Team:TU Darmstadt
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
} | } | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
#taskbar | #taskbar | ||
| Line 93: | Line 84: | ||
<!-- central main menu --> | <!-- central main menu --> | ||
| - | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/problem | + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/problem" > |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
<div id="mm_icon1"> | <div id="mm_icon1"> | ||
<img alt="Darmstadt_Grafik_1" src="/wiki/images/9/92/Darmstadt_Grafik_1..jpg" width="180" height="180"></br> | <img alt="Darmstadt_Grafik_1" src="/wiki/images/9/92/Darmstadt_Grafik_1..jpg" width="180" height="180"></br> | ||
| Line 101: | Line 90: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</a> | </a> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/solution"> | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:TU_Darmstadt/solution"> | ||
| Line 136: | Line 121: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 21:46, 6 September 2013
 Problem
Problem
 Solution
Solution
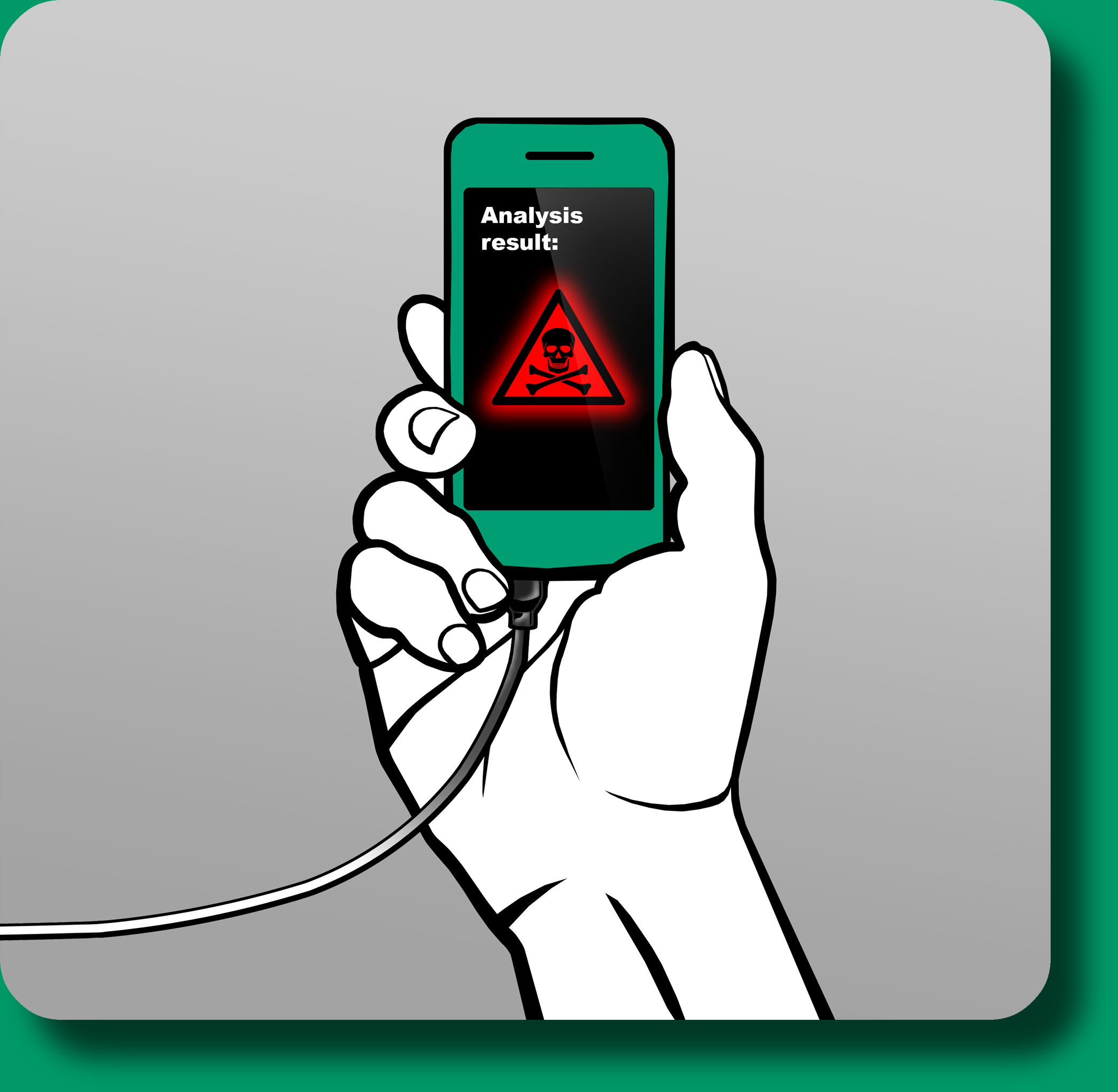 Result
Result
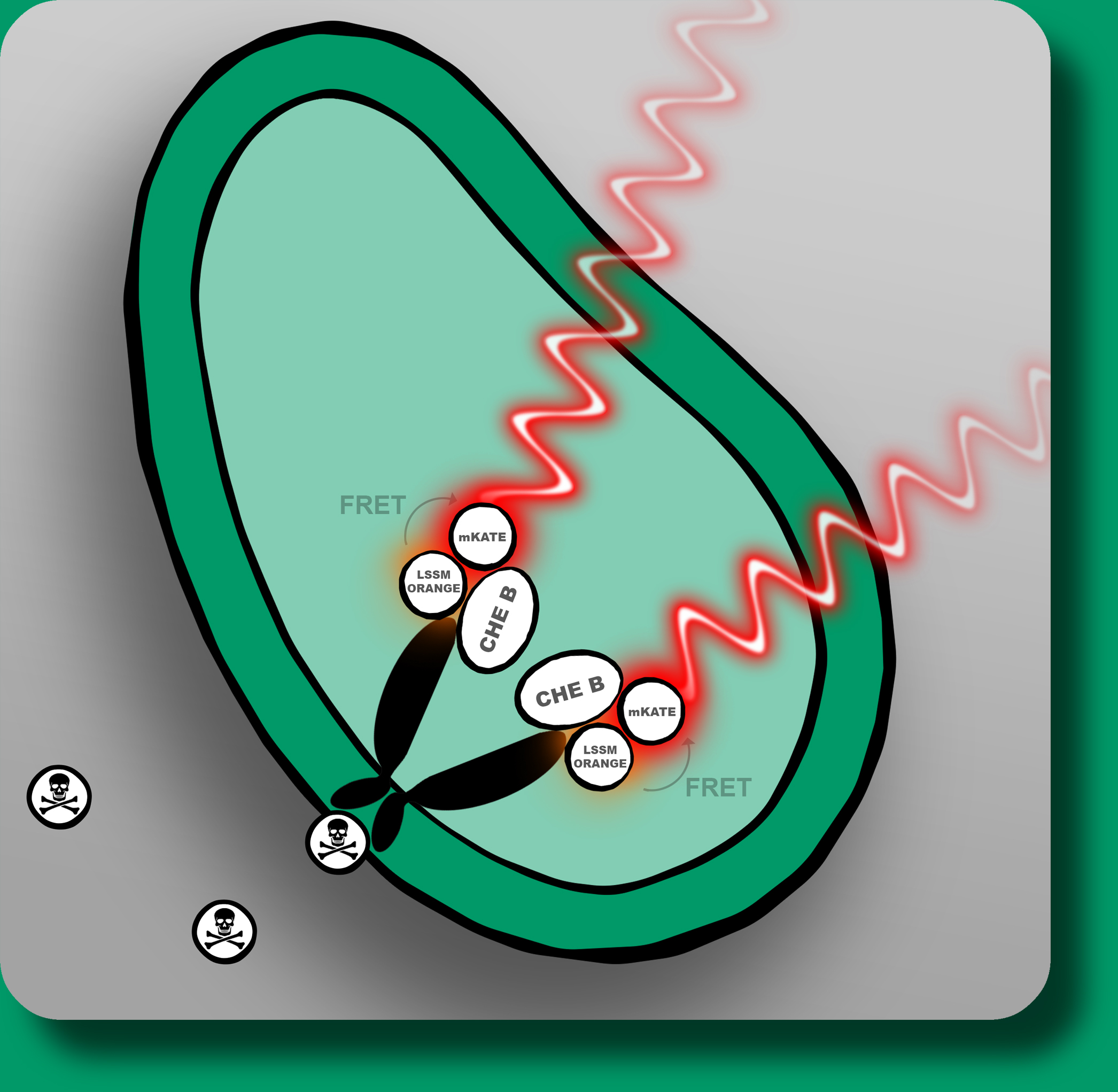
Mycotoxins produced by mould fungus are present in our daily life and are harmful for humans as well as for animals. The danger of contamination of gain and other natural products has fatal consequences for the economy and the supply of whole nations. The mycotoxins which are permanently formed by the fungus, can be used as biomarkers to detect contamination. We want to develop a handy device which allows an easy and reliable detection of mycotoxins. To achieve this goal our team uses various methods from the fields of synthetic biology, electrical engineering and information processing. The detection system relies on E.coli with modified aspartate receptors (TAR) which interact with specific mycotoxins. If these are present in the reviewed sample they will bind to the receptor and induce a conformational change and thereby generates a measurable FRET-beacon by bringing two flourophores in close distance to each other. The modified E.coli will be embedded in interchangeable capsules. Together with a handheld-device they will guarantee that measurements can be done quickly, easy to operate and secure. The data will be transferred from the handheld system to an Android smartphone app which will be able to analyze, illustrate and store the test results for the user.
 "
"