Team:Imperial College/Protocols
From 2013.igem.org
| Line 215: | Line 215: | ||
<p>Measure the absorbance at OD650 every 24 hours. </p> | <p>Measure the absorbance at OD650 every 24 hours. </p> | ||
| - | + | <h2>Clear plate assay</h2> | |
| + | <p><b>Prepare PHB plates</b></p> | ||
| + | <p>Mix 0.5g of P3HB powder with 300 ml LB agar, make P3HB plates.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Use sterilised pipette tip to cut two wells, each has a 0.5 mm diameter. </p> | ||
| + | <p>Pipette 500ul of PhaZ1 cell lysate sample in one of the wells, and same amount of empty vector cell lysate sample in the other well.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Observe the plate every 24 hours.</p> | ||
Revision as of 22:48, 30 September 2013
Contents |
Materials
Waste Conditioned Media (WCM)
We added 1g [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refuse-derived_fuel SRF] (Solid Recovered Fuel) /50 mL LB and then autoclaved the mixture. Once autoclaved, large waste chunks were removed through filter sterilisation (0.2 µm filters) before being used in growth assays as waste conditioned media (WCM). SRF refers to the refuse from recycling facilities that has no value currently and is incinerated to produce power at a cost to the recycling facility, it is composed of 30% plastics while the rest is cellulosic waste
3% glucose Nile Red plates
When making up LB agar media, add 3% glucose then autoclave. When autoclaving it is essential that you keep temperature <125°C. Failure to do so will result in caramelisation (160°C) of the media, which will show as a darkening of the media. With this complete, 60 µL Nile Red was added in addition to 150 µL chloramphenicol in a 300 mL final volume. Plates were then poured and left to dry. Another successful mechanism to thwart caramelisation is to autoclave the LB-agar then add the 3% glucose after. Follow this with a 30 second microwave step and then an 80°C water bath for a couple hours to thoroughly sterilise.
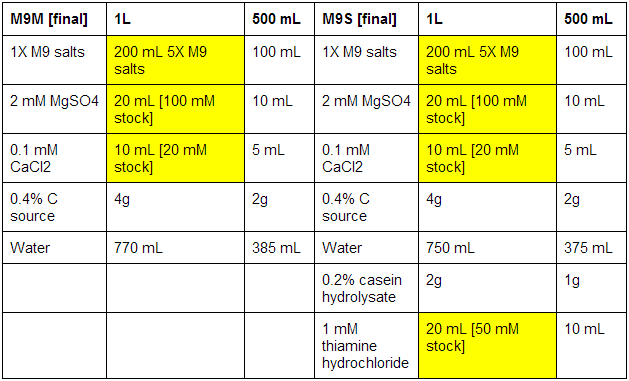
M9 minimal and supplemented media
First made stocks of MgSO4 (246.48 g/mol), CaCl2 (147.02 g/mol), and thiamine hydrochloride (337.3 g/mol):
MgSO4: 100 mM - 2.46g in 100 mL ddH2O
CaCl2: 20 mM - 0.29g in 100 mL ddH2O
Thiamine hydrochloride: 50 mM - 0.84g in 50 mL ddH2O
The bottles used were pre-autoclaved. When all media was prepared, it was sterile filtrated, as autoclaving results in the formation of magnesium precipitate. See below for correct volumes and mass to add where [final] represents desired values.
Xylose and Arabinose
For induction assays, 2% xylose was prepared, as was 6 µM arabinose.
Protocols and Assays
P3HB production and extraction
Extracting PHB
- Centrifuge settings: 4000RPM, 10mins.
- Scale as appropriate.
- After each centrifuge step the supernatant should be poured off.
- This should provide PHB with 99% purity and a high molecular weight.
- Centrifuge 50ml culture and resuspend in PBS.
- Resuspend pellet in 5ml Triton X-100(1% v/v in PBS) for 30mins at room temp.
- Centrifuge, resuspend in 5ml PBS.
- Centrifuge, add 5ml sodium hyperchlorite solution and incubate at 30˚C for 1 hour.
- Centrifuge, wash with 5ml distilled water and 70% EtOH several times.
- Allow powder to dry.
3HB assay
We are hydroxybutyrate colorimetric assay kit. You can download the description of the product and the protocol here. The chemical reaction behind the assay is illustrated on the image below:

sample preparation: 3HB from PHB
We treat about 0.5-0.1 grams of PHB purified from various experiments (and from Sigma) with 10uL of [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149010 phaZ1] enzyme in 800uL tris buffer. The next day, we heat sample up to 90°C to inactivate the phaZ1 enzyme, centrifuge and use the supernatant in different dilutions with Assay Buffer. (90%, 50%, 10%)
sample 1: bioplastic made by [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1149051 hybrid phaCAB] grown on 3% glucose LB
sample 2:"the grey stuff that is directly from waste".
sample 3: P(3HB) from Sigma treated with phaZ1
sample 4: P(3HB) from Sigma untreated, to determine signal from P(3HB)
We do all samples in the wells (96 well place) in triplicates.
Measurements are taken after 40 minute incubation with Developer solution at 20°C.
Cloning
PCR
We used Pfu Ultra polymerase for all reactions where we use the DNA for anything afterwards. Download the exact manual from here
We used MyTaq polymerase for colony PCR and checking plasmids. You can download the manual [http://www.bioline.com/documents/product_inserts/MyTaq%E2%84%A2%20DNA%20Polymerase.pdf#zoom=130 here].
Our super Thermal Cycler was provided by our generous sponsor, Eppendorf.
Running gels
We used SybrSafe to stain the DNA and imaged in a Transilluminator. We cut out bands under a bluebox.
Minipreps
We did minipreps from 4mL overnight cultures in LB, supplemented with antibiotics.
Chlo: 50 mg/mL
Amp:100 mg/mL
Kan: 100 mg/mL
We used [http://www.qiagen.com/Products/Catalog/Sample-Technologies/DNA-Sample-Technologies/Plasmid-DNA/QIAprep-Spin-Miniprep-Kit Quiagen Miniprep kit].
We got a sweet tabletop centrifuge from dear Eppendorf company which served us really well.
Digests and Ligations
For restriction digests, we used NEB enzymes and used the companys protocols accordingly. For ligations, we used T4 ligase. We treated backbones with alkaline phosphatase before ligations and we have used Dpn1 treatment sometimes to degrade the original plasmid.
Sequencing
We used VF2, VR, G1004 and G1005 primers in order to verify the sequence of most of the biobrick parts. We also designed internal sequencing primers to verify the reads in long parts, such as phaCAB.
[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_G00100 VF2 (BBa_G00100)] tgccacctgacgtctaagaa Tm=62 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_G00100 VR (BBa_G00101)] attaccgcctttgagtgagc Tm=60
[http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_G1004 BBa_G1004] (=prefix) gtttcttcgaattcgcggccgcttctag Tm=63 [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_G1004 BBa_G1005] (=revcompl sufix) gtttcttcctgcagcggccgctactagta Tm=64
Transformation
We transformed our plasmids finally into MG1655.
For ligations we used mainly NEB10 and some TOP10 and NEB5 cells for high efficiency.
Waste Growth Assay
Overnight (O/N) cultures of MG1655 transformed with (BBa_K639003) were diluted to OD 0.05 in either fresh LB or waste conditioned media and plated into 96 well plates (200 µl/well). OD600 was read at the indicated time points and media only (LB) was taken away as background signal. In addition to this a qualitative assay as performed. 9 mL mCherry bacteria were transferred into 300 mL of autoclaved SRF in LB, which were placed in a shaking incubator at 37°C. After 2 days 200 µL of this solution was plated out on chloramphenicol plates, this was then repeated a week later to gauge whether or not the bacteria were still alive. To show that the MG1655 could grow on waste solely, they were grown in PBS (phosphate buffered saline) and autoclaved waste. In 100 mL PBS + waste, 1 mL MG1655 mCherry E.coli were added. They were then grown in a shaking incubator at 37°C and samples were plated after 2 days and 6 days.
Growth assays
3HB and Acetoacetate LB and M9 growth for P3HB synthesis
3HB solutions were prepared in advance. An initial stock of 100mM 3HB was made from 0.315g 3HB (FW:126) dissolved in 25 mL ddH2O. This was then diluted down to 10mM, 1mM, 100µM, 1µM working solutions in LB. Furthermore, 3% glucose in LB was prepared with solutions made from 3g glucose in 100 mL LB.
O/N cultures were prepared, these were diluted to OD=0.05 by measuring O/N OD0.05. With this complete the required dilutions of cells were made into 1.5 mL reaction tubes to give a total volume of 800 µL, this was then divided up into 4 wells for quadruplicate technical repeats. Cells used were phaABC, which is involved in P3HB synthesis from glucose, phaBC which synthesises P3HB from acetoacetate and EV empty vector which was used as a growth control.
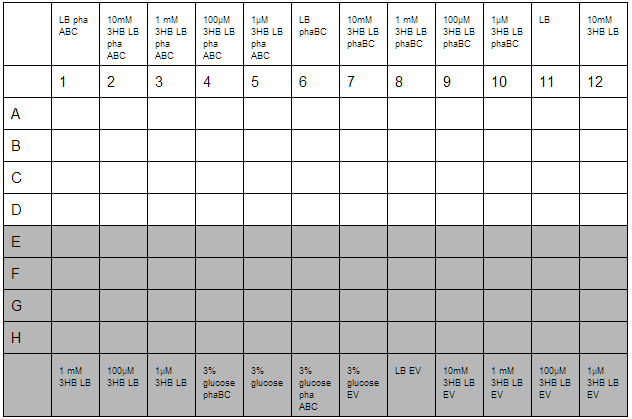
With the plate loaded, it was then placed in a shaking incubator at 700 rpm, 37°C for 30 minutes. After this, we took readings using a robotic plate reader for t=0 at OD600, then repeated this over a further 7 hours.
A second plate was prepared to measure acetoacetate as a sole carbon source. Lithium acetoacetate (FW: 108.02) was prepared by placing 10 mg in 9.2 mL water to give a stock concentration of acetoacetate of 10 mM. Dilutions were made to 100 µM and 1µM. Ethylene glycol growth assays were prepared by diluting 1.11 g/L stock solution by 1000 and 500 to give final concentration of 100 mM and 200 mM respectively. Emulsions were prepared as described below. These were further diluted from stock solutions of 1.25 g/L to working solutions of 31 mg/L and 31 µg/L.
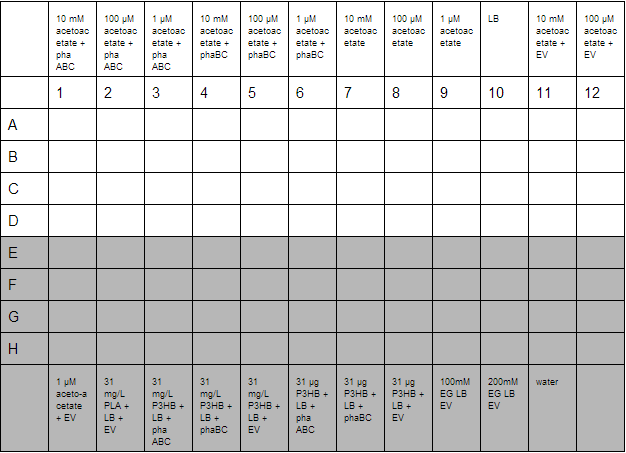
Preparation of Poly DEGA plates.
For 320 mL final media, place 1.5 mL 0.5% poly DEGA in 18.5 mL ddH20. As poly DEGA is very viscous, the 20 mL solution was sonicated for 45 minutes. This complete, it was added to LB agar kept at 70°C along with 25 ug/mL chloramphenicol. The solution was then separated into 3 separate duran bottles of 100 mL volume. 0.21g xylose was added to a bottle, 0.21g arabinose to another and the other did not have an inducer added. The media was then plated out.
Western blot
Sample preparation
Prepare concentrated induction media. (Dissolve 0.134g Arabinose in 8ml pre-sutoclaved LB, 1.52g xylose in 4ml pre-autoclaved LB). Filter sterile induction media.
Make 5 mL overnight culture from the transformed cells.
In the next morning, dilute 0.5 ml overnight culture in 9.5 ml of LB media. The subsequence inducer concentrations are 6mM arabinose and 2% xylose.
Then grow the diluted culture at 37°C, and measure OD600 every hour until the OD reaches 0.5-0.6.
Then induce protein expression with appropriate induction media, and grow the induced cells at 37°C for 5 hours.
Spin 2ml of induced cells, collect 60ul of the supernatant with a 1.5ml tube, and add 20 ul western loading buffer to the supernatant.
Resuspend the pellet with 100 ul of lysis buffer. Wait cell to lyse (15-20 minutes) at room temperature. Vortex is allowed.
Add 33 ul of western loading buffer to the lysate.
Boil the sample at 95°C for 5 minutes and freeze at -20°C.
Gel electrophoresis
Take 15ul of sample to each well. Run the gel at 60V for 1 hour and 20 minutes.
Transfer
Use [http://www.lifetechnologies.com/uk/en/home/life-science/protein-expression-and-analysis/western-blotting/western-blot-transfer/iblot-dry-blotting-system.html iBlot® Dry Blotting System (Invitrogen)] to perform dry blotting.
Antibody binding
All-in-one his antibody (from mouse) is used for proteins with his-tags. Primary and secondary Flag-antibodies are used for Flag-tagged proteins. Mix 7 ml of 5% w/v non-fat dry milk with diluted antibodies, and place the membrane in the mixture. Incubate for 1 hour at room temperature. Wash 210 min with 15 ml 0.05% PHB-Tween. Wash 25 min with 15 ml PBS.
Visualisation
Visualise the protein bands using [http://www.lifetechnologies.com/1/1/28062-novex-ap-mouse-chemiluminescent-detection-kit.html Chemiluminescence detection kit (Invitrogen)]. Protein-specific signal is then captured by a chemiluminescent-compatible X-ray film.
Turbidity assay
Sample preparation
Prepare 10 ml cell culture and induce phaZ1 expression using 2% xylose media.
Centrifuge the cell cultures at 4500 RCF (equivalent to 6221g) for 20 minutes at 4°C.
Add 2 ml of 50mM Tris buffer (pH 7.4) to the pellet and mix well by vortexing the tube.
Transfer the buffered pellet into 7ml tubes and keep the samples on ice.
Perform probe sonication with 2-minute cycles of 2 seconds on, 2 seconds off, at 60% amplitude. Keep the sample on ice while sonicating.
Centrifuge the samples again at 4000 g for 10 minutes and extract the supernatant, in order to separate cell debris and proteins.
Measure the absorbance
Each cuvette contains 700 ul of 0.5 mg/ml PHB emulsion and 300 ul of cell lysate. Use the 50mM Tris buffer as blank.
Measure the absorbance at OD650 every 24 hours.
Clear plate assay
Prepare PHB plates
Mix 0.5g of P3HB powder with 300 ml LB agar, make P3HB plates.
Use sterilised pipette tip to cut two wells, each has a 0.5 mm diameter.
Pipette 500ul of PhaZ1 cell lysate sample in one of the wells, and same amount of empty vector cell lysate sample in the other well.
Observe the plate every 24 hours.
 "
"



