Team:BYU Provo/Results/Experimental
From 2013.igem.org
(→Results of Mutant T4 Phage Isolation) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
===Results of Mutant T4 Phage Isolation=== | ===Results of Mutant T4 Phage Isolation=== | ||
| - | + | [[File:T4CsClmodel.JPG|750px|left|link=https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/67/BYUModelingTable.JPG]] | |
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 21:37, 27 September 2013
| |
|
|
Phage TeamIsolation of Phage Library
Results of Mutant T4 Phage IsolationResults of Mutant T7 Phage Isolation
Cholera TeamCholera Quorum Sensing Molecules Induce Lambda in an SdiA-dependent Fashion
Designing SdiA to be Specific for Cholera
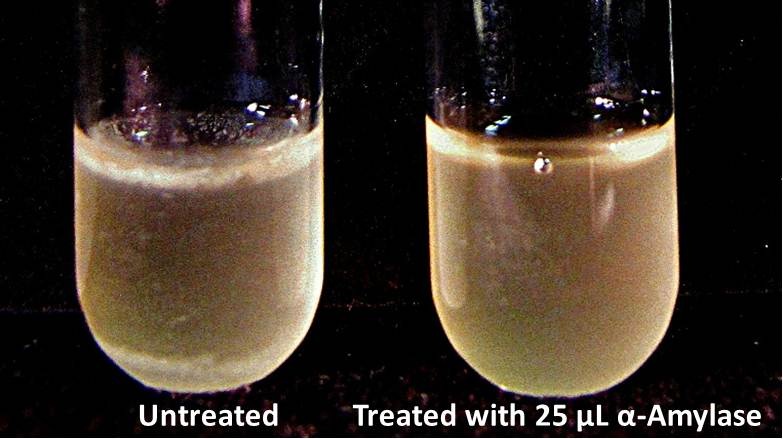
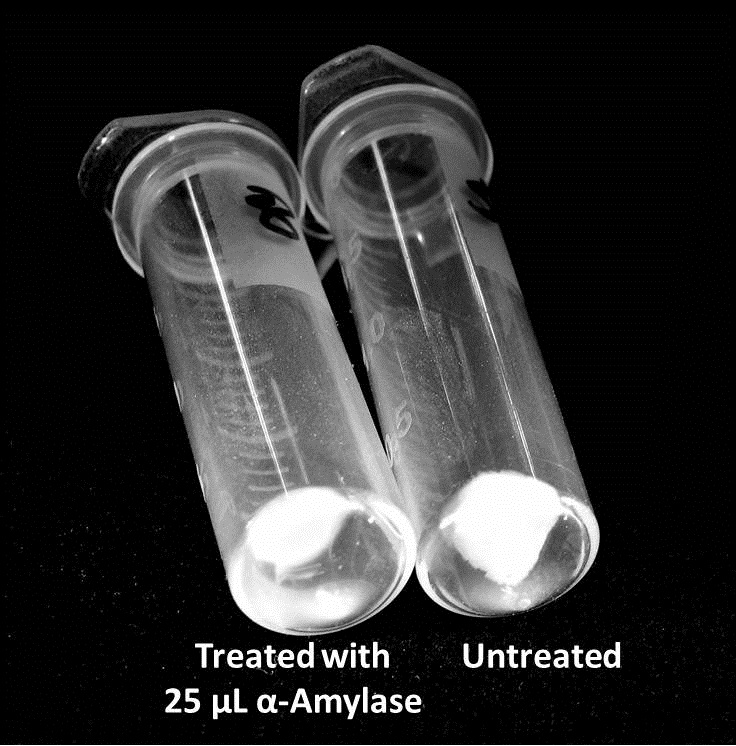
Biofilm inhibition by AmylaseThe enzymatic activity of α-Amylase was characterized to determine its capacity to inhibit biofilm formation by V. cholerae. Samples were prepared by adding 50 µL of V. cholerae culture to 1 mL of a high salt LB. The samples were then treated by the addition of purified α-Amylase in various concentrations and allowed to incubate at 30°C for 48 hours. After 48 hours the samples were examined and a distinct difference was seen in the amount of biofilm formed in the treated and untreated samples.
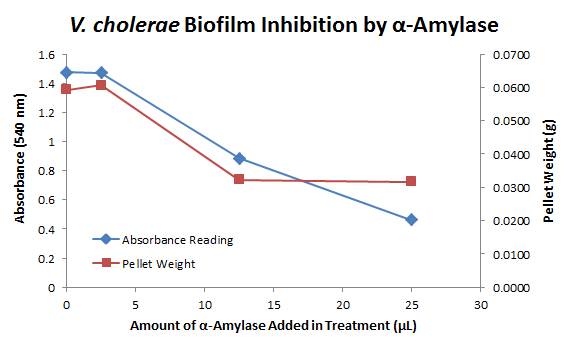
The above graph shows the average absorbance readings for samples treated with 0, 2.5, 12.5, and 25 µL of α-Amylase. There is a distinct reduction in the amount of biofilm growth between untreated and treated samples, with samples treated with 25 µL α-Amylase showing a 65.8% decrease in biofilm formation after 48 hours. While this clearly shows the ability of α-Amylase to inhibit biofilm formation by V. cholerae, further characterization is needed to determine the capacity of α-Amylase to degrade preexisting biofilms.
|
 "
"