Team:Tsinghua-E/Part1
From 2013.igem.org



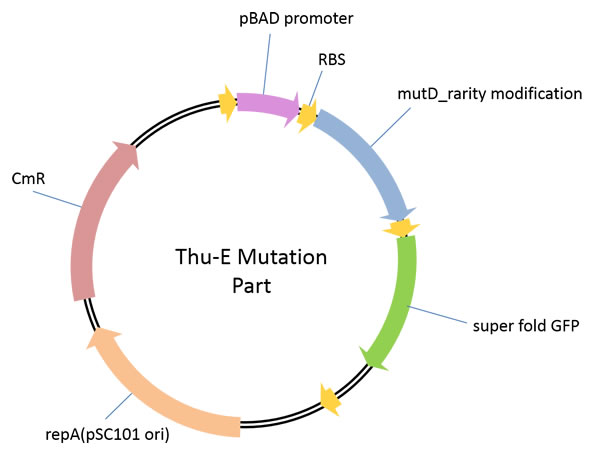
Part 1: THU-E Mutation Part
A plasmid used for the construction of high-diversity library in vivo ingenome level. In this vector, highly error-prone dnaQ mutant, mutD<a href="#_ENREF_1" title="Lou, 2012 #499">1</a> was cloned downstream of araBAD promoter to control the mutation rate of the target genome by the concentration of araBAD promoter’s inducer, L-arabinose, in a strict manner.E. Coli JM109 carrying different vectors of pBAD_B0030-mutD-sfGFP, pBAD_B0032-mutD-sfGFP and pBAD_SDA_RBS-mutD-sfGFP(this RBS sequence was derived from the RBS sequence upstream of sfGFP in original AraC_pBAD_CI_OR222-sfGFP vector<a href="#_ENREF_2" title="Lou, 2012 #499">2</a>)were constructed. By detecting the induced fluorescence intensity, we found that pBAD_B0030-mutD-sfGFP, andpBAD_SDA_RBS-mutD- sfGFPhave relatively higher mutD expression. The increaseof mutation rate induced by our mutation part was measured by quantifying the reversion of rifampinresistance caused by mutation in genome.pBAD_SDA_RBS-mutD- sfGFPcould increase the genome mutation rate up to 10 times compared with negative control with 1g/L induction concentration of L-arabinose.
</html>
<img border="0" width="446" src="/wiki/images/7/70/Part1I.png" />
Figure.2 rifampicin reversion mutants caused by mutD expression and the counts by agar plate
<img border="0" width="446" src="/wiki/images/a/a3/Part1II.png" />
Figure.3 Conception illustration of the working mechanism of mutD
1 Schaaper, R. M. MECHANISMS OF MUTAGENESIS IN THE ESCHERICHIA-COLI MUTATOR MUTD5 - ROLE OF DNA MISMATCH REPAIR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 85, 8126-8130,doi:10.1073/pnas.85.21.8126 (1988).
2 Lou, C. B., Stanton, B., Chen, Y. J., Munsky, B. & Voigt, C. A. Ribozyme-based insulator parts buffer synthetic circuits from genetic context. Nature Biotechnology 30, 1137-+, doi:10.1038/nbt.2401 (2012). </p>
</div> </html>
 "
"