font-family:Arial;line-height:150%;word-spacing:0.1em;} | ||
| + | .main li{list-style:disc;} | ||
| + | |||
| + | .box p{color:#000;font-family:Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;font-size:14px;line-height:150%;text-align:left; clear:both;} | ||
| + | .box h1{text-decoration:none;font-weight:normal;color:#0babe7;} | ||
| + | .img1{margin:0 150px 15px 150px;padding:5px 5px 5px 5px;background-color:#fafafa;border:thin solid #999; vertical-align:middle;width:400px;} | ||
| + | .img1 a{target="_blank";} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | </style> | ||
<script type="text/javascript"> | <script type="text/javascript"> | ||
| Line 200: | Line 177: | ||
$(window).scroll(function(e){ | $(window).scroll(function(e){ | ||
s = $(document).scrollTop(); | s = $(document).scrollTop(); | ||
| - | if(s > t - | + | if(s > t - 70){ |
$('.fixed').css('position','fixed'); | $('.fixed').css('position','fixed'); | ||
| - | if(s + fh - | + | if(s + fh - 2000 > mh){ |
$('.fixed').css('top',mh-s-fh+'px'); | $('.fixed').css('top',mh-s-fh+'px'); | ||
} | } | ||
| Line 212: | Line 189: | ||
</script> | </script> | ||
| - | <div class=" | + | |
| + | |||
| + | <div class="box"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <div class="sub"> | ||
| + | <div class="fixed"> | ||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| - | . | + | li{margin-bottom:0px;} |
| - | . | + | .cont ul,li{list-style: none;} |
| - | . | + | .cont ul {padding: 0; margin: 0;text-align:center;} |
| - | . | + | .cont .hmain{background-color:#0babe7 ;width: 220px;font-size:16px;float: left;border-top:#fff thin solid;border-bottom:#fff thin solid;} |
| - | + | ||
| - | . | + | .cont a {text-decoration: none; /* padding-left: 10px;*/ display: block; display: inline-block; width: 220px;padding-top: 7px;padding-bottom: 7px;} |
| - | + | .cont .hmain a{color:#fff; } | |
| - | + | .cont .hmain a:hover{color:#0babe7;background:#fff;border-top:#0babe7 thin solid;border-bottom:#0babe7 thin solid; } | |
| - | + | .cont .hmain ul {display: none;} | |
| - | } | + | .cont .hmain li a{font-size:14px;color:#fff;background-color:#8dc7e9;line-height:150%;border:#fff thin solid ;} |
| - | . | + | .cont .hmain li a:hover{color:#8dc7e9;background:#fff; line-height:150%;border:#8dc7e9 thin solid ;} |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
| - | < | + | <script type="text/javascript"> |
| - | + | $(document).ready(function(){ | |
| - | + | $(".hmain").hover(function(){ | |
| - | + | $(this).children("ul").slideDown(); | |
| - | + | changeIcon($(this).children("a")); | |
| - | + | },function(){ | |
| - | + | $(this).children("ul").slideUp(); | |
| - | + | changeIcon($(this).children("a")); | |
| - | + | }); | |
| - | < | + | }); |
| - | < | + | </script> |
| - | + | <div class="cont"> | |
| - | <ul> | + | <ul> |
| - | < | + | <li class="hmain" style="margin-top:20px;"> |
| - | + | <a href="#Model_Objective">Model Objective</a> | |
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | <li class="hmain"> | |
| - | + | <a href="#Problem_Description">Problem Description</a> | |
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | <li class="hmain"> | |
| - | <a href="#" > | + | <a href="#Problem_Abstraction">Problem Abstraction</a> |
| - | < | + | </li> |
| - | < | + | <li class="hmain"> |
| - | <a href="#" | + | <a href="#Assumption">Assumption</a> |
| - | < | + | </li> |
| - | + | <li class="hmain"> | |
| - | </ | + | <a href="#Model_Development">Model Development</a> |
| - | < | + | </li> |
| - | < | + | <li class="hmain"> |
| - | < | + | <a href="#Analysis_.26_Discussion">Analysis & Discussion</a> |
| - | < | + | </li> |
| - | + | <li class="hmain"> | |
| - | < | + | <a href="#Achievement">Achievement</a> |
| - | + | </li> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| + | <li> | ||
| + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Main_Page" title="Main Page"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/75/IGEM-logo-blue.png" width="200px" height="200px" border="none" /></a> | ||
| + | </li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | < | + | |
| - | </p> | + | |
| + | <div class="main"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | <center><span style="font-family:Arial;font-size:45px;color:#000;"> Mathematic Analysis on AlkSensor </span></center> | ||
| + | <br/> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | = Model Objective = | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | To perform a mathematic analysis on AlkSensor, to find out the relationship between AlkSensor’s input and output, to find ways to specifically regulate the function of AlkSensor, to find the factors affecting sensor’s leakage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Problem Description= | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
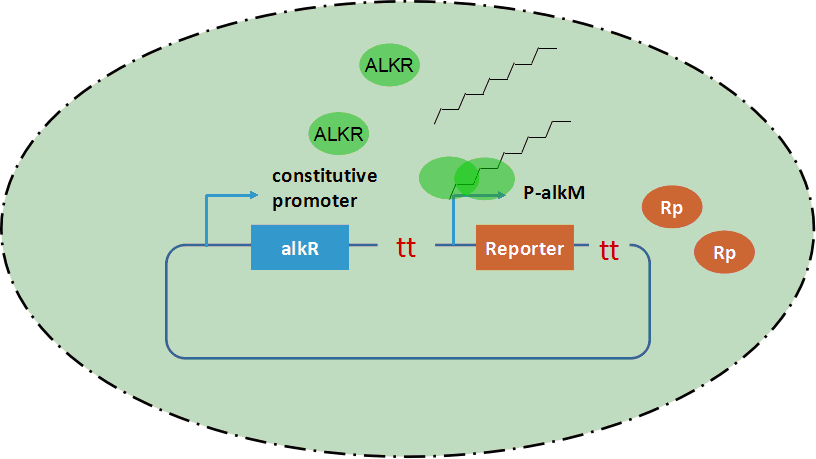
| + | AlkSensor is composed of protein ALKR and promoter alkM. Genes of ALKR and alkM were synthesized and constructed into a plasmid, as shown in figure 1. As mentioned in the introduction, protein ALKR is a transcription factor which can recognize certain alkanes. ALKR is under a constitutive promoter and is constitutively expressed. Alkane molecules is recognized by ALKR and a dimerized ALKR-alkane complex is formed. Subsequently the reporter’s promoter alkM is induced by the complex and the genes in the downstream of alkM are expressed. However, promoter alkM could also be slightly induced when inducers are absent from the system. There are possibilities that dierized ALKR binds on promoter alkM and activates the downstream genes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Modeling-01.png|thumb|600px|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> Scheme of AlkSensor’s mechanism]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Problem Abstraction= | ||
| + | <br> | ||
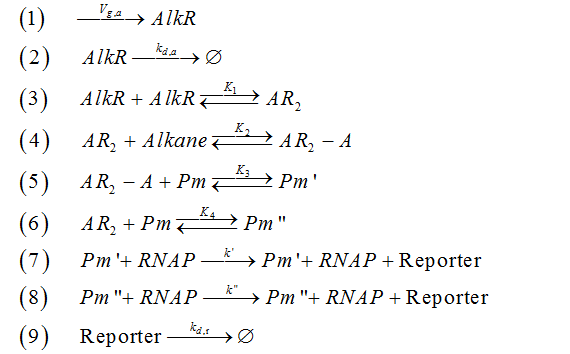
| + | The mechanism of AlkSensor can be represented by a set of chemical reactions, as shown below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-11.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><b>Figure 2.</b> Chemical reactions of AlkSensor</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 1: the generation of protein ALKR. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 2: the degradation of protein ALKR | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 3: the dimerization of protein ALKR(AR2-A denotes the dimerized ALKR-alkane complex) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 4: the combination of dimerized ALKR with alkane(Pm denotes promoter alkM) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 5: the combination of dimerized ALKR-alkane complex with promoter alkM(Pm’ denotes the promoter alkM binding with inducer) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 6: the combination of dimerized ALKR with promoter alkM(Pm’’ denotes the promoter alkM binding with dimerized ALKR) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 7: the generation of reporter (RNAP denote the RNA polymerase, Rp denotes reporter ) | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 8: the leakage of AlkSensor | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reaction 9: the the degradation of reporter | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Assumption = | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are several assumptions in the abstraction of AlkSensor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Because the genes of ALKR is under a constitutive promoter, we assume that the generation rate of ALKR is constant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *The four binding reactions, i.e, reaction 3, 4, 5 and 6 are fast reversible reactions since DNA binding and unbinding of the repressors dimers and the dimerization itself occur within seconds, whereas the synthesis (transcription, translation, folding) and degradation of monomers takes minutes to sometimes an hour. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reaction 3, 4, 5 and 6 can be integrated into two reversible questions. Therefore, the 9 reactions can be simplified as 7 reactions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-12.png|center|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <center><b>Figure 3.</b> Simplified form of AlkSensor’s chemical reactions</center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Model Development= | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reaction 3 and 4 are fast reversible reactions because DNA binding and unbinding of the transcription factor dimers and the dimerization itself occur within seconds. However the synthesis and degradation of monomers takes minutes to sometimes an hour. Therefore, the three reactions are in equilibrium and the steady state concentrations are given in terms of the equilibrium constants. The accumulation rates of ALKR and reporter are subject to their generation rate and degradation rate, which is described by two ordinary differential equations (ODE). So the mechanism of AlkSensor can be described by a mathematical model consisting of 2 ordinary differential equations (ODE) and three equilibrium equation. The input of AlkSensor can be defined as the concentration alkane, the output can be defined as the concentration of reporter protein, as shown in figure 2. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-model-4.png|thumb|600px|center|<b>Figure 4.</b> Mathematical representation of AlkSensor]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the first equation, there are four terms that determine the accumulation rate of reporter, the generation rate of reporter, the leakage rate of AlkSensor, the basal expression rate of reporter, the degradation rate of reporter. In the second equation, there are four terms that determine the accumulation rate of ALKR, the generation rate of ALKR, the degradation rate of ALKR, the dilution rate of ALKR. The last 3 equation describe the quantitative relation in reaction 3 and 4. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [Pm’] and [Pm’’] are still intermediate variables, we next deduce the value of [Pm’] and [Pm’’]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-1.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-2.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The total concentration of promoter alkM is thought to be a constant, which is proportional to the copy number of alkM. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-3.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | So we can get the expression of [Pm], [Pm’] and [Pm’’] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-4.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-5.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-6.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Then we substitute [Pm’] and [Pm’] with the terms on the right side of the equation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-7.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | When the leakage of ALKR’s promoter is little, the terms r can be ignored. When the system reach a steady state, the accumulation rate of Rp is zero. In such a condition, the response function of AlkSensor can be described as the equation below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-8.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We can simplify the response function into an elegant form, in which x denotes the input, y denotes the output, a, b and c are three parameters. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-9.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *k’: the expression rate constant of promoter alkM; | ||
| + | *k<sub>d</sub>: the degradation constant of protein ALKR, thought to be a constant; | ||
| + | *P<sub>0</sub>: the concentration of RNAP, constant; | ||
| + | *[P<sub>t</sub>]: the total concentration of promoter alkM, which is proportional to the copy number. This is easily changeable. We can change it through construct alkM on different plasmid with varying copy number. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Analysis & Discussion = | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The output has a monotone increasing relation with the input. When the input is large enough, the output reaches its maximum value, a, which is proportional to the amount of promoter alkM. When there is no input, the output has a smallest value, i.e. the value of leakage. We can easily obtain the value of dynamic range by dividing the maximum response into the value of leakage. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-F-10.png|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | There are two parameters that can be rationally regulated, [P<sub>t</sub>] and [ALKR]. We can control [P<sub>t</sub>] by adjust the copy number of promoter alkM and control [ALKR] by adjusting the strength of its promoter. Therefore, we have the ability to regulate the value of a and b, that is to say, the maximum response, leakage and dynamic range of AlkSensor can all be rationally regulated. | ||
| + | |||
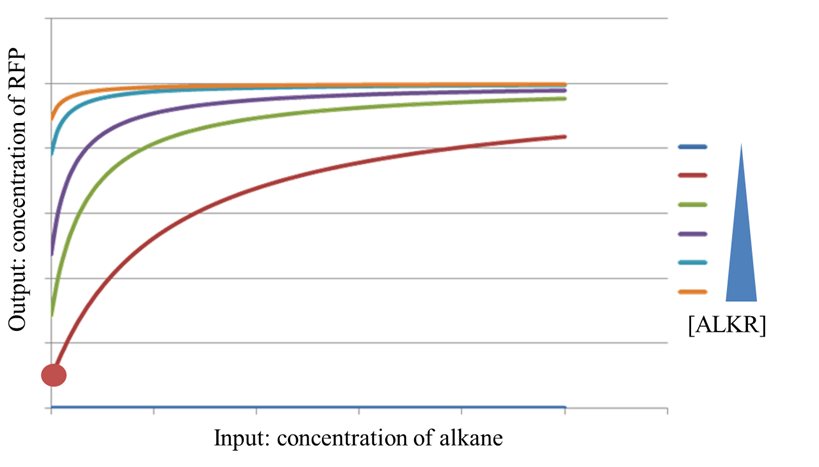
| + | Figure 5 shows a set of response curves of AlkSensor with different expression levels of ALKR. When there is no ALKR expressed, the response curve is a horizontal line, suggesting that AlkSensor has no ability to distinguish different inputs. With the increase of [ALKR], the leakage increase, however, the maximum response remains the same value, which makes the dynamic range decrease. When [ALKR] is too large, the response curve turns to be a horizontal line again. AlkSensor loses its function in this case. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TJU-model-5.png|thumb|600px|center|<b>Figure 5.</b> The influence of [ALKR] on the response curve of AlkSensor]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Achievement = | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | <p> In this model, we have</p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| + | .modeling-list{font-size:14px;line-height:150%;} | ||
| + | </style> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ul class="modeling-list" > | ||
| + | <li style="list-style-image: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ed/Tick.gif)"> identified the pattern of AlkSensor’s response curve,</li> | ||
| + | <li style="list-style-image: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ed/Tick.gif)"> proposed a template for experimental data of AlkSensor,</li> | ||
| + | <li style="list-style-image: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ed/Tick.gif)"> found ways to evaluate AlkSensor,</li> | ||
| + | <li style="list-style-image: url(https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/ed/Tick.gif)"> developed strategies to rationally regulate AlkSensor.</li> | ||
| + | </ul> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| Line 305: | Line 437: | ||
<!--top button section--> | <!--top button section--> | ||
<div style="display: block" id="goTopBtn"> | <div style="display: block" id="goTopBtn"> | ||
| - | <a href="#top"><img border=0 src=" | + | <a href="#top" title="Top"><img border=0 src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0b/Top-1.png"></a> |
</div> | </div> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 29 October 2013
Contents |
Model Objective
To perform a mathematic analysis on AlkSensor, to find out the relationship between AlkSensor’s input and output, to find ways to specifically regulate the function of AlkSensor, to find the factors affecting sensor’s leakage.
Problem Description
AlkSensor is composed of protein ALKR and promoter alkM. Genes of ALKR and alkM were synthesized and constructed into a plasmid, as shown in figure 1. As mentioned in the introduction, protein ALKR is a transcription factor which can recognize certain alkanes. ALKR is under a constitutive promoter and is constitutively expressed. Alkane molecules is recognized by ALKR and a dimerized ALKR-alkane complex is formed. Subsequently the reporter’s promoter alkM is induced by the complex and the genes in the downstream of alkM are expressed. However, promoter alkM could also be slightly induced when inducers are absent from the system. There are possibilities that dierized ALKR binds on promoter alkM and activates the downstream genes.
Problem Abstraction
The mechanism of AlkSensor can be represented by a set of chemical reactions, as shown below.
- Reaction 1: the generation of protein ALKR.
- Reaction 2: the degradation of protein ALKR
- Reaction 3: the dimerization of protein ALKR(AR2-A denotes the dimerized ALKR-alkane complex)
- Reaction 4: the combination of dimerized ALKR with alkane(Pm denotes promoter alkM)
- Reaction 5: the combination of dimerized ALKR-alkane complex with promoter alkM(Pm’ denotes the promoter alkM binding with inducer)
- Reaction 6: the combination of dimerized ALKR with promoter alkM(Pm’’ denotes the promoter alkM binding with dimerized ALKR)
- Reaction 7: the generation of reporter (RNAP denote the RNA polymerase, Rp denotes reporter )
- Reaction 8: the leakage of AlkSensor
- Reaction 9: the the degradation of reporter
Assumption
There are several assumptions in the abstraction of AlkSensor.
- Because the genes of ALKR is under a constitutive promoter, we assume that the generation rate of ALKR is constant.
- The four binding reactions, i.e, reaction 3, 4, 5 and 6 are fast reversible reactions since DNA binding and unbinding of the repressors dimers and the dimerization itself occur within seconds, whereas the synthesis (transcription, translation, folding) and degradation of monomers takes minutes to sometimes an hour.
Reaction 3, 4, 5 and 6 can be integrated into two reversible questions. Therefore, the 9 reactions can be simplified as 7 reactions.
Model Development
Reaction 3 and 4 are fast reversible reactions because DNA binding and unbinding of the transcription factor dimers and the dimerization itself occur within seconds. However the synthesis and degradation of monomers takes minutes to sometimes an hour. Therefore, the three reactions are in equilibrium and the steady state concentrations are given in terms of the equilibrium constants. The accumulation rates of ALKR and reporter are subject to their generation rate and degradation rate, which is described by two ordinary differential equations (ODE). So the mechanism of AlkSensor can be described by a mathematical model consisting of 2 ordinary differential equations (ODE) and three equilibrium equation. The input of AlkSensor can be defined as the concentration alkane, the output can be defined as the concentration of reporter protein, as shown in figure 2.
In the first equation, there are four terms that determine the accumulation rate of reporter, the generation rate of reporter, the leakage rate of AlkSensor, the basal expression rate of reporter, the degradation rate of reporter. In the second equation, there are four terms that determine the accumulation rate of ALKR, the generation rate of ALKR, the degradation rate of ALKR, the dilution rate of ALKR. The last 3 equation describe the quantitative relation in reaction 3 and 4.
The [Pm’] and [Pm’’] are still intermediate variables, we next deduce the value of [Pm’] and [Pm’’].
The total concentration of promoter alkM is thought to be a constant, which is proportional to the copy number of alkM.
So we can get the expression of [Pm], [Pm’] and [Pm’’]
Then we substitute [Pm’] and [Pm’] with the terms on the right side of the equation.
When the leakage of ALKR’s promoter is little, the terms r can be ignored. When the system reach a steady state, the accumulation rate of Rp is zero. In such a condition, the response function of AlkSensor can be described as the equation below.
We can simplify the response function into an elegant form, in which x denotes the input, y denotes the output, a, b and c are three parameters.
- k’: the expression rate constant of promoter alkM;
- kd: the degradation constant of protein ALKR, thought to be a constant;
- P0: the concentration of RNAP, constant;
- [Pt]: the total concentration of promoter alkM, which is proportional to the copy number. This is easily changeable. We can change it through construct alkM on different plasmid with varying copy number.
Analysis & Discussion
The output has a monotone increasing relation with the input. When the input is large enough, the output reaches its maximum value, a, which is proportional to the amount of promoter alkM. When there is no input, the output has a smallest value, i.e. the value of leakage. We can easily obtain the value of dynamic range by dividing the maximum response into the value of leakage.
There are two parameters that can be rationally regulated, [Pt] and [ALKR]. We can control [Pt] by adjust the copy number of promoter alkM and control [ALKR] by adjusting the strength of its promoter. Therefore, we have the ability to regulate the value of a and b, that is to say, the maximum response, leakage and dynamic range of AlkSensor can all be rationally regulated.
Figure 5 shows a set of response curves of AlkSensor with different expression levels of ALKR. When there is no ALKR expressed, the response curve is a horizontal line, suggesting that AlkSensor has no ability to distinguish different inputs. With the increase of [ALKR], the leakage increase, however, the maximum response remains the same value, which makes the dynamic range decrease. When [ALKR] is too large, the response curve turns to be a horizontal line again. AlkSensor loses its function in this case.
Achievement
In this model, we have
- identified the pattern of AlkSensor’s response curve,
- proposed a template for experimental data of AlkSensor,
- found ways to evaluate AlkSensor,
- developed strategies to rationally regulate AlkSensor.
 "
"