Header
Sensing
Overview
The Idea of this module was to transform the bacterium with a plasmid that would contain a promoter which senses a specific signal. Once this promoter senses the signal, it would initiate transcription of an enzyme which degrades the nanocapsule, thus releasing its contents. We decided to use pH as the specific trigger that activates the promoter. As a proof of principle, we inserted three different promoters into three plasmids in front of the bio brick BBa_I746916 which encodes superfolded GFP. Then we transformed cells with these plasmids and let them grow in media with different pHs in order to check the expression.
Experiments
We chose the following three pH sensitive promoters:
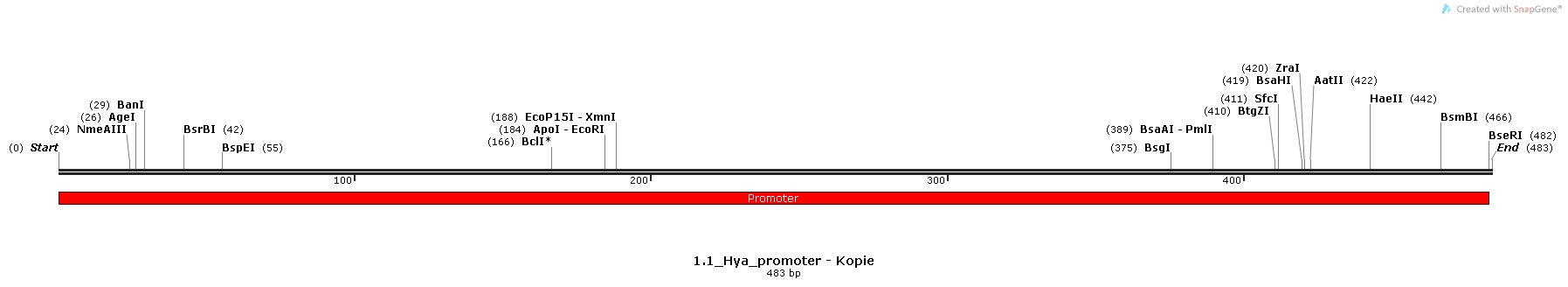
1.) Hya-promoter, isolated from the Escherichia Coli K-12 MG1655 strain
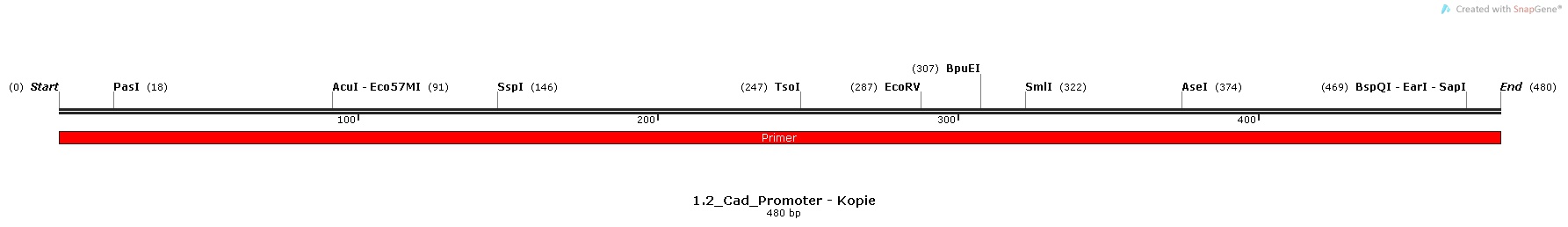
2.) Cad-promoter, isolated from the Escherichia Coli K-12 MG1655 strain
3.) BioBrick BBa_J23119, a constitutive promoter that was made by the 2006 Berkley team.
We digested the Plasmid containing the biobrick BBa_I746908 which would serve us as backbone for our constructs in order to qualitatively asses if it was indeed the expected plasmid.
All the promoters were isolated by PCR and then assembled into the pSB1C3 Plasmid in front of the superfolded GFP.
Then each of the constructs was used to transform DH5-alpha competent cells, which were first plated and then incubated into media with different pHs.
We used four media:
1.) LB-Chloramphenicol with 10X MOPS+HCl, with a final pH of 5
2.) LB-Chloramphenicol with 10X MOPS, with a final pH of 6
3.) LB-Chloramphenicol without any buffer, with a final pH of 7
4.) LB-Chloramphenicol with 10X HEPES, with a final pH of 8.5
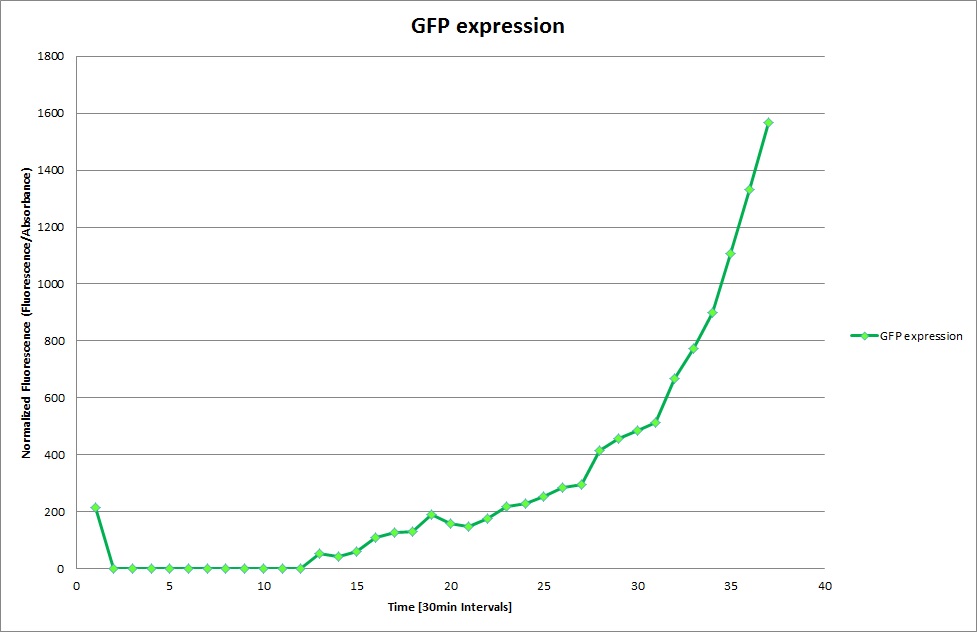
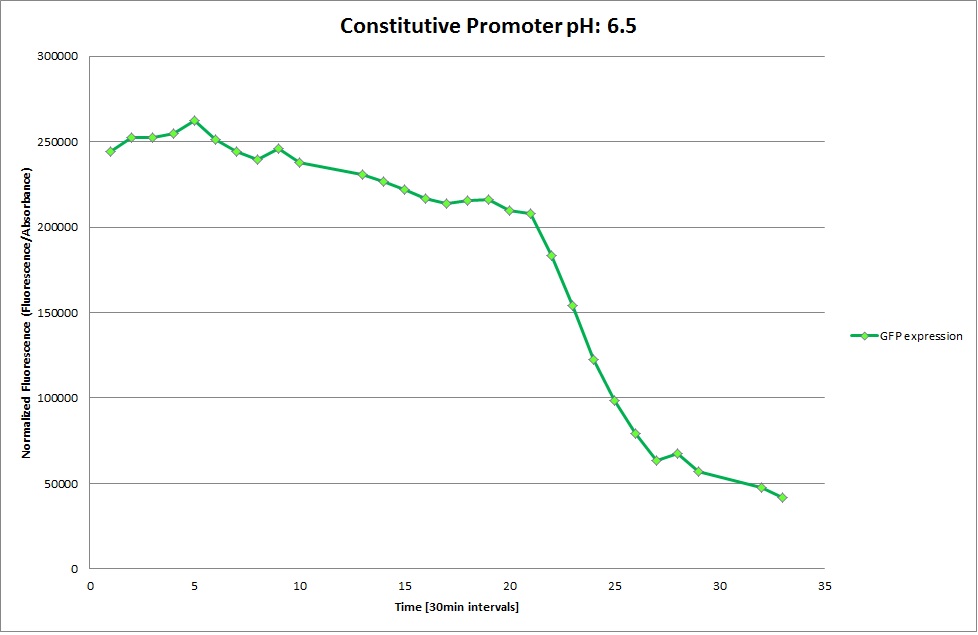
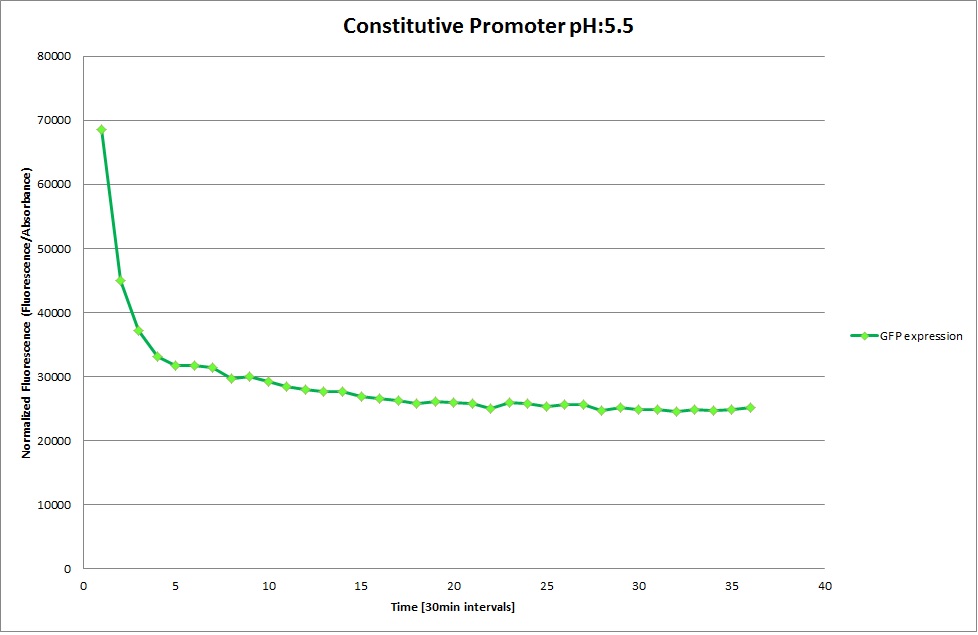
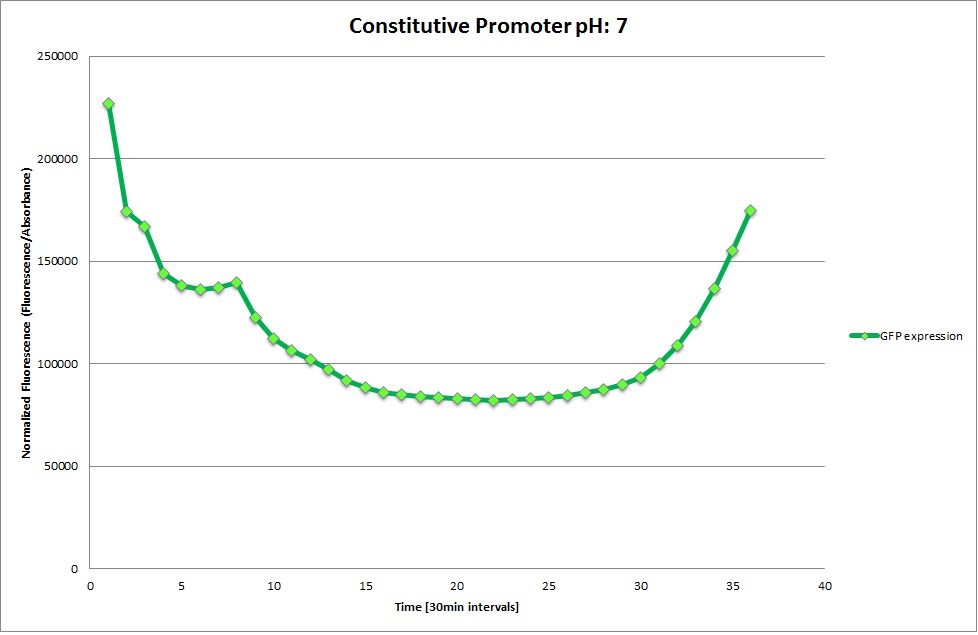
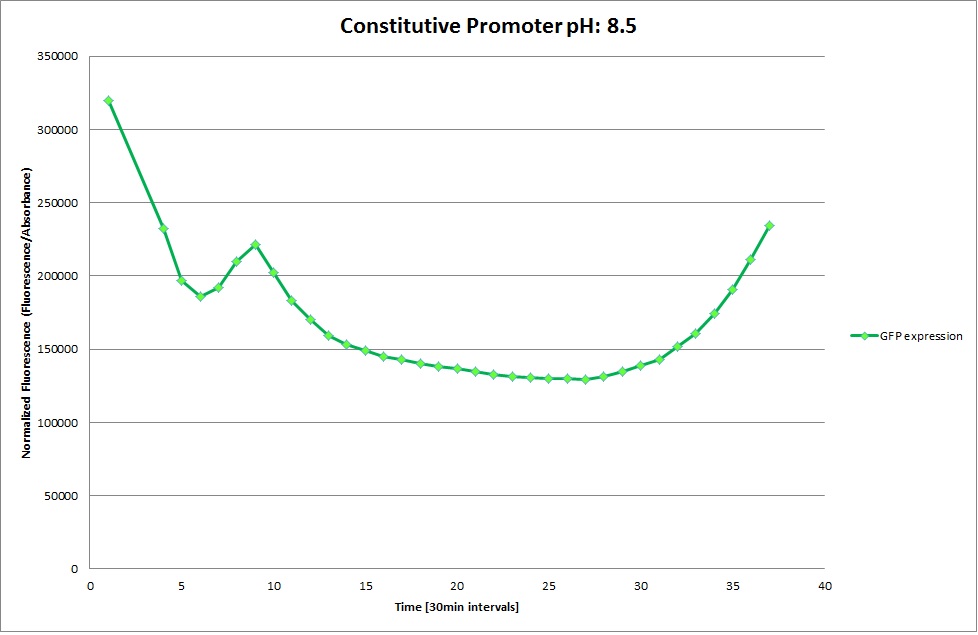
GFP expression was measured using a plate reader where we made three replicates of each promoter with each pH. Then, the average for each replicate was calculated and used to establish a curve depicting GFP expression within each medium.
Contents |
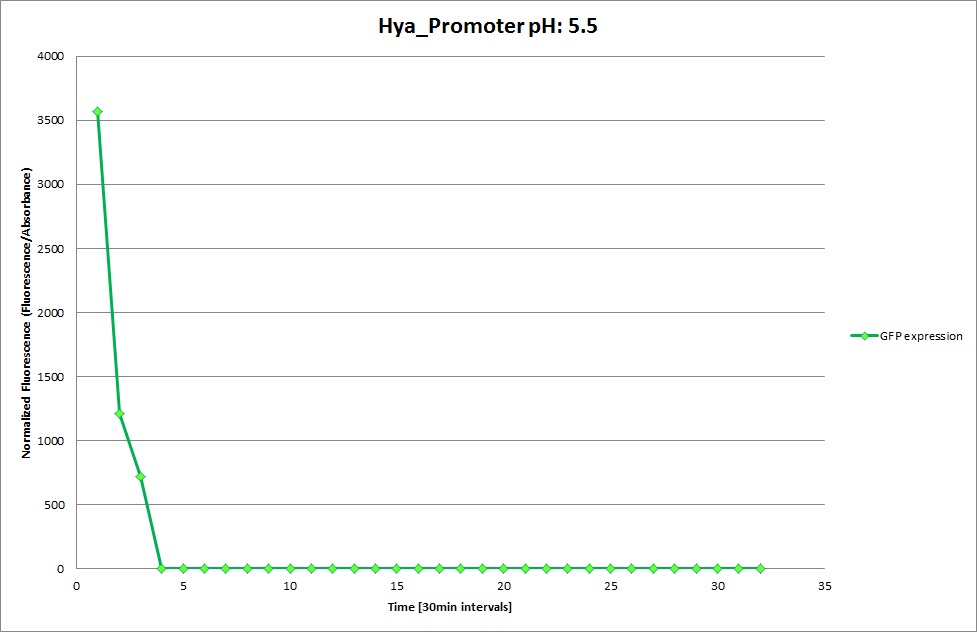
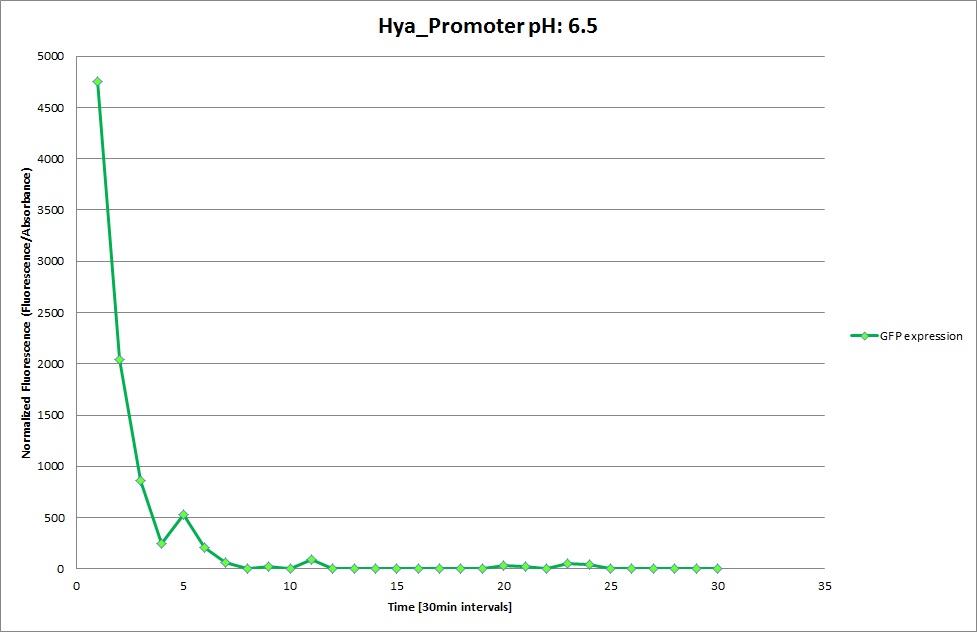
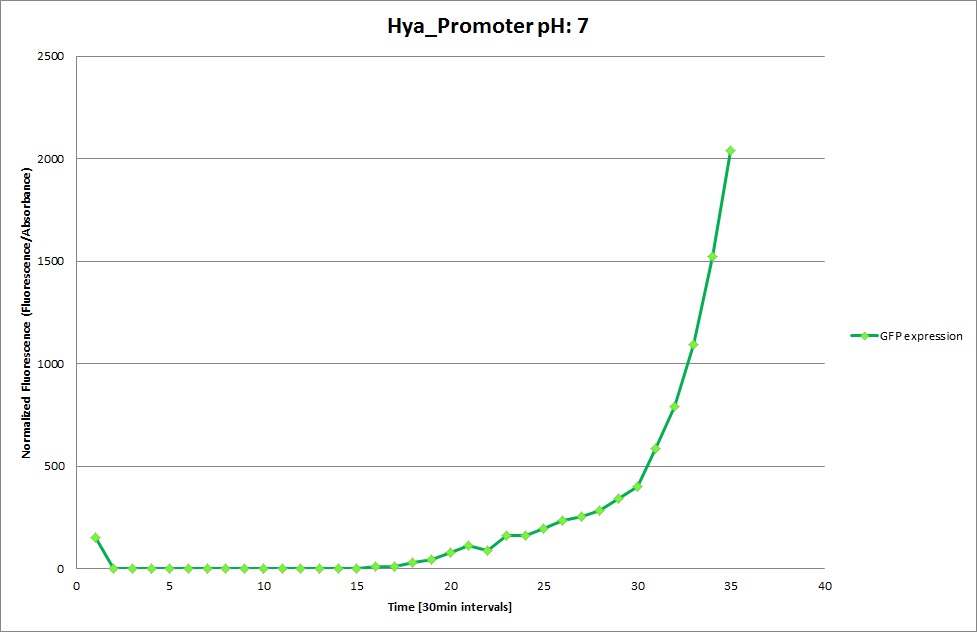
Hya Promoter
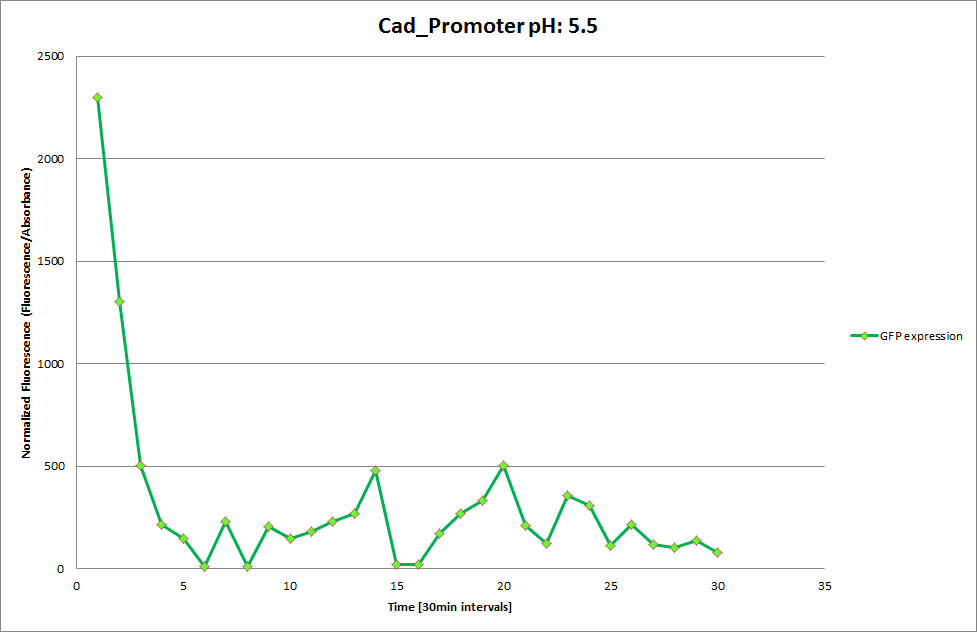
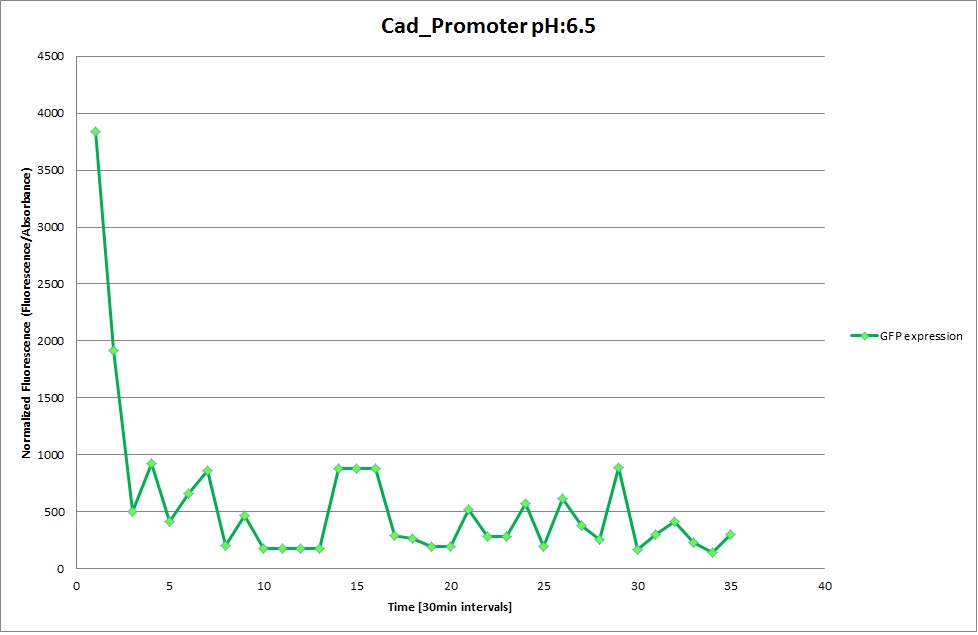
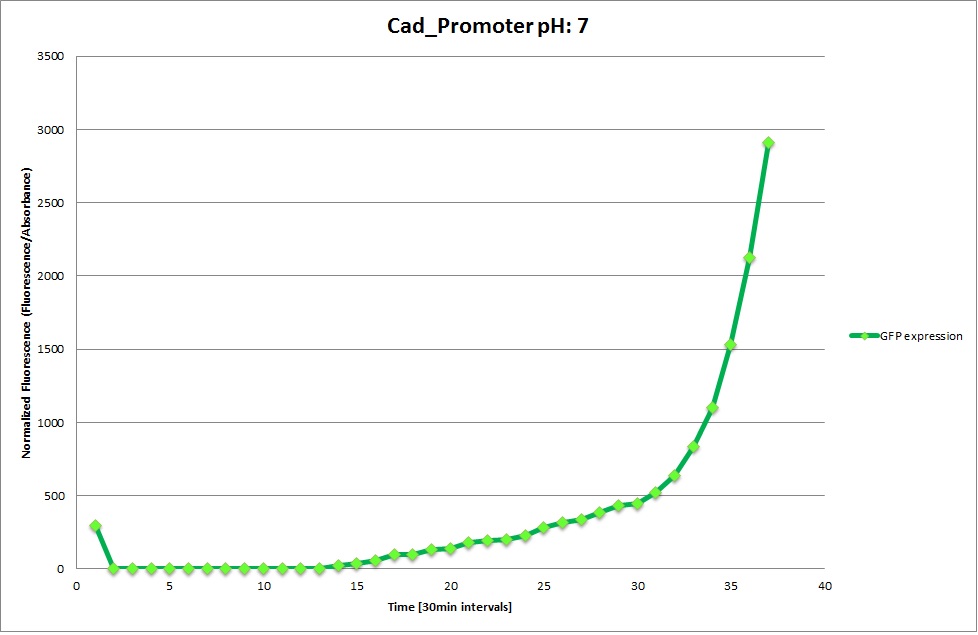
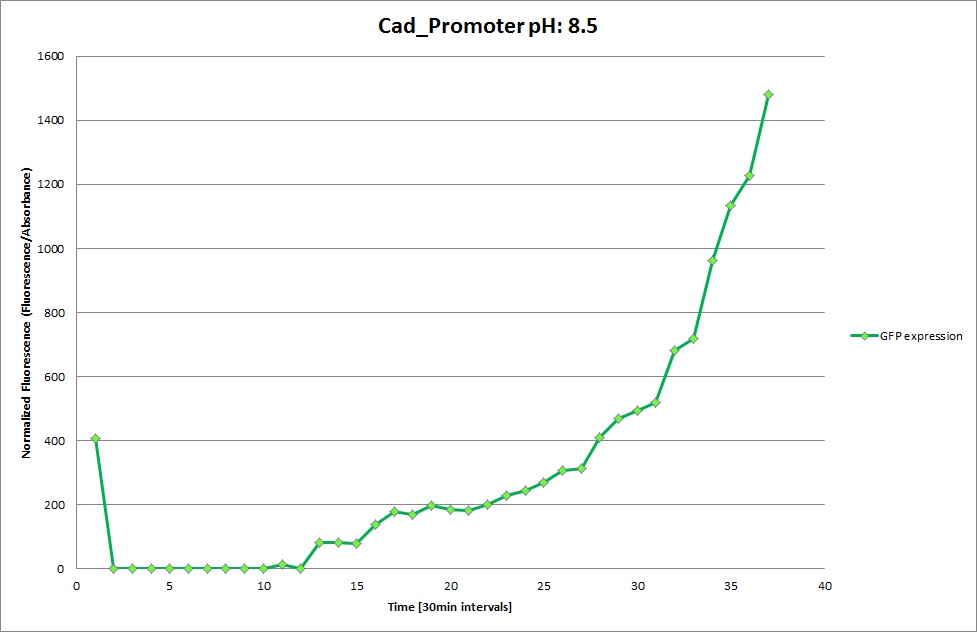
Cad Promoter
Constitutive Promoter
The Cells were also looked at under a microscope to qualitatively study their GFP expression.
Hya Promoter
Expected outcome:
The Promoters Hya and Cad were supposed to initiate transcription upon external acidification, which would then cause the bacteria to express superfolded GFP and turn bright green. The biobrick BBa_J23119, being a constitutive promoter, would turn the bacteria green independently of their medium.
Results:
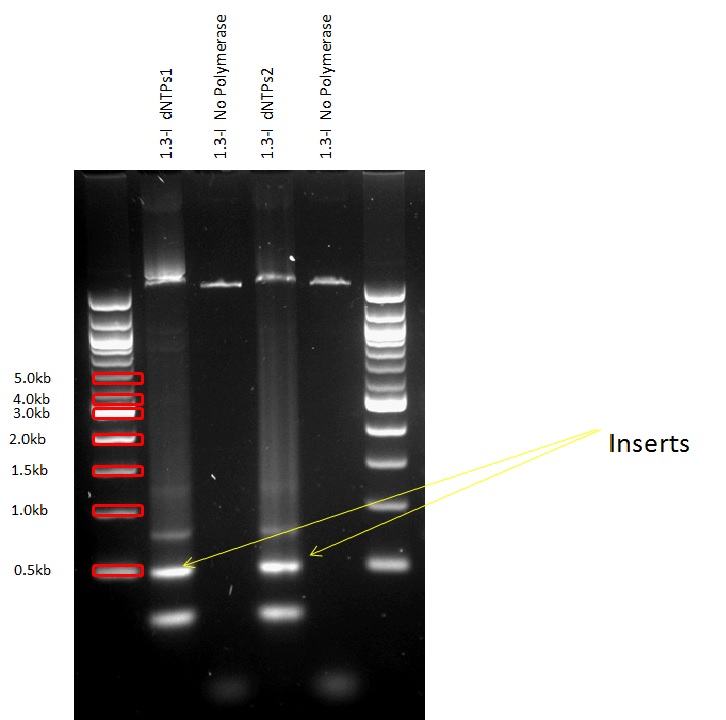
We successully managed to isolate and amplify each of the three promoters as well as inserting them into the pSB1C3 plasmid so that they would control the expression of superfolded GFP. The transformation that followed was also successful, which was determined by sequencing the plasmid isolated from the colonies on the plate. This sequencing result showed a 100% match between the original promoter sequence and the inserted sequence that the bacteria contained. Also, the bacteria containing the biobrick pH-promoter had turned green on the plates as well as in liquid culture, which was just as expected.
Effecting
Overview:
The goal of the effecting part of the project was to build a plasmid containing an arabinose promoter driving a tagged enzyme able to cleave gelatinase, the fabric used for our nano particles. We chose three different enzymes that would be inserted in part BBa_I746908, a pBAD promoter driving superfolder GFP, either between the promoter and GFP tag or instead of the GFP tag since it sometimes causes folding troubles. All of the constructs were planned to have a His tag as well, just in case something went wrong with the GFP tag, so we could extract and purify our expressed protein anyway.
Experiments:
The three different enzymes that we chose to use were gelatinase E (gelE) from Gram positive bacterium E. faecalis, metalloprotease 2 (MMP2) from H. sapiens and metalloprotease 9 (MMP9) from M. musculus. The genomic DNA of E. faecalis was ordered and a PCR was performed on it using Gibson primers that also added a His tag in front of the protein sequence. For MMP2 and MMP9, plasmids containing the coding sequence (CDS) of the proteins were ordered from plasmid.med.harvard.edu and the CDS were extracted in the same way as for gelatinase. In the meantime, PCRs were performed on the iGEM part BBa_I746908 to clone the backbone, add the overlap for the Gibson and, when needed, remove the GFP from the backbone (since we wanted to have a construct for each protein where GFP was replaced directly by the CDS). Competent cells were then transformed with the successful constructs, grown at 37C and later on activated, by adding 50ul of 20% arabinose solution to 5ml of inoculated culture, grown overnight, for 2h. A Western blot was then performed on the lysate and supernatural of the cells to check for the presence of the protein either out (if secreted as desired) or in (not secreted but at least expressed) the cells. A His-tag purification followed by SDS-PAGE were also executed.
Expected outcome:
We would expect the cells to be green and express/secrete a protein-GFP complex upon arabinose induction if everything works perfectly. The secreted protein, if correctly folded, could then break open the nano particles attached to the bacteria's surface, thus releasing the contained drug. However, we did not proceed to transform our bacteria with the coupling plasmid since the coupling section was stopped due to the lack of an antibody needed to prove that the coupling plasmid was complete.
Results:
The PCR reactions to amplify and extract the proteins CDSs and plasmid backbone were successful. We then proceeded to a Gibson assembly of the constructs that were meant to keep the GFP, for all three proteins. The Gibsons for the pBAD/araC-gelE-GFP and pBAD/araC-MMP2-GFP constructs worked, but not the one for the MMP9. We then transformed bacteria, isolated the plasmids and sent them for sequencing with the iGEM primers for the backbone and also with our own Gibson primers. This showed that the Gibson had been a success, but that a STOP codon had appeared in front of the GFP sequence, just after the linker. Indeed, the transformed bacteria did not appear green when induced with arabinose. Since a His tag had been added to the CDS of each protein using the Gibson primers, we did a Western blot with anti-his tag antibodies on the induced cell media and lysates. The result came out negative. We then proceeded to a his-tag purification of the cell lysates (Ni-NTA spin kit).
 "
"