Team:Paris Saclay/Open source
From 2013.igem.org
(→The Open Source thermal cycler project) |
|||
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[Team:Paris_Saclay/communication|Outreach]] | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/communication|Outreach]] | ||
[[Team:Paris_Saclay/Team_Collaboration|Team collaboration]] | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/Team_Collaboration|Team collaboration]] | ||
| + | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin_menu_navigation}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_menu_navigation}} | ||
| + | Reflection on Open Source | ||
| + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/Open_source|Intro]] | ||
| + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/opensourcereflexion|Reflection]] | ||
| + | [[Team:Paris_Saclay/ellen_interview|Interview]] | ||
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin_menu_navigation}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin_menu_navigation}} | ||
| Line 42: | Line 50: | ||
<u>'''Our conclusion'''</u> | <u>'''Our conclusion'''</u> | ||
| - | We | + | During our meetings, We learned and discussed about the definition of Open Source in computer science, of its history. We tried to make a comparison between open source in computer science and in synthetic biology. We debated about the advantages and disadvantages of this type of system. We learnt a lot about the historic biologic attacks and about the global democratization of science. According to us, the application of the open source in biology is not for today. The model where firms protect their discoveries/inventions with patents, is still predominant. But it is certain that a new movement is being born, students and non scientific people have more and more access to information thanks to the internet. We can not deny the power of the democratization of science. |
This reflection prepared us to the interview of Ellen Jorgensen. | This reflection prepared us to the interview of Ellen Jorgensen. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 71: | ||
<u>'''Our conclusion'''</u> | <u>'''Our conclusion'''</u> | ||
| - | Thanks to this interview, we | + | Thanks to this interview, we learned more about genspace and about the motivation of people who participate to this movment. People from a large diversity of backgrounds can experiment, can learn more about synBio, and design innovative projects. Experiments are controlled and secured. This is an important difference in comparison with biohakers working in their garage. We think that this reglementation shows a mature reflection about the open source in synthetic biology : everyone can make it, but security is the most important thing. After the interview we discussed about the question of DNA property : what are the consequences of putting personal DNA on the internet, can we modify every DNA or can we talk about DNA property (can DNA or its sequence belong to someone or a company)? |
We would like to thanks Ellen for answering to our questions. It was a great moment. | We would like to thanks Ellen for answering to our questions. It was a great moment. | ||
| - | ==''' | + | =='''Our Open Source thermal cycler project'''== |
| - | Our team decided to participate to the development of open source biology by designing an Open Source thermal cycler, the | + | Our team decided to participate to the development of open source biology by designing an Open Source thermal cycler, the PS-PCR. We have created a PCR thermal cycler, trying to keep its price as low as possible (about 30€,i.e. $40) and therefore using salvaged materials and common tools. The PS-PCR is the good example of the positive consequences of the development of Open Source in synthetic biology : everyone can make it, improve it and share it. The goal of this project was to share with other iGEM teams the PS-PCR and to use it like a basic tool that could be improved. |
Some parts of this project were carried out at the Electrolab in Nanterre (near Paris) | Some parts of this project were carried out at the Electrolab in Nanterre (near Paris) | ||
| Line 80: | Line 88: | ||
| - | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="font-size:1.5em;border:1px solid #000000;padding:3px;">[[Team:Paris_Saclay/ | + | <div style="text-align:center;"><span style="font-size:1.5em;border:1px solid #000000;padding:3px;">[[Team:Paris_Saclay/PS-PCR|OUR OPEN SOURCE PCR : PS-PCR]]</span></div> |
| Line 98: | Line 106: | ||
| - | + | Written by Caroline and Damir | |
{{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin}} | {{Team:Paris_Saclay/incl_fin}} | ||
Latest revision as of 16:29, 4 October 2013
Contents |
Reflection on the Open Source concept
As part of our reflection on our participation to the iGEM competition and on the future of synthetic biology, we decided to work on the Open Source concept and on its impact in our society. Our work was divided in three parts.
- Discussion about the open source concept during small meetings we organised
- Interview of Ellen Jorgensen (co-founder and president of Genspace) about her views regarding open source in biology
- Development of a new open source PCR thermal cycle project.
Reflections on the Open Source concept
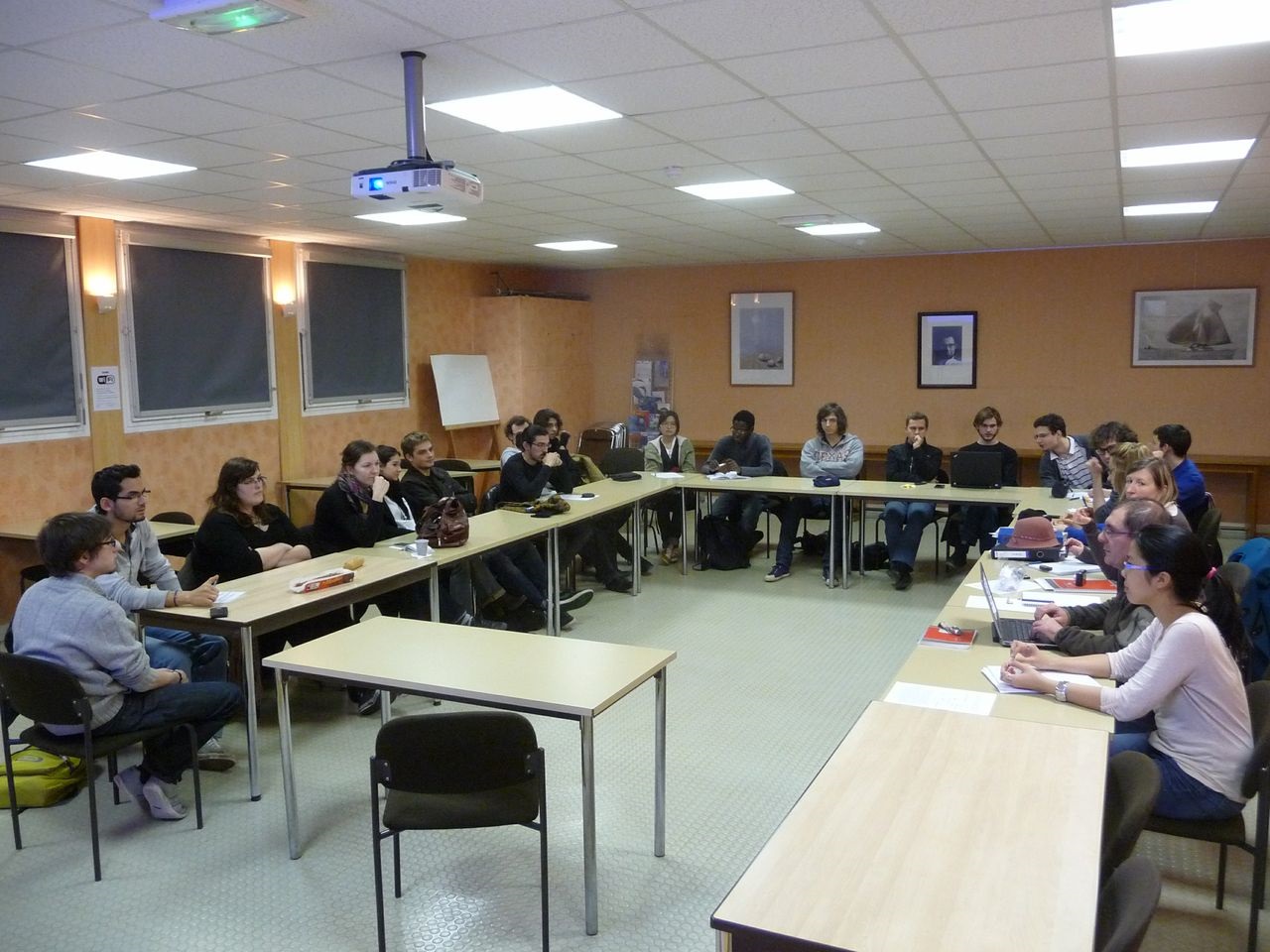
We organized meetings in which two or three of us presented a specific aspect of Open Source: what is open source, what is the place of the open source synbio in our economy, what comparison we can make between computer science and synbiology, what are the risks of biohacking.... After each presentation we debated, and we hightlighted the important questions we wanted to broach. A report on the different meetings we had is available here: .
Our conclusion
During our meetings, We learned and discussed about the definition of Open Source in computer science, of its history. We tried to make a comparison between open source in computer science and in synthetic biology. We debated about the advantages and disadvantages of this type of system. We learnt a lot about the historic biologic attacks and about the global democratization of science. According to us, the application of the open source in biology is not for today. The model where firms protect their discoveries/inventions with patents, is still predominant. But it is certain that a new movement is being born, students and non scientific people have more and more access to information thanks to the internet. We can not deny the power of the democratization of science.
This reflection prepared us to the interview of Ellen Jorgensen.
Interview of Ellen Jorgensen
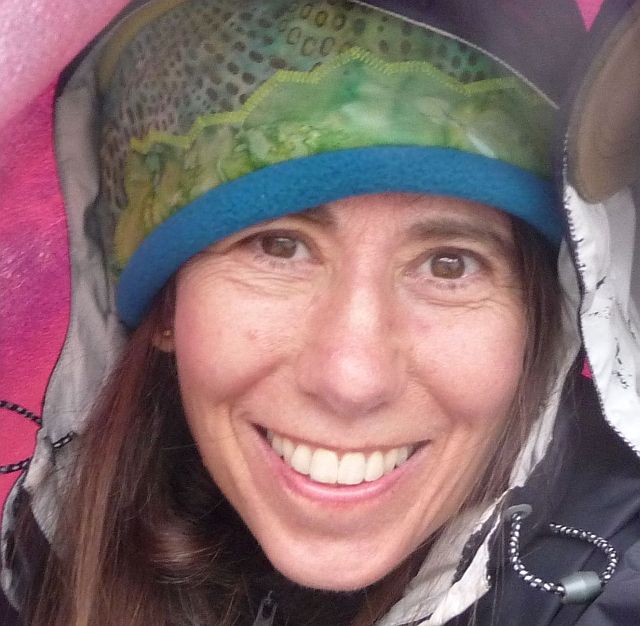
To further enrich our reflection on Open Source, we decided to interview Ellen Jorgensen about her views on Open Source in Biology. Ellen Jorgensen is the co-founder and president of Genspace (http://genspace.org/), a nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting citizen science and access to biotechnology.
Our conclusion
Thanks to this interview, we learned more about genspace and about the motivation of people who participate to this movment. People from a large diversity of backgrounds can experiment, can learn more about synBio, and design innovative projects. Experiments are controlled and secured. This is an important difference in comparison with biohakers working in their garage. We think that this reglementation shows a mature reflection about the open source in synthetic biology : everyone can make it, but security is the most important thing. After the interview we discussed about the question of DNA property : what are the consequences of putting personal DNA on the internet, can we modify every DNA or can we talk about DNA property (can DNA or its sequence belong to someone or a company)?
We would like to thanks Ellen for answering to our questions. It was a great moment.
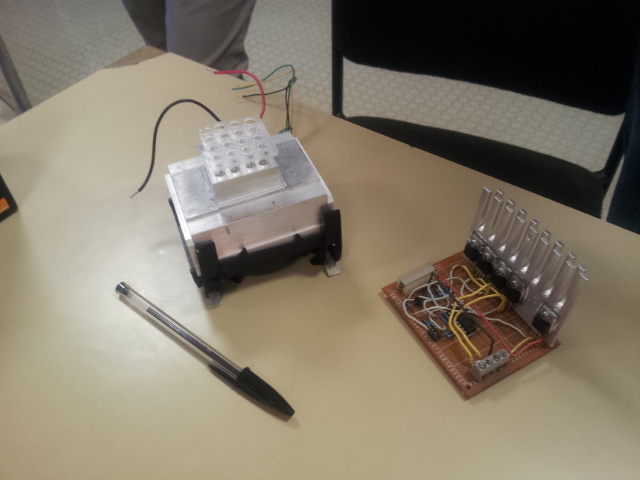
Our Open Source thermal cycler project
Our team decided to participate to the development of open source biology by designing an Open Source thermal cycler, the PS-PCR. We have created a PCR thermal cycler, trying to keep its price as low as possible (about 30€,i.e. $40) and therefore using salvaged materials and common tools. The PS-PCR is the good example of the positive consequences of the development of Open Source in synthetic biology : everyone can make it, improve it and share it. The goal of this project was to share with other iGEM teams the PS-PCR and to use it like a basic tool that could be improved.
Some parts of this project were carried out at the Electrolab in Nanterre (near Paris)
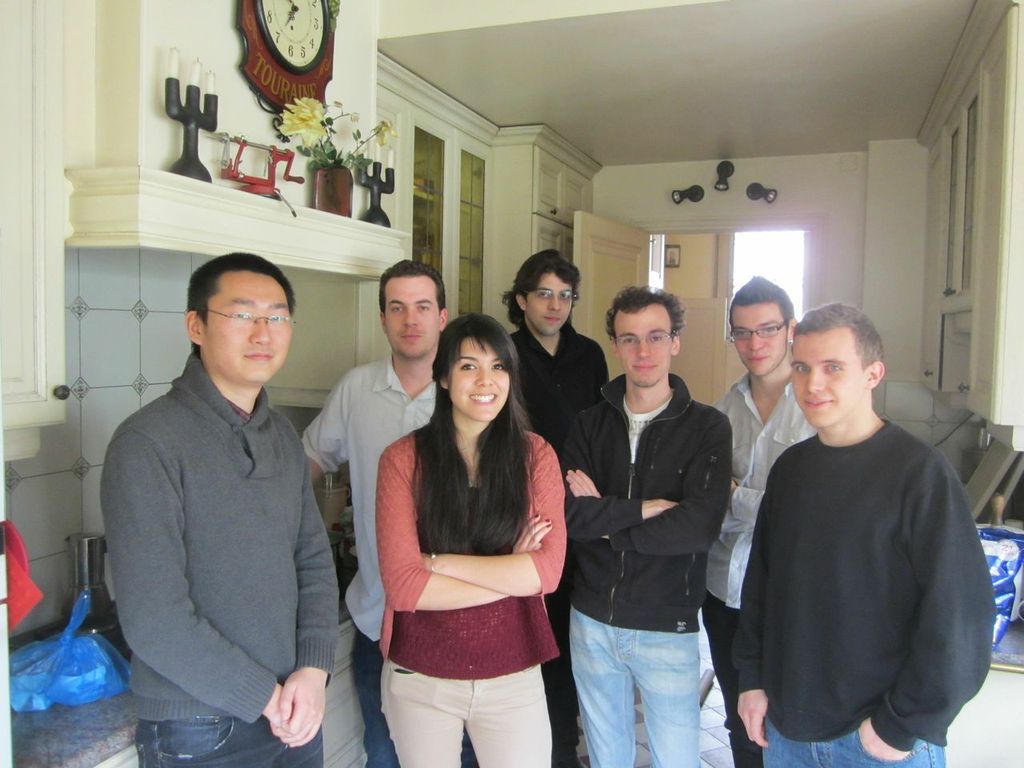
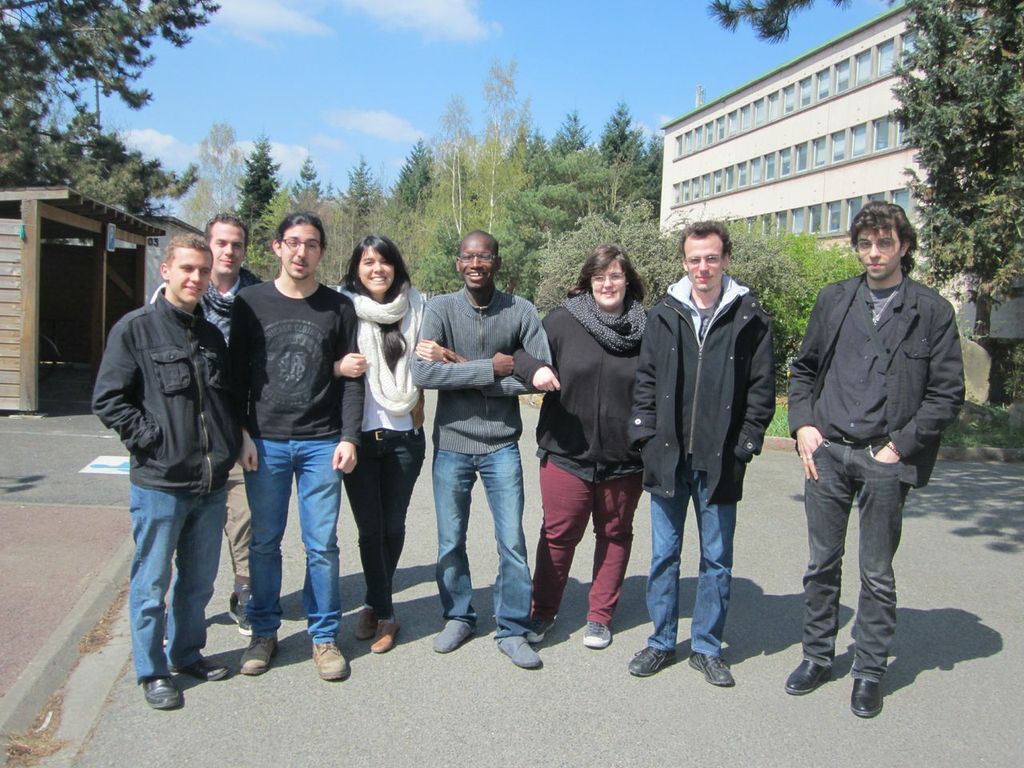
Photos of our meetings and of the human practice team:
Written by Caroline and Damir
 "
"