Team:TU Darmstadt/Modelling/Statistics
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 227: | Line 227: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | To validate the significance of our data we gathered in our human practice survey, we computed the DKL between our contestants and an artificial random distribution. High DKL values indicate a significant distribution. | ||
| + | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 233: | Line 236: | ||
<img alt="Test" src="/wiki/images/e/ea/DKL2.png" width="400" height="400"> | <img alt="Test" src="/wiki/images/e/ea/DKL2.png" width="400" height="400"> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | As can be seen in the graphic above, the DKL concerning our contestants indicate a significant data acquisition. For detailed analysis, see : LINKLINK | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<img alt="Test" src="/wiki/images/c/c4/Gender_Produkts.png" width="400" height="400"> | <img alt="Test" src="/wiki/images/c/c4/Gender_Produkts.png" width="400" height="400"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If we focus on the general opinion of male vs female contestants regarding basic research, we can observe a similar density distribution among the sexes. However, there seem to be more men, who tend to vote in the extreme end of the scale, with a tendency towards a positive opinion. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 242: | Line 253: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | If correlated to their age, men and women show the same density distribution. | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
Revision as of 02:30, 5 October 2013
Information Theory
The DKL Analysis
In information theory the Kullback-Leibler-Divergence (DKL[1]) describes and quantifies the distance between
two distributions P and Q. Where P denotes an experimental distribution, it is compared with Q, a reference distribution. DKL is also known as ‘relative entropy’ as well as ‘mutual information’.
Although DKL is often used as a metric or distance measurement, it is not a true measurement because it is not symmetric.

Here, P(i) and Q(i) denote the densities of P and Q at a position i. In our study, we use the DKL to describe the distances of the survey datasets from the human practice project. Therefore, we have to calculate a histogram out of the different datasets. Here, it is important to perform a constant binsize. In this approach we assume that a hypothetical distribution Q is uniformly distributed. To achieve this, we grate an appropriate test data set with the random generator runif in R.
Results
To validate the significance of our data we gathered in our human practice survey, we computed the DKL between our contestants and an artificial random distribution. High DKL values indicate a significant distribution.
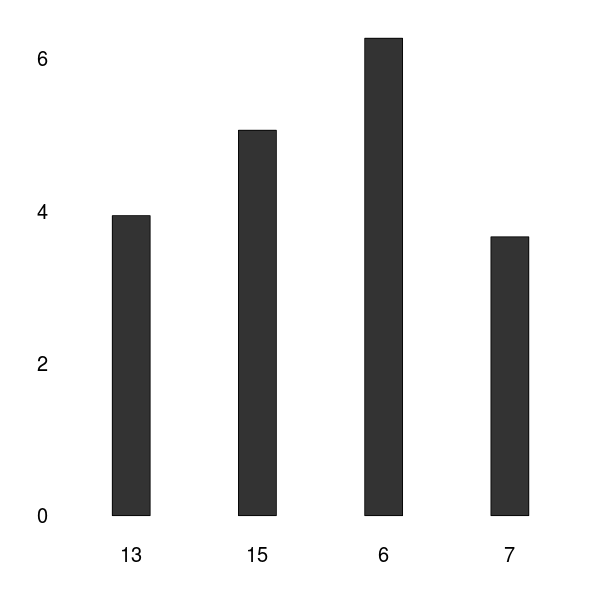
As can be seen in the graphic above, the DKL concerning our contestants indicate a significant data acquisition. For detailed analysis, see : LINKLINK
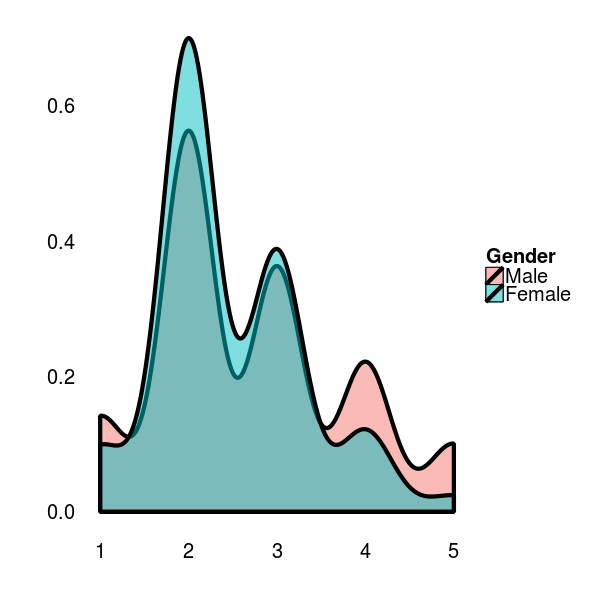
If we focus on the general opinion of male vs female contestants regarding basic research, we can observe a similar density distribution among the sexes. However, there seem to be more men, who tend to vote in the extreme end of the scale, with a tendency towards a positive opinion.

If correlated to their age, men and women show the same density distribution.
References
- Kullback, S.; Leibler, R.A. (1951) On Information and Sufficiency Annals of Mathematical Statistics 22 (1): 79–86. doi:10.1214/aoms/1177729694. MR 39968.
 "
"