Team:Leeds/Project
From 2013.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m |
|||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
<h2><font size="6">'''Our Project'''</font></h2> | <h2><font size="6">'''Our Project'''</font></h2> | ||
==What is MicroBeagle I hear you cry?== | ==What is MicroBeagle I hear you cry?== | ||
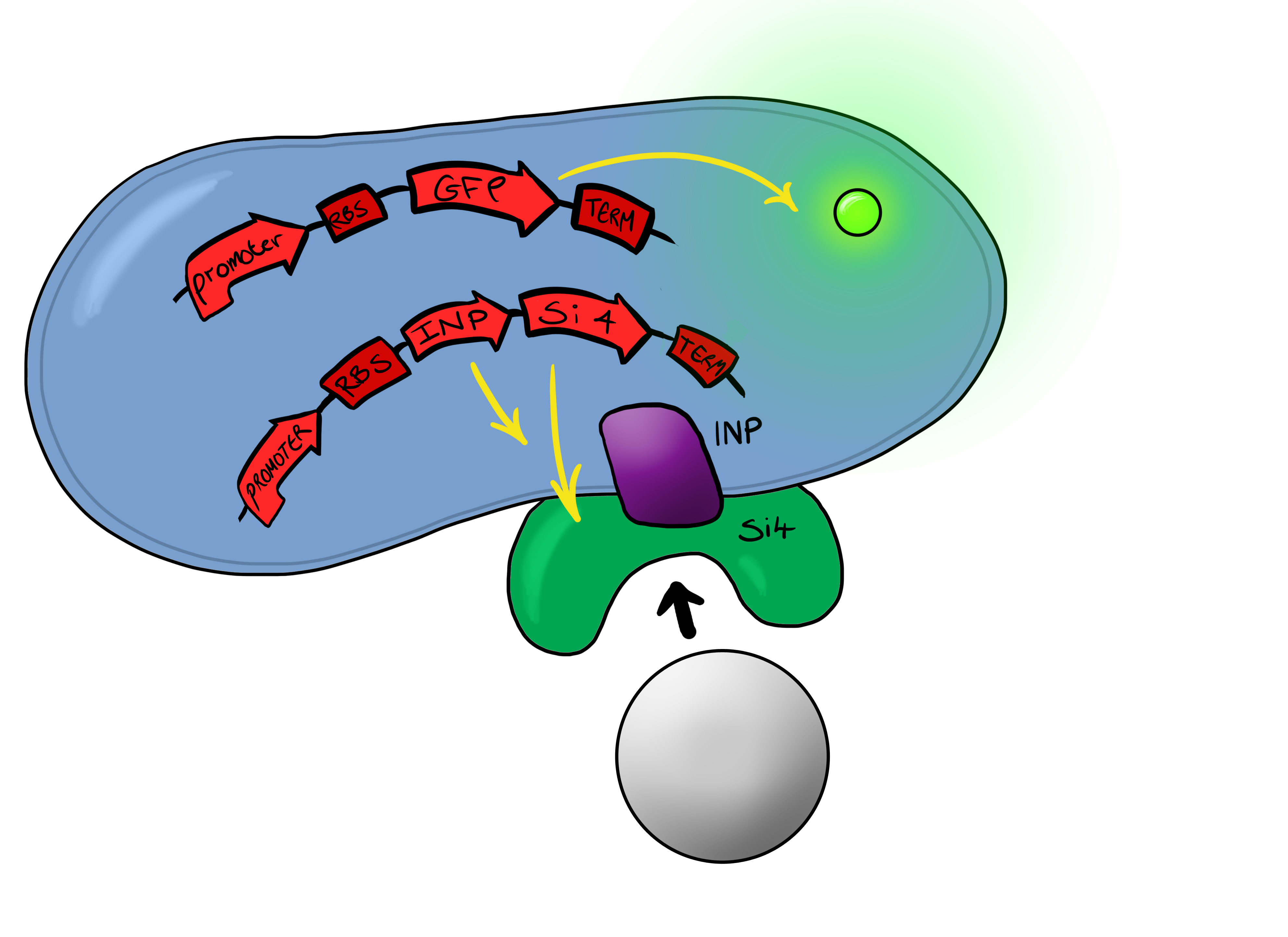
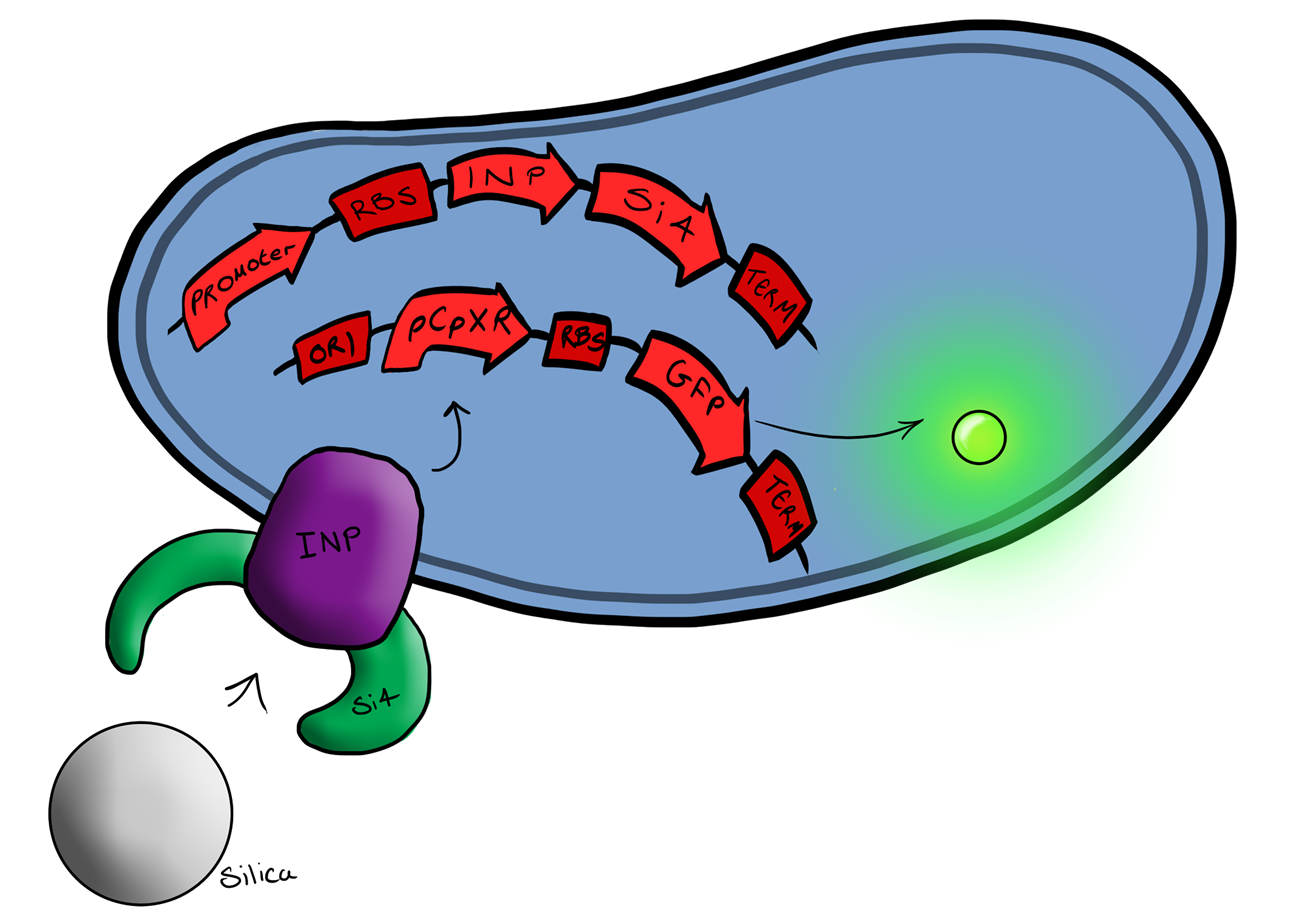
| - | Well, MicroBeagle is a E.coli cell that has been modified so that it can “hunt down” pathogens. Just like a Beagle, the hunting dog, searches | + | Well, MicroBeagle is a E.coli cell that has been modified so that it can help “hunt down” pathogens. Just like a Beagle, the hunting dog, searches for, finds, and indicates the presence of rabbits and hares, our MircoBeagle finds pathogens, detecting them through physical binding, and lights up to indicate their presence! By utilising the Cpx pathway, which responds to membrane stress (which we hypothesize would be induced by the binding event) and GFP (as a reporter) we hope to create a new biosensor that gives results that can be seen with the naked eye. |
<br style="clear:both"/> | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
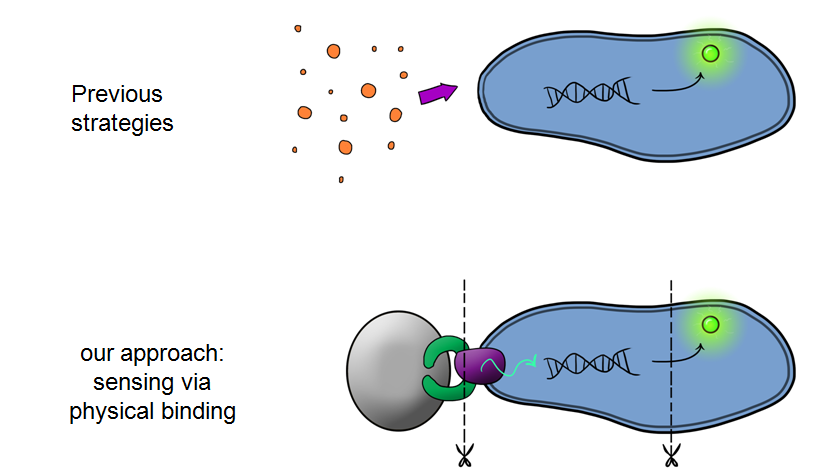
[[File:PhysicalBinding.png|left|300px|We are using Physical binding!|link=|frameless]] | [[File:PhysicalBinding.png|left|300px|We are using Physical binding!|link=|frameless]] | ||
| - | MicroBeagle is | + | Our MicroBeagle project is laying groundwork towards the development of a modular, general platform for pathogen detection. What makes Leeds iGEM's MicroBeagle distinctive to previous strategies used for analyte detection within iGEM is that we use physical binding as our detection mode. This should be well suited to detecting a wide range of pathogen targets, as tailored target-binding proteins or peptides can be displayed from the cell surface, allowing specific binding to the pathogen of interest. |
<br> | <br> | ||
<br style="clear:both"/> | <br style="clear:both"/> | ||
==Why is the MircoBeagle a useful device?== | ==Why is the MircoBeagle a useful device?== | ||
| - | There could be many different possible uses for our device as the pathogen detection mechanism we are using is modular and can easily be tailored to individual needs. This is achieved by swapping out the gene coding the binding domain to suit your need. We | + | There could be many different possible uses for our device, as the pathogen detection mechanism we are using is modular and can easily be tailored to individual needs. This is achieved by swapping out the gene coding the cell surface-displayed binding domain to suit your need. We envision the MircoBeagle being used for testing blood samples, detection of heavy metals and, in the application that is our main inspiration, detection of pathogens in water samples. |
<br> | <br> | ||
==Why Water Testing is so important== | ==Why Water Testing is so important== | ||
[[File:Dirtywater.png|right|300px|Would you like to have to drink this water?|link=|frameless]] | [[File:Dirtywater.png|right|300px|Would you like to have to drink this water?|link=|frameless]] | ||
Detecting pathogens in water is a really important application as 3.4 million people a year die from water related diseases. | Detecting pathogens in water is a really important application as 3.4 million people a year die from water related diseases. | ||
| - | 768 million people in the world do not have access to safe water. This is roughly one in ten of the world's population, the majority of which is caused by faecal contamination: poor sewage systems that flow back into the water supply | + | 768 million people in the world do not have access to safe water. This is roughly one in ten of the world's population, the majority of which is caused by faecal contamination: poor sewage systems that flow back into the water supply. |
| - | The issue is actually more complex and subtle than just direct health problems, the knock on economic problems that result from poor sanitation are phenomenal | + | The issue is actually more complex and subtle than just direct health problems, the knock on economic problems that result from poor sanitation are phenomenal. |
| - | Lack of water, sanitation and hygiene costs Sub-Saharan African countries more in lost GDP than the entire continent gets in development aid | + | Lack of water, sanitation and hygiene costs Sub-Saharan African countries more in lost GDP than the entire continent gets in development aid. |
The figures are shocking and we as a team want to create something that may, in the future, help to reduce those numbers. | The figures are shocking and we as a team want to create something that may, in the future, help to reduce those numbers. | ||
| - | + | While many organization are creating new, appropriate water purification devices and systems, we realize these will only be as good as the measurement technologies available to test their performance will allow. This bottleneck is particularly critical in infrastructure-poor areas with no access to the molecular biology labs typically used to assay water-borne pathogens. | |
| + | While many teams around the world are seeking new ways of transporting chassis and bio-devices in facile, safe, and reliable manners (e.g., through capsules or spores), we felt that efforts to develop modular pathogen detection systems were lacking. Once effective transport strategies are established, we hope to have a detection system ready-to-go to employ in on-site water testing and diagnostics. | ||
| + | To address this issue using a novel synthetic biological approach, the MircoBeagle was born! | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
===Below is a summary of our Device development strategy...=== | ===Below is a summary of our Device development strategy...=== | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
==Phase I== | ==Phase I== | ||
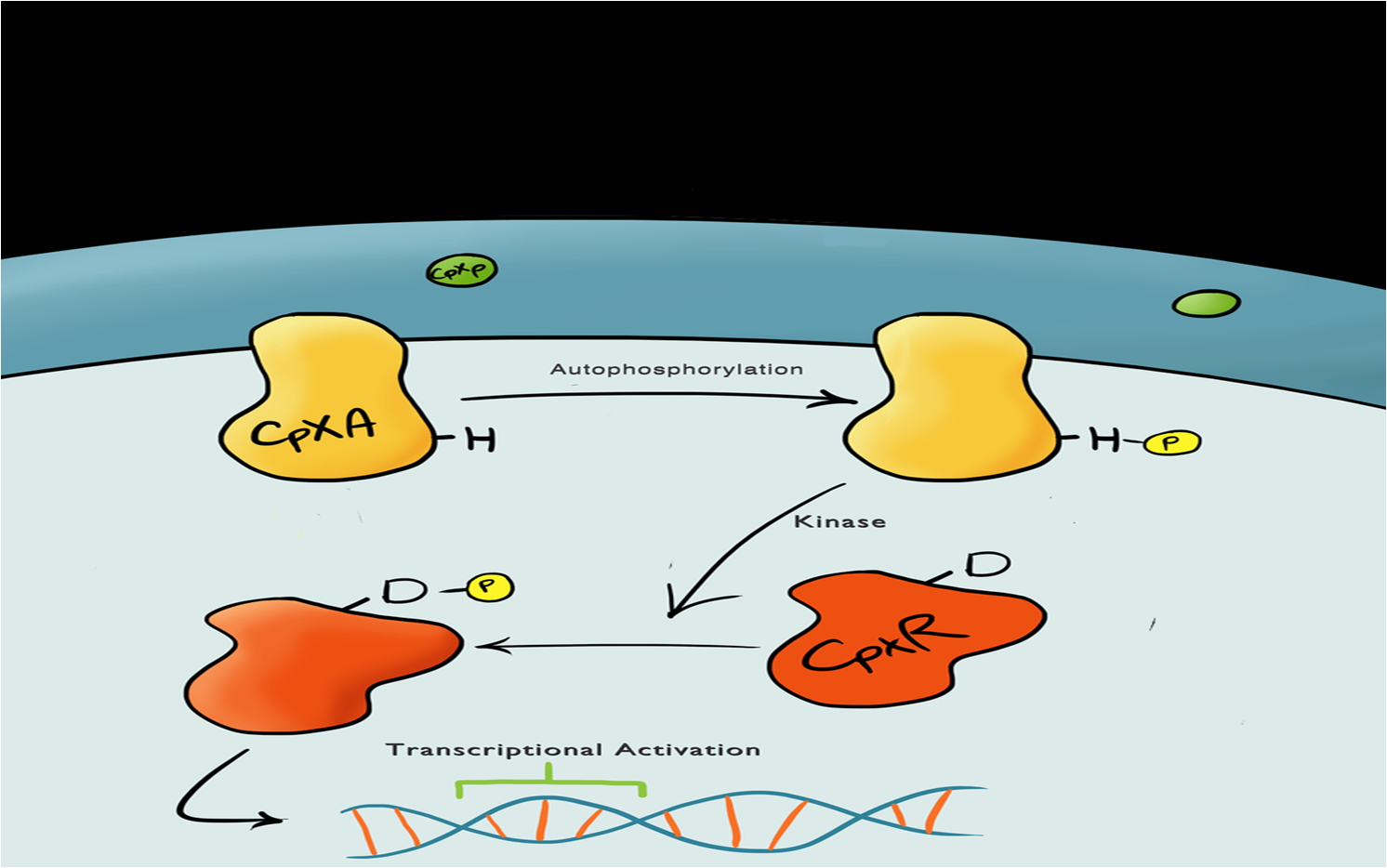
| - | We split our project into self-contained phases, to help better organise ourselves, but also lay out a road map for our own future work within | + | We split our project into self-contained phases, to help better organise ourselves, but also lay out a road map for our own future work within iGEM and beyond. Our two devices include a device for activating a reporter in response to membrane stress (Device 1) and a device for binding to a physical target at the cell surface and thereby activate the membrane-stress-reporter (Device 2). |
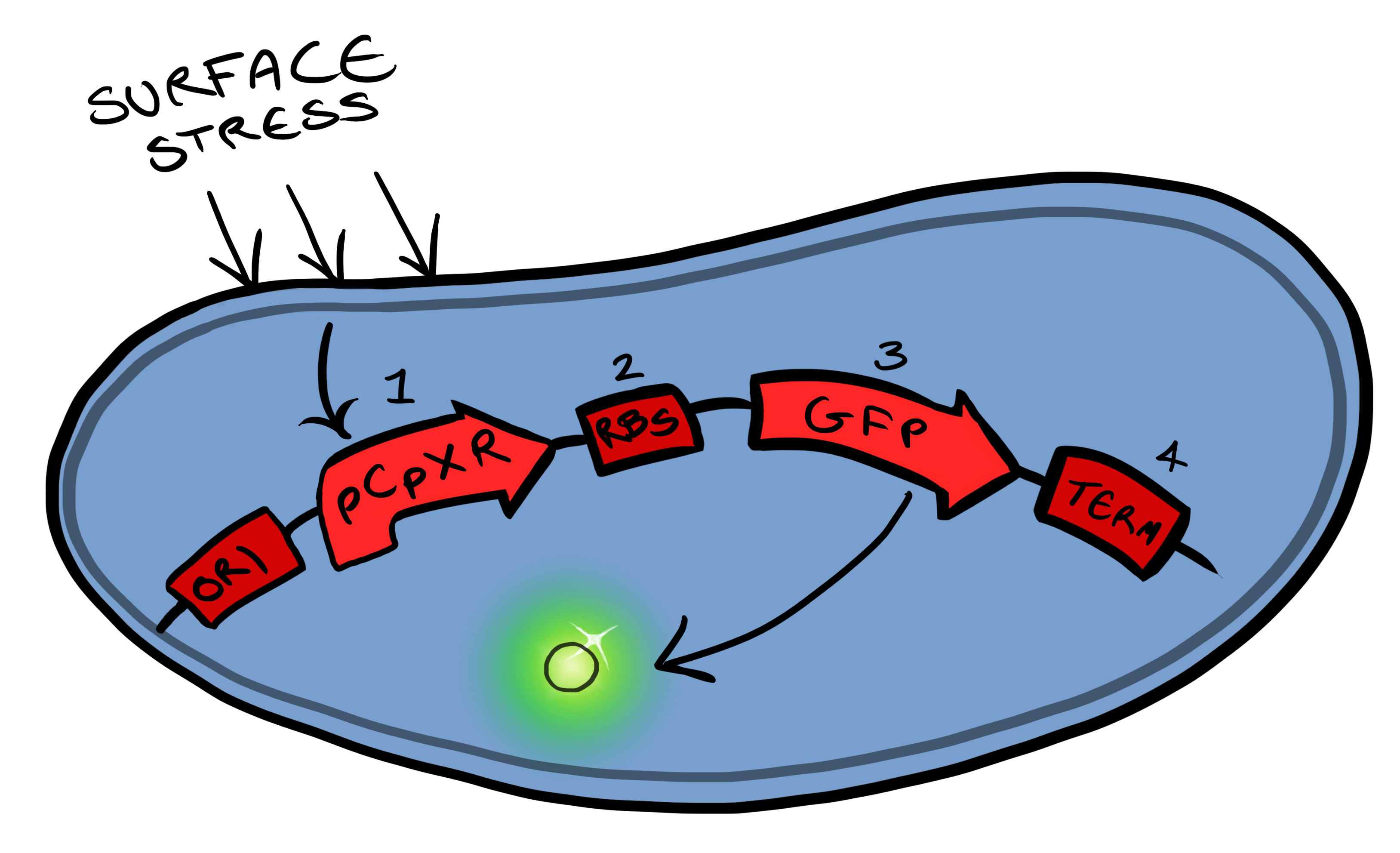
===Device 1=== | ===Device 1=== | ||
[[File:Leeds_bb1schematic.png|left|400px|Cartoon schematic of Biosystem 1|link=|frameless]] | [[File:Leeds_bb1schematic.png|left|400px|Cartoon schematic of Biosystem 1|link=|frameless]] | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 4 October 2013
 "
"