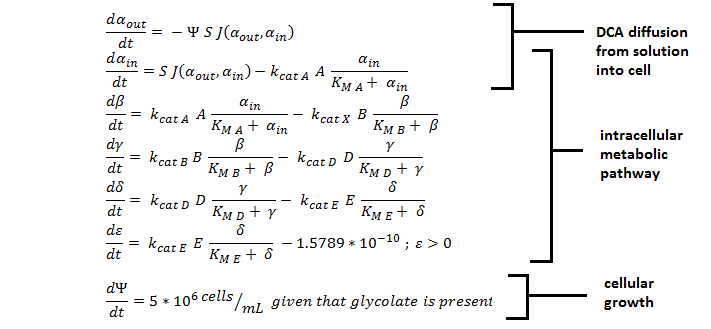Team:SydneyUni Australia/Modelling Model
From 2013.igem.org


Contents |
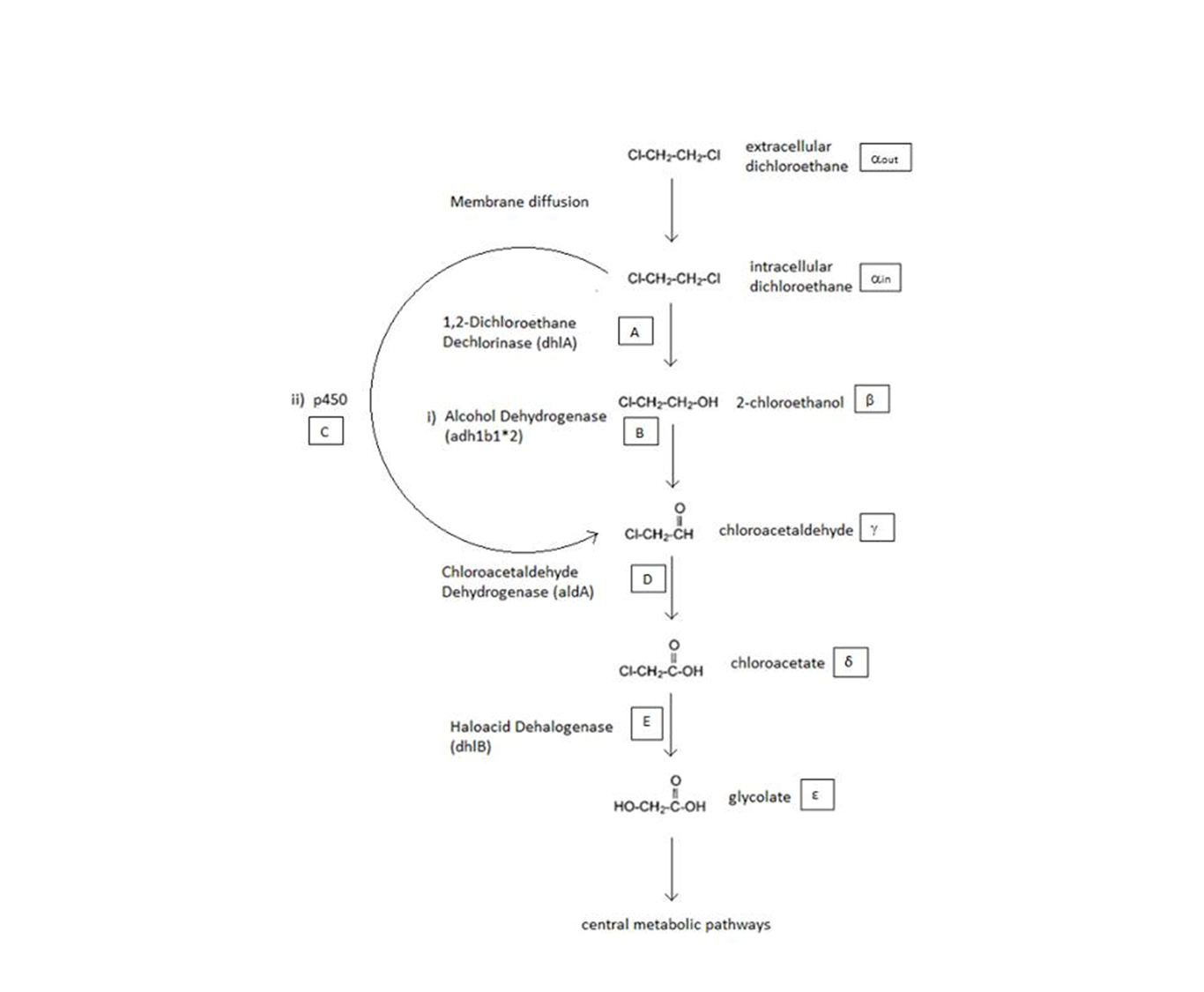
A Schematic of the Engineered Metabolic Pathway:
ODE Model
Shown below are the two systems of ODEs we used to model each pathway.
The non-monooxygenase pathway (with dhlA (A) and adh1b1*2 (B)).
The monooxygenase pathway (with p450 (C)).
Generally, each line represents how a metabolic intermediate changes over time; this is dictated by the relative rate at which the intermediate is formed vs. the rate at which it is removed.
The two above systems of ODEs were used to model two things:
1. The rate at which extracellular DCA is removed from solution (given the number of cells in solution). This is considering the rate at which DCA crosses the plasma membrane (from solution to cytoplasm) of all cells in solution.
2. The rate at which the intracellular concentrations of the metabolic intermediates change over time within a single cell. This considers the relative activities of the enzymes of the metabolic pathway.
Notation
General Information regarding the Enzymes Involved in the Metabolic Pathway
| Enzyme | Gene | Symbol | Constants | Substrate | Product | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2-Dichloroethane Dechlorinase | dhlA | A | KM A = 0.53 mM, kcat A = 3.3 s-1 | DCA (αin) | 2-chloroethanol (β) | [1] |
| Alcohol Dehydrogenase | Adhlb 1/2* | B | KM B = 0.94 mM, kcat B = 0.0871 s-1 | 2-chloroethanol (β) | chloroacetaldehyde (γ) | [2] |
| p450 | p450 | C | KM C = 0.120 mM, kcat C = 0.0113 s-1 | DCA (αin) | chloroacetaldehyde (γ) | [3] |
| Chloroacetaldehyde Dehydrogenase | aldA | D | KM D = 0.06mM, kcat D = 0.60 s-1 | chloroacetaldehyde (γ) | chloroacetate (δ) | [4] |
| Haloacetate Dehydrogenase | dhlB | E | KM E = 20 mM, kcat E = 25.4 s-1 | chloroacetate (δ) | glycolate (ε) | [5] |
A table that summarises the enzymes that compramise the engineered metabolic pathways. The constants presented were (painstakingly) obtained from the literature (referenced).
 "
"