Team:Duke/Project/Results/Part2
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→TALEs) |
Hyunsoo kim (Talk | contribs) (→TALEs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
*Relationship between beta-estradiol concentration and TALE-mCherry expression. Cells were grown in varied β-estradiol concentrations and fluorescence was compared to background levels using a control strain | *Relationship between beta-estradiol concentration and TALE-mCherry expression. Cells were grown in varied β-estradiol concentrations and fluorescence was compared to background levels using a control strain | ||
| - | |||
Revision as of 18:08, 27 September 2013
Contents |
Results: Part Characterization using Flow Cytometry
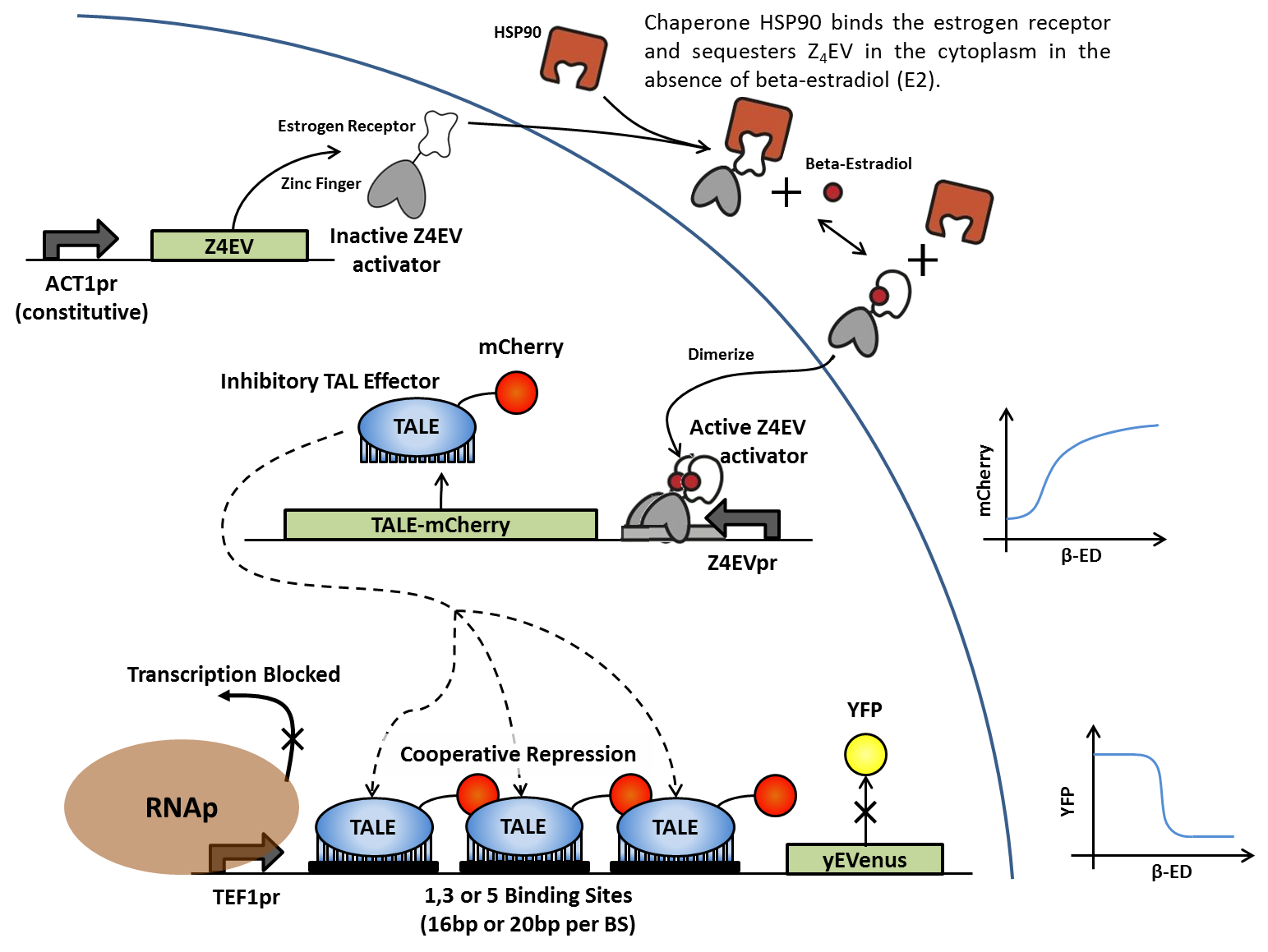
After being integrated into the yeast genome, parts were characterized individually by flow cytometry.
TALEs
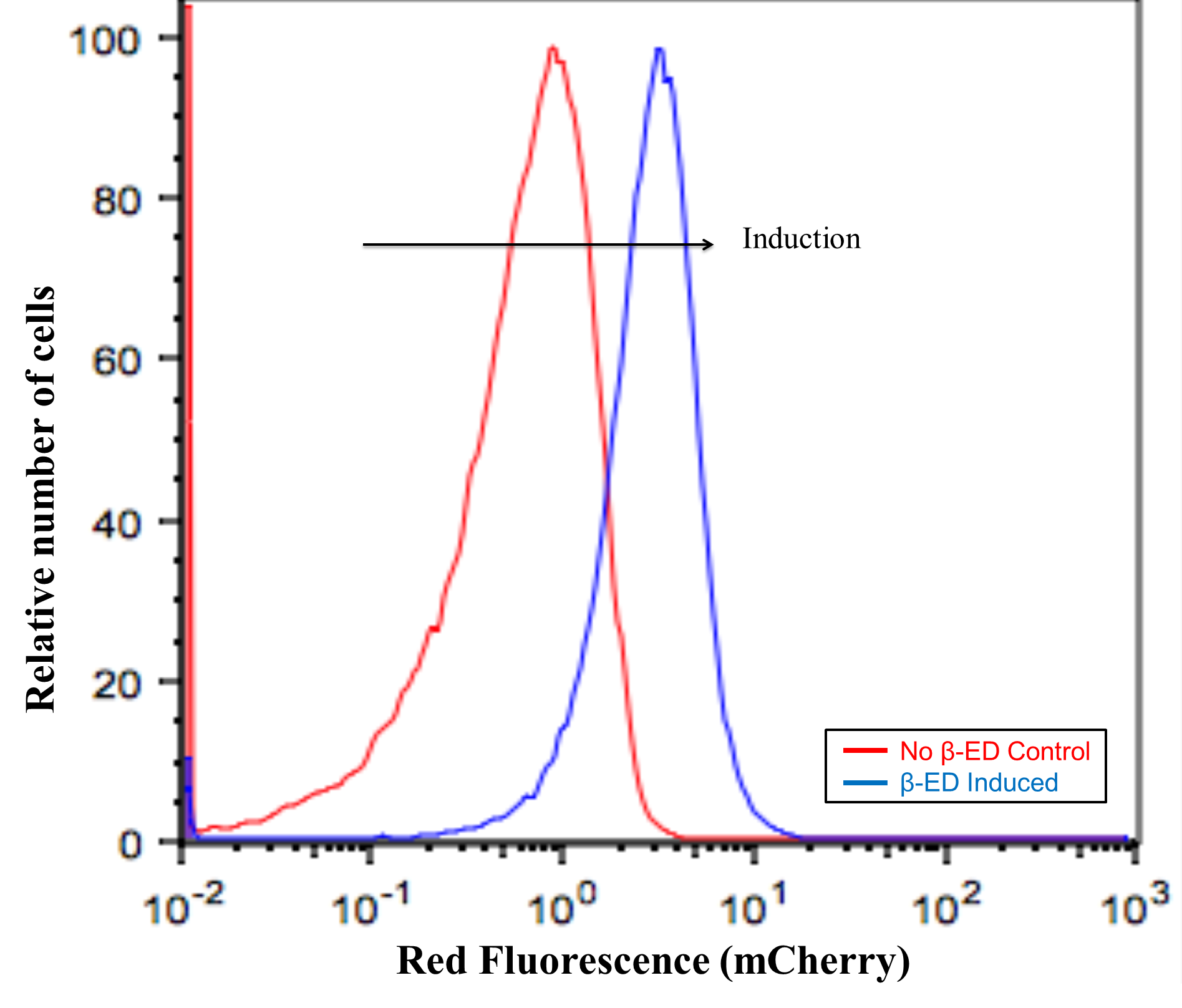
- Initial characterization: TALE-mCherry constructs are present and expression is inducible by β-estradiol. Cells were grown with and without β-estradiol and fluorescence was compared to background levels using a control strain.
Figure 1.5.1. insert graph/data here
- Relationship between beta-estradiol concentration and TALE-mCherry expression. Cells were grown in varied β-estradiol concentrations and fluorescence was compared to background levels using a control strain
Figure 1.5.2. insert input, output curve here
ACT1 reporters
- Initial characterization: ACT1-yEVenus constructs with no operators showed distinct constitutive gene expression. However, presence of operator sites in the 5' UTR knocked down constitutive expression almost to background levels. In lieu of these results, we decided to construct TEF1-promoter reporter constructs. TEF1 is a stronger constitutive promoter that we hoped would counteract the effects of the operator sequence on constitutive expression levels.
Figure 1.5.3. insert graph/data here
TEF1 reporters
- Initial characterization: TEF1-yEVenus constructs with operator sites in the 5' UTR showed expression levels significantly higher than background levels, and comparatively higher than the ACT1-yEVenus constructs.
Figure 1.5.4. insert graph/data here
 "
"