Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Inhibition/Id-Nosema
From 2013.igem.org
| (2 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Identifying ''Nosema ceranae''= | =Identifying ''Nosema ceranae''= | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | The identification of ''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceranae'' is important and still needs further research. So far the best differentiation method is the use of species–specific primers; however, the sequence differences are limited to the ribosomal RNA loci, leading to overestimation of Nosema infection rate. Thanks to recent genome study of ''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceranae'', we proposed new primers for differentiation of ''Nosema spp.'' based on highly conserved, species–specific protein coding genes rather than species–specific sequences in rRNA genes, which is likely to improve the accuracy of species identification and can be used to quantify ''Nosema ceranae''. | + | The identification of ''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceranae'' is important and still needs further research. So far the best differentiation method is the use of species–specific primers; however, the sequence differences are limited to the ribosomal RNA loci, leading to overestimation of Nosema infection rate. Thanks to recent genome study of ''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceranae'', we proposed new primers for differentiation of ''Nosema spp.'' based on highly conserved, species–specific protein coding genes rather than species–specific sequences in rRNA genes, which is likely to improve the accuracy of species identification and can be used to quantify ''Nosema ceranae''. We confirmed the new primers by Blast, PCR with Nosema genomic DNA and the latter was sent for DNA Sequencing. After the DNA Sequencing, the result showed that there was only N. ceranae and no N. apis in the sample, while old primers produced a ''fake'' N apis band and new primers did not make the mistake. |
| + | |||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
===''Nosema spp.'' Differentiation Methods=== | ===''Nosema spp.'' Differentiation Methods=== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
==Experiment== | ==Experiment== | ||
| - | === | + | ===The Protocol of OldPrimers=== |
| + | link to our [https://2013.igem.org/Team:NYMU-Taipei/Experiments/Protocols protocol] | ||
====''Nosema primers''==== | ====''Nosema primers''==== | ||
forward primer:ggcagttatgggaagtaaca | forward primer:ggcagttatgggaagtaaca | ||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
===Results of Old Primers=== | ===Results of Old Primers=== | ||
[[File:Nymu old primers testing.PNG|600px|thumb|center| '''Results of Old Primers''' Electrophoresis photo 1:From the left to the right shows the Nosema genomic DNA with the new primers of ''Nosema apis'' ,''Nosema ceanae'' ,''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceanae'' respectively]] | [[File:Nymu old primers testing.PNG|600px|thumb|center| '''Results of Old Primers''' Electrophoresis photo 1:From the left to the right shows the Nosema genomic DNA with the new primers of ''Nosema apis'' ,''Nosema ceanae'' ,''Nosema apis'' and ''Nosema ceanae'' respectively]] | ||
| + | The ''N. apis'' primers produced several bands rather than one, which was not coherent with the result of the previous paper; amd thus we sent the PCR mixtures for DNA Sequencing and found out that there was actually only ''N. ceranae'' and no ''N. apis'' existing in the sample. The old ''N. apis'' primers produced a fake ''N. apis'' band while our new ''N. apis'' primers did not make the mistake. | ||
===New Primers=== | ===New Primers=== | ||
| Line 80: | Line 83: | ||
Besides testing our new primers, we also chose traditional primers to double-check whether the bees were infected with ''N. app.'' The first step is to do real PCR with primers and spores extracted from infected bees, and then run the electrophoresis to check the length. | Besides testing our new primers, we also chose traditional primers to double-check whether the bees were infected with ''N. app.'' The first step is to do real PCR with primers and spores extracted from infected bees, and then run the electrophoresis to check the length. | ||
| - | + | ===The Protocol of New Primers=== | |
| - | ==== | + | ====Nosema primers==== |
forward primer:aatttatactggaacttttgaaaataaaagt | forward primer:aatttatactggaacttttgaaaataaaagt | ||
| Line 87: | Line 90: | ||
Product=1103bp for for ''N. apis''and 1089bp for ''N. ceranae'' | Product=1103bp for for ''N. apis''and 1089bp for ''N. ceranae'' | ||
| + | ====''N. ceranae'' primers==== | ||
| + | forward primer:tcatttaattaaactttcaacgtaattttctaaattct | ||
| - | ====''N. apis | + | reverse primer:atgttatcacgtaatattgagaagaaacttt |
| + | Product=861bp for ''N. ceranae'' | ||
| + | ====''N. apis'' primers==== | ||
forward primer:ttagtaacatccttcttcagaagctaaattttc | forward primer:ttagtaacatccttcttcagaagctaaattttc | ||
| Line 94: | Line 101: | ||
Product=1320bp for ''N. apis'' | Product=1320bp for ''N. apis'' | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Latest revision as of 03:23, 29 October 2013


Contents |
Identifying Nosema ceranae
Introduction
The identification of Nosema apis and Nosema ceranae is important and still needs further research. So far the best differentiation method is the use of species–specific primers; however, the sequence differences are limited to the ribosomal RNA loci, leading to overestimation of Nosema infection rate. Thanks to recent genome study of Nosema apis and Nosema ceranae, we proposed new primers for differentiation of Nosema spp. based on highly conserved, species–specific protein coding genes rather than species–specific sequences in rRNA genes, which is likely to improve the accuracy of species identification and can be used to quantify Nosema ceranae. We confirmed the new primers by Blast, PCR with Nosema genomic DNA and the latter was sent for DNA Sequencing. After the DNA Sequencing, the result showed that there was only N. ceranae and no N. apis in the sample, while old primers produced a fake N apis band and new primers did not make the mistake.
Background
Nosema spp. Differentiation Methods
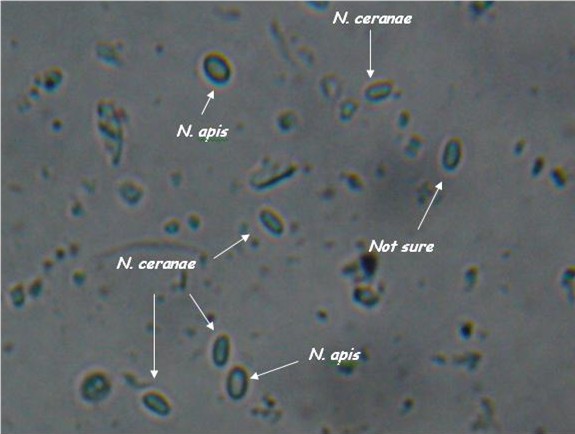
- Light microscopy method: It is based on morphology difference of N. apis and N. ceranae, revealing that N. ceranae are oval or rod shaped like a rice, and also slightly thinner than N. apis. Light microscopy method is convenient but not scientific enough since N. apis bears a striking resemblance to N. ceranae.
- Molecular methods: Species-specific primers are more accurate than light microscopy method. The problem is that so far nearly all protocols based on species–specific sequence differences are limited to the ribosomal RNA loci, which may lead to confusing results due to polymorphisms in and recombination between the multi-copy 16S rRNA genes, and hence overestimate the rate of Nosema infections.
- Our new primers: This year, we created new primers based on recently published, highly conserved and absolutely species–specific sequence differences in protein coding genes. To be more specific, the primers are based on species–specific genes instead of species–specific sequences. As more and more genes of Nosema spp. are revealed, we are able to choose the genes that are not homologs in N. apis and N. ceranae for new primers. Our new primers are confirmed by BLAST and PCR results and then sent for DNA Sequencing. We propose that our new primers should become the preferred molecular tool for differentiation of Nosema spp. and thus assist in apiculture.
Experiment
The Protocol of OldPrimers
link to our protocol
Nosema primers
forward primer:ggcagttatgggaagtaaca
reverse primer:ggtcgtcacatttcatctct
Product=208bp for Nosema
N. ceranae primers
forward primer:cggataaaagagtccgttacc
reverse primer:tgagcagggttctagggat
Product=250bp for N. ceranae
N. apis primers
forward primer:ccattgccggataagagagt
reverse primer:cacgcattgctgcatcattgac Product=401bp for N. apis
| Temperature | Time | |
|---|---|---|
| 94oC | 120s | |
| 94oC | 30s | 30 cycles |
| 53oC | 30s | |
| 72oC | 30s | |
| 72oC | 600s |
Results of Old Primers
The N. apis primers produced several bands rather than one, which was not coherent with the result of the previous paper; amd thus we sent the PCR mixtures for DNA Sequencing and found out that there was actually only N. ceranae and no N. apis existing in the sample. The old N. apis primers produced a fake N. apis band while our new N. apis primers did not make the mistake.
New Primers
1. Common gene of N. spp.--- NcORF_00182 hypothetical protein & NAPIS_ORF01775 chitin synthase d
NcORF_00182 for N. apis
Product=1089bp
NAPIS_ORF01775 N. ceranae
Product=1103bp
2. Specific gene of N. ceranae---NcORF_00714 hypothetical protein
NcORF_00714
Product=861bp for N. ceranae
3. Specific gene of N. apis---NAPIS_ORF02138 class iv chitinase
NAPIS_ORF02138 Product=1320bp for N. apis
Besides testing our new primers, we also chose traditional primers to double-check whether the bees were infected with N. app. The first step is to do real PCR with primers and spores extracted from infected bees, and then run the electrophoresis to check the length.
The Protocol of New Primers
Nosema primers
forward primer:aatttatactggaacttttgaaaataaaagt
reverse primer:catttatttaaaatcattgtttctccacaaat
Product=1103bp for for N. apisand 1089bp for N. ceranae
N. ceranae primers
forward primer:tcatttaattaaactttcaacgtaattttctaaattct
reverse primer:atgttatcacgtaatattgagaagaaacttt Product=861bp for N. ceranae
N. apis primers
forward primer:ttagtaacatccttcttcagaagctaaattttc
reverse primer:atgcaacttcaaaatccaataactactgtaac
Product=1320bp for N. apis
| Temperature | Time | |
|---|---|---|
| 94oC | 120s | |
| 94oC | 30s | 45 cycles |
| 55oC | 30s | |
| 72oC | 30s | |
| 72oC | 600s |
Results of New Primers
Reference
- Gisder, S., & Genersch, E. (May 01, 2013). Molecular differentiation of Nosema apis and Nosema ceranae based on species–specific sequence differences in a protein coding gene. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 113, 1, 1-6.[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022201113000165]
- Nabian, S., Ahmadi, K., Nazem, S. M., & Gerami, S. A. (January 01, 2011). First Detection of Nosema ceranae, a Microsporidian Protozoa of European Honeybees (Apis mellifera) In Iran. Iranian Journal of Parasitology, 6, 3, 89-95.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3279895/]
- Chen, Y., Pettis, J. S., Zhao, Y., Liu, X., Tallon, L. J., Sadzewicz, L. D., Li, R., ... Evans, J. D. (January 01, 2013). Genome sequencing and comparative genomics of honey bee microsporidia, Nosema apis reveal novel insights into host-parasite interactions. Bmc Genomics, 14.[http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2164/14/451/]
- Sagastume, S., del, A. C., Martín-Hernández, R., Higes, M., & Henriques-Gil, N. (January 01, 2011). Polymorphism and recombination for rDNA in the putatively asexual microsporidian Nosema ceranae, a pathogen of honeybees. #Environmental Microbiology, 13, 1, 84-95.[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21199250]
- Chen, Y. P., Evans, J. D., Murphy, C., Gutell, R., Zuker, M., Gundensen-Rindal, D., & Pettis, J. S. (January 01, 2009). Morphological, molecular, and phylogenetic characterization of Nosema ceranae, a microsporidian parasite isolated from the European honey bee, Apis mellifera. The Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology, 56, 2.)[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2779023/]
- Huang, W. F., Bocquet, M., Lee, K. C., Sung, I. H., Jiang, J. H., Chen, Y. W., & Wang, C. H. (January 01, 2008). The comparison of rDNA spacer regions of Nosema ceranae isolates from different hosts and locations. Journal of Invertebrate Pathology, 97, 1, 9-13. [http://ansc.niu.edu.tw/files/writing_journal/20/27_2fcb1cab.pdf]
- Bollan, K. A., Hothersall, J. D., Moffat, C., Durkacz, J., Saranzewa, N., Wright, G. A., Raine, N. E., ... Connolly, C. N. (January 01, 2013). The microsporidian parasites Nosema ceranae and Nosema apis are widespread in honeybee (Apis mellifera) colonies across Scotland. Parasitology Research, 112, 2, 751-9. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23180128]
- Huang, W. F., Solter, L. F., Yau, P. M., & Imai, B. S. (January 01, 2013). Nosema ceranae escapes fumagillin control in honey bees. Plos Pathogens, 9, 3.) [http://www.plospathogens.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.ppat.1003185]
 "
"