Team:Paris Bettencourt/Project/Target
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 119: | Line 119: | ||
<div class="rightparagraph"> | <div class="rightparagraph"> | ||
<center><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/60/Fnr_ribbons.png" target="_blank"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/52/Fnr_ribbons.png" width="267.5px"/></a></center> | <center><a href="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/6/60/Fnr_ribbons.png" target="_blank"><img src="https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2013/5/52/Fnr_ribbons.png" width="267.5px"/></a></center> | ||
| - | + | <p><b>Figure 5: Our 3D model shows the structure of FNR where negative residues are coloured in blue, positive residues in red and NAD in purple (ball and stick representation). The key amino acids at the active site are Glu211, Gly 366, Arg 110, Arg 199, Arg 200 and Asn155. Glu211 acts as a hydrogen acceptor whilst the latter four residues act as hydrogen donors.</div></p> | |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="Model"></div> | <div id="Model"></div> | ||
<div style="clear: both;"></div> | <div style="clear: both;"></div> | ||
| - | <p><b>Figure 6:Comparison of NADP interaction with Fpra's active site and Pyridoxine's interaction to it's active site. </div></p> | + | <p><b>Figure 6: Comparison of NADP interaction with Fpra's active site and Pyridoxine's interaction to it's active site. </div></p> |
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="Model"></div> | <div id="Model"></div> | ||
Revision as of 01:55, 29 October 2013


Background
SirA is an essential gene in latent tuberculosis infections
Results
- Produced an E. coli strain which relies upon mycobacterial sirA, fprA and fdxA genes to survive in M9 minimal media
- Demonstrated that E. coli can survive with mycobacterial sulfite reduction pathway with Flux Balance Analysis
- Located drug target sites on sirA as well as identified high structural similarity between cysI and sirA through structural anaylsis
Aims
To perform a drug screen targeted at the sirA gene from mycobacteria
Skip to Introduction
Skip to Modeling
Skip to Design
Skip to Results
Introduction
SirA is essential for M. tuberculosis persistence phenotype as sulfur containing amino acids are particularly sensitive to oxidative stress within the macrophage and must regularly be replaced (Pinto et al 2007). Currently, there are no drug candidates that are known to specifically inhibit SirA and conventional drug screens involve do not provide information regarding the mechanism of drug action nor do compounds that inhibit exponential growth necessarily have an effect on persistent TB. We designed a working drug screen assay to specifically target the mycobacterial sulfite reductase protein SirA. To this end we cloned Ito E. coli the sulfite reduction pathway of M. smegmatis, a non-pathogenic mycobacterial relative of M. Tuberculosis. Our model overcomes the problem of long doubling time of M. tuberculosis. Specific inhibition of the sulfite reduction pathway is scored by comparing a drug screen of our E. coli construct vs. wild-type. Any drug candidates that have activity against both the wild-type E. coli and our construct are non-specific inhibitors of E. coli growth. However, any drug candidates that inhibit only the growth of our E. coli construct will be SirA pathway specific.
Flux Balance Analysis of Sulfite Reduction Pathway
We used an E. coli model (iJR904) obtained from the BiGG database as a starting model to obtain wild-type growth rate (f = 0.9129 divisions/hour). We then deleted the reaction ‘SULR’ which encodes for the sulphite reduction pathway involving cysI and obtained a f= -8e-13=0 divisions/hour indicating that the sulphite reduction pathway is essential for growth. Finally we introduced two new reactions for sirA and fprA and a new species fdxA. We found that growth with the mycobacteria pathway reverts the growth phenotype back to wild-type levels (f = 0.9105 divisions/hour). We then wanted to expand our model to find new pathways that we could utilize for a targeted drug screen approach. We wrote a matlab script that finds all the essential reactions in M. tuberculosis and all the essential reactions in E. coli, and then tries to complement the essential reactions in the E. coli model with the essential reactions from M. tuberculosis. The model identified 100 metabolic reactions that we could target. Additionally, due to the modular nature of the model, it can be used to find target-able metabolic reactions in any SBML file. The Matlab scripts can be found here and requires Cobra Toolbox 2.0 to function. Please visit the FBA page for a detailed list of results.
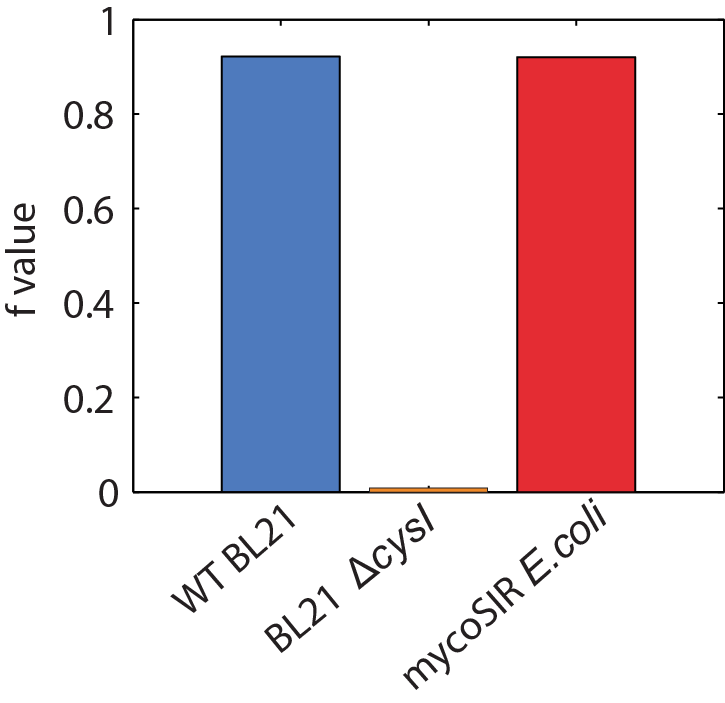
Figure 2: Biomass Flux through E. coli and mycoSIR E. coli
Structural Analysis of SirA
Superimposing the structures of M.tuberculosis SirA and E.coli CysI reveals high homology, in particular of the active sites. Both proteins have the same symmetry (psuedo 2 fold) indicative of a common evolutionary origin. Our analysis highlighted important conserved residues, involved in substrate binding to be Arg97, Arg130, Arg166, Lys207. These positively charged residues are conserved in the sulphite/nitrite reductase family. In addition, 4 Cys residues are conserved for iron-sulphur binding.
The most profound structural differences between the two enzymes are found in the ferredoxin binding site and SirA's most C terminal residues and several surface loop regions due to deletions or insertions. A stark difference is a covalent bond formed between Cys161 (thiolate) and Tyr69 (C carbon atom) found adjacent to the redox center (Cu ions) in SirA. The covalently bound residues act as a secondary cofactor in tyrosyl radical stabilization.

Figure 3: The superimposed 3D protein structures of SirA and CysI.
Identification of potential drug target binding sites
Our structural analysis provided the basis for our drug target prediction. Using Chembl and swiss pdb, we have shown a predicted drug target site. Our calculation gives strong favour for a drug to be effective at this site. The calculation reflects the suitability of small molecules to the binding site under the Lipinski's Rule of 5.
The drug target is located at the interface of the three domains. This binding pocket exhibits a dense hydrophobic region. Our analysis targets 48 amino acids of SirA within 6Å of a modelled small drug molecule. Of these residues, only 6 amino acids are charged: His409, Asp453, Asp474, His500, Asp504 and Arg541.
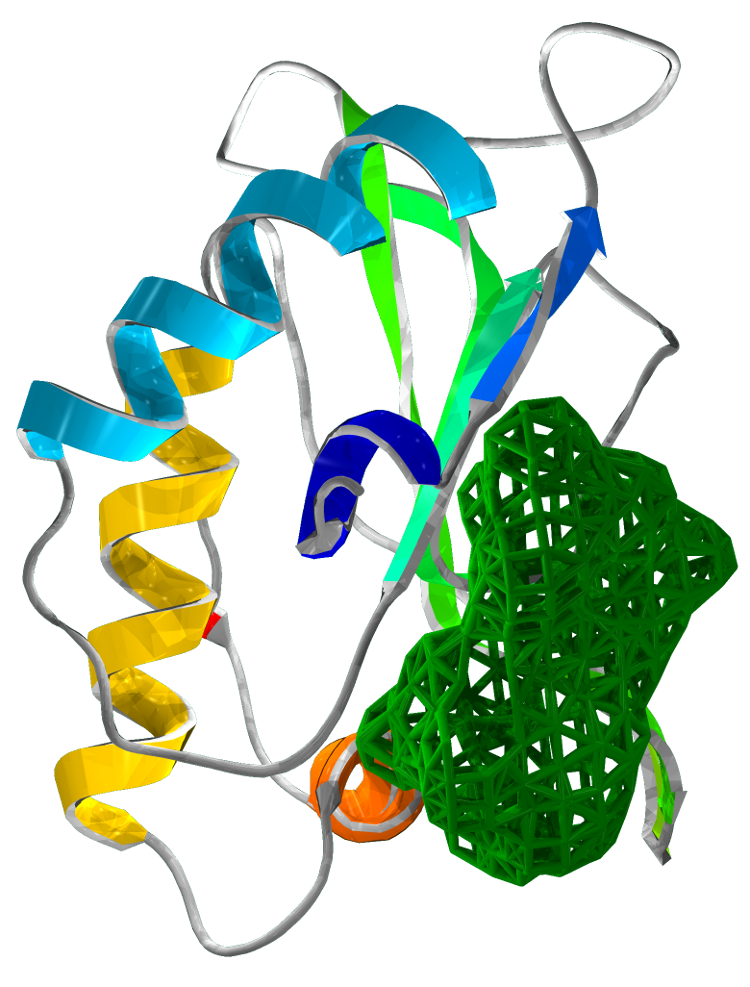
Figure 4 Drug target locations in SirA
Structure based pharmacophore modelling of mycobacterial Fpra
Using LigandScount 3.1, we searched over 8100 drug compounds from the BindingDB and Chembl databases for drugs targetting mycobacterial Fpra. Our search revealed Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) and Pyridoxine to be drug targets for Fpra. We used NADP interacting with the active site as the model of the pharmacore. Results showed pyridoxin to be a competitive inhibitor to NADP. Pyridoxin is a synthetic compound currently available as a prescribed drug.
Chembl analysis of Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) show that it's properties fulfill Lipinski's criteria of being an orally active drug in humans. These properties state that any small drug molecule must have: no more than 5 H bond donors, no more 10 H bond acceptors (N or O atoms), mol mass of less than 500 dalts and octanol-water partition coefficient log P of no greater than 5).
We have shown the proposed properties of Pyridoxine's interaction with Fpra as a competitive inhibitor to NADP at Fpra's active site. The key amino acids at the active site are Ala205, GLN204 and Thr208. GLN204 and Ala205 act as hydrogen bond acceptors whilst Thr208 interacts with a H via van der waals forces. Pyridoxin is a smaller, more lipid soluble molecule than NADP, thus more fitting to Lipinski's criteria.

Figure 5: Our 3D model shows the structure of FNR where negative residues are coloured in blue, positive residues in red and NAD in purple (ball and stick representation). The key amino acids at the active site are Glu211, Gly 366, Arg 110, Arg 199, Arg 200 and Asn155. Glu211 acts as a hydrogen acceptor whilst the latter four residues act as hydrogen donors.
Figure 6: Comparison of NADP interaction with Fpra's active site and Pyridoxine's interaction to it's active site.
 "
"











 +33 1 44 41 25 22/25
+33 1 44 41 25 22/25


