Team:SydneyUni Australia/Modelling Intro
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
C.Squirrel (Talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Style}} {{Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Header}} == '''Introduction'''== A pharmacokinetic model was constructed in order to determine the intracellular c...") |
Jbergfield (Talk | contribs) m |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
== '''Introduction'''== | == '''Introduction'''== | ||
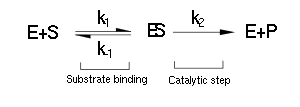
| - | A pharmacokinetic model was constructed in order to determine the intracellular concentration of the metabolites as a function of time and determine the rate at which DCA is removed from solution. The synthetic metabolic pathway involves four introduced enzymes which converts the substrate 1,2-dichloroethane (DCA)into the end product glycolate through 3 metabolic intermediates. The concentration of each metabolic species over time was modelled through a system of ordinary differential equations (ODE) where Michaelis-Menton (MM) equations were used to model the kinetics of each enzyme of our constructed metabolic pathway. | + | A pharmacokinetic model was constructed in order to determine the intracellular concentration of the metabolites as a function of time and determine the rate at which DCA is removed from solution. The synthetic metabolic pathway involves four introduced enzymes which converts the substrate 1,2-dichloroethane (DCA) into the end product glycolate through 3 metabolic intermediates. The concentration of each metabolic species over time was modelled through a system of ordinary differential equations (ODE) where Michaelis-Menton (MM) equations were used to model the kinetics of each enzyme of our constructed metabolic pathway. |
[[File:SydneyUni2013_Model_Intro.png|center]] | [[File:SydneyUni2013_Model_Intro.png|center]] | ||
{{Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Footer}} | {{Team:SydneyUni_Australia/Footer}} | ||
Revision as of 05:42, 27 September 2013


Introduction
A pharmacokinetic model was constructed in order to determine the intracellular concentration of the metabolites as a function of time and determine the rate at which DCA is removed from solution. The synthetic metabolic pathway involves four introduced enzymes which converts the substrate 1,2-dichloroethane (DCA) into the end product glycolate through 3 metabolic intermediates. The concentration of each metabolic species over time was modelled through a system of ordinary differential equations (ODE) where Michaelis-Menton (MM) equations were used to model the kinetics of each enzyme of our constructed metabolic pathway.
 "
"