Team:Imperial College/tour
From 2013.igem.org
Engineering microbes to make environmentally friendly plastics from non-recyclable waste
We have taken an expensive byproduct of recycling facilities, a type of mixed waste and turned it into something quite amazing. A material that can be used for a diverse range of applications from making your lunchbox to a 3D printed tissue scaffold; this material is the bioplastic poly-3-hydroxybutyric acid(P3HB). Our system is designed to maximise the recovery of resources from the waste and so we have also investigated how we can use the oil based plastics within the waste to produce the comommodity chemical ethylene glycol. We are passionate about using synthetic biology to help us move towards a more sustainable economy. We have also considered what happens to the material we produce after it is used. This led us to develop the first recycling system for P3HB and a biological one at that. The other well known bioplastic, poly lactic acid (PLA) is also expanding in use and so we developed a system to turn it back into its constituent monomers so that it can be chemically resynthesised or even created in vivo.
Click here to find out how we made P3HB and broke down oil derived plastics and here to see how we recycled P3HB and PLA.
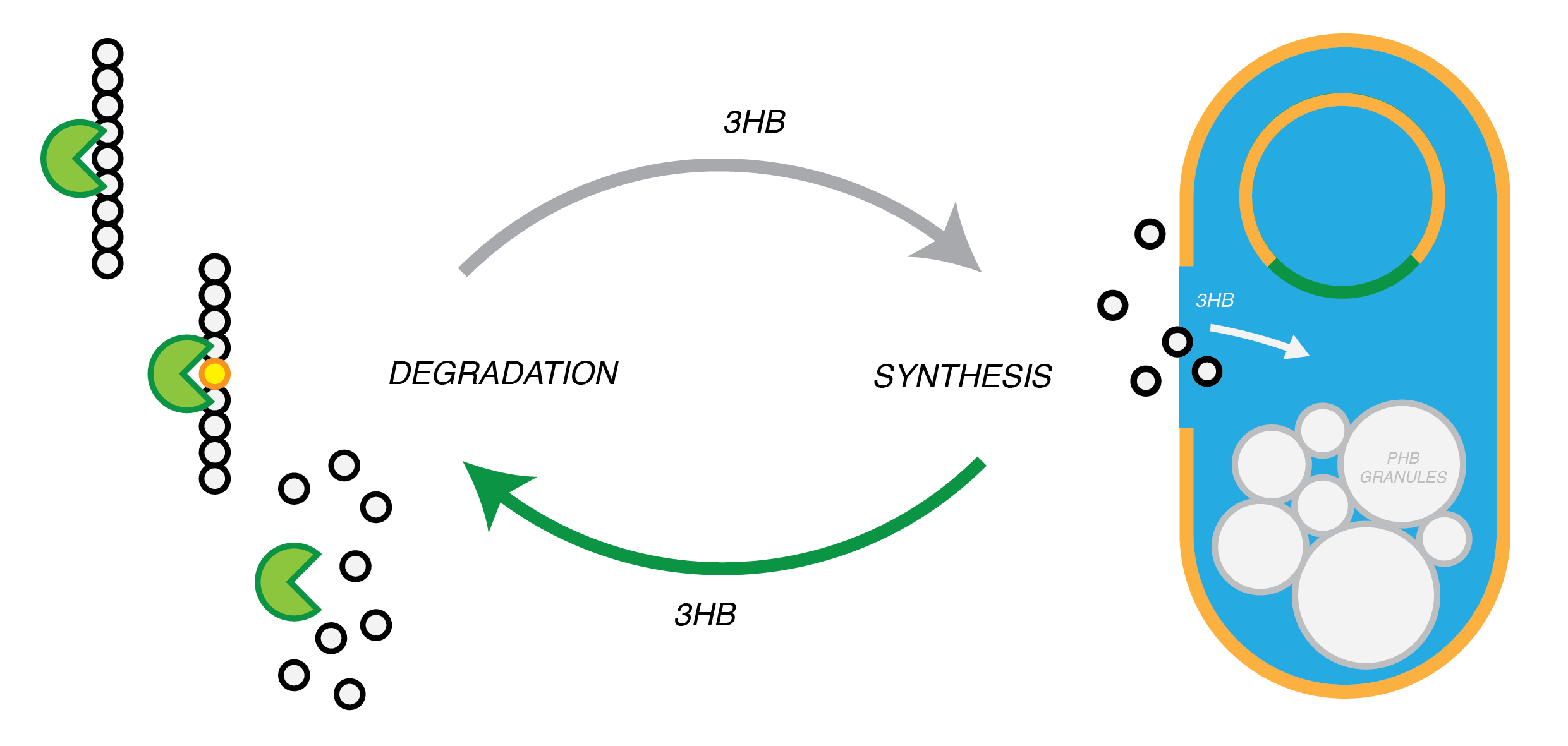
Our System: Modular and Plastic Looping E. coli (M.A.P.L.E.)
Module 1: Resourceful Waste
Non-recyclable waste is sourced from a recycling centre, placed in a bioreactor with our M.A.P.L.E system which degrades the waste and synthesises the bioplastic P(3HB).
Module 2: Plastic Fantastic
Plastic Fantastic is a complete P(3HB) bioplastic recycling platform, where P(3HB) is degraded into monomeric form and then re-polymerised back into de novo P(3HB) for future applications.
Understanding waste management
We thoroughly investigated how the system we have created would fit into the real world. We have identified a waste material which is an economic burden to those who produce it, this material is called Solid Recovered Fuel(SRF) but we'll refer to it as mixed waste from now on. By using this waste we can not only make a profit but also offer a more environmentally sound option for dealing with the waste where the alternative is polluting and resource inefficient.
The product we are producing has many intrinsic benefits such as being industrially biodegradable and produced from sustainable sources as well as being a commodity with increasing market share.
Trips to a materials recovery facility and London City Hall highlighted the fact that recovering value from waste materials is one of the primary aims of waste management in London, the UK and indeed Europe. Importantly it highlighted the need for social solutions combined with technical ones to reduce the waste we produce in the first place and then to maximise the recovery of as much of it as possible. We promoted reducing waste and recycling across campus with our posters highlighting 5 waste offenders and through a strong social media campaign highlighting shocking and interesting issues.
MAPLE- a technology to change your mind
We have thought a lot about how our technology could change into the future and the impacts it might have. From this MAPLE evolved - Modular and Plastic Looping E.coli. We pictured how the technology could be used in different settings with various implications. In picturing this we were influenced by the DIY biology culture which is springing up and the the homebrew industry. You can find out more here about MAPLE's different incarnations.<p>
 "
"