Team:BIOSINT Mexico/Chassis
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
:We adapt the minus origin mention before and change for the e.coli origin replication that psb1c3 actually have. In order to prove the efficiency of the plasmid we add GFP, to measure transformation efficiency. | :We adapt the minus origin mention before and change for the e.coli origin replication that psb1c3 actually have. In order to prove the efficiency of the plasmid we add GFP, to measure transformation efficiency. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Revision as of 18:32, 27 September 2013
Chassis
Lactobacillus chassis
L. plantarum?
- Lactobacillus plantarum is a gram-positive lactic acid bacterium, present naturally in dairy products, as well as in the gastrointestinal tract1.
- We chose to use L. plantarum as a chassis , because of its unique ability to grow and adapt to a large number of niches2. Studies have shown that L. plantarum has the capacity to optimize its genetic material in order to adapt to different environments, especially those with high levels of carbohydrates2. Another special property of L. plantarum is that it has a high tolerance towards acids, and it is present in many fermentative processes2.
- These characteristics among others make it a potential candidate for its use in different industries. Using recombinant DNA technology, this bacterium could be applied to food industries as a starter or marker in fermentative processes, in healthcare industry as a probiotic or in biofuel production2. As part of our project, we will be explore the potential of L. plantarum as a probiotic, and produce biobricks that can join all the beneficial properties of different probiotics and express it in our own chassis.
Vector design
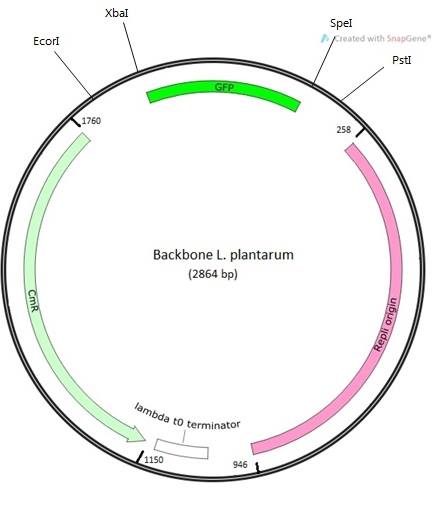
- Using psb1c3 as template we design a new backbone compatible with E.coli and lactobacilli. In our case we used the bases of a staphylococcal plasmid, pUB110, that replicates by a rolling-circle mechanism via a single-stranded (ss) DNA intermediate in Bacillus subtilis and Staphylococcus aureus, and this mechanism is widespread among gram-positive bacteria . When pUB110 replicates in cells of B.subtilis or S. aureus, the plasmid regions, rep, ori, and BA3, function as a structural gene that encodes a replication protein.
- We adapt the minus origin mention before and change for the e.coli origin replication that psb1c3 actually have. In order to prove the efficiency of the plasmid we add GFP, to measure transformation efficiency.
REFERENCES:
1Lee, J., Halgerson, J., Kim, J., and O’Sullivan, D. (2007). Comparative Sequence Analysis of Plasmids from Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Construction of a Shuttle Cloning Vector. [Online]. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1932812/ on April 16, 2013.
2Siezen, R. and Hylckama, J. (2011). Genomic diversity and versatility of Lactobacillus plantarum, a natural metabolic engineer. [Online]. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3271238/ on April 16, 2013.
 "
"