Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Inhibition/Prohibition
From 2013.igem.org


Contents |
Prohibiting Sprouting
Introduction
In order to deter the invasion of Nosema ceranae, the first step we take is to fully understand its life cycle which completes by bees. The picture beside indicates the relation betweenNosema ceranae stage and the place it grows. By observing these information, we can obviously analyze the advantages and drawbacks at each stage, as well as decide which stage is the best and most attainable for us to weaken the transmission ability of Nosema ceranae.
Background
Stop it at the very begining!!!
After N. ceranae invades epithelial cells of a bee's midgut, it will soon reproduce in two days and new generation appears. Since its lifecycle is so short that there is no time for biological methods to react and inhibit the development of the pathogen, we choose to inhibit it before entering bees' epithelial cells, which will be before N. ceranae’s germination. When N. ceranae's spore moves to bees' midgut, it will start to germinate and develop a structure called polar filament. This structure will then bind to epithelial cells of bees' midgut and poke a hole at the membrane of an epithelial cell, causing the bee eventually dead. In order to inhibit polar filament's development, we find out that there is a protein called PTP1 is highly relevant to the binding of the polar filament and epithelial cells. So we decide to suppress the growth of the polar filament by obstruct the production of PTP1. In the research that is done by other scientist, they have found out that in the process of PTP1 formation a mannose will bind to the protein. So we use mannosidase to prevent N. ceranae from producing proper PTP1 further to stop its polar filament to bind to the epithelial cell and of course, stop the infection of N. ceranae.
Alpha-Mannosidase
MngB, a passage of gene in Escherichia coli K-12 substr MG1655, can produce alpha-mannosidase; also, a new part that we created in partregistry: [http://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1104100 BBa_K1104100]. It is an enzyme that turns 2-O-(6-phospho-α-mannosyl)-D-glycerate into mannose-6-phosphate and glycerate, which is the reverse reaction of the post-translation (glycosylation) on polar filaments of Fungi. This degradation pathway is often seen in many organisms, and the reason why we choose from MG1655 is that this species of E-coli are able to live in bees' midgut. Besides, MG1655 is also the bacteria that we are going to transform our whole circuit into. This decision make our experiment more easier and more certain that this enzyme can well perform in our Bee. coli. . We tend to overexpress this gene in order to inhibit the production of the PTP1 in the polar filament of N. ceranae, the chosen target fungi that we are eager to eliminate.
Circuit Design
Since we cannot be sure when the spore of N. ceranae will start growing polar filament, also not having an accurate sensor to know when N. ceranae invades, we decided to add a constitutive promoter in front of mngB to let it express continuously.
The circuit design is shown as below:
Experiment
Mannosidase functional test
After cloning mngB gene into E. coli, it is a must to examine whether our part is properly combined and well-functioned. Therefore we decide to extract alpha-mannosidase from the cytoplasm of the E. coli and test its function by directly interact with 2-O-(6-phospho-α-D-mannosyl)-D-glycerate. With the aid of HPLC, we can see if it can successfully turn it into α-D-mannose-6-phosphate and D-glycerate.
Experimental process is listed below
1.Use Continuous High Pressure Cell Disrupter to crush E. coli that can produce alpha-mannosidase
2.Filter the product and save the filtrate in an eppendorf
3.Add 2-O-(6-phospho-α-D-mannosyl)-D-glycerate into eppendorf
4.Incubate it at 25℃ for 30 minutes.
5.Run HPLC and compare it with the two standard line of only 2-O-(6-phospho-α-D-mannosyl)-D-glycerate, and with only the extraction liquid of E. coli cytoplasm
6.Compare the area of the data lines with the area of the standard line to calculate the efficiency of the alpha-mannosidase produced by E. coli
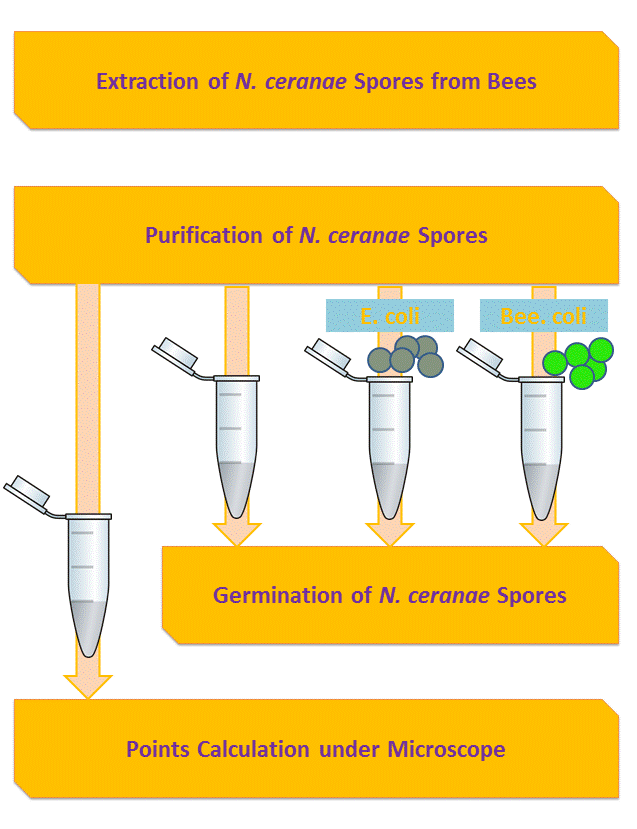
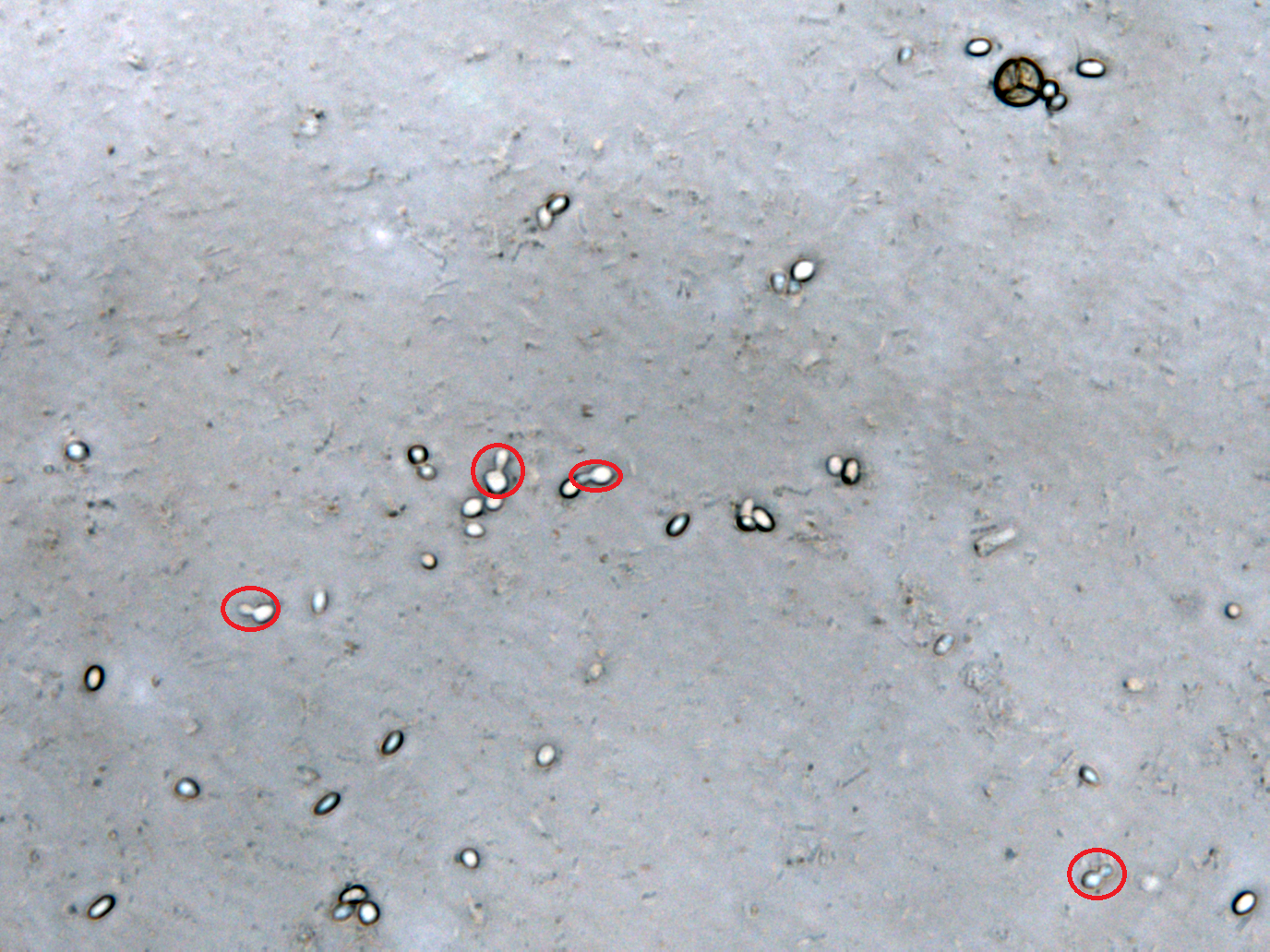
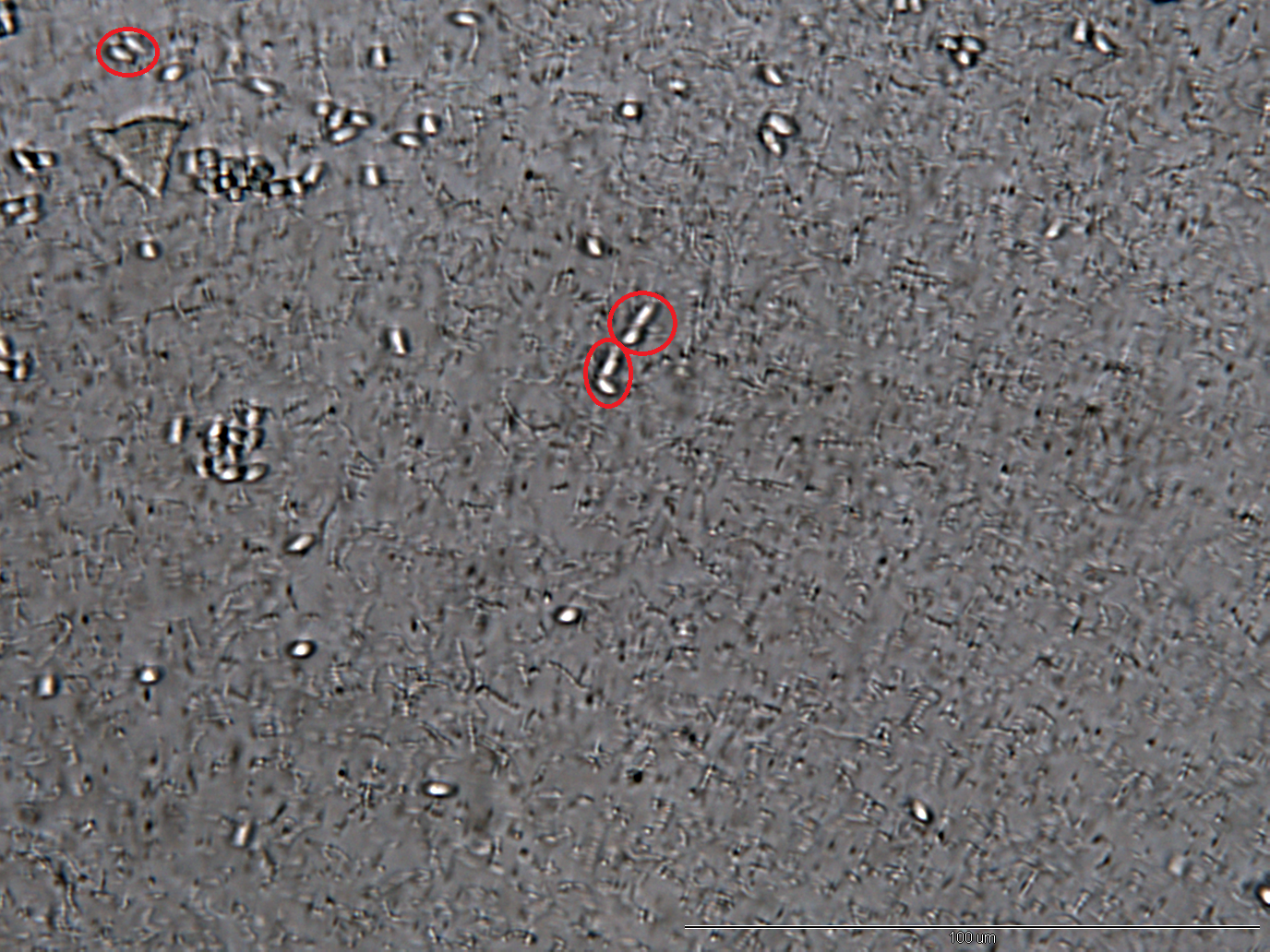
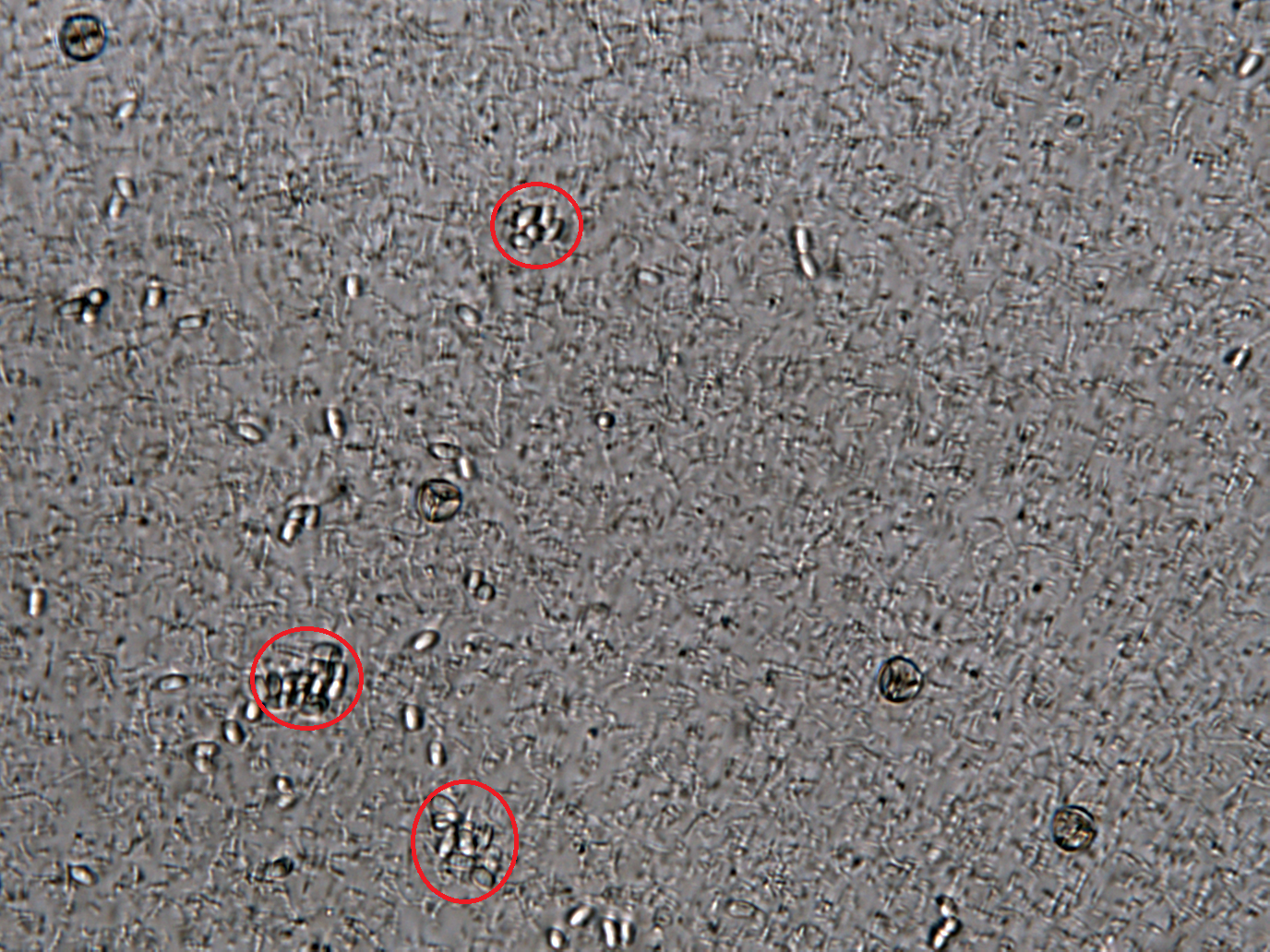
Inhibition of Spore Germination
We define the germination degree as follows:
And so far we have accomplished experiments of the first two groups, discovering that spores underwent the germination procesure got much more points than the control group. Next we will compare the points of group 3 and group 4 to see if Bee. coli can inhibit the germination of N. ceranae.
Reference
1:EcoCyc: Encyclopedia of Escherichia coli K-12 Genes and Metabolism [http://ecocyc.org/ECOLI/NEW-IMAGE?type=ENZYME&object=EG13236-MONOMER EcoCyc/ alpha mannosidase]
2: XU, Y., & WEISS, L. (August 01, 2005). The microsporidian polar tube: A highly specialised invasion organelle. International Journal for Parasitology, 35, 9, 941-953.
3: Xu, Yanji, Takvorian, Peter M., Cali, Ann, Orr, George, & Weiss, Louis M. (n.d.). Glycosylation of the Major Polar Tube Protein of Encephalitozoon hellem, a Microsporidian Parasite That Infects Humans. American Society for Microbiology.
 "
"