Team:Edinburgh/Project/Results/Metal binding Results
From 2013.igem.org
Hristianita (Talk | contribs) |
Hristianita (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
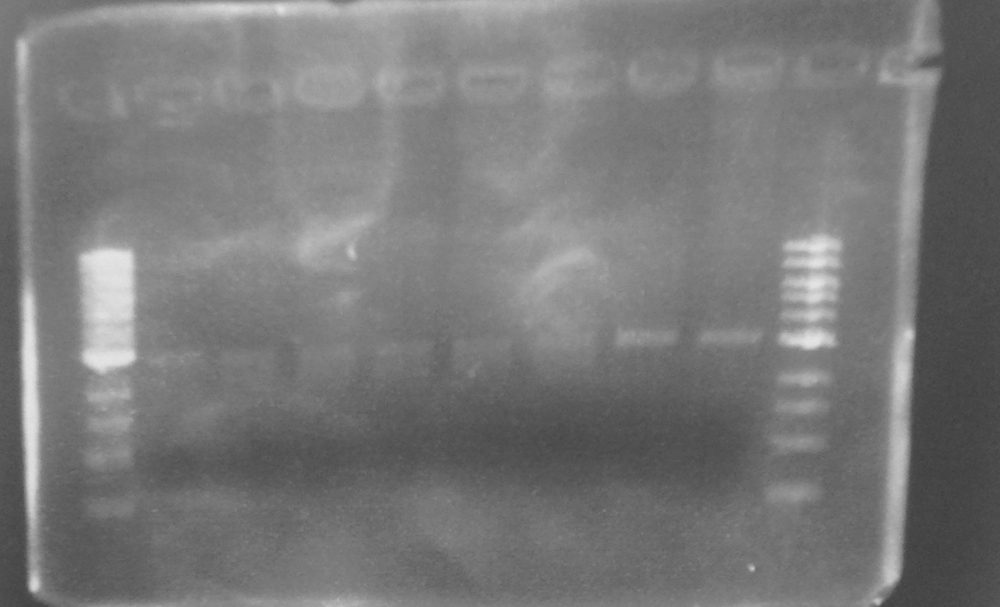
'''Figure 2.''' EcoR1 single digests of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA1 colony 2; FbpA1 colony 3; FbpA2 colony 1; FbpA colony 2; --; --; 1Kb ladder*. | '''Figure 2.''' EcoR1 single digests of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA1 colony 2; FbpA1 colony 3; FbpA2 colony 1; FbpA colony 2; --; --; 1Kb ladder*. | ||
| - | [[File:Metal_binding_Results3.png| | + | [[File:Metal_binding_Results3.png|150px]] |
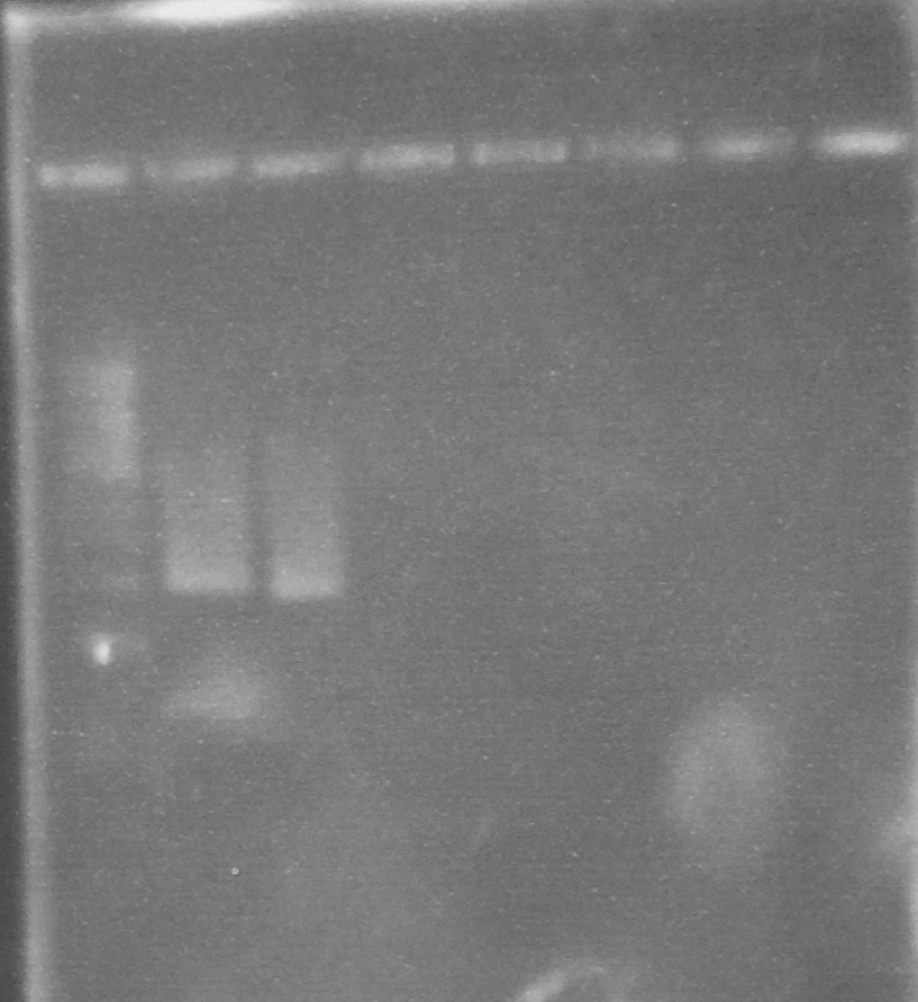
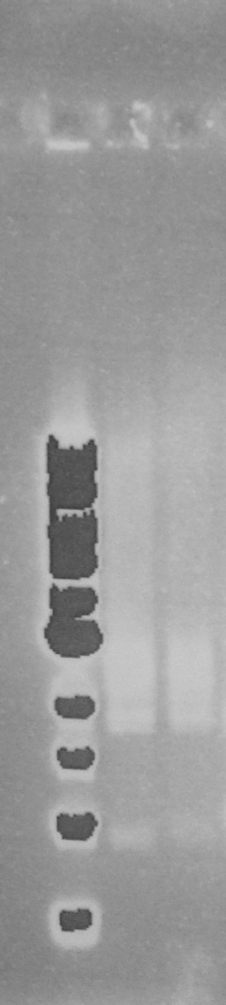
'''Figure 3.''' EcoR1 PstI double digest of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA2 colony 2. | '''Figure 3.''' EcoR1 PstI double digest of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA2 colony 2. | ||
Revision as of 15:55, 4 October 2013
Contents |
Cloning FbpA as a Biobrick
The coding sequence alone of the Neisserial FbpA protein was cloned from a plasmid obtained from within the University of Edinburgh. Two forms of the protein were cloned: the full length native coding sequence FbpA1 BBa_K1122702 and the coding sequence less the putative signal peptide FbpA2 BBa_K1122703. In both cases primers were designed such that each sequence was terminated by two consecutive stop codons, and flanked with biobrick enzyme cut sites for insertion into pSB1C3.
Primers
F1: cgcttctagatgaaaacatctatccgatacg
F2: cgcttctagatggacattaccgtgtacaacgg
R1: atcctgcagcggccgctactagtattattatttcataccggcttgctc
Native coding sequence used as PCR template indicating primer binding sites:
atgaaaacatctatccgatacgcactgcttgccgcagccctgaccgccgccacccccgcg ctggcagacattaccgtgtacaacggccaacacaaagaagcggcacaagccgttgcagat gcctttacccgggctaccggcatcaaagtcaaactcaacagtgccaaaggcgaccagctt gccggccaaatcaaagaagaaggcagccgaagccccgccgacgtattctattccgaacaa atcccggcactcgccaccctttccgcagccaacctcctagagcccctgcccgcctccacc atcaacgaaacacgcggcaaaggcgtgccggttgccgccaaaaaagactgggtggcactg agcggacgttcgcgcgtcgtcgtttacgacacccgcaaactgtctgaaaaagatttggaa aaatccgtcctgaattacgccacgccgaaatggaaaaaccgcatcggttacgtccccact tccggcgcgttcttggaacagattgtcgccatcgtcaaactgaaaggcgaagcggccgca ttgaaatggctcaaaggcctgaaagaatacggcaagccttacgctaaaaactccgtcgcc cttcaagcggttgaaaacggcgaaatcgatgccgccctcatcaacaactactactggcac gctttcgcgcgtgaaaaaggcgtacaaaatgtccacacccgcctgaatttcgtccgccac agagatcccggcgcactcgttacctattccggcgcagccgtgttaaaatcctcccaaaac aaggatgaggcgaaaaaattcgtcgccttcctcgccggcaaggaaggacagcgcgccctg accgccgtccgtgccgaatatcctttgaatccgcacgtggtatccaccttcaatttggaa cccatcgccaagttggaagcaccccaagtgtccgccaccactgtttccgaaaaagaacac gccacccggctgcttgagcaagccggtatgaaataa
Expected PCR fragment sizes:
FbpA1, Full length coding sequence 1032bp; FbpA2 Coding sequence less putative signal peptide 969bp. See figure 1.
Figure 1. A 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 native sequence PCR product (plus minor product); FbpA2 less signal peptide PCR product.
The two PCR products were double digested with Xba1 and Pst1, and ligated into pSB1C3 digested with the same enzymes. The ligation mixture was transformed into E. coli JM109, and plasmid DNA minipreps were done on transformant colonies. Aliquots of these minipreps were linearised by digested EcoR1 and run on a 0.8% agarose gel. See figure 2. One miniprep of each coding sequence was then double digested with EcoR1 and PstI, in order to confirm a size difference between the two biobricks of the two coding sequence. See figure 3. In each of the gels the size represented by the bands was as expected.
Figure 2. EcoR1 single digests of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA1 colony 2; FbpA1 colony 3; FbpA2 colony 1; FbpA colony 2; --; --; 1Kb ladder*.
Figure 3. EcoR1 PstI double digest of minipreps on a 0.8% agarose gel: 1Kb ladder*; FbpA1 colony 1; FbpA2 colony 2. Plasmid DNA of each sequence (FbpA1 colony 1 BBa_K1122702 and FbpA2 colony 2 BBa_K1122703) was sent for sequencing and submitted to the parts registry.
* 1Kb ladder from New England Biolabs. DNA band sizes: 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 10Kb.

| 
| | | | 
|
| This iGEM team has been funded by the MSD Scottish Life Sciences Fund. The opinions expressed by this iGEM team are those of the team members and do not necessarily represent those of MSD | |||||
 "
"