Team:Newcastle/Parts/HBsu-fp
From 2013.igem.org

Contents |
HBsu-xFP Fusion
Purpose and Justification
Bacillus subtilis contains HBsu, a non-specific DNA binding protein which is a homologue to eukaryotic histones. This protein is encoded by the gene hbs gene which is 263bp in length and involved not only in DNA binding but also SRP, DNA repair, HR, and pre-secretory protein translocation [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10224127 (Kouji, et al., 1999)]. It binds to DNA by forming homodimer.
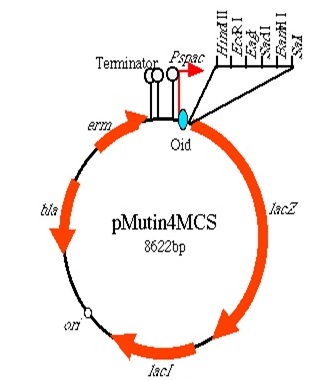
We conjugated the hbs gene with red fluorescent protein (RFP/GFP) in order to fluorescently tag the bacterial chromosome. We produced [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1185001 BBa_K1185001] which codes for a HBsu-sfGFP conjugate and [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1185002 BBa_K1185002] coding for a HBsu-RFP conjugate. Each bacterium was transformed with only one or the other. The expression of these BioBricks was regulated through an IPTG induce promoter (Pspac).
We fused one bacteria containing HBsu-RFP and another containing HBsu-sfGFP, and viewed the genomic shuffling via fluorescent microscopy. The formation of a colour mosaic allows us to confidently claim that recombination has occurred. Genomic shuffling has importance as it can be used to evolve and improve a cells phenotype.
Assembly
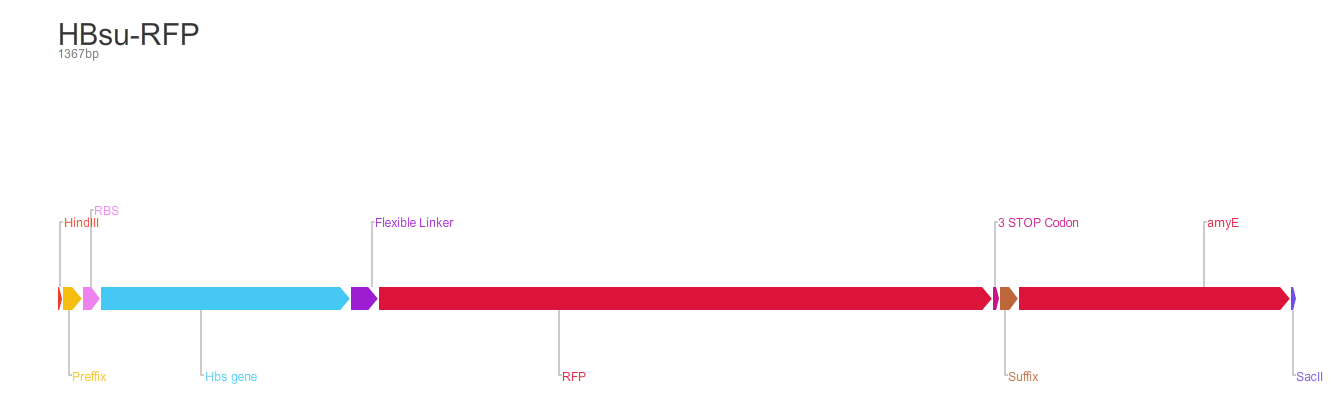
HBsu-(x)FP
BioBrick encodes a fusion protein HBsu-(x)FP protein by 10 amino acids flexible linker (BBa_K105012).
The first version of the BioBrick have superfolder GFP (BBa_E0040)conjugated to the HBsu.
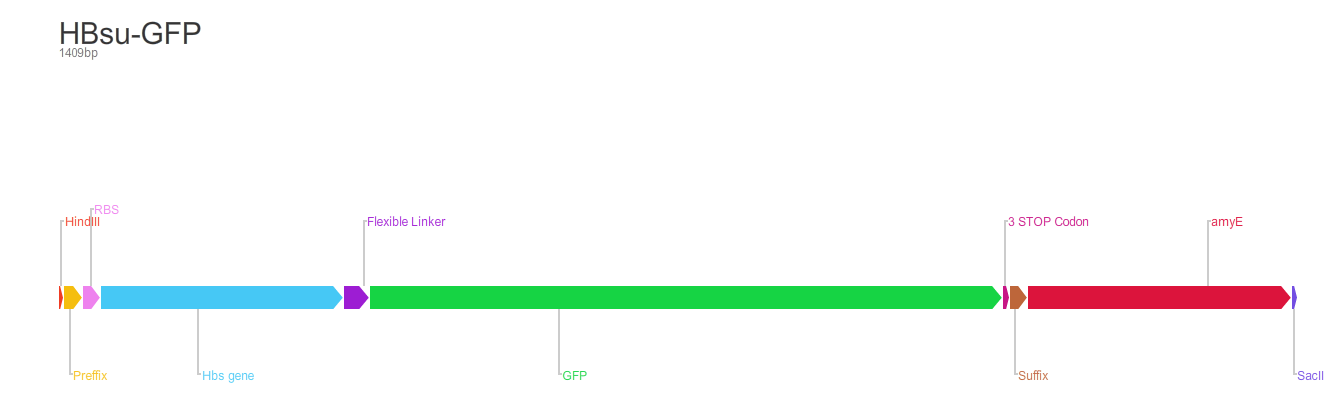
The second version of the BioBrick have RFP (BBa_E1010) conjugated to the HBsu.

Integration
Testing and Characterisation
References
[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10224127 Kouji, N., Shou-ichi, Y., Takao, Y. & Kunio , Y., 1999. Bacillus subtilis Histone-like Protein, HBsu, Is an Integral Component of a SRP-like Particle That Can Bind the Alu Domain of Small Cytoplasmic RNA. The Journal of Biological Chemistry , Volume 274, pp. 13569-13576.]
 "
"