Team:SydneyUni Australia/Project/Results
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Jbergfield (Talk | contribs) (cleaned up characterisation, gave images proper titles (i.e. not all "tomo cl assay")) |
m |
||
| (43 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<style type="text/css"> | <style type="text/css"> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
.pictext { | .pictext { | ||
| Line 60: | Line 48: | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| - | = | + | <html> |
| + | <a name="restart"></a> | ||
| + | <h2>Project Results</h2> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <table border="0" width="300"> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="#tomo">TOMO degrades DCA</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="#gibson">Gibson Assembly was Problematic</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="#assembly">Assembly of dhlB-dhlA in pSB1C3</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="#characterisation">Characterisation of dhlB-dhlA</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td><a href="#references">References</a></td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
| - | <div id="results" | + | <div id="results"> |
| - | < | + | <a name="tomo"></a> |
| + | <h2>ToMO degrades DCA</h2> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 72: | Line 87: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/90/DCApathwaysHartman.jpg" rel="ibox" title="DCA Degradation Pathways"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/90/DCApathwaysHartman.jpg" rel="ibox" title="DCA Degradation Pathways"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/90/DCApathwaysHartman.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/90/DCApathwaysHartman.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 79: | Line 94: | ||
<li>Toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase (ToMO) from <i>Pseuodomonas stutzeri</i> OX1 has been shown to oxidise xylenes, toluene, benzene, styrene, napthalene (Bertoni <i>et al.</i>, 1996) as well as tetrachloroethene, trichloroethene, dichloroethene and vinyl chloride (Shim <i>et al.</i>, 2001). The enzyme was optimised for chlorinated ethene degradation (Varder & Wood, 2005), and gifted to our host lab in the plasmid pBS(Kan)ToMO.</li> | <li>Toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase (ToMO) from <i>Pseuodomonas stutzeri</i> OX1 has been shown to oxidise xylenes, toluene, benzene, styrene, napthalene (Bertoni <i>et al.</i>, 1996) as well as tetrachloroethene, trichloroethene, dichloroethene and vinyl chloride (Shim <i>et al.</i>, 2001). The enzyme was optimised for chlorinated ethene degradation (Varder & Wood, 2005), and gifted to our host lab in the plasmid pBS(Kan)ToMO.</li> | ||
| - | + | <li>We learned that ToMO had activity on DCA by using a GC to measure the removal of DCA from headspace where resting cells were incubated with DCA overnight.</li> | |
| + | |||
| + | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| + | <div class="pictextl" style="height: 100px; line-height: 100px">Degradation of DCA by ToMO - GC Results</div> | ||
| + | <div class="pictextr" style="height: 100px;"> | ||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7d/ToMO_graphpretty.png" rel="ibox" title="Degradation of DCA by ToMO - GC Results"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/7/7d/ToMO_graphpretty.png" height="100"; width="100"> | ||
| + | </a> | ||
| + | </center> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <li>To confirm this, we showed that ToMO can begin degradation of DCA through an assay for | ||
<a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols#chloride">chloride ions</a> | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols#chloride">chloride ions</a> | ||
released as DCA is converted to chloroacetaldehyde. To our knowledge this hasn’t been shown by anyone else before. </li> | released as DCA is converted to chloroacetaldehyde. To our knowledge this hasn’t been shown by anyone else before. </li> | ||
| - | <li>This is pretty cool, but during the middle of the year we decided to try synthesising the whole pathway rather than building it by conventional cloning. The length of the ToMO gene cluster meant it was too expensive for us to continue working with it.</li> | + | <li>This is pretty cool, but during the middle of the year we decided to try synthesising the whole pathway rather than building it by conventional cloning. The length of the ToMO gene cluster meant it was too expensive for us to continue working with it. In place of ToMO we turned to a cytochrome p450 monooxygenase, which had been shown in early 2013 to play the same role as ToMO in the initial step of DCA-degradation (Nishino et al. 2013). </li> |
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| Line 89: | Line 117: | ||
<div class="pictextr" style="height: 100px;"> | <div class="pictextr" style="height: 100px;"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/97/SydneyUni2013_Results_TomoIndigo.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Production of indigo compound by ToMO activity on indole | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/97/SydneyUni2013_Results_TomoIndigo.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Production of indigo compound by ToMO activity on indole"> |
| - | "> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/97/SydneyUni2013_Results_TomoIndigo.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/9/97/SydneyUni2013_Results_TomoIndigo.jpg" height="100"> | + | |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | <a name="gibson"></a> | |
| - | + | <h2>Gibson Assembly was Problematic</h2> | |
| - | + | <h3>Progress</h3> | |
| - | < | + | <h4Transformation</h4> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>We spent a week | + | <li>We spent a week optimising the transformation of our <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Design">Gibson Assembly reaction product</a>. We initially tried transformation into <i><i>E. coli</i></i> EPI300 and yielded no transformants. We suspected that there may be a metabolic burden or harm to cells carrying our correctly assembled product, due to the strong constitutive expression of our <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Design">designed promoter, Psyn</a>. To account for this we tried transforming into <i><i>E. coli</i></i> EPI400, which carries plasmids at low copy-number with an inducible increase in copy-number. We also tried incubating and growing cells at room temperature to lessen their growth rate, so that they might be able to better cope with any possible toxicity of the transformed Gibson Assembly reaction product. Neither of these were successful; however, we were able to screen 87 clones by transforming into a different strain, <i><i>E. coli</i></i> TOP10.</li> |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h4> Screening </b></h4> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>We screened 87 clones for the presence of dhlB, a gene responsible for the breakdown of chloroacetate in our pathway, by incubating resting cells with chloroacetate and <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols#chloride">chloride assay</a>. A few clones from each type of pathway looked promising, so we proceeded to extract plasmids from these for further investigation.</li> | <li>We screened 87 clones for the presence of dhlB, a gene responsible for the breakdown of chloroacetate in our pathway, by incubating resting cells with chloroacetate and <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols#chloride">chloride assay</a>. A few clones from each type of pathway looked promising, so we proceeded to extract plasmids from these for further investigation.</li> | ||
<div class="pictext" style="height: 130px;"> | <div class="pictext" style="height: 130px;"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">dhlB | + | <div class="pictextl">dhlB PCR screening:<br>We expected a band at ~800 bp for an amplification of dhlB, the gene in our pathway responsible for the degradation of chloroacetate. We didn’t see it in any of the 87 clones used in the phenotypic chloride assay, where a few of the clones had exhibited increased production of Cl<sup>-</sup> ions from the chloroacetate substrate compared to control cells. </div> |
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/44/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRscreeningdhlBfail.jpg" rel="ibox" title="dhlB Screening"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/44/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRscreeningdhlBfail.jpg" rel="ibox" title="dhlB Screening"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/44/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRscreeningdhlBfail.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/4/44/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRscreeningdhlBfail.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 120: | Line 147: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h4>Plasmid Preps</b> </h4> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>None of the clones from which we extracted plasmids contained the correctly assembled insert. By PCR and diagnostic restriction digests on these plasmids we were able to distinguish two different misassembled versions of our desired Gibson Assembly reaction product. </li> | <li>None of the clones from which we extracted plasmids contained the correctly assembled insert. By PCR and diagnostic restriction digests on these plasmids we were able to distinguish two different misassembled versions of our desired Gibson Assembly reaction product. </li> | ||
<div class="pictext" style="height: 370px;"> | <div class="pictext" style="height: 370px;"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">Plasmid Digests<br>We did a second plasmid prep of our clones because the first weren’t very clear. Desmond figured out that by digesting the plasmids with EcoRV we ought to see a single | + | <div class="pictextl">Plasmid Digests:<br>We did a second plasmid prep of our clones because the first weren’t very clear. Desmond figured out that by digesting the plasmids with EcoRV we ought to see a single 2 kb band if pSB has closed on itself. We don't see anything like this in our clones, but we know from the rfp that this works (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J04450">BBa_J04450</a> is about 3 kb, and contains a single EcoRV site in the pSB backbone). If the plasmid contains our gBlocks (or at least iGEMBLOCK 1 with aldA), then we expect to see two bands - one at 1 kb, a second at 5 or 6 kb (depending on whether we're looking at p450 or the adh plasmid). We don't see this either. We think that in most of the plasmids, some of the gBlocks have assembled in pSB1C3 but not iGEMBLOCK 1. In one of the clones (64) we see a band at 1 kb but nothing else, so maybe iGEMBLOCK1 assembled in pSB, but not other gBlocks. |
| - | <br><br>Interestingly, rfp looks spot-on while our results are similar to that in the last plasmid prep (everything slightly higher than | + | <br><br>Interestingly, rfp looks spot-on while our results are similar to that in the last plasmid prep (everything slightly higher than 3 kb, except 64). With rfp we expect a single band at 3 kb (pSB is 2 kb plus the rfp 'part' is 1 kb, and the whole construct contains a single EcoRV site in pSB). Notably, 64 was one of the small p450 colonies we patched from Gibson Assembly Product transformations. |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/db/SydneyUniversity2013_results_plasmiddigest.jpg" rel="ibox" title="dhlB Plasmid Digest"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/db/SydneyUniversity2013_results_plasmiddigest.jpg" rel="ibox" title="dhlB Plasmid Digest"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/db/SydneyUniversity2013_results_plasmiddigest.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/d/db/SydneyUniversity2013_results_plasmiddigest.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 138: | Line 165: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | <br> | |
| - | <li>We thought it could have been possible to assemble our entire pathway from smaller fragments salvaged from our Gibson Assembly reaction product. This proved impossible, presumably due to the extent of heterogenous template including both correctly and incorrectly assembled gBlocks in the Gibson Assembly reaction product. It may have been possible to do something similar using IDT’s gBlocks as template, however, this was not possible as we’d used up all of one of gBlocks during a second Gibson Assembly. </li> | + | <h4>PCR from Gibson template</h4> |
| + | <ul><li>We thought it could have been possible to assemble our entire pathway from smaller fragments salvaged from our Gibson Assembly reaction product. This proved impossible, presumably due to the extent of heterogenous template including both correctly and incorrectly assembled gBlocks in the Gibson Assembly reaction product. It may have been possible to do something similar using IDT’s gBlocks as template, however, this was not possible as we’d used up all of one of gBlocks during a second Gibson Assembly. </li></ul> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">GA | + | <div class="pictextl">This is our gel analysis of our GA products. Ap, Bp, Cp are from the p450 pathway, using our GA reaction product as template. Aa, Ba and Ca are from the adh pathway. It looks like we can’t amplify what we want, or that it doesn’t exist in the GA reaction product.</div> |
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e9/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRfromGAreactionproduct.jpg" rel="ibox" title="GA Product PCR Assembly"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e9/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRfromGAreactionproduct.jpg" rel="ibox" title="GA Product PCR Assembly"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e9/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRfromGAreactionproduct.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/e/e9/SydneyUniversity2013_results_PCRfromGAreactionproduct.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | <h3>Lessons</h3> | |
| - | + | <h4>Constitutive Expression</h4> | |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>We suspect that some of the genes we tried to assemble (e.g., p450, Nishino <i>et al.</i>, 2013) can harm the cells they're expressed in. If this is the case, then by a sort of natural screening we were only able to find colonies on plates that contain misassembled gBlocks that did not express these genes. </li> | + | <li>We suspect that some of the genes we tried to assemble (e.g., p450, Nishino <i>et al.</i>, 2013) can harm the cells they're expressed in, whether this is by using up resources or unusual interactions with undesired targets in the cell. If this is the case, then by a sort of natural screening we were only able to find colonies on plates that contain misassembled gBlocks that did not successfully express these genes. </li> |
<li>Upon reflection, we approached the assembly of our pathway with an almost child-like ignorance and optimism. Our promoter was specifically designed to maximise expression of our construct, as if ‘the more pollutant degrading genes, the better’. If the hypothesis above is correct, then we might have had more success with an inducible promoter.</li> | <li>Upon reflection, we approached the assembly of our pathway with an almost child-like ignorance and optimism. Our promoter was specifically designed to maximise expression of our construct, as if ‘the more pollutant degrading genes, the better’. If the hypothesis above is correct, then we might have had more success with an inducible promoter.</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h4>Modularity</h4 |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li> Consider the parable of the watchmakers: <br><br> "There once were two watchmakers, named Hora and Tempus, who manufactured very fine watches. Both of them were highly regarded, and the phones in their workshops rang frequently - new customers were constantly calling them. However, Hora prospered, while Tempus became poorer and poorer and finally lost his shop. What was the reason?<br>The watches the men made consisted of about 1,000 parts each. Tempus had so constructed his that if he had one partly assembled and had to put it down - to answer the phone say - it immediately fell to pieces and had to be reassembled from the elements. The better the customers liked his watches, the more they phoned him, the more difficult it became for him to find enough uninterrupted time to finish a watch.<br>The watches that Hora made were no less complex than those of Tempus. But he had designed them so that he could put together subassemblies of about ten elements each. Ten of these subassemblies, again, could be put together into a larger subassembly; and a system of ten of the latter sub-assemblies constituted the whole watch. Hence, when Hora had to put down a partly assembled watch in order to answer the phone, he lost only a small part of his work, and he assembled his watches in only a fraction of the man-hours it took Tempus." | + | <li> Consider the parable of the watchmakers: <br><br> <i> "There once were two watchmakers, named Hora and Tempus, who manufactured very fine watches. Both of them were highly regarded, and the phones in their workshops rang frequently - new customers were constantly calling them. However, Hora prospered, while Tempus became poorer and poorer and finally lost his shop. What was the reason? |
| + | <br>The watches the men made consisted of about 1,000 parts each. Tempus had so constructed his that if he had one partly assembled and had to put it down - to answer the phone say - it immediately fell to pieces and had to be reassembled from the elements. The better the customers liked his watches, the more they phoned him, the more difficult it became for him to find enough uninterrupted time to finish a watch. | ||
| + | <br>The watches that Hora made were no less complex than those of Tempus. But he had designed them so that he could put together subassemblies of about ten elements each. Ten of these subassemblies, again, could be put together into a larger subassembly; and a system of ten of the latter sub-assemblies constituted the whole watch. Hence, when Hora had to put down a partly assembled watch in order to answer the phone, he lost only a small part of his work, and he assembled his watches in only a fraction of the man-hours it took Tempus." </i> | ||
| Line 170: | Line 202: | ||
<br><br></li> | <br><br></li> | ||
| - | <li>The sequences we had synthesised as gBlocks by IDT were designed so that they could only be assembled in the whole DCA-degradation pathway, rather than as parts within pSB1C3 which could then be assembled piece-by-piece. This meant that our success relied on the correct assembly of the entire pathway, and when this failed, that we were unable to access parts of the pathway | + | <li>The sequences we had synthesised as gBlocks by IDT were designed so that they could only be assembled in the whole DCA-degradation pathway, rather than as parts within pSB1C3 which could then be assembled piece-by-piece. This meant that our success relied on the correct assembly of the entire pathway, and when this failed, that we were unable to access parts of the pathway. </li> |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h4>Plans</b> </h4> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li> <b>Replacement of gBlocks</b> </li> | <li> <b>Replacement of gBlocks</b> </li> | ||
| Line 182: | Line 214: | ||
<li> <b>PCR Assembly</b> </li> | <li> <b>PCR Assembly</b> </li> | ||
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>It might be possible to PCR amplify genes directly from our gBlocks as template rather than our Gibson Assembly reaction product. Alternatively, with the design of new primers, the genes of interest might be amplified from gBlocks for cloning into a BioBrick vector. With either of these options, sequence fidelity may be an issue.</li> | + | <li><a href="https://www.idtdna.com/pages/decoded/decoded-articles/core-concepts/decoded/2012/09/21/assembly-pcr-for-novel-gene-synthesis">PCR Assembly</a> provided an alternative option to GA for us. It might be possible to PCR amplify genes directly from our gBlocks as template rather than our Gibson Assembly reaction product. Alternatively, with the design of new primers, the genes of interest might be amplified from gBlocks for cloning into a BioBrick vector. With either of these options, sequence fidelity may be an issue.</li> |
| + | |||
| + | <li>Since Hong Kong we have tried this, and it proved unsuccessful based on the protocol from (<a href="#xiong04">Xiong, 2004</a>), using our gBlocks of aldA, p450 and tetR and some primers. | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <br><br> |
| - | + | <a name="assembly"></a> | |
| - | + | <h2>Assembly of dhlB-dhlA in pSB1C3</h2> | |
| - | < | + | While struggling with Gibson Assembly of our whole pathway we turned to the extraction, cloning and characterisation of two parts in our pathway, dhlB and dhlA. These two genes had been cloned into pUC19 by <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Attributions">others in our lab.</a> |
| - | + | <h3>Amplification</h3> | |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>We designed primers specifically for amplifying dhlB and dhlA, while removing a forbidden EcoRI site between them. | + | <li>We designed primers specifically for amplifying dhlB and dhlA, while removing a forbidden EcoRI site between them. Our primer design allowed us to clone each gene by itself and also together into the shipping vector pSB1C3.</li> |
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| Line 199: | Line 234: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1c/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Amplification.jpg" rel="ibox" title="We successfully amplified dhlB and dhlA from pUC19."> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1c/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Amplification.jpg" rel="ibox" title="We successfully amplified dhlB and dhlA from pUC19."> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1c/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Amplification.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/1/1c/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Amplification.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 207: | Line 242: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | <h3> Cloning </h3> | |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| Line 216: | Line 251: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/55/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Screen.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Red-white screen for dhlA-dhlB inclusion into pSB1C3"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/55/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Screen.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Red-white screen for dhlA-dhlB inclusion into pSB1C3"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/55/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Screen.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/55/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Screen.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 222: | Line 257: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">PCR Junction Screening of <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115008">AB22</a> We used the red-white screen to find colonies that contained the dhlB-dhlA insert instead of rfp, and PCR junction screen was used to find correctly assembled inserts. We used NEB | + | <div class="pictextl">PCR Junction Screening of <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115008">AB22</a> We used the red-white screen to find colonies that contained the dhlB-dhlA insert instead of rfp, and PCR junction screen was used to find correctly assembled inserts. We used NEB 1 kb ladder. If the two-way ligation of dhlB and dhlA worked as desired, we should have observed a 110 bp PCR product (AB22s) spanning the junction between pSB1C3 and dhlB, an 874bp PCR product (AB22m) spanning the junction between dhlB and dhlA, and a 1086bp PCR product (AB22e) spanning the junction between dhlA and pSB1C3. |
</div> | </div> | ||
| Line 228: | Line 263: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/c7/SydneyUniversity2013_results_junctionscreen.jpg" rel="ibox" title="PCR junction screening of potential dhlA-dhlB transformants"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/c7/SydneyUniversity2013_results_junctionscreen.jpg" rel="ibox" title="PCR junction screening of potential dhlA-dhlB transformants"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/c7/SydneyUniversity2013_results_junctionscreen.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/c/c7/SydneyUniversity2013_results_junctionscreen.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 235: | Line 270: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">This digest confirmed the length and concentration of our plasmids before shipping to iGEM HQ.</div> | + | <div class="pictextl">After PCR screening of the junctions between our parts and pSB1C3, we extracted the plasmids from a few that looked promising for further confirmation and submission to the iGEM HQ. We performed a digest and ran the results on a gel. This digest confirmed the length and concentration of our plasmids before shipping to iGEM HQ.</div> |
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/54/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Digest.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Restriction digest of submitted parts"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/54/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Digest.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Restriction digest of submitted parts"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/54/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Digest.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/54/SydneyUni2013_Results_Assembly_Cloning_Digest.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | <br><br> | |
| - | + | <a name="characterisation"></a> | |
| - | + | <h2>Characterisation of dhlB-dhlA </h2> | |
| - | < | + | After sending dhlB and dhlA to iGEM HQ, we began characterisation by cloning a constitutive promoter from the Distribution Kit in front of our parts. |
| - | + | <h3>Amplification</h3> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | < | + | |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
| - | <li>PCat (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14033">BBa_I14033</a>) is 38bp, but with our primers produced a | + | <li>PCat (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14033">BBa_I14033</a>) is 38bp, but with our primers produced a 280 bp fragment, 4th well from left.</li> |
| + | |||
| + | <div class="pictext"0 style="height:120px;"> | ||
| + | <div class="pictextl"> Gel Electrophoresis demonstrating PCat Amplification:<br>1.0% agarose gel of PCR products from Distribution Kit: the gel loading order was 1 kb ladder, LacI generator PCR product, 100 bp ladder, PCat and PLac. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/ | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/59/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Pcatamplification2.jpg" rel="ibox" title="PCat Amplification"> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/ | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/59/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Pcatamplification2.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | <li>Ptet (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0040">BBa_R0040</a>) is ~ | + | <li>The PCat PCR products were combined and purified using the |
| + | <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols#qiaquick">QiaQuick Kit</a>. As we were attempting to construct an inducible system with PCat constitutively promoting the LacI generator and we had multiple LacI PCR products, we attempted a gel band extraction of the correct band but were unsuccessful. </li> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <li>Having lost our repressor part, we decided to construct two constitutively expressed systems using Pcat <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115009">BBa_K1115009</a> and Ptet <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115010">BBa_K1115010</a>. After PCR amplification, we digested these promoters with EcoRI and SpeI, and our dhlB-dhlA part BBa_K1115008 with EcoRI and XbaI, and the ligated fragments were transformed to chemically competent TOP10 cells.</li><br> | ||
| + | <li>Ptet (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0040">BBa_R0040</a>) is ~50 bp, but with our primers produced fragment ~300 bp, 2nd well from left.</li> | ||
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">The | + | <div class="pictextl">The gel demonstrating Ptet Amplification:<br> The first lane is the 100 bp ladder, and the Ptet PCR product is in the second lane.</div> |
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Ptetamplification.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Ptet Amplification"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Ptetamplification.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Ptet Amplification"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Ptetamplification.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/f/f3/SydneyUniversity2013_results_Ptetamplification.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 289: | Line 320: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h3>Phenotypic Assays</h3> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<li>After <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols">cloning</a> into a plasmid containing dhlB and dhlA, we screened for clones expressing our construct. We made <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols">screening plates</a> that allowed us to pick clones that looked like they were successfully expressing one of our genes of interest. Yellow regions have low pH, indicating the local degradation of chloroacetate in the growth media. This tells us which clones were successfully cloned with the promoter PCat, facilitating expression of the chloroacetate-degrading enzyme dhlB.</li> | <li>After <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols">cloning</a> into a plasmid containing dhlB and dhlA, we screened for clones expressing our construct. We made <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols">screening plates</a> that allowed us to pick clones that looked like they were successfully expressing one of our genes of interest. Yellow regions have low pH, indicating the local degradation of chloroacetate in the growth media. This tells us which clones were successfully cloned with the promoter PCat, facilitating expression of the chloroacetate-degrading enzyme dhlB.</li> | ||
<div class="pictext"> | <div class="pictext"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">Screening plates that allowed us to isolate clones</div> | + | <div class="pictextl">Screening plates that allowed us to isolate clones:</div> |
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/35/SydneyUniversity2013_results_screeningplates.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Screening Plates"> | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/35/SydneyUniversity2013_results_screeningplates.jpg" rel="ibox" title="Screening Plates"> | ||
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/35/SydneyUniversity2013_results_screeningplates.jpg" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/3/35/SydneyUniversity2013_results_screeningplates.jpg" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 304: | Line 335: | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <h3> Characterisation of submitted parts with the constitutive promoter PCat </h3> |
<ul> | <ul> | ||
<div class="pictext" style="height: 150px"> | <div class="pictext" style="height: 150px"> | ||
| - | <div class="pictextl">To characterize our dhlA and dhlB parts, we again used our colorimetric <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols Bergmann and Sanik">chloride assay</a> | + | <div class="pictextl">To characterize our dhlA and dhlB parts, we again used our colorimetric <a href="https://2013.igem.org/Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Project/Protocols Bergmann and Sanik">chloride assay</a>. |
| + | |||
| + | Cells containing our plasmids were incubated in chloroacetate (blue) or DCA (red) for 16 h. Data for each condition is in triplicate. The negative control was BBa_K1115008, the promoterless dhlB-dhlA coding region. <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115009">BBa_K1115009</a> is dhlB-dhlA constitutively expressed by PCat (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I14033">BBa_I14033</a>), <a href="http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1115010">BBa_K1115010</a> is dhlB-dhlA constitutively expressed by PTet (<a href="http://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_R0040">BBa_R0040</a>), and the positive control is the Coleman lab pUC19 house plasmid expressing dhlB-dhlA with the same RBS. </div> | ||
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/b5/Cl_assay_Graph_with_bars.png" rel="ibox" title=" "> | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/b5/Cl_assay_Graph_with_bars.png" rel="ibox" title="Chloride assay results for our submitted parts"> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/b5/Cl_assay_Graph_with_bars.png" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/b/b5/Cl_assay_Graph_with_bars.png" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 324: | Line 357: | ||
<div class="pictextr"> | <div class="pictextr"> | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
| - | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0a/Percentage_degradation.png" rel="ibox" title=" | + | <a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0a/Percentage_degradation.png" rel="ibox" title="dhlA and dhlB activity in our parts"> |
| - | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0a/Percentage_degradation.png" height="100"> | + | <img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/0/0a/Percentage_degradation.png" height="100"; width="100"> |
</a> | </a> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 331: | Line 364: | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
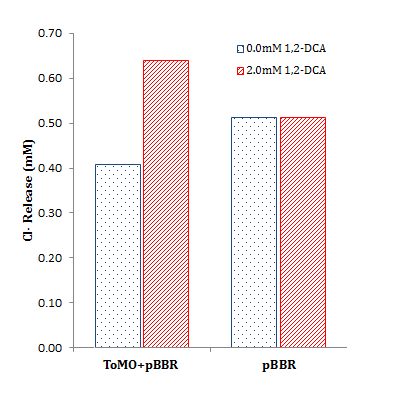
| - | <li>Estimated percentage degradation of chloroacetate and 1,2-DCA | + | <li>Estimated percentage degradation of chloroacetate and 1,2-DCA was determined by: <br><br> |
<center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/6f/Percentage_degradation_equation.png"></center><br><br> | <center><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/6f/Percentage_degradation_equation.png"></center><br><br> | ||
| - | + | Where the <i>test cell supernatant</i> is from our constitutively expressed parts (BBa_K1115009 or BBa_K1115010), the <i>negative cell supernatant</i> is from a negative control containing our parts without a promoter (BBa_K1115008), and the <i>substrate concentration</i> is 2 mM chloroacetate or 1,2-DCA. Note that values of over 100% degradation are misleading and likely indicate endogenous Cl<sup>-</sup> production (i.e. Cl<sup>-</sup> production from other cellular processes unrelated to target substrate metabolism. | |
</li> | </li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | |
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| - | < | + | <br><br> |
| + | <a name="references"></a> | ||
| + | <h2>References</h2> | ||
| - | < | + | <h3>ToMO degrades DCA</h3> |
| + | <ul> | ||
<li>Bertoni, G., Bolognese, F., Galli, E., & Barbieri, P. (1996). Cloning of the genes for and characterization of the early stages of toluene and o-xylene catabolism in <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1. <i>Applied and Environmental Microbiology</i>, <b>62</b>(10), 3704-3711.</li> | <li>Bertoni, G., Bolognese, F., Galli, E., & Barbieri, P. (1996). Cloning of the genes for and characterization of the early stages of toluene and o-xylene catabolism in <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1. <i>Applied and Environmental Microbiology</i>, <b>62</b>(10), 3704-3711.</li> | ||
<li>Shim, H., Ryoo, D., Barbieri, P., & Wood, T. (2001). Aerobic degradation of mixtures of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, dichloroethylenes, and vinyl chloride by toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase of <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1. <i>Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology</i>, <b>56</b>(1-2), 265-269.</li> | <li>Shim, H., Ryoo, D., Barbieri, P., & Wood, T. (2001). Aerobic degradation of mixtures of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, dichloroethylenes, and vinyl chloride by toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase of <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1. <i>Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology</i>, <b>56</b>(1-2), 265-269.</li> | ||
<li>Vardar, G., & Wood, T. K. (2005). Protein engineering of toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase from <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1 for enhanced chlorinated ethene degradation and o-xylene oxidation. <i>Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology</i>, <b>68</b>(4), 510-517.</li> | <li>Vardar, G., & Wood, T. K. (2005). Protein engineering of toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase from <i>Pseudomonas stutzeri</i> OX1 for enhanced chlorinated ethene degradation and o-xylene oxidation. <i>Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology</i>, <b>68</b>(4), 510-517.</li> | ||
| - | < | + | <li>Nishino, S. F., Shin, K. A., Gossett, J. M., & Spain, J. C. (2013). Cytochrome P450 Initiates Degradation of cis-Dichloroethene by <i>Polaromonas sp.</i> strain JS666. <i>Applied and environmental microbiology</i>, <b>79</b>(7), 2263-2272.</li> |
| - | <b>Gibson Assembly</ | + | </ul> |
| + | <h3>Gibson Assembly</h3> | ||
| + | <ul> | ||
<li>Simon, H. A. (1962) The architecture of complexity. <i> Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society </i>, <b>106</b>(6), 467-482.</li> | <li>Simon, H. A. (1962) The architecture of complexity. <i> Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society </i>, <b>106</b>(6), 467-482.</li> | ||
| + | <a name="xiong04"></a><li>Xiong, A, Yao, Q, et al. (2004) A Simple, rapid, high-fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis method for long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res, 32(12):e98</li> | ||
</ul> | </ul> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | <li><a href="#restart">Back to top</a></li> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:55, 29 October 2013


Project Results
| TOMO degrades DCA |
| Gibson Assembly was Problematic |
| Assembly of dhlB-dhlA in pSB1C3 |
| Characterisation of dhlB-dhlA |
| References |
ToMO degrades DCA
- Toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase (ToMO) from Pseuodomonas stutzeri OX1 has been shown to oxidise xylenes, toluene, benzene, styrene, napthalene (Bertoni et al., 1996) as well as tetrachloroethene, trichloroethene, dichloroethene and vinyl chloride (Shim et al., 2001). The enzyme was optimised for chlorinated ethene degradation (Varder & Wood, 2005), and gifted to our host lab in the plasmid pBS(Kan)ToMO.
- We learned that ToMO had activity on DCA by using a GC to measure the removal of DCA from headspace where resting cells were incubated with DCA overnight.
- To confirm this, we showed that ToMO can begin degradation of DCA through an assay for chloride ions released as DCA is converted to chloroacetaldehyde. To our knowledge this hasn’t been shown by anyone else before.
- This is pretty cool, but during the middle of the year we decided to try synthesising the whole pathway rather than building it by conventional cloning. The length of the ToMO gene cluster meant it was too expensive for us to continue working with it. In place of ToMO we turned to a cytochrome p450 monooxygenase, which had been shown in early 2013 to play the same role as ToMO in the initial step of DCA-degradation (Nishino et al. 2013).
- Back to top
Early in our project we needed to find a suitable monooxygenase to begin degradation of DCA by one of the two degradation pathways.
Gibson Assembly was Problematic
Progress
- We spent a week optimising the transformation of our Gibson Assembly reaction product. We initially tried transformation into E. coli EPI300 and yielded no transformants. We suspected that there may be a metabolic burden or harm to cells carrying our correctly assembled product, due to the strong constitutive expression of our designed promoter, Psyn. To account for this we tried transforming into E. coli EPI400, which carries plasmids at low copy-number with an inducible increase in copy-number. We also tried incubating and growing cells at room temperature to lessen their growth rate, so that they might be able to better cope with any possible toxicity of the transformed Gibson Assembly reaction product. Neither of these were successful; however, we were able to screen 87 clones by transforming into a different strain, E. coli TOP10.
Screening
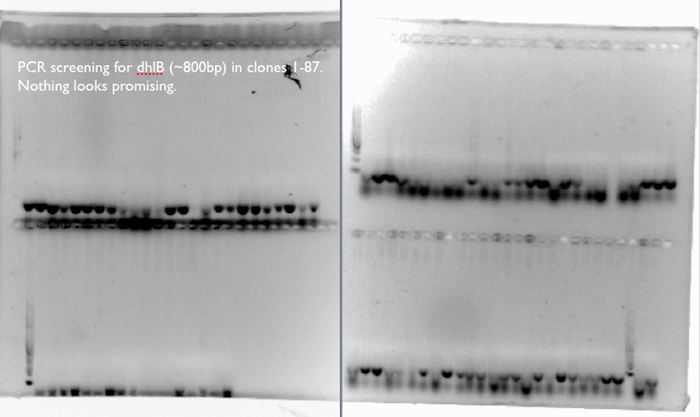
- We screened 87 clones for the presence of dhlB, a gene responsible for the breakdown of chloroacetate in our pathway, by incubating resting cells with chloroacetate and chloride assay. A few clones from each type of pathway looked promising, so we proceeded to extract plasmids from these for further investigation.
dhlB PCR screening:
We expected a band at ~800 bp for an amplification of dhlB, the gene in our pathway responsible for the degradation of chloroacetate. We didn’t see it in any of the 87 clones used in the phenotypic chloride assay, where a few of the clones had exhibited increased production of Cl- ions from the chloroacetate substrate compared to control cells.
We expected a band at ~800 bp for an amplification of dhlB, the gene in our pathway responsible for the degradation of chloroacetate. We didn’t see it in any of the 87 clones used in the phenotypic chloride assay, where a few of the clones had exhibited increased production of Cl- ions from the chloroacetate substrate compared to control cells.
Plasmid Preps
- None of the clones from which we extracted plasmids contained the correctly assembled insert. By PCR and diagnostic restriction digests on these plasmids we were able to distinguish two different misassembled versions of our desired Gibson Assembly reaction product.
Plasmid Digests:
We did a second plasmid prep of our clones because the first weren’t very clear. Desmond figured out that by digesting the plasmids with EcoRV we ought to see a single 2 kb band if pSB has closed on itself. We don't see anything like this in our clones, but we know from the rfp that this works (BBa_J04450 is about 3 kb, and contains a single EcoRV site in the pSB backbone). If the plasmid contains our gBlocks (or at least iGEMBLOCK 1 with aldA), then we expect to see two bands - one at 1 kb, a second at 5 or 6 kb (depending on whether we're looking at p450 or the adh plasmid). We don't see this either. We think that in most of the plasmids, some of the gBlocks have assembled in pSB1C3 but not iGEMBLOCK 1. In one of the clones (64) we see a band at 1 kb but nothing else, so maybe iGEMBLOCK1 assembled in pSB, but not other gBlocks.
Interestingly, rfp looks spot-on while our results are similar to that in the last plasmid prep (everything slightly higher than 3 kb, except 64). With rfp we expect a single band at 3 kb (pSB is 2 kb plus the rfp 'part' is 1 kb, and the whole construct contains a single EcoRV site in pSB). Notably, 64 was one of the small p450 colonies we patched from Gibson Assembly Product transformations.
We did a second plasmid prep of our clones because the first weren’t very clear. Desmond figured out that by digesting the plasmids with EcoRV we ought to see a single 2 kb band if pSB has closed on itself. We don't see anything like this in our clones, but we know from the rfp that this works (BBa_J04450 is about 3 kb, and contains a single EcoRV site in the pSB backbone). If the plasmid contains our gBlocks (or at least iGEMBLOCK 1 with aldA), then we expect to see two bands - one at 1 kb, a second at 5 or 6 kb (depending on whether we're looking at p450 or the adh plasmid). We don't see this either. We think that in most of the plasmids, some of the gBlocks have assembled in pSB1C3 but not iGEMBLOCK 1. In one of the clones (64) we see a band at 1 kb but nothing else, so maybe iGEMBLOCK1 assembled in pSB, but not other gBlocks.
Interestingly, rfp looks spot-on while our results are similar to that in the last plasmid prep (everything slightly higher than 3 kb, except 64). With rfp we expect a single band at 3 kb (pSB is 2 kb plus the rfp 'part' is 1 kb, and the whole construct contains a single EcoRV site in pSB). Notably, 64 was one of the small p450 colonies we patched from Gibson Assembly Product transformations.
PCR from Gibson template
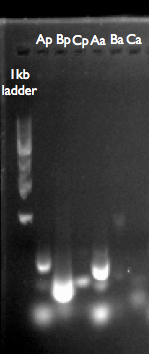
- We thought it could have been possible to assemble our entire pathway from smaller fragments salvaged from our Gibson Assembly reaction product. This proved impossible, presumably due to the extent of heterogenous template including both correctly and incorrectly assembled gBlocks in the Gibson Assembly reaction product. It may have been possible to do something similar using IDT’s gBlocks as template, however, this was not possible as we’d used up all of one of gBlocks during a second Gibson Assembly.
- Back to top
This is our gel analysis of our GA products. Ap, Bp, Cp are from the p450 pathway, using our GA reaction product as template. Aa, Ba and Ca are from the adh pathway. It looks like we can’t amplify what we want, or that it doesn’t exist in the GA reaction product.
Lessons
Constitutive Expression
- We suspect that some of the genes we tried to assemble (e.g., p450, Nishino et al., 2013) can harm the cells they're expressed in, whether this is by using up resources or unusual interactions with undesired targets in the cell. If this is the case, then by a sort of natural screening we were only able to find colonies on plates that contain misassembled gBlocks that did not successfully express these genes.
- Upon reflection, we approached the assembly of our pathway with an almost child-like ignorance and optimism. Our promoter was specifically designed to maximise expression of our construct, as if ‘the more pollutant degrading genes, the better’. If the hypothesis above is correct, then we might have had more success with an inducible promoter.
Modularity
"There once were two watchmakers, named Hora and Tempus, who manufactured very fine watches. Both of them were highly regarded, and the phones in their workshops rang frequently - new customers were constantly calling them. However, Hora prospered, while Tempus became poorer and poorer and finally lost his shop. What was the reason?
The watches the men made consisted of about 1,000 parts each. Tempus had so constructed his that if he had one partly assembled and had to put it down - to answer the phone say - it immediately fell to pieces and had to be reassembled from the elements. The better the customers liked his watches, the more they phoned him, the more difficult it became for him to find enough uninterrupted time to finish a watch.
The watches that Hora made were no less complex than those of Tempus. But he had designed them so that he could put together subassemblies of about ten elements each. Ten of these subassemblies, again, could be put together into a larger subassembly; and a system of ten of the latter sub-assemblies constituted the whole watch. Hence, when Hora had to put down a partly assembled watch in order to answer the phone, he lost only a small part of his work, and he assembled his watches in only a fraction of the man-hours it took Tempus." (Simon, 1962)
Plans
- Replacement of gBlocks
- By replacing a single gBlock, it might be possible to find correctly assembled Gibson products by substituting our strong constitutive promoter Psyn with a repressible promoter.
- With four new gBlocks, it might be possible to assemble some of the important genes in our pathway (aldA, p450, adh1b1) in a BioBrick vector, so that they could then be subsequently assembled piecewise.
- PCR Assembly
- PCR Assembly provided an alternative option to GA for us. It might be possible to PCR amplify genes directly from our gBlocks as template rather than our Gibson Assembly reaction product. Alternatively, with the design of new primers, the genes of interest might be amplified from gBlocks for cloning into a BioBrick vector. With either of these options, sequence fidelity may be an issue.
- Since Hong Kong we have tried this, and it proved unsuccessful based on the protocol from (Xiong, 2004), using our gBlocks of aldA, p450 and tetR and some primers.
Assembly of dhlB-dhlA in pSB1C3
While struggling with Gibson Assembly of our whole pathway we turned to the extraction, cloning and characterisation of two parts in our pathway, dhlB and dhlA. These two genes had been cloned into pUC19 by others in our lab.Amplification
- We designed primers specifically for amplifying dhlB and dhlA, while removing a forbidden EcoRI site between them. Our primer design allowed us to clone each gene by itself and also together into the shipping vector pSB1C3.
Cloning
- Back to top
We cloned the PCR fragments into pSB1C3 and transformed the ligation product. We were greatly assisted by ligating into a BBa_J04450, extracted from the linearised plasmid pSB1C3 in the Distribution Kit, which provided a neat red-white screen.
PCR Junction Screening of AB22 We used the red-white screen to find colonies that contained the dhlB-dhlA insert instead of rfp, and PCR junction screen was used to find correctly assembled inserts. We used NEB 1 kb ladder. If the two-way ligation of dhlB and dhlA worked as desired, we should have observed a 110 bp PCR product (AB22s) spanning the junction between pSB1C3 and dhlB, an 874bp PCR product (AB22m) spanning the junction between dhlB and dhlA, and a 1086bp PCR product (AB22e) spanning the junction between dhlA and pSB1C3.
After PCR screening of the junctions between our parts and pSB1C3, we extracted the plasmids from a few that looked promising for further confirmation and submission to the iGEM HQ. We performed a digest and ran the results on a gel. This digest confirmed the length and concentration of our plasmids before shipping to iGEM HQ.
Characterisation of dhlB-dhlA
After sending dhlB and dhlA to iGEM HQ, we began characterisation by cloning a constitutive promoter from the Distribution Kit in front of our parts.Amplification
- PCat (BBa_I14033) is 38bp, but with our primers produced a 280 bp fragment, 4th well from left.
- The PCat PCR products were combined and purified using the QiaQuick Kit. As we were attempting to construct an inducible system with PCat constitutively promoting the LacI generator and we had multiple LacI PCR products, we attempted a gel band extraction of the correct band but were unsuccessful.
- Having lost our repressor part, we decided to construct two constitutively expressed systems using Pcat BBa_K1115009 and Ptet BBa_K1115010. After PCR amplification, we digested these promoters with EcoRI and SpeI, and our dhlB-dhlA part BBa_K1115008 with EcoRI and XbaI, and the ligated fragments were transformed to chemically competent TOP10 cells.
- Ptet (BBa_R0040) is ~50 bp, but with our primers produced fragment ~300 bp, 2nd well from left.
Gel Electrophoresis demonstrating PCat Amplification:
1.0% agarose gel of PCR products from Distribution Kit: the gel loading order was 1 kb ladder, LacI generator PCR product, 100 bp ladder, PCat and PLac.
1.0% agarose gel of PCR products from Distribution Kit: the gel loading order was 1 kb ladder, LacI generator PCR product, 100 bp ladder, PCat and PLac.
Phenotypic Assays
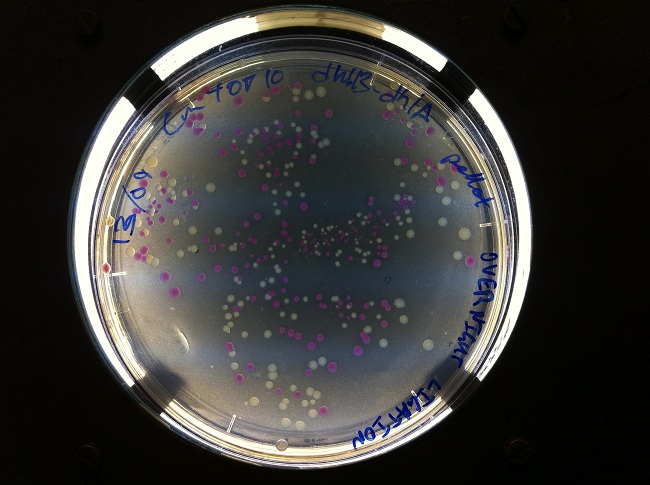
- After cloning into a plasmid containing dhlB and dhlA, we screened for clones expressing our construct. We made screening plates that allowed us to pick clones that looked like they were successfully expressing one of our genes of interest. Yellow regions have low pH, indicating the local degradation of chloroacetate in the growth media. This tells us which clones were successfully cloned with the promoter PCat, facilitating expression of the chloroacetate-degrading enzyme dhlB.
Characterisation of submitted parts with the constitutive promoter PCat
- Estimated percentage degradation of chloroacetate and 1,2-DCA was determined by:

Where the test cell supernatant is from our constitutively expressed parts (BBa_K1115009 or BBa_K1115010), the negative cell supernatant is from a negative control containing our parts without a promoter (BBa_K1115008), and the substrate concentration is 2 mM chloroacetate or 1,2-DCA. Note that values of over 100% degradation are misleading and likely indicate endogenous Cl- production (i.e. Cl- production from other cellular processes unrelated to target substrate metabolism.
To characterize our dhlA and dhlB parts, we again used our colorimetric chloride assay.
Cells containing our plasmids were incubated in chloroacetate (blue) or DCA (red) for 16 h. Data for each condition is in triplicate. The negative control was BBa_K1115008, the promoterless dhlB-dhlA coding region. BBa_K1115009 is dhlB-dhlA constitutively expressed by PCat (BBa_I14033), BBa_K1115010 is dhlB-dhlA constitutively expressed by PTet (BBa_R0040), and the positive control is the Coleman lab pUC19 house plasmid expressing dhlB-dhlA with the same RBS.
The data from the graph above is summarized to the right, showing total chloride release relative to initial substrate concentration. The calculations are summarized below.
References
ToMO degrades DCA
- Bertoni, G., Bolognese, F., Galli, E., & Barbieri, P. (1996). Cloning of the genes for and characterization of the early stages of toluene and o-xylene catabolism in Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62(10), 3704-3711.
- Shim, H., Ryoo, D., Barbieri, P., & Wood, T. (2001). Aerobic degradation of mixtures of tetrachloroethylene, trichloroethylene, dichloroethylenes, and vinyl chloride by toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase of Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 56(1-2), 265-269.
- Vardar, G., & Wood, T. K. (2005). Protein engineering of toluene-o-xylene monooxygenase from Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 for enhanced chlorinated ethene degradation and o-xylene oxidation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 68(4), 510-517.
- Nishino, S. F., Shin, K. A., Gossett, J. M., & Spain, J. C. (2013). Cytochrome P450 Initiates Degradation of cis-Dichloroethene by Polaromonas sp. strain JS666. Applied and environmental microbiology, 79(7), 2263-2272.
Gibson Assembly
- Simon, H. A. (1962) The architecture of complexity. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society , 106(6), 467-482.
- Xiong, A, Yao, Q, et al. (2004) A Simple, rapid, high-fidelity and cost-effective PCR-based two-step DNA synthesis method for long DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res, 32(12):e98
 "
"