Team:Imperial College/Enzyme Kinetics
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 84: | Line 84: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
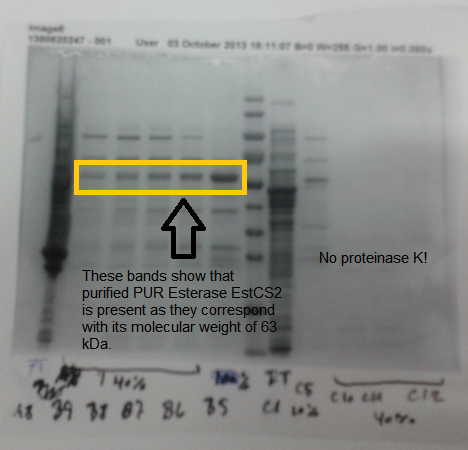
| + | We also successfully purified PUR esterase EstSC2 from the cells, in order to use in a clearing zone assay. Proteinase K was not purified; this may be because this enzyme self digest. | ||
| - | [[File:Purestpkgel.png|left|thumbnail|500px|<b> | + | [[File:Purestpkgel.png|left|thumbnail|500px|<b>SDS PAGE gel shows purified PUR esterase EstCS2. Figure by Imperial College London 2013 iGEM</b>]] |
{{:Team:Imperial_College/Templates:footer}} | {{:Team:Imperial_College/Templates:footer}} | ||
Latest revision as of 01:19, 5 October 2013
Contents |
Enzyme Activity assays
PUR Esterase
Cell lysate assay
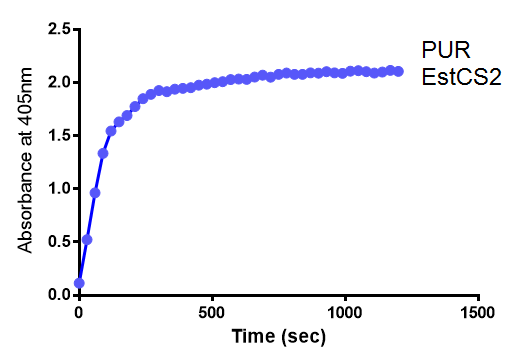
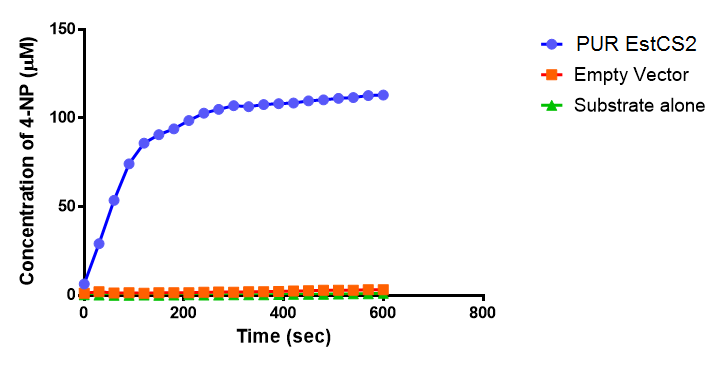
Since the PUR Esterases were not secreted, initially the cells were lysed to obtain crude cell extracts in order to test whether the enzymes are active. The Western Blot results showed that the constructs EstCS2 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149002 BBa_K1149002], PueB [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149004 BBa_K1149004] and PulA [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149006 BBa_K1149006] were being expressed. The cultures expressing these three constructs were grown, lysed by sonication and utilised in a colourimetric assay with the substrate analog para-Nitrophenyl butyrate. The data shows that PUR Esterase EstCS2 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149002 BBa_K1149002] is definitely active.
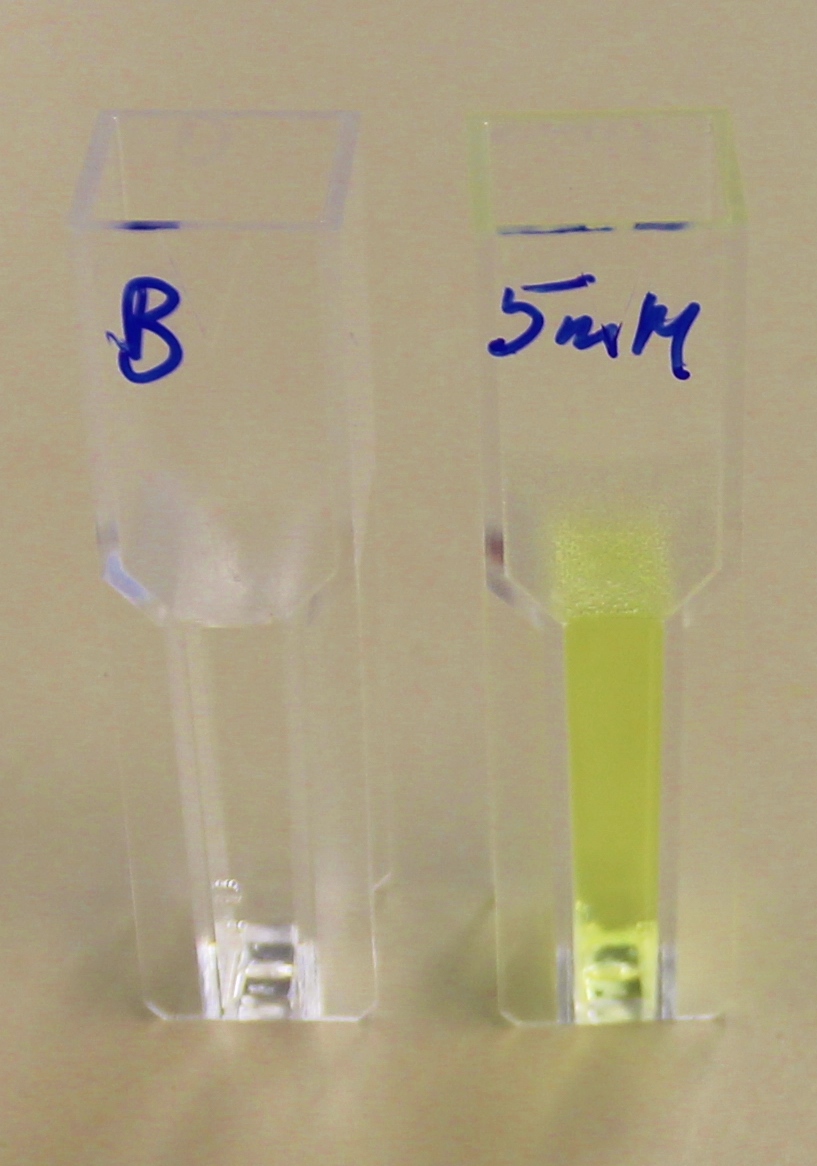
para-Nitrophenyl butyrate (p-NP) is commonly used to indicate an enzyme’s esterase activity. The enzyme cleaves the ester bond and releases the 4-nitrophenol (4-NP), thus causing a colour change from colourless to yellow and an increased absorbance at wavelength 405 nm.
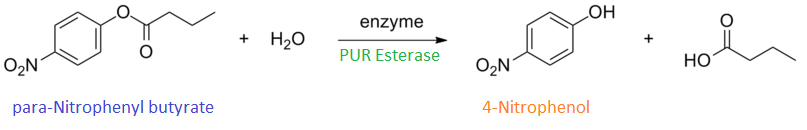
The assay was run in the [http://www.eppendorf.com/int/index.php?sitemap=2.1&action=products&contentid=1&catalognode=87236 Eppendorf BioSpectrometer] was used to automatically read the absorbance of the reaction mixture every 30 seconds. The concentration of 4-Nitrophenol produced from the reaction was calculated using the Beer-Lambert Law; the extinction coefficient of 4-NP is 18,000 M-1 cm-1 at 405 nm.
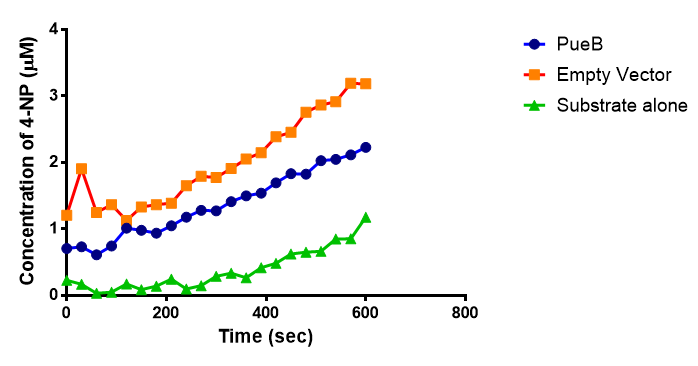
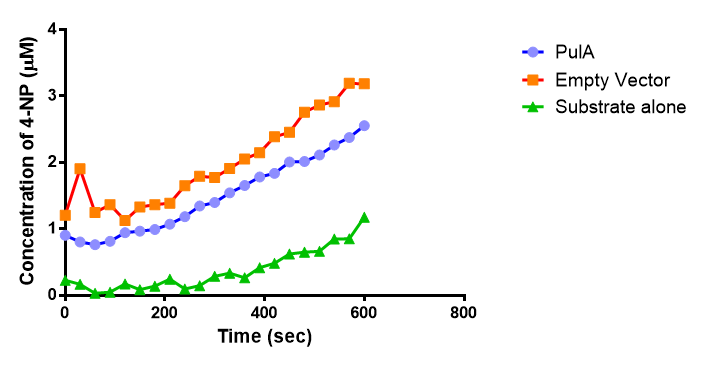
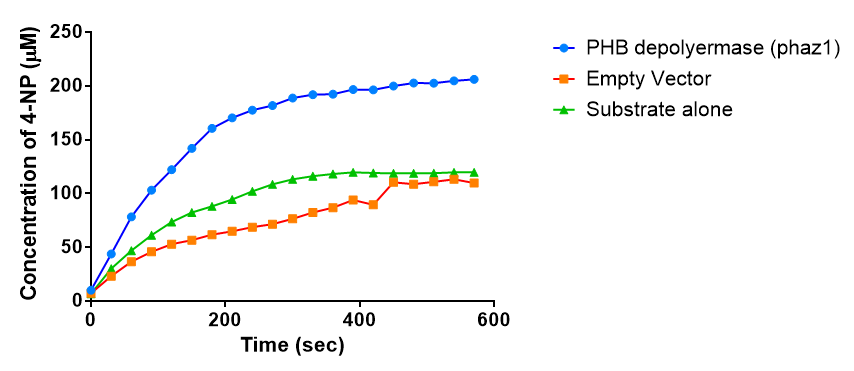
The results below show the concentration of 4-NP produced by the three different PUR esterases and compare them to the Empty Vector and Substrate alone as negative controls.
The above graphs clearly show that PUR Esterase EstCS2 is active and cleaving p-NP. The recorded concentrations of 4-NP, in the presence of this PUR Esterase, are much greater than with the Empty Vector or the Substrate alone. Is PUR Esterase EstCS2 active? Yes!
The enzymes expressed by both PueB and PulA do not appear to have esterase activity for this substrate. There is a tiny increase in 4-NP concentration for PueB, PulA, Empty Vector and Substrate alone. This probably indicates that the substrate is slowly degrading by itself. Other constituents of the cell lysates are likely to be causing a slight increase in p-NP degradation, as PueB, PulA and Empty Vector show higher concentrations of 4-NP than the Substrate alone.
Conclusion: PUR Esterase EstCS2 is active!
Enzyme activity of PHB depolymerase (phaz1)
It can be seen from the Western Blot results that phaz1 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149010 BBa_K1149010] was being expressed. To show that this enzyme has esterase activity, colourimetric assays were performed using the substrate analog para-Nitrophenyl butyrate. When the ester bond in this substrate is cleaved, 4-Nitrophenol is released. This is accompanied by an increase in absorbance at the wavelength 405 nm and a colour change from colourless to yellow. The concentration of 4-Nitrophenol produced could then be calculated with the Beer-Lambert Law, as the extinction coefficient of 4-NP at 405 nm is 18,000 M-1 cm-1. This experiment was performed with both the crude cell lysate and purified PHB depolymerase. Our data shows that this enzyme is definitely active.
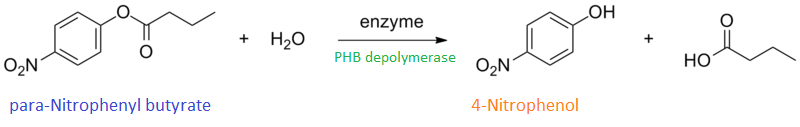
Cell lysate assay
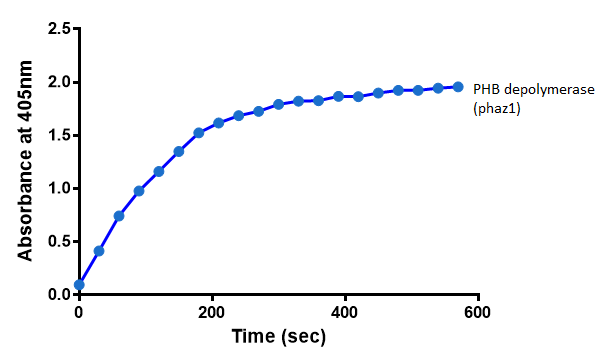
After 48 hours of growing and inducing the phaz1 culture, the cells were lysed by probe-sonication, spun down and resuspended in 50mM Tris-HCl buffer. A reaction mixture containing 5 µL of crude phaz1 lysate, 4 µL of para-Nitrophenyl butyrate solution and 1 mL of 50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4 buffer was incubated in the [http://www.eppendorf.com/int/index.php?sitemap=2.1&action=products&contentid=1&catalognode=87236 Eppendorf BioSpectrometer] for 570 seconds, whilst the absorbance at 405 nm was automatically recorded every 30 seconds.
The above graph shows that greater esterase activity occurs when the phaz1 cell lysate is in the reaction mixture. The graph shows that there is also esterase activity occuring in the Empty Vector and Substrate alone reaction mixtures, but this is due to the imidazole present in the Tris-HCl buffer, which acts as a general base catalysis. [http://pubs.acs.org/doi/pdf/10.1021/ja00874a035 (6)]
Purified enzyme assay
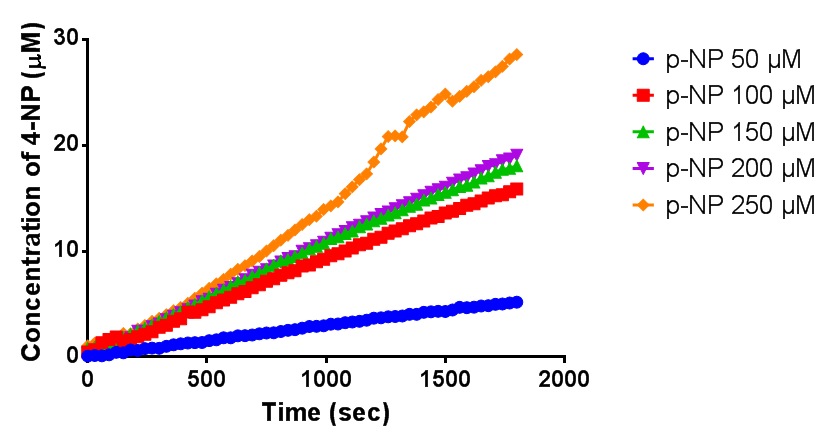
Since the phaz1 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149010 BBa_K1149010] construct contains a His tag, the protein could be purified by metal affinity chromatography. The colourimetric assay was carried out, as with the cell lysate. 100 mM potassium phosphate (pH 7.4) buffer was used instead of the Tris-HCl buffer, to eliminate the esterase activity caused by imidazole in the buffer used previously. Every 30 seconds for 30 minutes the absorbance at 405 nm of the reaction mixture was recorded. The reaction mixture contained 1 ml of phosphate buffer, 2.5 µL of purified PHB depolyermase (stock concentration 0.230 mg/ml) and para-Nitrophenyl butyrate to make final concentrations of 50 µM, 100 µM, 150 µM, 200 µM and 250 µM of substrate.
The above graph shows how the concentration of 4-Nitrophenol produced is greater when the para-Nitrophenyl butyrate substrate concentration is greater. This data shows that we have successfully purified active PHB depolyermase.
We also successfully purified PUR esterase EstSC2 from the cells, in order to use in a clearing zone assay. Proteinase K was not purified; this may be because this enzyme self digest.
 "
"