|
- Small Phage
- March-April
- May-June
- July-August
- September-October
|
5.13 Determining E coli Concentration With Spectrophotometer
I) Purpose
- To determine if OD600 can be used to determine E coli concentration
- According to reference The number of cells in a bacterial culture can be estimated by reading the absorbance at 600nm (OD600). For E. coli cells, an OD600 of 1.0 ≈ 5E8 cells/ml
II) Expected Outcome
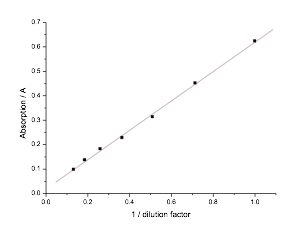
- linear relationship between absorption and 1/dilution factor
III) Reagants Used
- E. Coli BL21 overnight from 5.12; LB prepared by TA in 100mL flask
IV) Actual Procedure
1. Dilution series
- Label 6 tubes 1 through 6, to each of the test tubes add 2mL of LB.
- 5mL of E coli overnight (21 hours) was to test tube 1. The content was then pipetted up and down to mix well.
- Performing dilution series by transforming 5mL from tube n to tube n+1 in order of n=1,2,3,4,5. The dilution factor is thus 7/5
2. Measurements using spectrophotometer
- Spectrophotometer was warmed up and set to take measurements at 600nm.
- Pure LB was used to as blank
- Before each measurement, the cuvette was rinsed with 1mL of distilled water and 1mL of E coli solution to be measured.
- 1mL of E coli solution at various concentration was pipetted into each cuvette for measurement.
V) Results
1. Raw data
Data From Spectrophotometer Reading
| Test Tube
| Concentration with Respect to Overnight
| Absorption at 600nm
|
| 0
| 1
| 0.623
|
| 1
| 0.714
| 0.451
|
| 2
| 0.510
| 0.313
|
| 3
| 0.364
| 0.288
|
| 4
| 0.260
| 0.182
|
| 5
| 0.186
| 0.137
|
| 6
| 0.133
| 0.098
|
2. Plot
VI) Conclusion
- The results show us that there is a linear relationship between the optical density reading and bacteria concentration. This means that we can use the optical density reading to determine the concentration of bacteria.
|
 "
"
