Team:NCTU Formosa/biobricks
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(→Parts submitted to the Registry) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
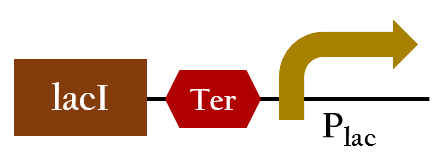
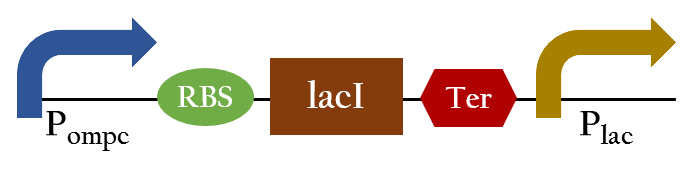
*Ompc promtor, which can sense red light with the presence of cph8. It will be turned on in the dark ,and be turned off in the bright. For the convenient use, we add lacI and lac promotor downstream the biobrick. This part, so called red promotor, can be activated under red light, and inactive in the dark. [[File:Nctu_Pred.jpg]] | *Ompc promtor, which can sense red light with the presence of cph8. It will be turned on in the dark ,and be turned off in the bright. For the convenient use, we add lacI and lac promotor downstream the biobrick. This part, so called red promotor, can be activated under red light, and inactive in the dark. [[File:Nctu_Pred.jpg]] | ||
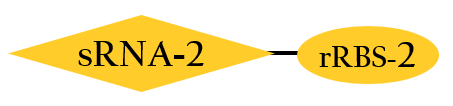
| - | *The sRNA, base pair with target mRNA, including the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. Thus it prevent ribosome from binding to initiate the translation. The rRBS is designed for sRNA perfect binding, and this rRBS is the RBS which can be bound only for our artificial sRNA(BBa_K1017404).[[File:Nctu_rbs2.jpg]] | + | *The sRNA, base pair with target mRNA, including the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. Thus it prevent ribosome from binding to initiate the translation. The rRBS is designed for sRNA perfect binding, and this rRBS is the RBS which can be bound only for our artificial sRNA(BBa_K1017404). |
| + | <br>[[File:Nctu_rbs2.jpg]] | ||
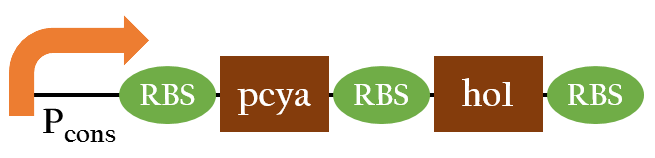
*[[File:Nctu_cph8.jpg]] | *[[File:Nctu_cph8.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 18 October 2013
Biobricks
To strive for the best results, we made a number of experiment. Our team always hang together in spite of many losses.
Parts submitted to the Registry
<groupparts>iGEM013 NCTU_Formosa</groupparts>
- Ompc promtor, which can sense red light with the presence of cph8. It will be turned on in the dark ,and be turned off in the bright. For the convenient use, we add lacI and lac promotor downstream the biobrick. This part, so called red promotor, can be activated under red light, and inactive in the dark.
- The sRNA, base pair with target mRNA, including the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. Thus it prevent ribosome from binding to initiate the translation. The rRBS is designed for sRNA perfect binding, and this rRBS is the RBS which can be bound only for our artificial sRNA(BBa_K1017404).
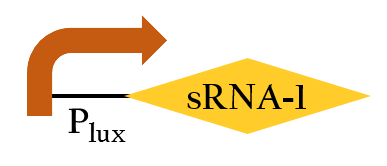
- This part, BBa_K1017401, includes our artificial sRNA-1 and rRBS-1. The non-coding small RNA can bind to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence on rRBS-1 by base-pairing. Once the rRBS-1 is blocked, ribosomes cannot bind to it to translate, thus, gene expressions downstream are decreased. Because of specific binding, rRBS-1 can only be bound by sRNA-1. We add Plux upstream, so this part can be regulated by luxR/AHL complex.

- This part, BBa_K1017402, is similar to BBa_K1017401 mentioned above, but without Plux. rRBS-2 can only be bound by sRNA-2 due to specificity, then gene expressions downstream are decreased.
 "
"