Team:BYU Provo/Results/Modeling
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
__NOTOC__==Basic Design== | __NOTOC__==Basic Design== | ||
| - | [[File:BYUModelingDesign.JPG|360px|right]] | + | [[File:BYUModelingDesign.JPG|360px|right|link=]] |
Experiments with bacteriophage growth is often performed either in liquid broth or in solid agar medium. In contrast to the relative uniform distribution of phages in liquid broth, phages form individual clearings in bacterial lawn within solid agar medium. These clearings are termed plaques. They are the product of bacterial cell lysis as phage replicate and spread outward. | Experiments with bacteriophage growth is often performed either in liquid broth or in solid agar medium. In contrast to the relative uniform distribution of phages in liquid broth, phages form individual clearings in bacterial lawn within solid agar medium. These clearings are termed plaques. They are the product of bacterial cell lysis as phage replicate and spread outward. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
For our modeling experiments, we hypothesized that multiple experimental factors may influence the size of plaque formation in solid agar medium (Fig. 1). We decided to start with identifying the relationships between plaque sizes and each of these factors. With these data, we can generate a mathematical model that take into account all experimental variability. Such model can be used by researcher to design the optimal experimental conditions that will produce plaques of the ideal size for their experiments. | For our modeling experiments, we hypothesized that multiple experimental factors may influence the size of plaque formation in solid agar medium (Fig. 1). We decided to start with identifying the relationships between plaque sizes and each of these factors. With these data, we can generate a mathematical model that take into account all experimental variability. Such model can be used by researcher to design the optimal experimental conditions that will produce plaques of the ideal size for their experiments. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ==Experimental Results== | ||
| - | + | [[File:BYUModelingPlatePics.JPG|360px|right|link=]] | |
| - | + | We decided to start with determining the relationship between phage plaque size and phage particle particle size. Specifically, 0.5 mL of E coli B liquid culture (OD 600 = 0.5) was transfected with 20uL of the respective phage (T1, T3, T4, and T7) at approximately the same concentration for 10 minutes. After this, the bacteria/phage mixture was plated on standard LB plates using x1 top agar. Plates were allowed to solidify for 30 minutes, before placing in an incubator at 37 Celsius for 24 hours. Following incubation, pictures of plates were taken with '''<add name of instrument>''' and plaque sizes were analyzed using imageJ. | |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
Revision as of 05:03, 26 September 2013
| |
|
|
Basic Design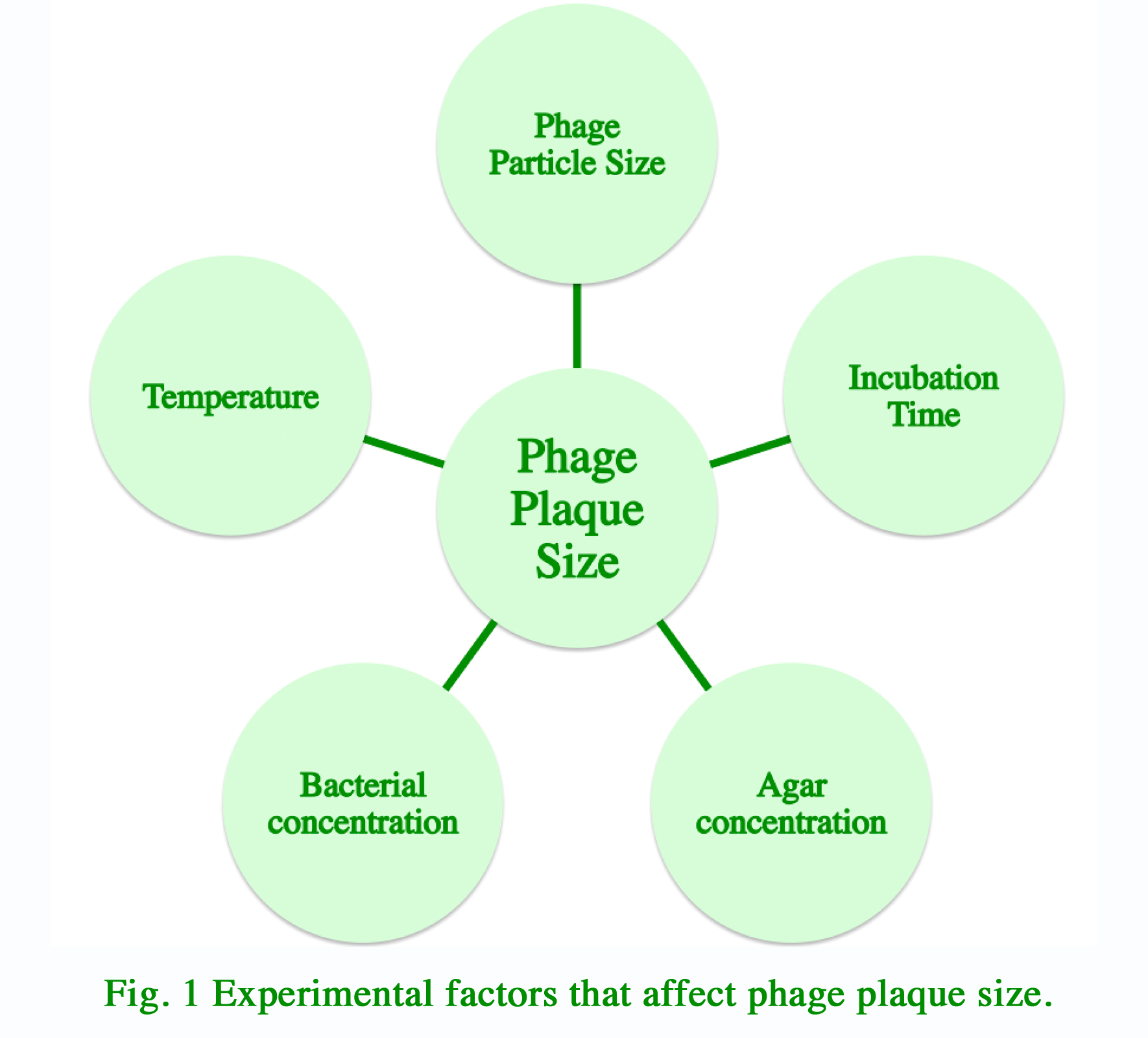 Experiments with bacteriophage growth is often performed either in liquid broth or in solid agar medium. In contrast to the relative uniform distribution of phages in liquid broth, phages form individual clearings in bacterial lawn within solid agar medium. These clearings are termed plaques. They are the product of bacterial cell lysis as phage replicate and spread outward. For our modeling experiments, we hypothesized that multiple experimental factors may influence the size of plaque formation in solid agar medium (Fig. 1). We decided to start with identifying the relationships between plaque sizes and each of these factors. With these data, we can generate a mathematical model that take into account all experimental variability. Such model can be used by researcher to design the optimal experimental conditions that will produce plaques of the ideal size for their experiments.
Experimental Results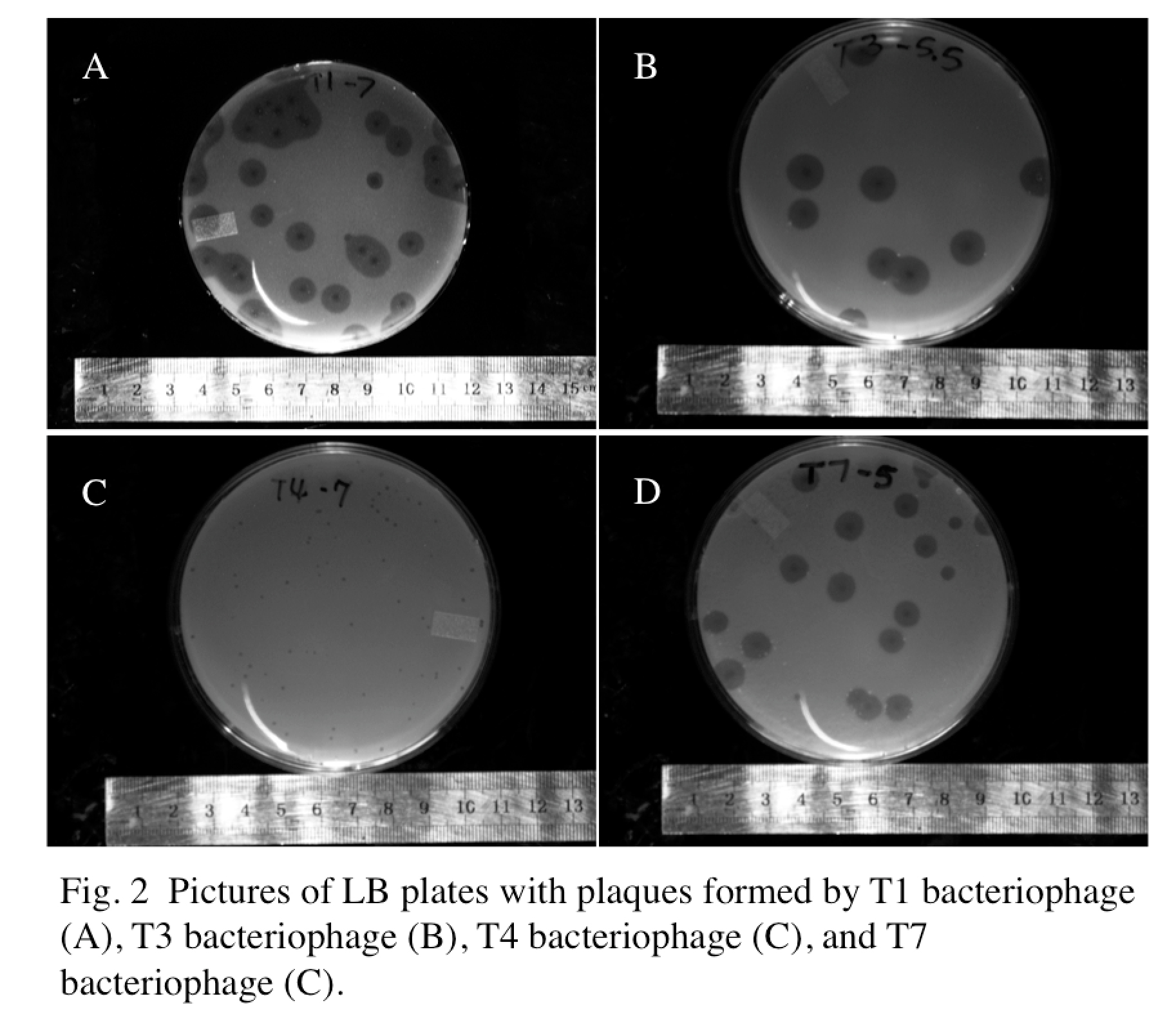 We decided to start with determining the relationship between phage plaque size and phage particle particle size. Specifically, 0.5 mL of E coli B liquid culture (OD 600 = 0.5) was transfected with 20uL of the respective phage (T1, T3, T4, and T7) at approximately the same concentration for 10 minutes. After this, the bacteria/phage mixture was plated on standard LB plates using x1 top agar. Plates were allowed to solidify for 30 minutes, before placing in an incubator at 37 Celsius for 24 hours. Following incubation, pictures of plates were taken with <add name of instrument> and plaque sizes were analyzed using imageJ.
|
 "
"