Team:British Columbia/Project/Cinnamaldehyde
From 2013.igem.org
AnnaMüller (Talk | contribs) (→Cinnamaldehyde) |
AnnaMüller (Talk | contribs) m (→Cinnamaldehyde) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Cinnamaldehyde makes up about 65% of cinnamon oil, which is extracted from the bark of cinnamon tress, and it provides the characteristic flavor and aroma to cinnamon products (1). The potential uses of cinnamaldehyde go far beyond its common flavor and aroma properties a review of the literature will show that cinnamaldehyde has characteristics that make it a potential food safety additive as well as a type two diabetes therapeutic. | Cinnamaldehyde makes up about 65% of cinnamon oil, which is extracted from the bark of cinnamon tress, and it provides the characteristic flavor and aroma to cinnamon products (1). The potential uses of cinnamaldehyde go far beyond its common flavor and aroma properties a review of the literature will show that cinnamaldehyde has characteristics that make it a potential food safety additive as well as a type two diabetes therapeutic. | ||
| - | Though cinnamon has been used to keep food from spoiling in parts of India and China for years, scientific evidence has only recently been able support these claims. To date cinnamaldehyde has been shown to inhibit growth of common food born pathogens such as; Lysteria monocytogenes, various Salmonella species, E. | + | Though cinnamon has been used to keep food from spoiling in parts of India and China for years, scientific evidence has only recently been able support these claims. To date cinnamaldehyde has been shown to inhibit growth of common food born pathogens such as; <i>Lysteria monocytogenes</i>, various <i>Salmonella</i> species, <i>E. Coli</i> O157:H7, as well as viruses, and some fungi(2,3) Yet, members of the <i>Lactobacillus</i> family, such as lactobacillus sakei, have demonstrated resistance to cinnamaldehyde up to 0.5M, much lower than the 30mM needed to inhibit listeria, suggesting that its antimicrobial properties could be hosted in our lactobacillus bulgaris chasis(3). Thus, one could imagine a biosynthetic approach to creating cinnamaldehyde would provide the food industry with a useful tool to make food safer. |
| - | This antimicrobial activity has applications to human health as well. Heliobacter pylori is a common pathogen found in the stomach that is responsible for pH induced gastritis and peptic ulcers. It is estimated that ½ the world’s population is infected with Heliobacter pylori (3). In severe cases, such as those often found in the third world, Heliobacter | + | This antimicrobial activity has applications to human health as well. <i>Heliobacter pylori</i> is a common pathogen found in the stomach that is responsible for pH induced gastritis and peptic ulcers. It is estimated that ½ the world’s population is infected with <i>Heliobacter pylori</i> (3). In severe cases, such as those often found in the third world, <i>Heliobacter pylori</i> can result in gastric cancer formation. <i>In vitro</i> studies however, have shown that doses of cinnamaldehyde at 2ug/ml are capable of wiping out said bacterium. Furthermore, evidence suggests that bacterial resistance to cinnamaldehyde does not develop easily (3). This suggests that cinnamaldehyde might be a potent alternative to antibiotic therapy. Though treating gastric illness is a potent application of this chemical entity, cinnamaldehyde offers a more impressive solution to an ongoing global epidemic; type II diabetes. |
The WHO estimates that there are 347 million people globally living with diabetes, 90% of which suffer from type 2, as of 2030 diabetes is projected to be the 7th leading cause of death globally.(4) | The WHO estimates that there are 347 million people globally living with diabetes, 90% of which suffer from type 2, as of 2030 diabetes is projected to be the 7th leading cause of death globally.(4) | ||
Revision as of 03:55, 27 September 2013
iGEM Home


Contents |
Cinnamaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde makes up about 65% of cinnamon oil, which is extracted from the bark of cinnamon tress, and it provides the characteristic flavor and aroma to cinnamon products (1). The potential uses of cinnamaldehyde go far beyond its common flavor and aroma properties a review of the literature will show that cinnamaldehyde has characteristics that make it a potential food safety additive as well as a type two diabetes therapeutic.
Though cinnamon has been used to keep food from spoiling in parts of India and China for years, scientific evidence has only recently been able support these claims. To date cinnamaldehyde has been shown to inhibit growth of common food born pathogens such as; Lysteria monocytogenes, various Salmonella species, E. Coli O157:H7, as well as viruses, and some fungi(2,3) Yet, members of the Lactobacillus family, such as lactobacillus sakei, have demonstrated resistance to cinnamaldehyde up to 0.5M, much lower than the 30mM needed to inhibit listeria, suggesting that its antimicrobial properties could be hosted in our lactobacillus bulgaris chasis(3). Thus, one could imagine a biosynthetic approach to creating cinnamaldehyde would provide the food industry with a useful tool to make food safer.
This antimicrobial activity has applications to human health as well. Heliobacter pylori is a common pathogen found in the stomach that is responsible for pH induced gastritis and peptic ulcers. It is estimated that ½ the world’s population is infected with Heliobacter pylori (3). In severe cases, such as those often found in the third world, Heliobacter pylori can result in gastric cancer formation. In vitro studies however, have shown that doses of cinnamaldehyde at 2ug/ml are capable of wiping out said bacterium. Furthermore, evidence suggests that bacterial resistance to cinnamaldehyde does not develop easily (3). This suggests that cinnamaldehyde might be a potent alternative to antibiotic therapy. Though treating gastric illness is a potent application of this chemical entity, cinnamaldehyde offers a more impressive solution to an ongoing global epidemic; type II diabetes.
The WHO estimates that there are 347 million people globally living with diabetes, 90% of which suffer from type 2, as of 2030 diabetes is projected to be the 7th leading cause of death globally.(4)
It appears as though there is justification for the search for new and novel solutions to this ever-growing problem. In a study from 2007 mice suffering from type 2 diabetes showed a significant reduction in blood glucose, total cholesterol, tri glyceride levels, and an increase in plasma insulin levels when administered cinnamaldehyde orally (20mg/kg)(5). Furthermore, it has been suggested that a 120mg/day-6g/day dose of cinnamon can produce similar effects in humans (6).
What purpose Does it Have in our Project
The ubiquitous use of cinnamon in food products and aroma products, in combination with its potential benefit to food safety and our personal health through its make this compound an exciting one to target for synthesis and incorporation in our ultrabiotic. When combined with the other two flavoring compounds it offers us an opportunity to exhibit CRISPR’s ability to tune bacterial populations through immunity to phage. This mechanism of tunable populations is demonstrated in the “population control” section of our Wiki.
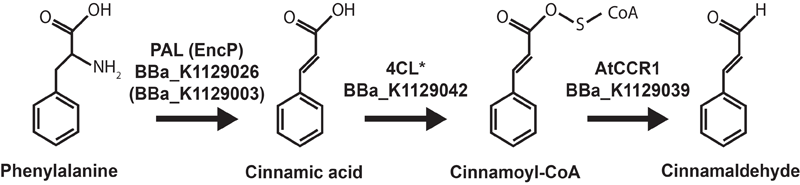
Chemistry
Characterization
References
1) Sara burt review international journal of food microbiology
2) http://www.ann-clinmicrob.com/content/4/1/20
3) http://aem.asm.org/content/70/10/5750.full
4) http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs312/en/)
5) http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944711306001772)
6) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24019277)
 "
"